diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index b4e14815a7..b7763837a4 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ PaddleScience 是一个基于深度学习框架 PaddlePaddle 开发的科学计
|-----|---------|-----|---------|----|---------|---------|
| 天气预报 | [FourCastNet 气象预报](https://paddlescience-docs.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/zh/examples/fourcastnet) | 数据驱动 | FourCastNet | 监督学习 | [ERA5](https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=945b3c9e-0f8c-11ed-8daf-9f359c660fbd&origin_path=%2F~%2Fdata%2F) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.11214.pdf) |
| 天气预报 | [NowCastNet 气象预报](https://paddlescience-docs.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/zh/examples/nowcastnet) | 数据驱动 | NowCastNet | 监督学习 | [MRMS](https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=945b3c9e-0f8c-11ed-8daf-9f359c660fbd&origin_path=%2F~%2Fdata%2F) | [Paper](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06184-4) |
-| 天气预报 | [GraphCast 气象预报](jointContribution/graphcast/README.md) | 数据驱动 | GraphCastNet | 监督学习 | - | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.12794) |
+| 天气预报 | [GraphCast 气象预报](https://paddlescience-docs.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/zh/examples/graphcast) | 数据驱动 | GraphCastNet | 监督学习 | - | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.12794) |
| 大气污染物 | [UNet 污染物扩散](https://aistudio.baidu.com/projectdetail/5663515?channel=0&channelType=0&sUid=438690&shared=1&ts=1698221963752) | 数据驱动 | UNet | 监督学习 | [Data](https://aistudio.baidu.com/datasetdetail/198102) | - |
| 天气预报 | [DGMR 气象预报](https://paddlescience-docs.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/zh/examples/dgmr.md) | 数据驱动 | DGMR | 监督学习 | [UK dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/openclimatefix/nimrod-uk-1km) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.00954.pdf) |
diff --git a/docs/index.md b/docs/index.md
index 975ec6b841..195da54656 100644
--- a/docs/index.md
+++ b/docs/index.md
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@
|-----|---------|-----|---------|----|---------|---------|
| 天气预报 | [FourCastNet 气象预报](./zh/examples/fourcastnet.md) | 数据驱动 | FourCastNet | 监督学习 | [ERA5](https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=945b3c9e-0f8c-11ed-8daf-9f359c660fbd&origin_path=%2F~%2Fdata%2F) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.11214.pdf) |
| 天气预报 | [NowCastNet 气象预报](./zh/examples/nowcastnet.md) | 数据驱动 | NowCastNet | 监督学习 | [MRMS](https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=945b3c9e-0f8c-11ed-8daf-9f359c660fbd&origin_path=%2F~%2Fdata%2F) | [Paper](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06184-4) |
-| 天气预报 | [GraphCast 气象预报](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleScience/blob/develop/jointContribution/graphcast/README.md) | 数据驱动 | GraphCastNet | 监督学习 | - | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.12794) |
+| 天气预报 | [GraphCast 气象预报](./zh/examples/graphcast.md) | 数据驱动 | GraphCastNet | 监督学习 | - | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.12794) |
| 大气污染物 | [UNet 污染物扩散](https://aistudio.baidu.com/projectdetail/5663515?channel=0&channelType=0&sUid=438690&shared=1&ts=1698221963752) | 数据驱动 | UNet | 监督学习 | [Data](https://aistudio.baidu.com/datasetdetail/198102) | - |
| 天气预报 | [DGMR 气象预报](./zh/examples/dgmr.md) | 数据驱动 | DGMR | 监督学习 | [UK dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/openclimatefix/nimrod-uk-1km) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.00954.pdf) |
diff --git a/docs/zh/examples/graphcast.md b/docs/zh/examples/graphcast.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e02e86e0e4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/zh/examples/graphcast.md
@@ -0,0 +1,269 @@
+# GraphCast
+
+=== "模型评估命令"
+
+ ``` sh
+
+ # linux
+ wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset.zip
+ wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset-step12.zip
+ wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/models/graphcast/params.zip
+ wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/models/graphcast/template_graph.zip
+ wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/stats.zip
+ wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/graphcast-jax2paddle.csv -P ./data/
+
+ # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset.zip -o dataset.zip
+ # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset-step12.zip -o dataset-step12.zip
+ # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/models/graphcast/template_graph.zip -o template_graph.zip
+ # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/stats.zip -o stats.zip
+ # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/graphcast-jax2paddle.csv --create-dirs -o ./data/graphcast-jax2paddle.csv
+
+ unzip -q dataset.zip -d data/
+ unzip -q dataset-step12.zip -d data/
+ unzip -q params.zip -d data/
+ unzip -q stats.zip -d data/
+ unzip -q template_graph.zip -d data/
+
+ python graphcast.py mode=eval EVAL.pretrained_model_path="data/params/GraphCast_small---ERA5-1979-2015---resolution-1.0---pressure-levels-13---mesh-2to5---precipitation-input-and-output.pdparams"
+ ```
+
+## 1. 背景简介
+
+全球中期天气预报往往是社会和经济领域相关决策的重要依据。传统的数值天气预报模型一般需要通过增加计算资源来提高预报的精度,而无法直接利用历史天气数据来提升基础模型的预测精度。基于机器学习的天气预报模型能够直接利用历史数据训练模型,提升精度,优化计算资源。同时,这种数据驱动的方法使得模型可从数据中的学习到那些不易用显式方程表示的数量关系,从而提高预测的准确性。
+
+GraphCast 是一种基于机器学习的天气预报模型,该模型可以直接从再分析数据中进行训练,并且能够在一分钟内以 0.25° 的分辨率在全球范围内预测超过 10 天的数百个天气变量。论文表明,GraphCast 在 1380 个验证目标的实验中,有 90% 的预测结果显著优于最准确的操作确定性系统(operational deterministic systems),并且模型能很好地预测严重天气事件,包括热带气旋、大气河流和极端温度。
+
+## 2. 模型原理
+
+$X^t$ 表示 t 时刻的天气状态预测,
+
+$$ X^{t+1}=GraphCast(X^{t}, X^{t-1}) $$
+
+GraphCast 通过自回归迭代,产生任意长度 T 的预测序列。
+
+$$ X^{t+1:t+T}=(GraphCast(X^{t}, X^{t-1}), GraphCast(X^{t+1}, X^{t}), ... , GraphCast(X^{t+T-1}, X^{t+T-2}))$$
+
+### 2.1 模型结构
+
+GraphCast 的核心架构采用基于图神经网络(GNN)的“编码‑处理‑解码”结构。基于 GNN 的学习模拟器在学习流体和其他材料的复杂物理动力学方面非常有效,因为它们的表示和计算结构类似于学习型有限元求解器。
+
+
+ 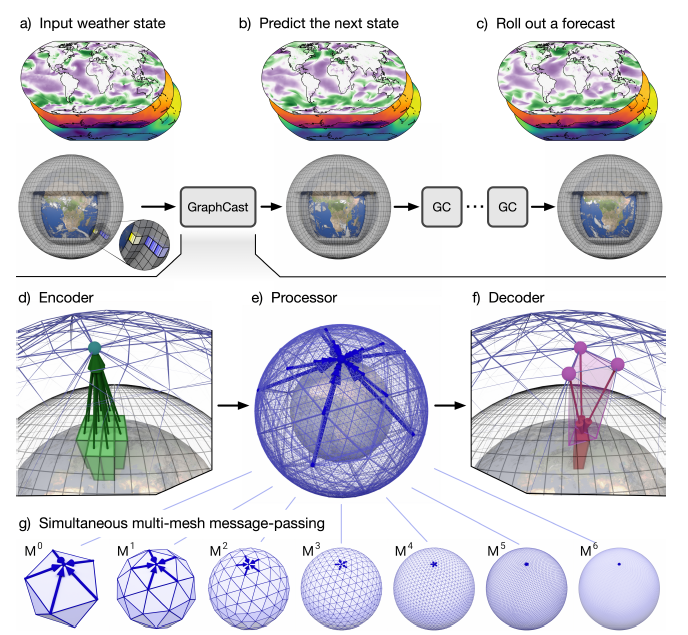{ loading=lazy style="margin:0 auto;"}
+ GraphCast 的结构图
+
+
+由于经纬度网格密度是不均匀的,GraphCast 内部不使用经纬度网格,而是使用了“multi-mesh”表示。“multi-mesh”是通过将正二十面体进行 6 次迭代细化来构建的,如下图所示,每次迭代将多面体上的三角面分成 4 个更小的面。
+
+GraphCast 模型运行在图 $\mathcal{G(V^\mathrm{G}, V^\mathrm{M}, E^\mathrm{M}, E^\mathrm{G2M}, E^\mathrm{M2G})}$ 上。
+
+$\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}$ 是网格点的集合,每个网格节点代表对应经纬度点的大气垂直切片,节点 $v_𝑖^\mathrm{G}$ 的特征用 $\mathbf{v}_𝑖^\mathrm{G,features}$ 表示。
+
+$V^\mathrm{M}$ 是 mesh 节点的集合,mesh 节点是通过将正二十面体迭代划分生成的,节点 $v_𝑖^\mathrm{M}$ 的特征用 $\mathbf{v}_𝑖^\mathrm{M,features}$ 表示。
+
+$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}$ 是一个无向边集合,其中的每条边连接一个发送mesh节点和接收mesh节点,用 $e^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}$ 表示,对应的特征用 $\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M,features}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}$ 表示。
+
+$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}$ 是一个无向边集合,其中的每条边连接一个发送网格节点和一个接收 mesh 节点,用 $e^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^M_r}$ 表示,对应的特征用 $\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M,features}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}$ 表示。
+
+$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}$ 是一个无向边集合,其中的每条边连接一个发送mesh节点和一个接收网格节点,用 $e^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^M_s \rightarrow v^G_r}$ 表示,对应的特征用 $\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G,features}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r}$ 表示。
+
+### 2.2 编码器
+
+编码器的作用是将数据转化为 GraphCast 内部的数据表示。首先利用五个多层感知机(MLP)将上述五个集合的特征嵌入至内部空间。
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G,features}_i) \\
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{M}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M,features}_i) \\
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}(\mathbf{e}^{\mathrm{M,features}}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}) \\
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}(\mathbf{e}^{\mathrm{G2M,features}}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}) \\
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}(\mathbf{e}^{\mathrm{M2G,features}}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r}) \\
+\end{aligned}
+$$
+
+之后通过一个 Grid2Mesh GNN 层,将信息从网格节点传递到 mesh 节点。$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}$ 中的边通过关联的节点更新信息。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Grid2Mesh}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}([\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}, \mathbf{v}_r^\mathrm{G}, \mathbf{v}_s^\mathrm{M}])
+$$
+
+mesh 节点通过其关联的边更新信息。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Grid2Mesh}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{M}}([\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i, \sum_{\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} : v^\mathrm{M}_r=v^\mathrm{M}_i} \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}])
+$$
+
+同样网格节点也进行信息更新。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Grid2Mesh}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i)
+$$
+
+最后通过残差连接更新三个元素。
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} \\
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} \\
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} = \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} + \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}
+\end{aligned}
+$$
+
+### 2.3 处理器
+
+处理器包含一个Multi-mesh GNN 层,$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}$ 中的边通过关联的节点更新信息。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}([\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}, \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_s, \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_r])
+$$
+
+mesh 节点通过其关联的边更新信息。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{M}}([\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i, \sum_{\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} : v^\mathrm{M}_r=v^\mathrm{M}_i} \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}])
+$$
+
+最后通过残差连接更新元素。
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} \\
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} \leftarrow \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} + \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}\\
+\end{aligned}
+$$
+
+### 2.4 解码器
+
+解码器的作用是将 mesh 内的信息取回网格中,并进行预测。解码器包含一个Mesh2Grid GNN 层。
+
+$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}$ 中的边通过关联的节点的更新信息。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh2Grid}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}([\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r},\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_s, \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_r])
+$$
+
+网格节点通过其关联的边更新信息。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh2Grid}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}([\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i, \sum_{\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} : v^\mathrm{G}_r=v^\mathrm{G}_i} \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} {'}])
+$$
+
+通过残差连接对网格节点进行更新。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'}
+$$
+
+接着利用另一个 MLP 对网格信息进行处理,得到预测值。
+
+$$
+\mathbf{\hat{y}}^\mathrm{G}_i= \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Output}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i)
+$$
+
+将输入状态 $X^{t}$ 与预测值 $\hat{Y}^{t}$ 相加得到下一个天气状态 $\hat{X}^{t+1}$
+
+$$ \hat{X}^{t+1} = GraphCast(X^{t}, X^{t-1}) = X^{t} + \hat{Y}^{t} $$
+
+## 3. 模型构建
+
+接下来开始讲解如何基于 PaddleScience 代码,实现 GraphCast。关于该案例中的其余细节请参考 [API文档](../api/arch.md)。
+
+### 3.1 数据集介绍
+
+数据集采用了 ECMWF 的 ERA5 数据集 的 [2020年再分析存档子集](https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset.zip),数据时间段为1979-2018 年,时间间隔为6小时(对应每天的00z、06z、12z和18z),水平分辨率为0.25°,包含 37 个垂直大气压力层。
+
+模型预测总共227个目标变量,其中包括5个地面变量,以及在13个压力层中的每个层次的6个大气变量。
+
+### 3.2 加载预训练模型
+
+在执行命令中设定预训练模型的文件路径,如下。
+
+``` sh
+python graphcast.py mode=eval EVAL.pretrained_model_path="data/params/GraphCast_small---ERA5-1979-2015---resolution-1.0---pressure-levels-13---mesh-2to5---precipitation-input-and-output.pdparams"
+```
+
+### 3.3 模型构建
+
+我们使用神经网络 `GraphCastNet` 作为模型,其接收天气数据,输出预测结果。
+
+``` py linenums="28"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:28:29
+--8<--
+```
+
+### 3.4 评估器构建
+
+我们使用 `ppsci.validate.SupervisedValidator` 构建评估器。首先定义数据加载器的配置,然后创建评估器。
+
+``` py linenums="31"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:31:39
+--8<--
+```
+
+我们需要定义训练损失函数的计算过程。
+
+``` py linenums="50"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:50:67
+--8<--
+```
+
+接着我们还需要定义 metric 指标。
+
+``` py linenums="69"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:69:86
+--8<--
+```
+
+最后完成评估器的构建。
+
+``` py linenums="88"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:88:92
+--8<--
+```
+
+### 3.5 模型评估
+
+完成上述设置之后,只需要将上述实例化的对象按顺序传递给 `ppsci.solver.Solver`,然后启动评估。
+
+``` py linenums="94"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:94:104
+--8<--
+```
+
+### 3.6 结果可视化
+
+评估完成后,我们以图片的形式对结果进行可视化,如下所示。
+
+``` py linenums="106"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:106:118
+--8<--
+```
+
+## 4. 完整代码
+
+``` py linenums="1" title="graphcast.py"
+--8<--
+examples/graphcast/graphcast.py
+--8<--
+```
+
+## 5. 结果展示
+
+下图展示了温度的真值结果、预测结果和误差。
+
+
+ 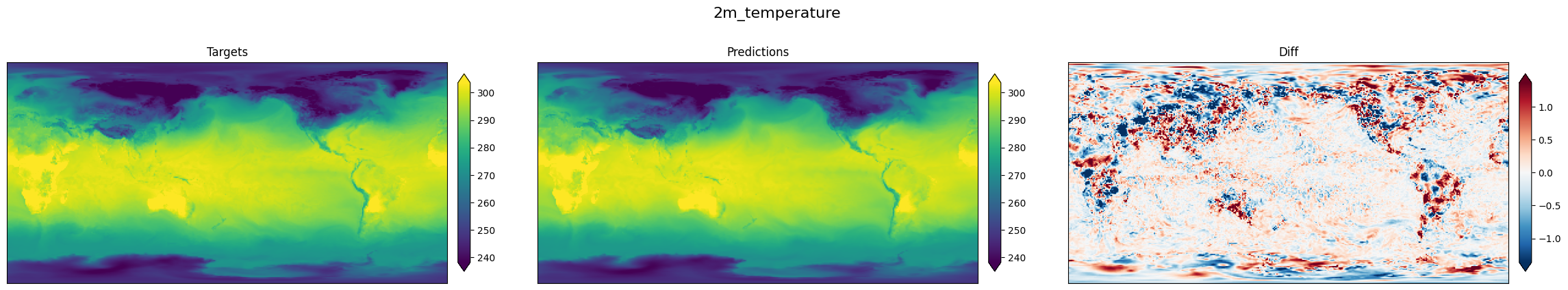{ loading=lazy style="margin:0 auto;"}
+ 真值结果("targets")、预测结果("prediction")和误差("diff")
+
+
+可以看到模型预测结果与真实结果基本一致。
+
+## 6. 参考文献
+
+- [GraphCast: Learning skillful medium-range global weather forecasting](https://doi.org/10.1080/09540091.2022.2131737)
diff --git a/examples/earthformer/enso_metric.py b/examples/earthformer/enso_metric.py
index ab1cd9d0bc..7e398e0b89 100644
--- a/examples/earthformer/enso_metric.py
+++ b/examples/earthformer/enso_metric.py
@@ -22,7 +22,6 @@ def compute_enso_score(
y_true (paddle.Tensor): The label data.
acc_weight (Optional[Union[str, np.ndarray, paddle.Tensor]], optional): The wight of accuracy. Defaults to None.use
default acc_weight specified at https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/531871/information.
-
"""
pred = y_pred - y_pred.mean(axis=0, keepdim=True) # (N, 24)
diff --git a/examples/graphcast/conf/graphcast_small.yaml b/examples/graphcast/conf/graphcast_small.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b0f1b5550d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/graphcast/conf/graphcast_small.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+defaults:
+ - ppsci_default
+ - TRAIN: train_default
+ - TRAIN/ema: ema_default
+ - TRAIN/swa: swa_default
+ - EVAL: eval_default
+ - INFER: infer_default
+ - hydra/job/config/override_dirname/exclude_keys: exclude_keys_default
+ - _self_
+
+hydra:
+ run:
+ # dynamic output directory according to running time and override name
+ dir: outputs_graphcast_small/${now:%Y-%m-%d}/${now:%H-%M-%S}/${hydra.job.override_dirname}
+ job:
+ name: ${mode} # name of logfile
+ chdir: false # keep current working direcotry unchaned
+ callbacks:
+ init_callback:
+ _target_: ppsci.utils.callbacks.InitCallback
+ sweep:
+ # output directory for multirun
+ dir: ${hydra.run.dir}
+ subdir: ./
+
+# general settings
+mode: eval # running mode: train/eval
+seed: 2024
+output_dir: ${hydra:run.dir}
+log_freq: 20
+
+DATA:
+ data_path: "data/dataset/source-era5_date-2022-01-01_res-1.0_levels-13_steps-01.nc"
+ mean_path: "data/stats/mean_by_level.nc"
+ stddev_diffs_path: "data/stats/diffs_stddev_by_level.nc"
+ stddev_path: "data/stats/stddev_by_level.nc"
+ type: "graphcast_small"
+ mesh_size: 5
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor: 0.6180338738074472
+ radius_query_fraction_edge_length: 0.6
+ resolution: 1.0
+
+MODEL:
+ input_keys: ["input"]
+ output_keys: ["pred"]
+ grid_node_dim: 186
+ grid_node_num: 65160
+ grid_node_emb_dim: 512
+ mesh_node_dim: 186
+ mesh_node_num: 10242
+ mesh_edge_dim: 4
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: 512
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: 512
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim: 4
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: 512
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim: 4
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: 512
+ gnn_msg_steps: 16
+ node_output_dim: 83
+
+TRAIN:
+ epochs: 1
+
+EVAL:
+ batch_size: 1
+ pretrained_model_path: null
+ eval_with_no_grad: true
diff --git a/examples/graphcast/graphcast.py b/examples/graphcast/graphcast.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..60c0bc64c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/graphcast/graphcast.py
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2024 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+from typing import Dict
+
+import hydra
+import numpy as np
+import paddle
+import plot
+from omegaconf import DictConfig
+
+import ppsci
+from ppsci.data.dataset import atmospheric_dataset
+
+
+def eval(cfg: DictConfig):
+ model = ppsci.arch.GraphCastNet(**cfg.MODEL)
+
+ # set dataloader config
+ eval_dataloader_cfg = {
+ "dataset": {
+ "name": "GridMeshAtmosphericDataset",
+ "input_keys": ("input",),
+ "label_keys": ("label",),
+ **cfg.DATA,
+ },
+ "batch_size": cfg.EVAL.batch_size,
+ }
+
+ # set validator
+ error_validator = ppsci.validate.SupervisedValidator(
+ eval_dataloader_cfg,
+ loss=None,
+ output_expr={"pred": lambda out: out["pred"]},
+ metric=None,
+ name="error_validator",
+ )
+
+ def loss(
+ output_dict: Dict[str, paddle.Tensor],
+ label_dict: Dict[str, paddle.Tensor],
+ *args,
+ ) -> Dict[str, paddle.Tensor]:
+ graph = output_dict["pred"]
+ pred = dataset.denormalize(graph.grid_node_feat.numpy())
+ pred = graph.grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(pred, dataset.targets_template)
+
+ target = graph.grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(
+ label_dict["label"][0].numpy(), dataset.targets_template
+ )
+
+ pred = atmospheric_dataset.dataset_to_stacked(pred)
+ target = atmospheric_dataset.dataset_to_stacked(target)
+ loss = np.average(np.square(pred.data - target.data))
+ loss = paddle.to_tensor(loss)
+ return {"loss": loss}
+
+ def metric(
+ output_dict: Dict[str, paddle.Tensor],
+ label_dict: Dict[str, paddle.Tensor],
+ *args,
+ ) -> Dict[str, paddle.Tensor]:
+ graph = output_dict["pred"][0]
+ pred = dataset.denormalize(graph.grid_node_feat.numpy())
+ pred = graph.grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(pred, dataset.targets_template)
+
+ target = graph.grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(
+ label_dict["label"][0].numpy(), dataset.targets_template
+ )
+
+ metric_dic = {
+ var_name: np.average(target[var_name].data - pred[var_name].data)
+ for var_name in list(target)
+ }
+ return metric_dic
+
+ dataset = error_validator.data_loader.dataset
+ error_validator.loss = ppsci.loss.FunctionalLoss(loss)
+ error_validator.metric = {"error": ppsci.metric.FunctionalMetric(metric)}
+
+ validator = {error_validator.name: error_validator}
+
+ # initialize solver
+ solver = ppsci.solver.Solver(
+ model,
+ validator=validator,
+ cfg=cfg,
+ pretrained_model_path=cfg.EVAL.pretrained_model_path,
+ eval_with_no_grad=cfg.EVAL.eval_with_no_grad,
+ )
+
+ # evaluate model
+ solver.eval()
+
+ # visualize prediction
+ with solver.no_grad_context_manager(True):
+ for index, (input_, label_, _) in enumerate(error_validator.data_loader):
+ output_ = model(input_)
+ graph = output_["pred"]
+ pred = dataset.denormalize(graph.grid_node_feat.numpy())
+ pred = graph.grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(pred, dataset.targets_template)
+
+ target = graph.grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(
+ label_["label"][0].numpy(), dataset.targets_template
+ )
+
+ plot.log_images(target, pred, "2m_temperature", level=50, file="result.png")
+
+
+@hydra.main(version_base=None, config_path="./conf", config_name="graphcast_small.yaml")
+def main(cfg: DictConfig):
+ if cfg.mode == "eval":
+ eval(cfg)
+ else:
+ raise ValueError(f"cfg.mode should in ['eval'], but got '{cfg.mode}'")
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
diff --git a/examples/graphcast/plot.py b/examples/graphcast/plot.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85f5f8d5d2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/graphcast/plot.py
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2024 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+import datetime
+import math
+from typing import Dict
+from typing import Optional
+from typing import Tuple
+
+import matplotlib
+import matplotlib.animation as animation
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import numpy as np
+
+from ppsci.utils import checker
+
+if not checker.dynamic_import_to_globals("IPython"):
+ raise ImportError(
+ "Could not import IPython python package. "
+ "Please install it with pip install IPython."
+ )
+import IPython
+
+if not checker.dynamic_import_to_globals("xarray"):
+ raise ImportError(
+ "Could not import xarray python package. "
+ "Please install it with pip install xarray."
+ )
+import xarray
+
+
+def select(
+ data: xarray.Dataset,
+ variable: str,
+ level: Optional[int] = None,
+ max_steps: Optional[int] = None,
+) -> xarray.Dataset:
+ data = data[variable]
+ if "batch" in data.dims:
+ data = data.isel(batch=0)
+ if (
+ max_steps is not None
+ and "time" in data.sizes
+ and max_steps < data.sizes["time"]
+ ):
+ data = data.isel(time=range(0, max_steps))
+ if level is not None and "level" in data.coords:
+ data = data.sel(level=level)
+ return data
+
+
+def scale(
+ data: xarray.Dataset,
+ center: Optional[float] = None,
+ robust: bool = False,
+) -> Tuple[xarray.Dataset, matplotlib.colors.Normalize, str]:
+ vmin = np.nanpercentile(data, (2 if robust else 0))
+ vmax = np.nanpercentile(data, (98 if robust else 100))
+ if center is not None:
+ diff = max(vmax - center, center - vmin)
+ vmin = center - diff
+ vmax = center + diff
+ return (
+ data,
+ matplotlib.colors.Normalize(vmin, vmax),
+ ("RdBu_r" if center is not None else "viridis"),
+ )
+
+
+def plot_data(
+ data: Dict[str, xarray.Dataset],
+ fig_title: str,
+ plot_size: float = 5,
+ robust: bool = False,
+ cols: int = 4,
+ file: str = "result.png",
+) -> Tuple[xarray.Dataset, matplotlib.colors.Normalize, str]:
+
+ first_data = next(iter(data.values()))[0]
+ max_steps = first_data.sizes.get("time", 1)
+ assert all(max_steps == d.sizes.get("time", 1) for d, _, _ in data.values())
+
+ cols = min(cols, len(data))
+ rows = math.ceil(len(data) / cols)
+ figure = plt.figure(figsize=(plot_size * 2 * cols, plot_size * rows))
+ figure.suptitle(fig_title, fontsize=16)
+ figure.subplots_adjust(wspace=0, hspace=0)
+ figure.tight_layout()
+
+ images = []
+ for i, (title, (plot_data, norm, cmap)) in enumerate(data.items()):
+ ax = figure.add_subplot(rows, cols, i + 1)
+ ax.set_xticks([])
+ ax.set_yticks([])
+ ax.set_title(title)
+ im = ax.imshow(
+ plot_data.isel(time=0, missing_dims="ignore"),
+ norm=norm,
+ origin="lower",
+ cmap=cmap,
+ )
+ plt.colorbar(
+ mappable=im,
+ ax=ax,
+ orientation="vertical",
+ pad=0.02,
+ aspect=16,
+ shrink=0.75,
+ cmap=cmap,
+ extend=("both" if robust else "neither"),
+ )
+ images.append(im)
+
+ def _update(frame):
+ if "time" in first_data.dims:
+ td = datetime.timedelta(
+ microseconds=first_data["time"][frame].item() / 1000
+ )
+ figure.suptitle(f"{fig_title}, {td}", fontsize=16)
+ else:
+ figure.suptitle(fig_title, fontsize=16)
+ for im, (plot_data, norm, cmap) in zip(images, data.values()):
+ im.set_data(plot_data.isel(time=frame, missing_dims="ignore"))
+
+ ani = animation.FuncAnimation(
+ fig=figure, func=_update, frames=max_steps, interval=250
+ )
+ plt.savefig(
+ file,
+ bbox_inches="tight",
+ )
+ plt.close(figure.number)
+ return IPython.display.HTML(ani.to_jshtml())
+
+
+def log_images(
+ target: xarray.Dataset,
+ pred: xarray.Dataset,
+ variable_name: str,
+ level: int,
+ robust=True,
+ file="result.png",
+):
+ plot_size = 5
+ plot_max_steps = pred.sizes["time"]
+
+ data = {
+ "Targets": scale(
+ select(target, variable_name, level, plot_max_steps), robust=robust
+ ),
+ "Predictions": scale(
+ select(pred, variable_name, level, plot_max_steps), robust=robust
+ ),
+ "Diff": scale(
+ (
+ select(target, variable_name, level, plot_max_steps)
+ - select(pred, variable_name, level, plot_max_steps)
+ ),
+ robust=robust,
+ center=0,
+ ),
+ }
+ fig_title = variable_name
+ if "level" in pred[variable_name].coords:
+ fig_title += f" at {level} hPa"
+
+ plot_data(data, fig_title, plot_size, robust, file=file)
diff --git a/jointContribution/graphGalerkin/utils/ChebConv.py b/jointContribution/graphGalerkin/utils/ChebConv.py
index d8c11bfcfb..20d18d503e 100644
--- a/jointContribution/graphGalerkin/utils/ChebConv.py
+++ b/jointContribution/graphGalerkin/utils/ChebConv.py
@@ -1,15 +1,19 @@
from typing import Optional
-import paddle
-from message_passing import MessagePassing
+import paddle
from init import zeros
-from utils import add_self_loops, remove_self_loops, get_laplacian, masked_fill
-
-from paddle.nn import LayerList
from linear import Linear
+from message_passing import MessagePassing
from paddle import Tensor
+from paddle.nn import LayerList
+from utils import add_self_loops
+from utils import get_laplacian
+from utils import masked_fill
+from utils import remove_self_loops
OptTensor = Optional[Tensor]
+
+
class ChebConv(MessagePassing):
r"""The chebyshev spectral graph convolutional operator from the
`"Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral
@@ -68,31 +72,38 @@ class ChebConv(MessagePassing):
batch vector :math:`(|\mathcal{V}|)` *(optional)*,
maximum :obj:`lambda` value :math:`(|\mathcal{G}|)` *(optional)*
- **output:** node features :math:`(|\mathcal{V}|, F_{out})`
-
"""
- def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int, K: int,
- normalization: Optional[str] = 'sym', bias: bool = True,
- **kwargs):
- kwargs.setdefault('aggr', 'add')
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ in_channels: int,
+ out_channels: int,
+ K: int,
+ normalization: Optional[str] = "sym",
+ bias: bool = True,
+ **kwargs,
+ ):
+ kwargs.setdefault("aggr", "add")
super().__init__(**kwargs)
assert K > 0
- assert normalization in [None, 'sym', 'rw'], 'Invalid normalization'
+ assert normalization in [None, "sym", "rw"], "Invalid normalization"
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.normalization = normalization
- weight_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(
- name="weight",
- initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(value=0.5))
- self.lins = LayerList([
- Linear(in_channels, out_channels, bias=False,
- weight_initializer='glorot') for _ in range(K)
- ])
+ self.lins = LayerList(
+ [
+ Linear(
+ in_channels, out_channels, bias=False, weight_initializer="glorot"
+ )
+ for _ in range(K)
+ ]
+ )
if bias:
self.bias = paddle.create_parameter([out_channels], paddle.float32)
else:
- self.register_parameter('bias', None)
+ self.register_parameter("bias", None)
self.reset_parameters()
@@ -101,34 +112,50 @@ def reset_parameters(self):
lin.reset_parameters()
zeros(self.bias)
- def __norm__(self, edge_index, num_nodes: Optional[int],
- edge_weight: OptTensor, normalization: Optional[str],
- lambda_max, dtype: Optional[int] = None,
- batch: OptTensor = None):
-
- edge_index, edge_weight = remove_self_loops(edge_index, edge_weight)
- edge_index, edge_weight = get_laplacian(edge_index, edge_weight,
- normalization, dtype,
- num_nodes)
+ def __norm__(
+ self,
+ edge_index,
+ num_nodes: Optional[int],
+ edge_weight: OptTensor,
+ normalization: Optional[str],
+ lambda_max,
+ dtype: Optional[int] = None,
+ batch: OptTensor = None,
+ ):
+
+ edge_index, edge_weight = remove_self_loops(edge_index, edge_weight)
+ edge_index, edge_weight = get_laplacian(
+ edge_index, edge_weight, normalization, dtype, num_nodes
+ )
if batch is not None and lambda_max.numel() > 1:
lambda_max = lambda_max[batch[edge_index[0]]]
edge_weight = (2.0 * edge_weight) / lambda_max
- edge_weight = masked_fill(edge_weight, edge_weight == float('inf'), 0) ###########
+ edge_weight = masked_fill(
+ edge_weight, edge_weight == float("inf"), 0
+ ) ###########
- edge_index, edge_weight = add_self_loops(edge_index, edge_weight,
- fill_value=-1.,
- num_nodes=num_nodes)
+ edge_index, edge_weight = add_self_loops(
+ edge_index, edge_weight, fill_value=-1.0, num_nodes=num_nodes
+ )
assert edge_weight is not None
return edge_index, edge_weight
-
- def forward(self, x, edge_index, edge_weight: OptTensor = None,
- batch: OptTensor = None, lambda_max: OptTensor = None):
+
+ def forward(
+ self,
+ x,
+ edge_index,
+ edge_weight: OptTensor = None,
+ batch: OptTensor = None,
+ lambda_max: OptTensor = None,
+ ):
""""""
- if self.normalization != 'sym' and lambda_max is None:
- raise ValueError('You need to pass `lambda_max` to `forward() in`'
- 'case the normalization is non-symmetric.')
+ if self.normalization != "sym" and lambda_max is None:
+ raise ValueError(
+ "You need to pass `lambda_max` to `forward() in`"
+ "case the normalization is non-symmetric."
+ )
if lambda_max is None:
lambda_max = paddle.to_tensor(2.0, dtype=x.dtype)
@@ -136,10 +163,15 @@ def forward(self, x, edge_index, edge_weight: OptTensor = None,
lambda_max = paddle.to_tensor(lambda_max, dtype=x.dtype)
assert lambda_max is not None
- edge_index, norm = self.__norm__(edge_index, x.shape[self.node_dim],
- edge_weight, self.normalization,
- lambda_max, dtype=x.dtype,
- batch=batch)
+ edge_index, norm = self.__norm__(
+ edge_index,
+ x.shape[self.node_dim],
+ edge_weight,
+ self.normalization,
+ lambda_max,
+ dtype=x.dtype,
+ batch=batch,
+ )
Tx_0 = x
Tx_1 = x # Dummy.
out = self.lins[0](Tx_0)
@@ -150,7 +182,7 @@ def forward(self, x, edge_index, edge_weight: OptTensor = None,
for lin in self.lins[2:]:
Tx_2 = self.propagate(edge_index, x=Tx_1, norm=norm, size=None)
- Tx_2 = 2. * Tx_2 - Tx_0
+ Tx_2 = 2.0 * Tx_2 - Tx_0
out = out + lin.forward(Tx_2)
Tx_0, Tx_1 = Tx_1, Tx_2
@@ -163,6 +195,8 @@ def message(self, x_j, norm):
return norm.reshape([-1, 1]) * x_j
def __repr__(self) -> str:
- return (f'{self.__class__.__name__}({self.in_channels}, '
- f'{self.out_channels}, K={len(self.lins)}, '
- f'normalization={self.normalization})')
\ No newline at end of file
+ return (
+ f"{self.__class__.__name__}({self.in_channels}, "
+ f"{self.out_channels}, K={len(self.lins)}, "
+ f"normalization={self.normalization})"
+ )
diff --git a/jointContribution/graphcast/graphtype.py b/jointContribution/graphcast/graphtype.py
index fd9210f459..9ba09b9648 100644
--- a/jointContribution/graphcast/graphtype.py
+++ b/jointContribution/graphcast/graphtype.py
@@ -461,8 +461,8 @@ def faces_to_edges(faces: np.ndarray):
adjacent to each face.
Returns:
Tuple with sender/receiver indices, each of shape [num_edges=num_faces*3].
-
"""
+
assert faces.ndim == 2
assert faces.shape[-1] == 3
senders = np.concatenate([faces[:, 0], faces[:, 1], faces[:, 2]])
diff --git a/jointContribution/graphcast/utils.py b/jointContribution/graphcast/utils.py
index eeb8bb0fc4..1f1f2e0307 100644
--- a/jointContribution/graphcast/utils.py
+++ b/jointContribution/graphcast/utils.py
@@ -68,7 +68,6 @@ def get_graph_spatial_features(
Returns:
Arrays of shape: [num_nodes, num_features] and [num_edges, num_features].
with node and edge features.
-
"""
num_nodes = node_lat.shape[0]
@@ -328,7 +327,6 @@ def get_rotation_matrices_to_local_coordinates(
this is computationally different from rotating the longitude only
and is. We do it like this, so the polar geodesic curve, continues
to be aligned with one of the axis after the rotation.
-
"""
if rotate_longitude and rotate_latitude:
@@ -429,7 +427,6 @@ def get_bipartite_graph_spatial_features(
Returns:
Arrays of shape: [num_nodes, num_features] and [num_edges, num_features].
with node and edge features.
-
"""
num_senders = senders_node_lat.shape[0]
diff --git a/mkdocs.yml b/mkdocs.yml
index 7909f08eb7..e024b2a460 100644
--- a/mkdocs.yml
+++ b/mkdocs.yml
@@ -88,6 +88,7 @@ nav:
- NowcastNet: zh/examples/nowcastnet.md
- DGMR: zh/examples/dgmr.md
- EarthFormer: zh/examples/earthformer.md
+ - GraphCast: zh/examples/graphcast.md
- API 文档:
- ppsci:
- ppsci.arch: zh/api/arch.md
diff --git a/ppsci/arch/__init__.py b/ppsci/arch/__init__.py
index bcb0bfcc97..507364dc05 100644
--- a/ppsci/arch/__init__.py
+++ b/ppsci/arch/__init__.py
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@
import copy
+from ppsci.arch.graphcast import GraphCastNet
from ppsci.arch.phycrnet import PhyCRNet
from ppsci.arch.base import Arch # isort:skip
@@ -84,6 +85,7 @@
"UNONet",
"build_model",
"CFDGCN",
+ "GraphCastNet",
]
diff --git a/ppsci/arch/cuboid_transformer_encoder.py b/ppsci/arch/cuboid_transformer_encoder.py
index 7e210734bd..34ec3efa53 100644
--- a/ppsci/arch/cuboid_transformer_encoder.py
+++ b/ppsci/arch/cuboid_transformer_encoder.py
@@ -26,7 +26,6 @@ class PatchMerging3D(paddle.nn.Layer):
padding_type (str, optional): The type of padding. Defaults to "nearest".
linear_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of linear init. Defaults to "0".
norm_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of normalization init. Defaults to "0".
-
"""
def __init__(
@@ -995,7 +994,6 @@ class StackCuboidSelfAttentionBlock(paddle.nn.Layer):
attn_linear_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of attention linear initialization. Defaults to "0".
ffn_linear_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of FFN linear initialization. Defaults to "0".
norm_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of normalization initialization. Defaults to "0".
-
"""
def __init__(
@@ -1277,7 +1275,6 @@ class CuboidTransformerEncoder(paddle.nn.Layer):
conv_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of conv initialization. Defaults to "0".
down_linear_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of downsample linear initialization. Defaults to "0".
norm_init_mode (str, optional): The mode of normalization. Defaults to "0".
-
"""
def __init__(
diff --git a/ppsci/arch/fno_block.py b/ppsci/arch/fno_block.py
index f5fa86d208..751e68b115 100644
--- a/ppsci/arch/fno_block.py
+++ b/ppsci/arch/fno_block.py
@@ -153,7 +153,6 @@ class SoftGating(nn.Layer):
n_dim (int, optional): Dimensionality of the input (excluding batch-size and channels).
``n_dim=2`` corresponds to having Module2D. Defaults to 2.
bias (bool, optional): Whether to use bias. Defaults to False.
-
"""
def __init__(
@@ -469,7 +468,6 @@ def resample(x, res_scale, axis, output_shape=None):
'axis' parameter. If res_scale is scaler, then isotropic scaling is performed.
axis (int): Axis or dimensions along which interpolation will be performed.
output_shape (optional[None ,tuple[int]]): The output shape. Defaults to None.
-
"""
if isinstance(res_scale, (float, int)):
@@ -576,7 +574,6 @@ class FactorizedSpectralConv(nn.Layer):
single tensor. Defaults to False.
init_std (str, optional): The std to use for the init. Defaults to "auto".
fft_norm (str, optional):The normalization mode for the FFT. Defaults to "backward".
-
"""
def __init__(
diff --git a/ppsci/arch/graphcast.py b/ppsci/arch/graphcast.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..79a1c0aeae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ppsci/arch/graphcast.py
@@ -0,0 +1,492 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2024 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+#
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+#
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+#
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+from typing import Dict
+from typing import Tuple
+
+import paddle
+import paddle.nn as nn
+
+from ppsci.arch import base
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ import ppsci.data.dataset.atmospheric_dataset as atmospheric_dataset
+
+
+class ResidualConnection(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, fn):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.fn = fn
+
+ def forward(self, inputs):
+ return inputs + self.fn(inputs)
+
+
+class GraphCastMLP(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self, in_features, out_features, latent_features=None, layer_norm=True
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ if latent_features is None:
+ latent_features = out_features
+
+ self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
+ nn.Linear(in_features, latent_features, bias_attr=True),
+ nn.Silu(),
+ nn.Linear(latent_features, out_features, bias_attr=True),
+ )
+ self.layer_norm = layer_norm
+ if layer_norm:
+ self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(out_features)
+
+ def forward(self, feat):
+ if self.layer_norm:
+ out = self.layer_norm(self.mlp(feat))
+ else:
+ out = self.mlp(feat)
+ return out
+
+
+class GraphCastGNN(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ src_type: str = "mesh",
+ dst_type: str = "mesh",
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.src = src_type
+ self.dst = dst_type
+ self.grid_node_num = grid_node_num
+ self.mesh_node_num = mesh_node_num
+ self.edge_in_dim = grid_node_emb_dim + mesh_node_emb_dim
+
+ if src_type == "mesh" and dst_type == "mesh":
+ self.edge_in_dim += mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ self.edge_out_dim = mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ self.node_in_dim = mesh_node_emb_dim + mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ self.node_out_dim = mesh_node_emb_dim
+ elif src_type == "grid" and dst_type == "mesh":
+ self.edge_in_dim += grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ self.edge_out_dim = grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ self.node_in_dim = mesh_node_emb_dim + grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ self.node_out_dim = mesh_node_emb_dim
+ elif src_type == "mesh" and dst_type == "grid":
+ self.edge_in_dim += mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim
+ self.edge_out_dim = mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim
+ self.node_in_dim = grid_node_emb_dim + mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim
+ self.node_out_dim = grid_node_emb_dim
+ else:
+ raise ValueError
+
+ self.edge_layer = GraphCastMLP(self.edge_in_dim, self.edge_out_dim)
+ self.node_layer = GraphCastMLP(self.node_in_dim, self.node_out_dim)
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ if self.src == "mesh" and self.dst == "mesh":
+ edge_feats = graph.mesh_edge_feat
+ src_node_feats = graph.mesh_node_feat
+ dst_node_feats = graph.mesh_node_feat
+ src_idx = graph.mesh2mesh_src_index
+ dst_idx = graph.mesh2mesh_dst_index
+ dst_node_num = self.mesh_node_num
+ elif self.src == "grid" and self.dst == "mesh":
+ edge_feats = graph.grid2mesh_edge_feat
+ src_node_feats = graph.grid_node_feat
+ dst_node_feats = graph.mesh_node_feat
+ src_idx = graph.grid2mesh_src_index
+ dst_idx = graph.grid2mesh_dst_index
+ dst_node_num = self.mesh_node_num
+ elif self.src == "mesh" and self.dst == "grid":
+ edge_feats = graph.mesh2grid_edge_feat
+ src_node_feats = graph.mesh_node_feat
+ dst_node_feats = graph.grid_node_feat
+ src_idx = graph.mesh2grid_src_index
+ dst_idx = graph.mesh2grid_dst_index
+ dst_node_num = self.grid_node_num
+
+ # update edge features
+ edge_feats_concat = paddle.concat(
+ [
+ edge_feats,
+ paddle.gather(src_node_feats, src_idx),
+ paddle.gather(dst_node_feats, dst_idx),
+ ],
+ axis=-1,
+ )
+ edge_feats_out = self.edge_layer(edge_feats_concat)
+
+ _, batch_dim, _ = edge_feats_out.shape
+
+ # update node features
+ edge_feats_scatter = paddle.zeros([dst_node_num, batch_dim, self.edge_out_dim])
+ node_feats_concat = paddle.concat(
+ [
+ dst_node_feats,
+ paddle.scatter(
+ edge_feats_scatter, dst_idx, edge_feats_out, overwrite=False
+ ),
+ ],
+ axis=-1,
+ )
+ node_feats_out = self.node_layer(node_feats_concat)
+
+ if self.src == "mesh" and self.dst == "mesh":
+ graph.mesh_edge_feat += edge_feats_out
+ graph.mesh_node_feat += node_feats_out
+ elif self.src == "grid" and self.dst == "mesh":
+ graph.grid2mesh_edge_feat += edge_feats_out
+ graph.mesh_node_feat += node_feats_out
+ elif self.src == "mesh" and self.dst == "grid":
+ graph.mesh2grid_edge_feat += edge_feats_out
+ graph.grid_node_feat += node_feats_out
+
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastEmbedding(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_dim: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.grid_node_embedding = GraphCastMLP(grid_node_dim, grid_node_emb_dim)
+ self.mesh_node_embedding = GraphCastMLP(mesh_node_dim, mesh_node_emb_dim)
+ self.mesh_edge_embedding = GraphCastMLP(mesh_edge_dim, mesh_edge_emb_dim)
+ self.grid2mesh_edge_embedding = GraphCastMLP(
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim, grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim
+ )
+ self.mesh2grid_edge_embedding = GraphCastMLP(
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim, mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim
+ )
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ grid_node_emb = self.grid_node_embedding(graph.grid_node_feat)
+ mesh_node_emb = self.mesh_node_embedding(graph.mesh_node_feat)
+ mesh_edge_emb = self.mesh_edge_embedding(graph.mesh_edge_feat)
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb = self.grid2mesh_edge_embedding(graph.grid2mesh_edge_feat)
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb = self.mesh2grid_edge_embedding(graph.mesh2grid_edge_feat)
+
+ graph.grid_node_feat = grid_node_emb
+ graph.mesh_node_feat = mesh_node_emb
+ graph.mesh_edge_feat = mesh_edge_emb
+ graph.grid2mesh_edge_feat = grid2mesh_edge_emb
+ graph.mesh2grid_edge_feat = mesh2grid_edge_emb
+
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastGrid2Mesh(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.grid2mesh_gnn = GraphCastGNN(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ src_type="grid",
+ dst_type="mesh",
+ )
+ self.grid_node_layer = ResidualConnection(
+ GraphCastMLP(grid_node_emb_dim, grid_node_emb_dim)
+ )
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ graph = self.grid2mesh_gnn(graph)
+ graph.grid_node_feat = self.grid_node_layer(graph.grid_node_feat)
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastMesh2Grid(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.mesh2grid_gnn = GraphCastGNN(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ src_type="mesh",
+ dst_type="grid",
+ )
+ self.mesh_node_layer = ResidualConnection(
+ GraphCastMLP(mesh_node_emb_dim, mesh_node_emb_dim)
+ )
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ graph = self.mesh2grid_gnn(graph)
+ graph.mesh_node_feat = self.mesh_node_layer(graph.mesh_node_feat)
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastEncoder(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_dim: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.embedding = GraphCastEmbedding(
+ grid_node_dim=grid_node_dim,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_dim=mesh_node_dim,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_dim=mesh_edge_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim=grid2mesh_edge_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim=mesh2grid_edge_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ )
+ self.grid2mesh_gnn = GraphCastGrid2Mesh(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ )
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ graph = self.embedding(graph)
+ graph = self.grid2mesh_gnn(graph)
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastDecoder(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ node_output_dim: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.mesh2grid_gnn = GraphCastMesh2Grid(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ )
+ self.grid_node_layer = GraphCastMLP(
+ grid_node_emb_dim,
+ node_output_dim,
+ latent_features=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ layer_norm=False,
+ )
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ graph = self.mesh2grid_gnn(graph)
+ graph.grid_node_feat = self.grid_node_layer(graph.grid_node_feat)
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastProcessor(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ gnn_msg_steps: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.processor = nn.Sequential()
+ for idx in range(gnn_msg_steps):
+ self.processor.add_sublayer(
+ f"{idx}",
+ GraphCastGNN(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ src_type="mesh",
+ dst_type="mesh",
+ ),
+ )
+
+ def forward(self, graph: "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"):
+ graph = self.processor(graph)
+ return graph
+
+
+class GraphCastNet(base.Arch):
+ """GraphCast Network
+
+ Args:
+ input_keys (Tuple[str, ...]): Name of input keys.
+ output_keys (Tuple[str, ...]): Name of output keys.
+ grid_node_num (int): Number of grid nodes.
+ grid_node_dim (int): Dimension of grid nodes.
+ grid_node_emb_dim (int): Dimension of emdding grid nodes.
+ mesh_node_num (int): Number of mesh nodes.
+ mesh_node_dim (int): Dimension of mesh nodes.
+ mesh_node_emb_dim (int): Dimension of emdding mesh nodes.
+ mesh_edge_dim (int): Dimension of mesh edges.
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim (int): Dimension of emdding mesh edges.
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim (int): Dimension of mesh edges in Grid2Mesh GNN.
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim (int): Dimension of emdding mesh edges in Grid2Mesh GNN.
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim (int): Dimension of mesh edges in Mesh2Grid GNN.
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim (int): Dimension of emdding mesh edges in Mesh2Grid GNN.
+ gnn_msg_steps (int): Step of gnn messages.
+ node_output_dim (int): Dimension of output nodes.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ input_keys: Tuple[str, ...],
+ output_keys: Tuple[str, ...],
+ grid_node_num: int,
+ grid_node_dim: int,
+ grid_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_num: int,
+ mesh_node_dim: int,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_dim: int,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim: int,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim: int,
+ gnn_msg_steps: int,
+ node_output_dim: int,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.input_keys = input_keys
+ self.output_keys = output_keys
+ self.graphcast = nn.Sequential(
+ (
+ "encoder",
+ GraphCastEncoder(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_dim=grid_node_dim,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_dim=mesh_node_dim,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_dim=mesh_edge_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_dim=grid2mesh_edge_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_dim=mesh2grid_edge_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ ),
+ ),
+ (
+ "processor",
+ GraphCastProcessor(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ gnn_msg_steps=gnn_msg_steps,
+ ),
+ ),
+ (
+ "decoder",
+ GraphCastDecoder(
+ grid_node_num=grid_node_num,
+ grid_node_emb_dim=grid_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_node_num=mesh_node_num,
+ mesh_node_emb_dim=mesh_node_emb_dim,
+ mesh_edge_emb_dim=mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim=grid2mesh_edge_emb_dim,
+ mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim=mesh2grid_edge_emb_dim,
+ node_output_dim=node_output_dim,
+ ),
+ ),
+ )
+
+ def forward(
+ self, x: Dict[str, "atmospheric_dataset.GraphGridMesh"]
+ ) -> Dict[str, paddle.Tensor]:
+ if self._input_transform is not None:
+ x = self._input_transform(x)
+
+ graph = x[self.input_keys[0]]
+ y = self.graphcast(graph)
+
+ if self._output_transform is not None:
+ y = self._output_transform(x, y)
+ return {self.output_keys[0]: y}
diff --git a/ppsci/arch/paddle_harmonics/sht.py b/ppsci/arch/paddle_harmonics/sht.py
index d9965b62bc..bf5e685a04 100644
--- a/ppsci/arch/paddle_harmonics/sht.py
+++ b/ppsci/arch/paddle_harmonics/sht.py
@@ -235,7 +235,6 @@ class RealVectorSHT(nn.Layer):
[2] Wang, B., Wang, L., Xie, Z.; Accurate calculation of spherical and vector spherical harmonic expansions via spectral element grids; Adv Comput Math.
Initializes the vector SHT Layer, precomputing the necessary quadrature weights.
-
"""
def __init__(
diff --git a/ppsci/arch/sfnonet.py b/ppsci/arch/sfnonet.py
index 7629ad3721..aa7e2456a7 100644
--- a/ppsci/arch/sfnonet.py
+++ b/ppsci/arch/sfnonet.py
@@ -90,7 +90,6 @@ def get_contract_fun(weight, implementation="reconstructed", separable=False):
{'reconstructed', 'factorized'} Defaults to "reconstructed".
separable (bool, optional): Whether to use the separable implementation of contraction. This arg is
only checked when `implementation=reconstructed`. Defaults to False.
-
"""
if implementation == "reconstructed":
@@ -208,7 +207,6 @@ class SphericalConv(nn.Layer):
sht_norm (str, optional): The normalization mode of the SHT. Defaults to "ortho".
sht_grids (str, optional): The grid of the SHT. Defaults to "equiangular".
dtype (paddle.float32, optional): The data type. Defaults to paddle.float32.
-
"""
def __init__(
diff --git a/ppsci/data/__init__.py b/ppsci/data/__init__.py
index 55288c26af..4da6b99ad7 100644
--- a/ppsci/data/__init__.py
+++ b/ppsci/data/__init__.py
@@ -101,7 +101,6 @@ def build_dataloader(_dataset, cfg):
# build collate_fn if specified
batch_transforms_cfg = cfg.pop("batch_transforms", None)
-
collate_fn = None
if isinstance(batch_transforms_cfg, (list, tuple)):
collate_fn = batch_transform.build_batch_transforms(batch_transforms_cfg)
@@ -135,6 +134,20 @@ def build_dataloader(_dataset, cfg):
num_workers=cfg.get("num_workers", _DEFAULT_NUM_WORKERS),
collate_fn=collate_fn,
)
+ elif getattr(_dataset, "use_graph_grid_mesh", False):
+ # Use special dataloader `GridMeshAtmosphericDataset`.
+
+ if collate_fn is None:
+ collate_fn = batch_transform.default_collate_fn
+ dataloader_ = io.DataLoader(
+ dataset=_dataset,
+ places=device.get_device(),
+ batch_sampler=batch_sampler,
+ collate_fn=collate_fn,
+ num_workers=cfg.get("num_workers", _DEFAULT_NUM_WORKERS),
+ use_shared_memory=cfg.get("use_shared_memory", False),
+ worker_init_fn=init_fn,
+ )
else:
if (
cfg.get("auto_collation", not getattr(_dataset, "batch_index", False))
diff --git a/ppsci/data/dataset/__init__.py b/ppsci/data/dataset/__init__.py
index c85a126951..4f5a187bb4 100644
--- a/ppsci/data/dataset/__init__.py
+++ b/ppsci/data/dataset/__init__.py
@@ -20,6 +20,7 @@
from ppsci.data.dataset.array_dataset import ContinuousNamedArrayDataset
from ppsci.data.dataset.array_dataset import IterableNamedArrayDataset
from ppsci.data.dataset.array_dataset import NamedArrayDataset
+from ppsci.data.dataset.atmospheric_dataset import GridMeshAtmosphericDataset
from ppsci.data.dataset.csv_dataset import CSVDataset
from ppsci.data.dataset.csv_dataset import IterableCSVDataset
from ppsci.data.dataset.cylinder_dataset import MeshCylinderDataset
@@ -56,6 +57,7 @@
"IterableCSVDataset",
"ERA5Dataset",
"ERA5SampledDataset",
+ "GridMeshAtmosphericDataset",
"IterableMatDataset",
"MatDataset",
"MRMSDataset",
diff --git a/ppsci/data/dataset/atmospheric_dataset.py b/ppsci/data/dataset/atmospheric_dataset.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ab46f126da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ppsci/data/dataset/atmospheric_dataset.py
@@ -0,0 +1,1781 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2024 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+from typing import List
+from typing import NamedTuple
+from typing import Optional
+from typing import Sequence
+from typing import Tuple
+
+import numpy as np
+import paddle
+import pandas as pd
+import scipy
+from paddle import io
+
+try:
+ import trimesh
+ import xarray
+except ModuleNotFoundError:
+ pass
+
+# https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/dataset/ecmwf-reanalysis-v5
+PRESSURE_LEVELS_ERA5_37 = (
+ 1,
+ 2,
+ 3,
+ 5,
+ 7,
+ 10,
+ 20,
+ 30,
+ 50,
+ 70,
+ 100,
+ 125,
+ 150,
+ 175,
+ 200,
+ 225,
+ 250,
+ 300,
+ 350,
+ 400,
+ 450,
+ 500,
+ 550,
+ 600,
+ 650,
+ 700,
+ 750,
+ 775,
+ 800,
+ 825,
+ 850,
+ 875,
+ 900,
+ 925,
+ 950,
+ 975,
+ 1000,
+)
+
+# https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/set-i
+PRESSURE_LEVELS_HRES_25 = (
+ 1,
+ 2,
+ 3,
+ 5,
+ 7,
+ 10,
+ 20,
+ 30,
+ 50,
+ 70,
+ 100,
+ 150,
+ 200,
+ 250,
+ 300,
+ 400,
+ 500,
+ 600,
+ 700,
+ 800,
+ 850,
+ 900,
+ 925,
+ 950,
+ 1000,
+)
+
+# https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2020MS002203
+PRESSURE_LEVELS_WEATHERBENCH_13 = (
+ 50,
+ 100,
+ 150,
+ 200,
+ 250,
+ 300,
+ 400,
+ 500,
+ 600,
+ 700,
+ 850,
+ 925,
+ 1000,
+)
+
+PRESSURE_LEVELS = {
+ 13: PRESSURE_LEVELS_WEATHERBENCH_13,
+ 25: PRESSURE_LEVELS_HRES_25,
+ 37: PRESSURE_LEVELS_ERA5_37,
+}
+
+
+TARGET_SURFACE_VARS = (
+ "2m_temperature",
+ "mean_sea_level_pressure",
+ "10m_v_component_of_wind",
+ "10m_u_component_of_wind",
+ "total_precipitation_6hr",
+)
+TARGET_SURFACE_NO_PRECIP_VARS = (
+ "2m_temperature",
+ "mean_sea_level_pressure",
+ "10m_v_component_of_wind",
+ "10m_u_component_of_wind",
+)
+TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS = (
+ "temperature",
+ "geopotential",
+ "u_component_of_wind",
+ "v_component_of_wind",
+ "vertical_velocity",
+ "specific_humidity",
+)
+TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_NO_W_VARS = (
+ "temperature",
+ "geopotential",
+ "u_component_of_wind",
+ "v_component_of_wind",
+ "specific_humidity",
+)
+EXTERNAL_FORCING_VARS = ("toa_incident_solar_radiation",)
+GENERATED_FORCING_VARS = (
+ "year_progress_sin",
+ "year_progress_cos",
+ "day_progress_sin",
+ "day_progress_cos",
+)
+FORCING_VARS = EXTERNAL_FORCING_VARS + GENERATED_FORCING_VARS
+STATIC_VARS = (
+ "geopotential_at_surface",
+ "land_sea_mask",
+)
+
+TASK_input_variables = (
+ TARGET_SURFACE_VARS + TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS + FORCING_VARS + STATIC_VARS
+)
+TASK_target_variables = TARGET_SURFACE_VARS + TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS
+TASK_forcing_variables = FORCING_VARS
+TASK_pressure_levels = PRESSURE_LEVELS_ERA5_37
+TASK_input_duration = ("12h",)
+
+TASK_13_input_variables = (
+ TARGET_SURFACE_VARS + TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS + FORCING_VARS + STATIC_VARS
+)
+TASK_13_target_variables = TARGET_SURFACE_VARS + TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS
+TASK_13_forcing_variables = FORCING_VARS
+TASK_13_pressure_levels = PRESSURE_LEVELS_WEATHERBENCH_13
+TASK_13_input_duration = ("12h",)
+
+
+TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_input_variables = (
+ TARGET_SURFACE_NO_PRECIP_VARS + TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS + FORCING_VARS + STATIC_VARS
+)
+TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_target_variables = TARGET_SURFACE_VARS + TARGET_ATMOSPHERIC_VARS
+TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_forcing_variables = FORCING_VARS
+TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_pressure_levels = PRESSURE_LEVELS_WEATHERBENCH_13
+TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_input_duration = ("12h",)
+
+_SEC_PER_HOUR = 3600
+_HOUR_PER_DAY = 24
+SEC_PER_DAY = _SEC_PER_HOUR * _HOUR_PER_DAY
+_AVG_DAY_PER_YEAR = 365.24219
+AVG_SEC_PER_YEAR = SEC_PER_DAY * _AVG_DAY_PER_YEAR
+
+DAY_PROGRESS = "day_progress"
+YEAR_PROGRESS = "year_progress"
+
+
+def stacked_to_dataset(
+ stacked_array: "xarray.Variable",
+ template_dataset: "xarray.Dataset",
+ preserved_dims: Tuple[str, ...] = ("batch", "lat", "lon"),
+) -> "xarray.Dataset":
+ """The inverse of dataset_to_stacked.
+
+ Requires a template dataset to demonstrate the variables/shapes/coordinates
+ required.
+ All variables must have preserved_dims dimensions.
+
+ Args:
+ stacked_array: Data in BHWC layout, encoded the same as dataset_to_stacked would if it was asked to encode `template_dataset`.
+ template_dataset: A template Dataset (or other mapping of DataArrays) demonstrating the shape of output required (variables, shapes, coordinates etc).
+ preserved_dims: dimensions from the target_template that were not folded in the predictions channels. The preserved_dims need to be a subset of the dims of all the variables of template_dataset.
+
+ Returns:
+ An xarray.Dataset (or other mapping of DataArrays) with the same shape and type as template_dataset.
+ """
+ unstack_from_channels_sizes = {}
+ var_names = sorted(template_dataset.keys())
+ for name in var_names:
+ template_var = template_dataset[name]
+ if not all(dim in template_var.dims for dim in preserved_dims):
+ raise ValueError(
+ f"stacked_to_dataset requires all Variables to have {preserved_dims} "
+ f"dimensions, but found only {template_var.dims}."
+ )
+ unstack_from_channels_sizes[name] = {
+ dim: size
+ for dim, size in template_var.sizes.items()
+ if dim not in preserved_dims
+ }
+
+ channels = {
+ name: np.prod(list(unstack_sizes.values()), dtype=np.int64)
+ for name, unstack_sizes in unstack_from_channels_sizes.items()
+ }
+ total_expected_channels = sum(channels.values())
+ found_channels = stacked_array.sizes["channels"]
+ if total_expected_channels != found_channels:
+ raise ValueError(
+ f"Expected {total_expected_channels} channels but found "
+ f"{found_channels}, when trying to convert a stacked array of shape "
+ f"{stacked_array.sizes} to a dataset of shape {template_dataset}."
+ )
+
+ data_vars = {}
+ index = 0
+ for name in var_names:
+ template_var = template_dataset[name]
+ var = stacked_array.isel({"channels": slice(index, index + channels[name])})
+ index += channels[name]
+ var = var.unstack({"channels": unstack_from_channels_sizes[name]})
+ var = var.transpose(*template_var.dims)
+ data_vars[name] = xarray.DataArray(
+ data=var,
+ coords=template_var.coords,
+ # This might not always be the same as the name it's keyed under; it
+ # will refer to the original variable name, whereas the key might be
+ # some alias e.g. temperature_850 under which it should be logged:
+ name=template_var.name,
+ )
+ return type(template_dataset)(
+ data_vars
+ ) # pytype:disable=not-callable,wrong-arg-count
+
+
+def get_graph_spatial_features(
+ *,
+ node_lat: np.ndarray,
+ node_lon: np.ndarray,
+ senders: np.ndarray,
+ receivers: np.ndarray,
+ add_node_positions: bool,
+ add_node_latitude: bool,
+ add_node_longitude: bool,
+ add_relative_positions: bool,
+ relative_longitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+ relative_latitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+ sine_cosine_encoding: bool = False,
+ encoding_num_freqs: int = 10,
+ encoding_multiplicative_factor: float = 1.2,
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ """Computes spatial features for the nodes.
+
+ Args:
+ node_lat: Latitudes in the [-90, 90] interval of shape [num_nodes]
+ node_lon: Longitudes in the [0, 360] interval of shape [num_nodes]
+ senders: Sender indices of shape [num_edges]
+ receivers: Receiver indices of shape [num_edges]
+ add_node_positions: Add unit norm absolute positions.
+ add_node_latitude: Add a feature for latitude (cos(90 - lat))
+ Note even if this is set to False, the model may be able to infer the longitude from relative features, unless `relative_latitude_local_coordinates` is also True, or if there is any bias on the relative edge sizes for different longitudes.
+ add_node_longitude: Add features for longitude (cos(lon), sin(lon)).
+ Note even if this is set to False, the model may be able to infer the longitude from relative features, unless `relative_longitude_local_coordinates` is also True, or if there is any bias on the relative edge sizes for different longitudes.
+ add_relative_positions: Whether to relative positions in R3 to the edges.
+ relative_longitude_local_coordinates: If True, relative positions are computed in a local space where the receiver is at 0 longitude.
+ relative_latitude_local_coordinates: If True, relative positions are computed in a local space where the receiver is at 0 latitude.
+ sine_cosine_encoding: If True, we will transform the node/edge features with sine and cosine functions, similar to NERF.
+ encoding_num_freqs: frequency parameter
+ encoding_multiplicative_factor: used for calculating the frequency.
+
+ Returns:
+ Arrays of shape: [num_nodes, num_features] and [num_edges, num_features].
+ with node and edge features.
+ """
+
+ num_nodes = node_lat.shape[0]
+ num_edges = senders.shape[0]
+ dtype = node_lat.dtype
+ node_phi, node_theta = lat_lon_deg_to_spherical(node_lat, node_lon)
+
+ # Computing some node features.
+ node_features = []
+ if add_node_positions:
+ # Already in [-1, 1.] range.
+ node_features.extend(spherical_to_cartesian(node_phi, node_theta))
+
+ if add_node_latitude:
+ # Using the cos of theta.
+ # From 1. (north pole) to -1 (south pole).
+ node_features.append(np.cos(node_theta))
+
+ if add_node_longitude:
+ # Using the cos and sin, which is already normalized.
+ node_features.append(np.cos(node_phi))
+ node_features.append(np.sin(node_phi))
+
+ if not node_features:
+ node_features = np.zeros([num_nodes, 0], dtype=dtype)
+ else:
+ node_features = np.stack(node_features, axis=-1)
+
+ # Computing some edge features.
+ edge_features = []
+
+ if add_relative_positions:
+
+ relative_position = get_relative_position_in_receiver_local_coordinates(
+ node_phi=node_phi,
+ node_theta=node_theta,
+ senders=senders,
+ receivers=receivers,
+ latitude_local_coordinates=relative_latitude_local_coordinates,
+ longitude_local_coordinates=relative_longitude_local_coordinates,
+ )
+
+ # Note this is L2 distance in 3d space, rather than geodesic distance.
+ relative_edge_distances = np.linalg.norm(
+ relative_position, axis=-1, keepdims=True
+ )
+
+ # Normalize to the maximum edge distance. Note that we expect to always
+ # have an edge that goes in the opposite direction of any given edge
+ # so the distribution of relative positions should be symmetric around
+ # zero. So by scaling by the maximum length, we expect all relative
+ # positions to fall in the [-1., 1.] interval, and all relative distances
+ # to fall in the [0., 1.] interval.
+ max_edge_distance = relative_edge_distances.max()
+ edge_features.append(relative_edge_distances / max_edge_distance)
+ edge_features.append(relative_position / max_edge_distance)
+
+ if not edge_features:
+ edge_features = np.zeros([num_edges, 0], dtype=dtype)
+ else:
+ edge_features = np.concatenate(edge_features, axis=-1)
+
+ if sine_cosine_encoding:
+
+ def sine_cosine_transform(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
+ freqs = encoding_multiplicative_factor ** np.arange(encoding_num_freqs)
+ phases = freqs * x[..., None]
+ x_sin = np.sin(phases)
+ x_cos = np.cos(phases)
+ x_cat = np.concatenate([x_sin, x_cos], axis=-1)
+ return x_cat.reshape([x.shape[0], -1])
+
+ node_features = sine_cosine_transform(node_features)
+ edge_features = sine_cosine_transform(edge_features)
+
+ return node_features, edge_features
+
+
+def lat_lon_to_leading_axes(grid_xarray: "xarray.DataArray") -> "xarray.DataArray":
+ """Reorders xarray so lat/lon axes come first."""
+ # leading + ["lat", "lon"] + trailing
+ # to
+ # ["lat", "lon"] + leading + trailing
+ return grid_xarray.transpose("lat", "lon", ...)
+
+
+def restore_leading_axes(grid_xarray: "xarray.DataArray") -> "xarray.DataArray":
+ """Reorders xarray so batch/time/level axes come first (if present)."""
+
+ # ["lat", "lon"] + [(batch,) (time,) (level,)] + trailing
+ # to
+ # [(batch,) (time,) (level,)] + ["lat", "lon"] + trailing
+
+ input_dims = list(grid_xarray.dims)
+ output_dims = list(input_dims)
+ for leading_key in ["level", "time", "batch"]: # reverse order for insert
+ if leading_key in input_dims:
+ output_dims.remove(leading_key)
+ output_dims.insert(0, leading_key)
+ return grid_xarray.transpose(*output_dims)
+
+
+def lat_lon_deg_to_spherical(
+ node_lat: np.ndarray,
+ node_lon: np.ndarray,
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ phi = np.deg2rad(node_lon)
+ theta = np.deg2rad(90 - node_lat)
+ return phi, theta
+
+
+def spherical_to_lat_lon(
+ phi: np.ndarray,
+ theta: np.ndarray,
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ lon = np.mod(np.rad2deg(phi), 360)
+ lat = 90 - np.rad2deg(theta)
+ return lat, lon
+
+
+def cartesian_to_spherical(
+ x: np.ndarray,
+ y: np.ndarray,
+ z: np.ndarray,
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ phi = np.arctan2(y, x)
+ with np.errstate(invalid="ignore"): # circumventing b/253179568
+ theta = np.arccos(z) # Assuming unit radius.
+ return phi, theta
+
+
+def spherical_to_cartesian(
+ phi: np.ndarray, theta: np.ndarray
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ # Assuming unit radius.
+ return (np.cos(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta))
+
+
+def get_relative_position_in_receiver_local_coordinates(
+ node_phi: np.ndarray,
+ node_theta: np.ndarray,
+ senders: np.ndarray,
+ receivers: np.ndarray,
+ latitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+ longitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Returns relative position features for the edges.
+
+ The relative positions will be computed in a rotated space for a local
+ coordinate system as defined by the receiver. The relative positions are
+ simply obtained by subtracting sender position minues receiver position in
+ that local coordinate system after the rotation in R^3.
+
+ Args:
+ node_phi: [num_nodes] with polar angles.
+ node_theta: [num_nodes] with azimuthal angles.
+ senders: [num_edges] with indices.
+ receivers: [num_edges] with indices.
+ latitude_local_coordinates: Whether to rotate edges such that in the positions are computed such that the receiver is always at latitude 0.
+ longitude_local_coordinates: Whether to rotate edges such that in the positions are computed such that the receiver is always at longitude 0.
+
+ Returns:
+ Array of relative positions in R3 [num_edges, 3]
+ """
+
+ node_pos = np.stack(spherical_to_cartesian(node_phi, node_theta), axis=-1)
+
+ # No rotation in this case.
+ if not (latitude_local_coordinates or longitude_local_coordinates):
+ return node_pos[senders] - node_pos[receivers]
+
+ # Get rotation matrices for the local space space for every node.
+ rotation_matrices = get_rotation_matrices_to_local_coordinates(
+ reference_phi=node_phi,
+ reference_theta=node_theta,
+ rotate_latitude=latitude_local_coordinates,
+ rotate_longitude=longitude_local_coordinates,
+ )
+
+ # Each edge will be rotated according to the rotation matrix of its receiver
+ # node.
+ edge_rotation_matrices = rotation_matrices[receivers]
+
+ # Rotate all nodes to the rotated space of the corresponding edge.
+ # Note for receivers we can also do the matmul first and the gather second:
+ # ```
+ # receiver_pos_in_rotated_space = rotate_with_matrices(
+ # rotation_matrices, node_pos)[receivers]
+ # ```
+ # which is more efficient, however, we do gather first to keep it more
+ # symmetric with the sender computation.
+ receiver_pos_in_rotated_space = rotate_with_matrices(
+ edge_rotation_matrices, node_pos[receivers]
+ )
+ sender_pos_in_in_rotated_space = rotate_with_matrices(
+ edge_rotation_matrices, node_pos[senders]
+ )
+ # Note, here, that because the rotated space is chosen according to the
+ # receiver, if:
+ # * latitude_local_coordinates = True: latitude for the receivers will be
+ # 0, that is the z coordinate will always be 0.
+ # * longitude_local_coordinates = True: longitude for the receivers will be
+ # 0, that is the y coordinate will be 0.
+
+ # Now we can just subtract.
+ # Note we are rotating to a local coordinate system, where the y-z axes are
+ # parallel to a tangent plane to the sphere, but still remain in a 3d space.
+ # Note that if both `latitude_local_coordinates` and
+ # `longitude_local_coordinates` are True, and edges are short,
+ # then the difference in x coordinate between sender and receiver
+ # should be small, so we could consider dropping the new x coordinate if
+ # we wanted to the tangent plane, however in doing so
+ # we would lose information about the curvature of the mesh, which may be
+ # important for very coarse meshes.
+ return sender_pos_in_in_rotated_space - receiver_pos_in_rotated_space
+
+
+def get_rotation_matrices_to_local_coordinates(
+ reference_phi: np.ndarray,
+ reference_theta: np.ndarray,
+ rotate_latitude: bool,
+ rotate_longitude: bool,
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Returns a rotation matrix to rotate to a point based on a reference vector.
+
+ The rotation matrix is build such that, a vector in the
+ same coordinate system at the reference point that points towards the pole
+ before the rotation, continues to point towards the pole after the rotation.
+
+ Args:
+ reference_phi: [leading_axis] Polar angles of the reference.
+ reference_theta: [leading_axis] Azimuthal angles of the reference.
+ rotate_latitude: Whether to produce a rotation matrix that would rotate R^3 vectors to zero latitude.
+ rotate_longitude: Whether to produce a rotation matrix that would rotate R^3 vectors to zero longitude.
+
+ Returns:
+ Matrices of shape [leading_axis] such that when applied to the reference
+ position with `rotate_with_matrices(rotation_matrices, reference_pos)`
+
+ * phi goes to 0. if "rotate_longitude" is True.
+
+ * theta goes to np.pi / 2 if "rotate_latitude" is True.
+
+ The rotation consists of:
+ * rotate_latitude = False, rotate_longitude = True:
+ Latitude preserving rotation.
+ * rotate_latitude = True, rotate_longitude = True:
+ Latitude preserving rotation, followed by longitude preserving rotation.
+ * rotate_latitude = True, rotate_longitude = False:
+ Latitude preserving rotation, followed by longitude preserving rotation, and the inverse of the latitude preserving rotation. Note this is computationally different from rotating the longitude only and is. We do it like this, so the polar geodesic curve, continues to be aligned with one of the axis after the rotation.
+ """
+
+ if rotate_longitude and rotate_latitude:
+
+ # We first rotate around the z axis "minus the azimuthal angle", to get the
+ # point with zero longitude
+ azimuthal_rotation = -reference_phi
+
+ # One then we will do a polar rotation (which can be done along the y
+ # axis now that we are at longitude 0.), "minus the polar angle plus 2pi"
+ # to get the point with zero latitude.
+ polar_rotation = -reference_theta + np.pi / 2
+
+ return scipy.spatial.transform.Rotation.from_euler(
+ "zy", np.stack([azimuthal_rotation, polar_rotation], axis=1)
+ ).as_matrix()
+ elif rotate_longitude:
+ # Just like the previous case, but applying only the azimuthal rotation.
+ azimuthal_rotation = -reference_phi
+ return scipy.spatial.transform.Rotation.from_euler(
+ "z", -reference_phi
+ ).as_matrix()
+ elif rotate_latitude:
+ # Just like the first case, but after doing the polar rotation, undoing
+ # the azimuthal rotation.
+ azimuthal_rotation = -reference_phi
+ polar_rotation = -reference_theta + np.pi / 2
+
+ return scipy.spatial.transform.Rotation.from_euler(
+ "zyz",
+ np.stack([azimuthal_rotation, polar_rotation, -azimuthal_rotation], axis=1),
+ ).as_matrix()
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("At least one of longitude and latitude should be rotated.")
+
+
+def rotate_with_matrices(
+ rotation_matrices: np.ndarray, positions: np.ndarray
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ return np.einsum("bji,bi->bj", rotation_matrices, positions)
+
+
+def get_bipartite_graph_spatial_features(
+ *,
+ senders_node_lat: np.ndarray,
+ senders_node_lon: np.ndarray,
+ senders: np.ndarray,
+ receivers_node_lat: np.ndarray,
+ receivers_node_lon: np.ndarray,
+ receivers: np.ndarray,
+ add_node_positions: bool,
+ add_node_latitude: bool,
+ add_node_longitude: bool,
+ add_relative_positions: bool,
+ edge_normalization_factor: Optional[float] = None,
+ relative_longitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+ relative_latitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ """Computes spatial features for the nodes.
+
+ This function is almost identical to `get_graph_spatial_features`. The only
+ difference is that sender nodes and receiver nodes can be in different arrays.
+ This is necessary to enable combination with typed Graph.
+
+ Args:
+ senders_node_lat: Latitudes in the [-90, 90] interval of shape [num_sender_nodes]
+ senders_node_lon: Longitudes in the [0, 360] interval of shape [num_sender_nodes]
+ senders: Sender indices of shape [num_edges], indices in [0, num_sender_nodes)
+ receivers_node_lat: Latitudes in the [-90, 90] interval of shape [num_receiver_nodes]
+ receivers_node_lon: Longitudes in the [0, 360] interval of shape [num_receiver_nodes]
+ receivers: Receiver indices of shape [num_edges], indices in [0, num_receiver_nodes)
+ add_node_positions: Add unit norm absolute positions.
+ add_node_latitude: Add a feature for latitude (cos(90 - lat)).
+ Note even ifthis is set to False, the model may be able to infer the longitude from relative features, unless `relative_latitude_local_coordinates` is also True, or if there is any bias on the relative edge sizes for different longitudes.
+ add_node_longitude: Add features for longitude (cos(lon), sin(lon)).
+ Note even if this is set to False, the model may be able to infer the longitude from relative features, unless `relative_longitude_local_coordinates` is also True, or if there is any bias on the relative edge sizes for different longitudes.
+ add_relative_positions: Whether to relative positions in R3 to the edges.
+ edge_normalization_factor: Allows explicitly controlling edge normalization. If None, defaults to max edge length. This supports using pre-trained model weights with a different graph structure to what it was trained on.
+ relative_longitude_local_coordinates: If True, relative positions are computed in a local space where the receiver is at 0 longitude.
+ relative_latitude_local_coordinates: If True, relative positions are computed in a local space where the receiver is at 0 latitude.
+
+ Returns:
+ Arrays of shape: [num_nodes, num_features] and [num_edges, num_features]. with node and edge features.
+ """
+
+ num_senders = senders_node_lat.shape[0]
+ num_receivers = receivers_node_lat.shape[0]
+ num_edges = senders.shape[0]
+ dtype = senders_node_lat.dtype
+ assert receivers_node_lat.dtype == dtype
+ senders_node_phi, senders_node_theta = lat_lon_deg_to_spherical(
+ senders_node_lat, senders_node_lon
+ )
+ receivers_node_phi, receivers_node_theta = lat_lon_deg_to_spherical(
+ receivers_node_lat, receivers_node_lon
+ )
+
+ # Computing some node features.
+ senders_node_features = []
+ receivers_node_features = []
+ if add_node_positions:
+ # Already in [-1, 1.] range.
+ senders_node_features.extend(
+ spherical_to_cartesian(senders_node_phi, senders_node_theta)
+ )
+ receivers_node_features.extend(
+ spherical_to_cartesian(receivers_node_phi, receivers_node_theta)
+ )
+
+ if add_node_latitude:
+ # Using the cos of theta.
+ # From 1. (north pole) to -1 (south pole).
+ senders_node_features.append(np.cos(senders_node_theta))
+ receivers_node_features.append(np.cos(receivers_node_theta))
+
+ if add_node_longitude:
+ # Using the cos and sin, which is already normalized.
+ senders_node_features.append(np.cos(senders_node_phi))
+ senders_node_features.append(np.sin(senders_node_phi))
+
+ receivers_node_features.append(np.cos(receivers_node_phi))
+ receivers_node_features.append(np.sin(receivers_node_phi))
+
+ if not senders_node_features:
+ senders_node_features = np.zeros([num_senders, 0], dtype=dtype)
+ receivers_node_features = np.zeros([num_receivers, 0], dtype=dtype)
+ else:
+ senders_node_features = np.stack(senders_node_features, axis=-1)
+ receivers_node_features = np.stack(receivers_node_features, axis=-1)
+
+ # Computing some edge features.
+ edge_features = []
+
+ if add_relative_positions:
+
+ relative_position = (
+ get_bipartite_relative_position_in_receiver_local_coordinates(
+ senders_node_phi=senders_node_phi,
+ senders_node_theta=senders_node_theta,
+ receivers_node_phi=receivers_node_phi,
+ receivers_node_theta=receivers_node_theta,
+ senders=senders,
+ receivers=receivers,
+ latitude_local_coordinates=relative_latitude_local_coordinates,
+ longitude_local_coordinates=relative_longitude_local_coordinates,
+ )
+ )
+
+ # Note this is L2 distance in 3d space, rather than geodesic distance.
+ relative_edge_distances = np.linalg.norm(
+ relative_position, axis=-1, keepdims=True
+ )
+
+ if edge_normalization_factor is None:
+ # Normalize to the maximum edge distance. Note that we expect to always
+ # have an edge that goes in the opposite direction of any given edge
+ # so the distribution of relative positions should be symmetric around
+ # zero. So by scaling by the maximum length, we expect all relative
+ # positions to fall in the [-1., 1.] interval, and all relative distances
+ # to fall in the [0., 1.] interval.
+ edge_normalization_factor = relative_edge_distances.max()
+
+ edge_features.append(relative_edge_distances / edge_normalization_factor)
+ edge_features.append(relative_position / edge_normalization_factor)
+
+ if not edge_features:
+ edge_features = np.zeros([num_edges, 0], dtype=dtype)
+ else:
+ edge_features = np.concatenate(edge_features, axis=-1)
+
+ return senders_node_features, receivers_node_features, edge_features
+
+
+def get_bipartite_relative_position_in_receiver_local_coordinates(
+ senders_node_phi: np.ndarray,
+ senders_node_theta: np.ndarray,
+ senders: np.ndarray,
+ receivers_node_phi: np.ndarray,
+ receivers_node_theta: np.ndarray,
+ receivers: np.ndarray,
+ latitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+ longitude_local_coordinates: bool,
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Returns relative position features for the edges.
+
+ This function is equivalent to
+ `get_relative_position_in_receiver_local_coordinates`, but adapted to work
+ with bipartite typed graphs.
+
+ The relative positions will be computed in a rotated space for a local
+ coordinate system as defined by the receiver. The relative positions are
+ simply obtained by subtracting sender position minues receiver position in
+ that local coordinate system after the rotation in R^3.
+
+ Args:
+ senders_node_phi: [num_sender_nodes] with polar angles.
+ senders_node_theta: [num_sender_nodes] with azimuthal angles.
+ senders: [num_edges] with indices into sender nodes.
+ receivers_node_phi: [num_sender_nodes] with polar angles.
+ receivers_node_theta: [num_sender_nodes] with azimuthal angles.
+ receivers: [num_edges] with indices into receiver nodes.
+ latitude_local_coordinates: Whether to rotate edges such that in the positions are computed such that the receiver is always at latitude 0.
+ longitude_local_coordinates: Whether to rotate edges such that in the positions are computed such that the receiver is always at longitude 0.
+
+ Returns:
+ Array of relative positions in R3 [num_edges, 3]
+ """
+
+ senders_node_pos = np.stack(
+ spherical_to_cartesian(senders_node_phi, senders_node_theta), axis=-1
+ )
+
+ receivers_node_pos = np.stack(
+ spherical_to_cartesian(receivers_node_phi, receivers_node_theta), axis=-1
+ )
+
+ # No rotation in this case.
+ if not (latitude_local_coordinates or longitude_local_coordinates):
+ return senders_node_pos[senders] - receivers_node_pos[receivers]
+
+ # Get rotation matrices for the local space space for every receiver node.
+ receiver_rotation_matrices = get_rotation_matrices_to_local_coordinates(
+ reference_phi=receivers_node_phi,
+ reference_theta=receivers_node_theta,
+ rotate_latitude=latitude_local_coordinates,
+ rotate_longitude=longitude_local_coordinates,
+ )
+
+ # Each edge will be rotated according to the rotation matrix of its receiver
+ # node.
+ edge_rotation_matrices = receiver_rotation_matrices[receivers]
+
+ # Rotate all nodes to the rotated space of the corresponding edge.
+ # Note for receivers we can also do the matmul first and the gather second:
+ # ```
+ # receiver_pos_in_rotated_space = rotate_with_matrices(
+ # rotation_matrices, node_pos)[receivers]
+ # ```
+ # which is more efficient, however, we do gather first to keep it more
+ # symmetric with the sender computation.
+ receiver_pos_in_rotated_space = rotate_with_matrices(
+ edge_rotation_matrices, receivers_node_pos[receivers]
+ )
+ sender_pos_in_in_rotated_space = rotate_with_matrices(
+ edge_rotation_matrices, senders_node_pos[senders]
+ )
+ # Note, here, that because the rotated space is chosen according to the
+ # receiver, if:
+ # * latitude_local_coordinates = True: latitude for the receivers will be
+ # 0, that is the z coordinate will always be 0.
+ # * longitude_local_coordinates = True: longitude for the receivers will be
+ # 0, that is the y coordinate will be 0.
+
+ # Now we can just subtract.
+ # Note we are rotating to a local coordinate system, where the y-z axes are
+ # parallel to a tangent plane to the sphere, but still remain in a 3d space.
+ # Note that if both `latitude_local_coordinates` and
+ # `longitude_local_coordinates` are True, and edges are short,
+ # then the difference in x coordinate between sender and receiver
+ # should be small, so we could consider dropping the new x coordinate if
+ # we wanted to the tangent plane, however in doing so
+ # we would lose information about the curvature of the mesh, which may be
+ # important for very coarse meshes.
+ return sender_pos_in_in_rotated_space - receiver_pos_in_rotated_space
+
+
+class GraphGridMesh:
+ """Graph datatype of GraphCast.
+
+ Args:
+ mesh_size (int): size of mesh.
+ radius_query_fraction_edge_length (float): _description_
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor (float): Normalization factor of edge in Mesh2Grid GNN.
+ resolution (float): resolution of atmospheric data.
+ mesh2mesh_src_index (np.array, optional): Index of Mesh2Mesh source node. Defaults to None.
+ mesh2mesh_dst_index (np.array, optional): Index of Mesh2Mesh destination node. Defaults to None.
+ grid2mesh_src_index (np.array, optional): Index of Grid2Mesh source node. Defaults to None.
+ grid2mesh_dst_index (np.array, optional): Index of Grid2Mesh destination node.
+ mesh2grid_src_index (np.array, optional): Index of Mesh2Grid source node. Defaults to None.
+ mesh2grid_dst_index (np.array, optional): Index of Mesh2Grid destination node. Defaults to None.
+ mesh_num_nodes (int, optional): Number of mesh nodes. Defaults to None.
+ grid_num_nodes (int, optional): Number of grid nodes. Defaults to None.
+ mesh_num_edges (int, optional): Number of mesh edges. Defaults to None.
+ grid2mesh_num_edges (int, optional): Number of edges in Grid2Mesh GNN. Defaults to None.
+ mesh2grid_num_edges (int, optional): Number of edges in Mesh2Grid GNN. Defaults to None.
+ grid_node_feat (np.array, optional): Feature of grid nodes. Defaults to None.
+ mesh_node_feat (np.array, optional): Feature of mehs nodes. Defaults to None.
+ mesh_edge_feat (np.array, optional): Feature of mesh edges. Defaults to None.
+ grid2mesh_edge_feat (np.array, optional): Feature of edges in Grid2Mesh GNN. Defaults to None.
+ mesh2grid_edge_feat (np.array, optional): Feature of edges in Mesh2Grid GNN. Defaults to None.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ mesh_size: int,
+ radius_query_fraction_edge_length: float,
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor: float,
+ resolution: float,
+ mesh2mesh_src_index: np.array = None,
+ mesh2mesh_dst_index: np.array = None,
+ grid2mesh_src_index: np.array = None,
+ grid2mesh_dst_index: np.array = None,
+ mesh2grid_src_index: np.array = None,
+ mesh2grid_dst_index: np.array = None,
+ mesh_num_nodes: int = None,
+ grid_num_nodes: int = None,
+ mesh_num_edges: int = None,
+ grid2mesh_num_edges: np.array = None,
+ mesh2grid_num_edges: np.array = None,
+ grid_node_feat: np.array = None,
+ mesh_node_feat: np.array = None,
+ mesh_edge_feat: np.array = None,
+ grid2mesh_edge_feat: np.array = None,
+ mesh2grid_edge_feat: np.array = None,
+ ):
+ self.meshes = get_hierarchy_of_triangular_meshes_for_sphere(mesh_size)
+
+ all_input_vars = [
+ mesh2mesh_src_index,
+ mesh2mesh_dst_index,
+ grid2mesh_src_index,
+ grid2mesh_dst_index,
+ mesh2grid_src_index,
+ mesh2grid_dst_index,
+ mesh_num_nodes,
+ grid_num_nodes,
+ mesh_num_edges,
+ grid2mesh_num_edges,
+ mesh2grid_num_edges,
+ grid_node_feat,
+ mesh_node_feat,
+ mesh_edge_feat,
+ grid2mesh_edge_feat,
+ mesh2grid_edge_feat,
+ ]
+ should_init = any(var is None for var in all_input_vars)
+
+ if should_init:
+ self.query_radius = (
+ self._get_max_edge_distance(self.finest_mesh)
+ * radius_query_fraction_edge_length
+ )
+ self._mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor = (
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor
+ )
+ self._spatial_features_kwargs = dict(
+ add_node_positions=False,
+ add_node_latitude=True,
+ add_node_longitude=True,
+ add_relative_positions=True,
+ relative_longitude_local_coordinates=True,
+ relative_latitude_local_coordinates=True,
+ )
+
+ self.init_mesh_properties()
+ self._init_grid_properties(
+ grid_lat=np.arange(-90.0, 90.0 + resolution, resolution),
+ grid_lon=np.arange(0.0, 360.0, resolution),
+ )
+ self._grid2mesh_graph_structure = self._init_grid2mesh_graph()
+ self._mesh_graph_structure = self._init_mesh_graph()
+ self._mesh2grid_graph_structure = self._init_mesh2grid_graph()
+ else:
+ self.mesh2mesh_src_index = mesh2mesh_src_index
+ self.mesh2mesh_dst_index = mesh2mesh_dst_index
+ self.grid2mesh_src_index = grid2mesh_src_index
+ self.grid2mesh_dst_index = grid2mesh_dst_index
+ self.mesh2grid_src_index = mesh2grid_src_index
+ self.mesh2grid_dst_index = mesh2grid_dst_index
+
+ self.mesh_num_nodes = mesh_num_nodes
+ self.grid_num_nodes = grid_num_nodes
+
+ self.mesh_num_edges = mesh_num_edges
+ self.grid2mesh_num_edges = grid2mesh_num_edges
+ self.mesh2grid_num_edges = mesh2grid_num_edges
+
+ self.grid_node_feat = grid_node_feat
+ self.mesh_node_feat = mesh_node_feat
+ self.mesh_edge_feat = mesh_edge_feat
+ self.grid2mesh_edge_feat = grid2mesh_edge_feat
+ self.mesh2grid_edge_feat = mesh2grid_edge_feat
+
+ def update(self, name, value):
+ if hasattr(self, name):
+ setattr(self, name, value)
+ else:
+ raise ValueError
+
+ def tensor(self):
+ self.mesh2mesh_src_index = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh2mesh_src_index, dtype=paddle.int64
+ )
+
+ self.mesh2mesh_dst_index = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh2mesh_dst_index, dtype=paddle.int64
+ )
+ self.grid2mesh_src_index = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.grid2mesh_src_index, dtype=paddle.int64
+ )
+ self.grid2mesh_dst_index = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.grid2mesh_dst_index, dtype=paddle.int64
+ )
+ self.mesh2grid_src_index = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh2grid_src_index, dtype=paddle.int64
+ )
+ self.mesh2grid_dst_index = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh2grid_dst_index, dtype=paddle.int64
+ )
+ self.grid_node_feat = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.grid_node_feat, dtype=paddle.get_default_dtype()
+ )
+ self.mesh_node_feat = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh_node_feat, dtype=paddle.get_default_dtype()
+ )
+ self.mesh_edge_feat = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh_edge_feat, dtype=paddle.get_default_dtype()
+ )
+ self.grid2mesh_edge_feat = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.grid2mesh_edge_feat, dtype=paddle.get_default_dtype()
+ )
+ self.mesh2grid_edge_feat = paddle.to_tensor(
+ self.mesh2grid_edge_feat, dtype=paddle.get_default_dtype()
+ )
+ return self
+
+ @property
+ def finest_mesh(self):
+ return self.meshes[-1]
+
+ def init_mesh_properties(self):
+ """Inits static properties that have to do with mesh nodes."""
+ self.mesh_num_nodes = self.finest_mesh.vertices.shape[0]
+ mesh_phi, mesh_theta = cartesian_to_spherical(
+ self.finest_mesh.vertices[:, 0],
+ self.finest_mesh.vertices[:, 1],
+ self.finest_mesh.vertices[:, 2],
+ )
+ (mesh_nodes_lat, mesh_nodes_lon) = spherical_to_lat_lon(
+ phi=mesh_phi,
+ theta=mesh_theta,
+ )
+ # Convert to f32 to ensure the lat/lon features aren't in f64.
+ self._mesh_nodes_lat = mesh_nodes_lat.astype(np.float32)
+ self._mesh_nodes_lon = mesh_nodes_lon.astype(np.float32)
+
+ def _init_grid_properties(self, grid_lat: np.ndarray, grid_lon: np.ndarray):
+ """Inits static properties that have to do with grid nodes."""
+ self._grid_lat = grid_lat.astype(np.float32)
+ self._grid_lon = grid_lon.astype(np.float32)
+ # Initialized the counters.
+ self.grid_num_nodes = grid_lat.shape[0] * grid_lon.shape[0]
+
+ # Initialize lat and lon for the grid.
+ grid_nodes_lon, grid_nodes_lat = np.meshgrid(grid_lon, grid_lat)
+ self._grid_nodes_lon = grid_nodes_lon.reshape([-1]).astype(np.float32)
+ self._grid_nodes_lat = grid_nodes_lat.reshape([-1]).astype(np.float32)
+
+ def _init_grid2mesh_graph(self):
+ """Build Grid2Mesh graph."""
+
+ # Create some edges according to distance between mesh and grid nodes.
+ assert self._grid_lat is not None and self._grid_lon is not None
+ (grid_indices, mesh_indices) = radius_query_indices(
+ grid_latitude=self._grid_lat,
+ grid_longitude=self._grid_lon,
+ mesh=self.finest_mesh,
+ radius=self.query_radius,
+ )
+
+ # Edges sending info from grid to mesh.
+ senders = grid_indices
+ receivers = mesh_indices
+
+ # Precompute structural node and edge features according to config options.
+ # Structural features are those that depend on the fixed values of the
+ # latitude and longitudes of the nodes.
+ (
+ senders_node_features,
+ _,
+ edge_features,
+ ) = get_bipartite_graph_spatial_features(
+ senders_node_lat=self._grid_nodes_lat,
+ senders_node_lon=self._grid_nodes_lon,
+ receivers_node_lat=self._mesh_nodes_lat,
+ receivers_node_lon=self._mesh_nodes_lon,
+ senders=senders,
+ receivers=receivers,
+ edge_normalization_factor=None,
+ **self._spatial_features_kwargs,
+ )
+
+ self.grid_node_feat = np.expand_dims(senders_node_features, axis=1)
+
+ self.grid2mesh_src_index = senders
+ self.grid2mesh_dst_index = receivers
+ self.grid2mesh_edge_feat = np.expand_dims(edge_features, axis=1)
+ self.grid2mesh_num_edges = len(edge_features)
+
+ def _init_mesh_graph(self):
+ """Build Mesh graph."""
+ merged_mesh = merge_meshes(self.meshes)
+ # Work simply on the mesh edges.
+ senders, receivers = faces_to_edges(merged_mesh.faces)
+ # Precompute structural node and edge features according to config options.
+ # Structural features are those that depend on the fixed values of the
+ # latitude and longitudes of the nodes.
+ assert self._mesh_nodes_lat is not None and self._mesh_nodes_lon is not None
+ node_features, edge_features = get_graph_spatial_features(
+ node_lat=self._mesh_nodes_lat,
+ node_lon=self._mesh_nodes_lon,
+ senders=senders,
+ receivers=receivers,
+ **self._spatial_features_kwargs,
+ )
+
+ self.mesh_node_feat = np.expand_dims(node_features, axis=1)
+ self.mesh2mesh_src_index = senders
+ self.mesh2mesh_dst_index = receivers
+ self.mesh_edge_feat = np.expand_dims(edge_features, axis=1)
+ self.mesh_num_edges = len(edge_features)
+
+ def _init_mesh2grid_graph(self):
+ """Build Mesh2Grid graph."""
+
+ # Create some edges according to how the grid nodes are contained by
+ # mesh triangles.
+ (grid_indices, mesh_indices) = in_mesh_triangle_indices(
+ grid_latitude=self._grid_lat,
+ grid_longitude=self._grid_lon,
+ mesh=self.finest_mesh,
+ )
+
+ # Edges sending info from mesh to grid.
+ senders = mesh_indices
+ receivers = grid_indices
+
+ # Precompute structural node and edge features according to config options.
+ assert self._mesh_nodes_lat is not None and self._mesh_nodes_lon is not None
+ (_, _, edge_features) = get_bipartite_graph_spatial_features(
+ senders_node_lat=self._mesh_nodes_lat,
+ senders_node_lon=self._mesh_nodes_lon,
+ receivers_node_lat=self._grid_nodes_lat,
+ receivers_node_lon=self._grid_nodes_lon,
+ senders=senders,
+ receivers=receivers,
+ edge_normalization_factor=self._mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor,
+ **self._spatial_features_kwargs,
+ )
+
+ self.mesh2grid_src_index = senders
+ self.mesh2grid_dst_index = receivers
+ self.mesh2grid_edge_feat = np.expand_dims(edge_features, axis=1)
+ self.mesh2grid_num_edges = len(edge_features)
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _get_max_edge_distance(mesh):
+ senders, receivers = faces_to_edges(mesh.faces)
+ edge_distances = np.linalg.norm(
+ mesh.vertices[senders] - mesh.vertices[receivers], axis=-1
+ )
+ return edge_distances.max()
+
+ def grid_node_outputs_to_prediction(
+ self,
+ grid_node_outputs: np.ndarray,
+ targets_template: "xarray.Dataset",
+ ) -> "xarray.Dataset":
+ """[num_grid_nodes, batch, num_outputs] -> xarray."""
+ # numpy array with shape [lat_lon_node, batch, channels]
+ # to xarray `DataArray` (batch, lat, lon, channels)
+ assert self._grid_lat is not None and self._grid_lon is not None
+ grid_shape = (self._grid_lat.shape[0], self._grid_lon.shape[0])
+ grid_outputs_lat_lon_leading = grid_node_outputs.reshape(
+ grid_shape + grid_node_outputs.shape[1:]
+ )
+ dims = ("lat", "lon", "batch", "channels")
+ grid_xarray_lat_lon_leading = xarray.DataArray(
+ data=grid_outputs_lat_lon_leading, dims=dims
+ )
+ grid_xarray = restore_leading_axes(grid_xarray_lat_lon_leading)
+
+ # xarray `DataArray` (batch, lat, lon, channels)
+ # to xarray `Dataset` (batch, one time step, lat, lon, level, multiple vars)
+ return stacked_to_dataset(grid_xarray.variable, targets_template)
+
+
+class TriangularMesh(NamedTuple):
+ vertices: np.ndarray
+ faces: np.ndarray
+
+
+def merge_meshes(mesh_list: Sequence[TriangularMesh]) -> TriangularMesh:
+ for i in range(len(mesh_list) - 1):
+ mesh_i, mesh_ip1 = mesh_list[i], mesh_list[i + 1]
+ num_nodes_mesh_i = mesh_i.vertices.shape[0]
+ assert np.allclose(mesh_i.vertices, mesh_ip1.vertices[:num_nodes_mesh_i])
+
+ return TriangularMesh(
+ vertices=mesh_list[-1].vertices,
+ faces=np.concatenate([mesh.faces for mesh in mesh_list], axis=0),
+ )
+
+
+def get_icosahedron():
+ phi = (1 + np.sqrt(5)) / 2
+ product = [[1.0, phi], [1.0, -phi], [-1.0, phi], [-1.0, -phi]]
+ vertices = []
+ for p in product:
+ c1 = p[0]
+ c2 = p[1]
+ vertices.append((c1, c2, 0.0))
+ vertices.append((0.0, c1, c2))
+ vertices.append((c2, 0.0, c1))
+
+ vertices = np.array(vertices, dtype=np.float32)
+ vertices /= np.linalg.norm([1.0, phi])
+
+ faces = [
+ (0, 1, 2),
+ (0, 6, 1),
+ (8, 0, 2),
+ (8, 4, 0),
+ (3, 8, 2),
+ (3, 2, 7),
+ (7, 2, 1),
+ (0, 4, 6),
+ (4, 11, 6),
+ (6, 11, 5),
+ (1, 5, 7),
+ (4, 10, 11),
+ (4, 8, 10),
+ (10, 8, 3),
+ (10, 3, 9),
+ (11, 10, 9),
+ (11, 9, 5),
+ (5, 9, 7),
+ (9, 3, 7),
+ (1, 6, 5),
+ ]
+
+ angle_between_faces = 2 * np.arcsin(phi / np.sqrt(3))
+ rotation_angle = (np.pi - angle_between_faces) / 2
+ rotation = scipy.spatial.transform.Rotation.from_euler(
+ seq="y", angles=rotation_angle
+ )
+ rotation_matrix = rotation.as_matrix()
+ vertices = np.dot(vertices, rotation_matrix)
+
+ return TriangularMesh(
+ vertices=vertices.astype(np.float32), faces=np.array(faces, dtype=np.int32)
+ )
+
+
+def get_hierarchy_of_triangular_meshes_for_sphere(
+ splits: int,
+) -> List[TriangularMesh]:
+ current_mesh = get_icosahedron()
+ output_meshes = [current_mesh]
+ for _ in range(splits):
+ current_mesh = _two_split_unit_sphere_triangle_faces(current_mesh)
+ output_meshes.append(current_mesh)
+ return output_meshes
+
+
+def _two_split_unit_sphere_triangle_faces(
+ triangular_mesh: TriangularMesh,
+) -> TriangularMesh:
+ """Splits each triangular face into 4 triangles keeping the orientation."""
+ new_vertices_builder = _ChildVerticesBuilder(triangular_mesh.vertices)
+
+ new_faces = []
+ for ind1, ind2, ind3 in triangular_mesh.faces:
+ ind12 = new_vertices_builder.get_new_child_vertex_index((ind1, ind2))
+ ind23 = new_vertices_builder.get_new_child_vertex_index((ind2, ind3))
+ ind31 = new_vertices_builder.get_new_child_vertex_index((ind3, ind1))
+ new_faces.extend(
+ [
+ [ind1, ind12, ind31], # 1
+ [ind12, ind2, ind23], # 2
+ [ind31, ind23, ind3], # 3
+ [ind12, ind23, ind31], # 4
+ ]
+ )
+ return TriangularMesh(
+ vertices=new_vertices_builder.get_all_vertices(),
+ faces=np.array(new_faces, dtype=np.int32),
+ )
+
+
+class _ChildVerticesBuilder:
+ """Bookkeeping of new child vertices added to an existing set of vertices."""
+
+ def __init__(self, parent_vertices):
+ self._child_vertices_index_mapping = {}
+ self._parent_vertices = parent_vertices
+ # We start with all previous vertices.
+ self._all_vertices_list = list(parent_vertices)
+
+ def _get_child_vertex_key(self, parent_vertex_indices):
+ return tuple(sorted(parent_vertex_indices))
+
+ def _create_child_vertex(self, parent_vertex_indices):
+ """Creates a new vertex."""
+ # Position for new vertex is the middle point, between the parent points,
+ # projected to unit sphere.
+ child_vertex_position = self._parent_vertices[list(parent_vertex_indices)].mean(
+ 0
+ )
+ child_vertex_position /= np.linalg.norm(child_vertex_position)
+
+ # Add the vertex to the output list. The index for this new vertex will
+ # match the length of the list before adding it.
+ child_vertex_key = self._get_child_vertex_key(parent_vertex_indices)
+ self._child_vertices_index_mapping[child_vertex_key] = len(
+ self._all_vertices_list
+ )
+ self._all_vertices_list.append(child_vertex_position)
+
+ def get_new_child_vertex_index(self, parent_vertex_indices):
+ """Returns index for a child vertex, creating it if necessary."""
+ # Get the key to see if we already have a new vertex in the middle.
+ child_vertex_key = self._get_child_vertex_key(parent_vertex_indices)
+ if child_vertex_key not in self._child_vertices_index_mapping:
+ self._create_child_vertex(parent_vertex_indices)
+ return self._child_vertices_index_mapping[child_vertex_key]
+
+ def get_all_vertices(self):
+ """Returns an array with old vertices."""
+ return np.array(self._all_vertices_list)
+
+
+def faces_to_edges(faces: np.ndarray):
+ """Transforms polygonal faces to sender and receiver indices.
+
+ It does so by transforming every face into N_i edges. Such if the triangular
+ face has indices [0, 1, 2], three edges are added 0->1, 1->2, and 2->0.
+
+ If all faces have consistent orientation, and the surface represented by the
+ faces is closed, then every edge in a polygon with a certain orientation
+ is also part of another polygon with the opposite orientation. In this
+ situation, the edges returned by the method are always bidirectional.
+
+ Args:
+ faces: Integer array of shape [num_faces, 3]. Contains node indices adjacent to each face.
+ Returns:
+ Tuple with sender/receiver indices, each of shape [num_edges=num_faces*3].
+ """
+
+ assert faces.ndim == 2
+ assert faces.shape[-1] == 3
+ senders = np.concatenate([faces[:, 0], faces[:, 1], faces[:, 2]])
+ receivers = np.concatenate([faces[:, 1], faces[:, 2], faces[:, 0]])
+ return senders, receivers
+
+
+def _grid_lat_lon_to_coordinates(
+ grid_latitude: np.ndarray, grid_longitude: np.ndarray
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Lat [num_lat] lon [num_lon] to 3d coordinates [num_lat, num_lon, 3]."""
+ # Convert to spherical coordinates phi and theta defined in the grid.
+ # Each [num_latitude_points, num_longitude_points]
+ phi_grid, theta_grid = np.meshgrid(
+ np.deg2rad(grid_longitude), np.deg2rad(90 - grid_latitude)
+ )
+
+ # [num_latitude_points, num_longitude_points, 3]
+ # Note this assumes unit radius, since for now we model the earth as a
+ # sphere of unit radius, and keep any vertical dimension as a regular grid.
+ return np.stack(
+ [
+ np.cos(phi_grid) * np.sin(theta_grid),
+ np.sin(phi_grid) * np.sin(theta_grid),
+ np.cos(theta_grid),
+ ],
+ axis=-1,
+ )
+
+
+def radius_query_indices(
+ *,
+ grid_latitude: np.ndarray,
+ grid_longitude: np.ndarray,
+ mesh: TriangularMesh,
+ radius: float,
+) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ """Returns mesh-grid edge indices for radius query.
+
+ Args:
+ grid_latitude: Latitude values for the grid [num_lat_points]
+ grid_longitude: Longitude values for the grid [num_lon_points]
+ mesh: Mesh object.
+ radius: Radius of connectivity in R3. for a sphere of unit radius.
+
+ Returns:
+ tuple with `grid_indices` and `mesh_indices` indicating edges between the grid and the mesh such that the distances in a straight line (not geodesic) are smaller than or equal to `radius`.
+ grid_indices: Indices of shape [num_edges], that index into a
+ [num_lat_points, num_lon_points] grid, after flattening the leading axes.
+ mesh_indices: Indices of shape [num_edges], that index into mesh.vertices.
+ """
+
+ # [num_grid_points=num_lat_points * num_lon_points, 3]
+ grid_positions = _grid_lat_lon_to_coordinates(
+ grid_latitude, grid_longitude
+ ).reshape([-1, 3])
+
+ # [num_mesh_points, 3]
+ mesh_positions = mesh.vertices
+ kd_tree = scipy.spatial.cKDTree(mesh_positions)
+
+ # [num_grid_points, num_mesh_points_per_grid_point]
+ # Note `num_mesh_points_per_grid_point` is not constant, so this is a list
+ # of arrays, rather than a 2d array.
+ query_indices = kd_tree.query_ball_point(x=grid_positions, r=radius)
+
+ grid_edge_indices = []
+ mesh_edge_indices = []
+ for grid_index, mesh_neighbors in enumerate(query_indices):
+ grid_edge_indices.append(np.repeat(grid_index, len(mesh_neighbors)))
+ mesh_edge_indices.append(mesh_neighbors)
+
+ # [num_edges]
+ grid_edge_indices = np.concatenate(grid_edge_indices, axis=0).astype(int)
+ mesh_edge_indices = np.concatenate(mesh_edge_indices, axis=0).astype(int)
+
+ return grid_edge_indices, mesh_edge_indices
+
+
+def in_mesh_triangle_indices(
+ *, grid_latitude: np.ndarray, grid_longitude: np.ndarray, mesh: TriangularMesh
+) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ """Returns mesh-grid edge indices for grid points contained in mesh triangles.
+
+ Args:
+ grid_latitude: Latitude values for the grid [num_lat_points]
+ grid_longitude: Longitude values for the grid [num_lon_points]
+ mesh: Mesh object.
+
+ Returns:
+ tuple with `grid_indices` and `mesh_indices` indicating edges between the grid and the mesh vertices of the triangle that contain each grid point. The number of edges is always num_lat_points * num_lon_points * 3
+ grid_indices: Indices of shape [num_edges], that index into a [num_lat_points, num_lon_points] grid, after flattening the leading axes.
+ mesh_indices: Indices of shape [num_edges], that index into mesh.vertices.
+ """
+
+ # [num_grid_points=num_lat_points * num_lon_points, 3]
+ grid_positions = _grid_lat_lon_to_coordinates(
+ grid_latitude, grid_longitude
+ ).reshape([-1, 3])
+
+ mesh_trimesh = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices=mesh.vertices, faces=mesh.faces)
+
+ # [num_grid_points] with mesh face indices for each grid point.
+ _, _, query_face_indices = trimesh.proximity.closest_point(
+ mesh_trimesh, grid_positions
+ )
+
+ # [num_grid_points, 3] with mesh node indices for each grid point.
+ mesh_edge_indices = mesh.faces[query_face_indices]
+
+ # [num_grid_points, 3] with grid node indices, where every row simply contains
+ # the row (grid_point) index.
+ grid_indices = np.arange(grid_positions.shape[0])
+ grid_edge_indices = np.tile(grid_indices.reshape([-1, 1]), [1, 3])
+
+ # Flatten to get a regular list.
+ # [num_edges=num_grid_points*3]
+ mesh_edge_indices = mesh_edge_indices.reshape([-1])
+ grid_edge_indices = grid_edge_indices.reshape([-1])
+
+ return grid_edge_indices, mesh_edge_indices
+
+
+def get_year_progress(seconds_since_epoch: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Computes year progress for times in seconds.
+ Args:
+ seconds_since_epoch: Times in seconds since the "epoch" (the point at which UNIX time starts).
+ Returns:
+ Year progress normalized to be in the `[0, 1)` interval for each time point.
+ """
+ # Start with the pure integer division, and then float at the very end.
+ # We will try to keep as much precision as possible.
+ years_since_epoch = (
+ seconds_since_epoch / SEC_PER_DAY / np.float64(_AVG_DAY_PER_YEAR)
+ )
+ # Note depending on how these ops are down, we may end up with a "weak_type"
+ # which can cause issues in subtle ways, and hard to track here.
+ # In any case, casting to float32 should get rid of the weak type.
+ # [0, 1.) Interval.
+ return np.mod(years_since_epoch, 1.0).astype(np.float32)
+
+
+def get_day_progress(
+ seconds_since_epoch: np.ndarray,
+ longitude: np.ndarray,
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Computes day progress for times in seconds at each longitude.
+ Args:
+ seconds_since_epoch: 1D array of times in seconds since the 'epoch' (the point at which UNIX time starts).
+ longitude: 1D array of longitudes at which day progress is computed.
+ Returns:
+ 2D array of day progress values normalized to be in the [0, 1) inverval for each time point at each longitude.
+ """
+ # [0.0, 1.0) Interval.
+ day_progress_greenwich = np.mod(seconds_since_epoch, SEC_PER_DAY) / SEC_PER_DAY
+ # Offset the day progress to the longitude of each point on Earth.
+ longitude_offsets = np.deg2rad(longitude) / (2 * np.pi)
+ day_progress = np.mod(
+ day_progress_greenwich[..., np.newaxis] + longitude_offsets, 1.0
+ )
+ return day_progress.astype(np.float32)
+
+
+def datetime_features(seconds_since_epoch, longitude_offsets):
+ year_progress = get_year_progress(seconds_since_epoch)
+ day_progress = get_day_progress(seconds_since_epoch, longitude_offsets)
+ year_progress_phase = year_progress * (2 * np.pi)
+ day_progress_phase = day_progress * (2 * np.pi)
+ returned_data = {
+ "year_progress_sin": np.sin(year_progress_phase),
+ "year_progress_cos": np.cos(year_progress_phase),
+ "day_progress_sin": np.sin(day_progress_phase),
+ "day_progress_cos": np.cos(day_progress_phase),
+ }
+ return returned_data
+
+
+def add_var_into_nc_dataset(
+ nc_dataset,
+ var_name,
+ var_value,
+ var_dims=(
+ "batch",
+ "time",
+ ),
+):
+ new_var = nc_dataset.createVariable(var_name, "f8", var_dims)
+ new_var[:] = var_value
+ return nc_dataset
+
+
+def extract_input_target_times(
+ dataset: "xarray.Dataset",
+ input_duration: str,
+ target_lead_times: str,
+):
+ (target_lead_times, target_duration) = _process_target_lead_times_and_get_duration(
+ target_lead_times
+ )
+ time = dataset.coords["time"]
+ dataset = dataset.assign_coords(time=time + target_duration - time[-1])
+
+ targets = dataset.sel({"time": target_lead_times})
+
+ input_duration = pd.Timedelta(input_duration)
+ zero = pd.Timedelta(0)
+ epsilon = pd.Timedelta(1, "ns")
+ inputs = dataset.sel({"time": slice(-input_duration + epsilon, zero)})
+ return inputs, targets
+
+
+def _process_target_lead_times_and_get_duration(target_lead_times: str):
+ """Returns the minimum duration for the target lead times."""
+ if isinstance(target_lead_times, slice):
+ if target_lead_times.start is None:
+ target_lead_times = slice(
+ pd.Timedelta(1, "ns"), target_lead_times.stop, target_lead_times.step
+ )
+ target_duration = pd.Timedelta(target_lead_times.stop)
+ else:
+ if not isinstance(target_lead_times, (list, tuple, set)):
+ target_lead_times = [target_lead_times]
+
+ target_lead_times = [pd.Timedelta(x) for x in target_lead_times]
+ target_lead_times.sort()
+ target_duration = target_lead_times[-1]
+ return target_lead_times, target_duration
+
+
+def variable_to_stacked(
+ variable: "xarray.Variable",
+ sizes: "xarray.core.utils.Frozen",
+ preserved_dims=("batch", "lat", "lon"),
+) -> "xarray.Variable":
+ """Converts an xarray.Variable to preserved_dims + ("channels",).
+
+ Any dimensions other than those included in preserved_dims get stacked into a final "channels" dimension. If any of the preserved_dims are missing then they are added, with the data broadcast/tiled to match the sizes specified in `sizes`.
+
+ Args:
+ variable: An xarray.Variable.
+ sizes: Mapping including sizes for any dimensions which are not present in `variable` but are needed for the output. This may be needed for example for a static variable with only ("lat", "lon") dims, or if you want to encode just the latitude coordinates (a variable with dims ("lat",)).
+ preserved_dims: dimensions of variable to not be folded in channels.
+
+ Returns:
+ An xarray.Variable with dimensions preserved_dims + ("channels",).
+ """
+ stack_to_channels_dims = [d for d in variable.dims if d not in preserved_dims]
+ if stack_to_channels_dims:
+ variable = variable.stack(channels=stack_to_channels_dims)
+ dims = {dim: variable.sizes.get(dim) or sizes[dim] for dim in preserved_dims}
+ dims["channels"] = variable.sizes.get("channels", 1)
+ return variable.set_dims(dims)
+
+
+def dataset_to_stacked(
+ dataset: "xarray.Dataset",
+ sizes=None,
+ preserved_dims=("batch", "lat", "lon"),
+) -> "xarray.DataArray":
+ """Converts an xarray.Dataset to a single stacked array.
+
+ This takes each consistuent data_var, converts it into BHWC layout
+ using `variable_to_stacked`, then concats them all along the channels axis.
+
+ Args:
+ dataset: An xarray.Dataset.
+ sizes: Mapping including sizes for any dimensions which are not present in the `dataset` but are needed for the output. See variable_to_stacked.
+ preserved_dims: dimensions from the dataset that should not be folded in the predictions channels.
+
+ Returns:
+ An xarray.DataArray with dimensions preserved_dims + ("channels",). Existing coordinates for preserved_dims axes will be preserved, however there will be no coordinates for "channels".
+ """
+ data_vars = [
+ variable_to_stacked(
+ dataset.variables[name], sizes or dataset.sizes, preserved_dims
+ )
+ for name in sorted(dataset.data_vars.keys())
+ ]
+ coords = {
+ dim: coord for dim, coord in dataset.coords.items() if dim in preserved_dims
+ }
+ return xarray.DataArray(
+ data=xarray.Variable.concat(data_vars, dim="channels"), coords=coords
+ )
+
+
+class GridMeshAtmosphericDataset(io.Dataset):
+ """This class is used to process ERA5 re-analyze data, and is used to generate the dataset generator supported by MindSpore. This class inherits the Data class.
+
+ Args:
+ input_keys (Tuple[str, ...]): Name of input data.
+ label_keys (Tuple[str, ...]): Name of label data.
+ data_path: Path of atmospheric datafile.
+ mean_path: Path of mean datafile.
+ stddev_path: Path of standard deviation datafile.
+ stddev_diffs_path: Path of standard deviation different datafile.
+ type: Type of GraphCast network.
+ mesh_size: Size of mesh.
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor: Factor of normalization of edges in Mesh2Grid GNN.
+ radius_query_fraction_edge_length: Length of radius query fraction edges.
+ resolution: Resolution of atmospheric data.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> import ppsci
+ >>> dataset = ppsci.data.dataset.GridMeshAtmosphericDataset(
+ ... "input_keys": ("input",),
+ ... "label_keys": ("output",),
+ ... "data_path": "/path/to/file.nc",
+ ... "mean_path": "/path/to/file.nc",
+ ... "stddev_path": "/path/to/file.nc",
+ ... "stddev_diffs_path": "/path/to/file.nc",
+ ... "type": "graphcast_small",
+ ... "mesh_size": 5,
+ ... "mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor": 0.06,
+ ... "radius_query_fraction_edge_length": 0.6180338738074472,
+ ... "resolution": 1,
+ ... ) # doctest: +SKIP
+ """
+
+ use_graph_grid_mesh: bool = True
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ input_keys: Tuple[str, ...],
+ label_keys: Tuple[str, ...],
+ data_path: str,
+ mean_path: str,
+ stddev_path: str,
+ stddev_diffs_path: str,
+ type: str,
+ mesh_size: int,
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor: float,
+ radius_query_fraction_edge_length: float,
+ resolution: float,
+ ):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.input_keys = input_keys
+ self.label_keys = label_keys
+ if type == "graphcast":
+ self.input_variables = TASK_input_variables
+ self.forcing_variables = TASK_forcing_variables
+ self.target_variables = TASK_target_variables
+ self.level_variables = PRESSURE_LEVELS[37]
+ elif type == "graphcast_small":
+ self.input_variables = TASK_13_input_variables
+ self.forcing_variables = TASK_13_forcing_variables
+ self.target_variables = TASK_13_target_variables
+ self.level_variables = PRESSURE_LEVELS[13]
+ elif type == "graphcast_operational":
+ self.input_variables = TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_input_variables
+ self.forcing_variables = TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_forcing_variables
+ self.target_variables = TASK_13_PRECIP_OUT_target_variables
+ self.level_variables = PRESSURE_LEVELS[13]
+
+ nc_dataset = xarray.open_dataset(data_path)
+
+ longitude_offsets = nc_dataset.coords["lon"].data
+ second_since_epoch = (
+ nc_dataset.coords["datetime"].data.astype("datetime64[s]").astype(np.int64)
+ )
+ datetime_feats = datetime_features(second_since_epoch, longitude_offsets)
+ nc_dataset.update(
+ {
+ "year_progress_sin": xarray.Variable(
+ ("batch", "time"), datetime_feats["year_progress_sin"]
+ ),
+ "year_progress_cos": xarray.Variable(
+ ("batch", "time"), datetime_feats["year_progress_cos"]
+ ),
+ "day_progress_sin": xarray.Variable(
+ ("batch", "time", "lon"), datetime_feats["day_progress_sin"]
+ ),
+ "day_progress_cos": xarray.Variable(
+ ("batch", "time", "lon"), datetime_feats["day_progress_cos"]
+ ),
+ }
+ )
+
+ inputs, targets = extract_input_target_times(
+ nc_dataset, input_duration="12h", target_lead_times="6h"
+ )
+
+ stddev_data = xarray.open_dataset(stddev_path).sel(
+ level=list(self.level_variables)
+ )
+ stddev_diffs_data = xarray.open_dataset(stddev_diffs_path).sel(
+ level=list(self.level_variables)
+ )
+ mean_data = xarray.open_dataset(mean_path).sel(level=list(self.level_variables))
+
+ missing_variables = set(self.target_variables) - set(self.input_variables)
+ exist_variables = set(self.target_variables) - missing_variables
+ targets_stddev = stddev_diffs_data[list(exist_variables)]
+ target_mean = inputs[list(exist_variables)].isel(time=-1)
+ if missing_variables:
+ targets_stddev.update({var: stddev_data[var] for var in missing_variables})
+ target_mean.update(
+ {var: mean_data.variables[var] for var in missing_variables}
+ )
+
+ stacked_targets_stddev = dataset_to_stacked(targets_stddev, preserved_dims=())
+ stacked_targets_mean = dataset_to_stacked(target_mean)
+ stacked_targets_mean = stacked_targets_mean.transpose("lat", "lon", ...)
+
+ inputs = inputs[list(self.input_variables)]
+ forcings = targets[list(self.forcing_variables)]
+ targets = targets[list(self.target_variables)]
+ inputs = self.normalize(inputs, stddev_data, mean_data)
+ forcings = self.normalize(forcings, stddev_data, mean_data)
+
+ self.targets_template = targets
+
+ stacked_inputs = dataset_to_stacked(inputs)
+ stacked_forcings = dataset_to_stacked(forcings)
+ stacked_targets = dataset_to_stacked(targets)
+ stacked_inputs = xarray.concat(
+ [stacked_inputs, stacked_forcings], dim="channels"
+ )
+
+ stacked_inputs = stacked_inputs.transpose("lat", "lon", ...)
+ stacked_targets = stacked_targets.transpose("lat", "lon", ...)
+
+ lat_dim, lon_dim, batch_dim, feat_dim = stacked_inputs.shape
+ stacked_inputs = stacked_inputs.data.reshape(lat_dim * lon_dim, batch_dim, -1)
+ stacked_targets = stacked_targets.data.reshape(lat_dim * lon_dim, batch_dim, -1)
+ self.stacked_targets_stddev = stacked_targets_stddev.data
+ self.stacked_targets_mean = stacked_targets_mean.data.reshape(
+ lat_dim * lon_dim, batch_dim, -1
+ )
+
+ self.input_data = []
+ self.target_data = []
+
+ graph = GraphGridMesh(
+ mesh_size=mesh_size,
+ radius_query_fraction_edge_length=radius_query_fraction_edge_length,
+ mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor=mesh2grid_edge_normalization_factor,
+ resolution=resolution,
+ )
+
+ graph.grid_node_feat = np.concatenate(
+ [stacked_inputs, graph.grid_node_feat], axis=-1
+ )
+ mesh_node_feat = np.zeros([graph.mesh_num_nodes, batch_dim, feat_dim])
+ graph.mesh_node_feat = np.concatenate(
+ [mesh_node_feat, graph.mesh_node_feat], axis=-1
+ )
+
+ self.input_data.append(graph)
+ self.target_data.append(stacked_targets)
+
+ def __len__(self):
+ return len(self.input_data)
+
+ def __getitem__(self, idx):
+ return (
+ {
+ self.input_keys[0]: self.input_data[idx],
+ },
+ {
+ self.label_keys[0]: self.target_data[idx],
+ },
+ None,
+ )
+
+ def normalize(self, inputs_data, stddev_data, mean_data):
+ for name in list(inputs_data.keys()):
+ inputs_data[name] = (inputs_data[name] - mean_data[name]) / stddev_data[
+ name
+ ]
+ return inputs_data
+
+ def denormalize(self, inputs_data):
+ return inputs_data * self.stacked_targets_stddev + self.stacked_targets_mean
diff --git a/ppsci/data/dataset/darcyflow_dataset.py b/ppsci/data/dataset/darcyflow_dataset.py
index 6a02164754..3e748eb785 100644
--- a/ppsci/data/dataset/darcyflow_dataset.py
+++ b/ppsci/data/dataset/darcyflow_dataset.py
@@ -62,7 +62,6 @@ def get_grid_positional_encoding(
input_tensor (paddle.Tensor): The input tensor.
grid_boundaries (list, optional): The boundaries of the grid. Defaults to [[0, 1], [0, 1]].
channel_dim (int, optional): The location of unsqueeze. Defaults to 1.
-
"""
shape = list(input_tensor.shape)
diff --git a/ppsci/data/dataset/enso_dataset.py b/ppsci/data/dataset/enso_dataset.py
index e78b7a94a4..601fcec413 100644
--- a/ppsci/data/dataset/enso_dataset.py
+++ b/ppsci/data/dataset/enso_dataset.py
@@ -56,8 +56,8 @@ def prepare_inputs_targets(
pred_shift (int): The lead_time of the last target to be predicted.
pred_length (int): The number of frames to be predicted.
samples_gap (int): Stride of seq sampling.
-
"""
+
if pred_shift < pred_length:
raise ValueError("pred_shift should be small than pred_length")
input_span = input_gap * (input_length - 1) + 1
@@ -105,7 +105,6 @@ def data_transform(data, num_years_per_model):
Args:
data (Tuple[list,...]): The input data.Shape of (N, 36, *).
num_years_per_model (int): The number of years associated with each model.151/140.
-
"""
length = data.shape[0]
assert length % num_years_per_model == 0
@@ -136,6 +135,7 @@ def read_raw_data(ds_dir, out_dir=None):
ds_dir (str): The path of the dataset.
out_dir (str): The path of output. Defaults to None.
"""
+
import xarray as xr
train_cmip = xr.open_dataset(Path(ds_dir) / "CMIP_train.nc").transpose(
@@ -211,7 +211,6 @@ def cat_over_last_dim(data):
"""Treat different models (15 from CMIP6, 17 from CMIP5) as batch_size
e.g., cmip6sst.shape = (178, 38, 24, 48, 15), converted_cmip6sst.shape = (2670, 38, 24, 48)
e.g., cmip5sst.shape = (165, 38, 24, 48, 15), converted_cmip6sst.shape = (2475, 38, 24, 48)
-
"""
return np.concatenate(np.moveaxis(data, -1, 0), axis=0)
@@ -236,7 +235,6 @@ class ENSODataset(io.Dataset):
batch_size (int, optional): Batch size. Defaults to 1.
num_workers (int, optional): The num of workers. Defaults to 1.
training (str, optional): Training pathse. Defaults to "train".
-
"""
# Whether support batch indexing for speeding up fetching process.
diff --git a/ppsci/data/dataset/spherical_swe_dataset.py b/ppsci/data/dataset/spherical_swe_dataset.py
index 42cd9f84f9..68e29e7883 100644
--- a/ppsci/data/dataset/spherical_swe_dataset.py
+++ b/ppsci/data/dataset/spherical_swe_dataset.py
@@ -23,7 +23,6 @@ class SphericalSWEDataset(io.Dataset):
train_resolution (str, optional): The resolutions to train dataset. Defaults to "34x64".
data_split (str, optional): Specify the dataset split, either 'train' , 'test_32x64',or 'test_64x128'.
Defaults to "train".
-
"""
def __init__(
diff --git a/ppsci/data/process/batch_transform/__init__.py b/ppsci/data/process/batch_transform/__init__.py
index 67d74a3469..24b0c192c0 100644
--- a/ppsci/data/process/batch_transform/__init__.py
+++ b/ppsci/data/process/batch_transform/__init__.py
@@ -84,10 +84,17 @@ def default_collate_fn(batch: List[Any]) -> Any:
graph.tensor()
graph.shape = [len(batch)]
return graph
-
+ elif (
+ str(type(sample))
+ == ""
+ ):
+ graph = sample
+ graph.tensor()
+ graph.shape = [1]
+ return graph
raise TypeError(
"batch data can only contains: paddle.Tensor, numpy.ndarray, "
- f"dict, list, number, None, pgl.Graph, but got {type(sample)}"
+ f"dict, list, number, None, pgl.Graph, GraphGridMesh, but got {type(sample)}"
)
diff --git a/ppsci/utils/logger.py b/ppsci/utils/logger.py
index bad37a3087..a904fad259 100644
--- a/ppsci/utils/logger.py
+++ b/ppsci/utils/logger.py
@@ -243,8 +243,8 @@ def advertise():
== ==
== https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleScience ==
===========================================================
-
"""
+
_copyright = "PaddleScience is powered by PaddlePaddle !"
ad = "Please refer to the following website for more info."
website = "https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleScience"