Fiber is an Express inspired web framework built on top of Fasthttp, the fastest HTTP engine for Go. Designed to ease things up for fast development with zero memory allocation and performance in mind.
Fiber v3 is currently in beta and under active development. While it offers exciting new features, please note that it may not be stable for production use. We recommend sticking to the latest stable release (v2.x) for mission-critical applications. If you choose to use v3, be prepared for potential bugs and breaking changes. Always check the official documentation and release notes for updates and proceed with caution. Happy coding! 🚀
Fiber requires Go version 1.22 or higher to run. If you need to install or upgrade Go, visit the official Go download page. To start setting up your project. Create a new directory for your project and navigate into it. Then, initialize your project with Go modules by executing the following command in your terminal:
go mod init github.com/your/repoTo learn more about Go modules and how they work, you can check out the Using Go Modules blog post.
After setting up your project, you can install Fiber with the go get command:
go get -u github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3This command fetches the Fiber package and adds it to your project's dependencies, allowing you to start building your web applications with Fiber.
Getting started with Fiber is easy. Here's a basic example to create a simple web server that responds with "Hello, World 👋!" on the root path. This example demonstrates initializing a new Fiber app, setting up a route, and starting the server.
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
)
func main() {
// Initialize a new Fiber app
app := fiber.New()
// Define a route for the GET method on the root path '/'
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) error {
// Send a string response to the client
return c.SendString("Hello, World 👋!")
})
// Start the server on port 3000
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}This simple server is easy to set up and run. It introduces the core concepts of Fiber: app initialization, route definition, and starting the server. Just run this Go program, and visit http://localhost:3000 in your browser to see the message.
Fiber is optimized for high-performance, meaning values returned from fiber.Ctx are not immutable by default and will be re-used across requests. As a rule of thumb, you must only use context values within the handler and must not keep any references. Once you return from the handler, any values obtained from the context will be re-used in future requests. Visit our documentation to learn more.
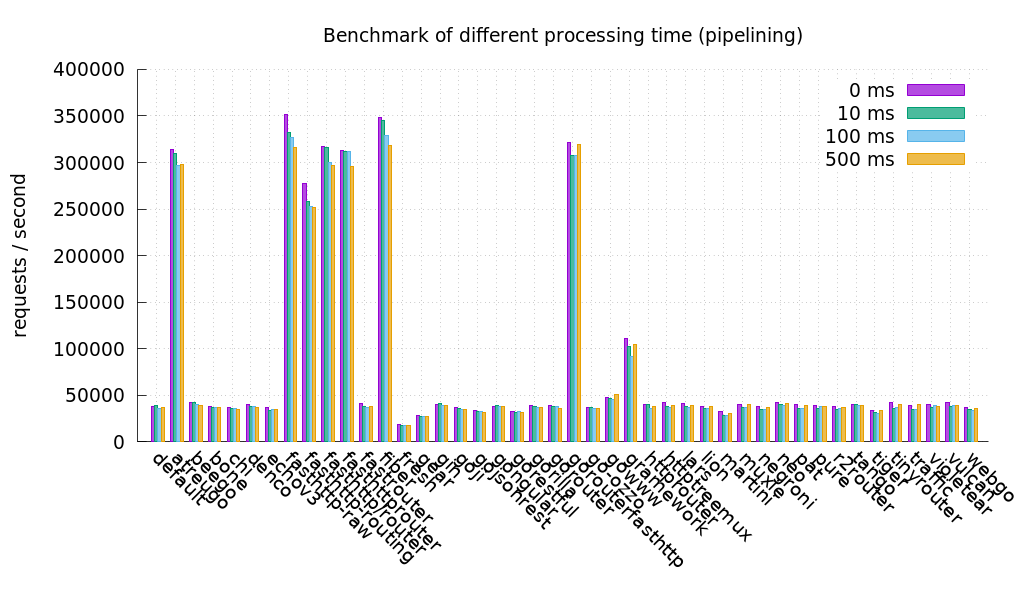
These tests are performed by TechEmpower and Go Web. If you want to see all the results, please visit our Wiki.
- Robust Routing
- Serve Static Files
- Extreme Performance
- Low Memory footprint
- API Endpoints
- Middleware & Next support
- Rapid server-side programming
- Template Engines
- WebSocket Support
- Socket.io Support
- Server-Sent Events
- Rate Limiter
- And much more, explore Fiber
New gophers that make the switch from Node.js to Go are dealing with a learning curve before they can start building their web applications or microservices. Fiber, as a web framework, was created with the idea of minimalism and follows the UNIX way, so that new gophers can quickly enter the world of Go with a warm and trusted welcome.
Fiber is inspired by Express, the most popular web framework on the Internet. We combined the ease of Express and raw performance of Go. If you have ever implemented a web application in Node.js (using Express or similar), then many methods and principles will seem very common to you.
We listen to our users in issues, Discord channel and all over the Internet to create a fast, flexible and friendly Go web framework for any task, deadline and developer skill! Just like Express does in the JavaScript world.
- Due to Fiber's usage of unsafe, the library may not always be compatible with the latest Go version. Fiber v3 has been tested with Go versions 1.22 and 1.23.
- Fiber is not compatible with net/http interfaces. This means you will not be able to use projects like gqlgen, go-swagger, or any others which are part of the net/http ecosystem.
Listed below are some of the common examples. If you want to see more code examples, please visit our Recipes repository or visit our hosted API documentation.
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
// GET /api/register
app.Get("/api/*", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("✋ %s", c.Params("*"))
return c.SendString(msg) // => ✋ register
})
// GET /flights/LAX-SFO
app.Get("/flights/:from-:to", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("💸 From: %s, To: %s", c.Params("from"), c.Params("to"))
return c.SendString(msg) // => 💸 From: LAX, To: SFO
})
// GET /dictionary.txt
app.Get("/:file.:ext", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("📃 %s.%s", c.Params("file"), c.Params("ext"))
return c.SendString(msg) // => 📃 dictionary.txt
})
// GET /john/75
app.Get("/:name/:age/:gender?", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("👴 %s is %s years old", c.Params("name"), c.Params("age"))
return c.SendString(msg) // => 👴 john is 75 years old
})
// GET /john
app.Get("/:name", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Hello, %s 👋!", c.Params("name"))
return c.SendString(msg) // => Hello john 👋!
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}func main() {
app := fiber.New()
// GET /api/register
app.Get("/api/*", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("✋ %s", c.Params("*"))
return c.SendString(msg) // => ✋ register
}).Name("api")
data, _ := json.MarshalIndent(app.GetRoute("api"), "", " ")
fmt.Print(string(data))
// Prints:
// {
// "method": "GET",
// "name": "api",
// "path": "/api/*",
// "params": [
// "*1"
// ]
// }
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/*", static.New("./public"))
// => http://localhost:3000/js/script.js
// => http://localhost:3000/css/style.css
app.Get("/prefix*", static.New("./public"))
// => http://localhost:3000/prefix/js/script.js
// => http://localhost:3000/prefix/css/style.css
app.Get("*", static.New("./public/index.html"))
// => http://localhost:3000/any/path/shows/index/html
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}func main() {
app := fiber.New()
// Match any route
app.Use(func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
fmt.Println("🥇 First handler")
return c.Next()
})
// Match all routes starting with /api
app.Use("/api", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
fmt.Println("🥈 Second handler")
return c.Next()
})
// GET /api/list
app.Get("/api/list", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
fmt.Println("🥉 Last handler")
return c.SendString("Hello, World 👋!")
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}📚 Show more code examples
Fiber defaults to the html/template when no view engine is set.
If you want to execute partials or use a different engine like amber, handlebars, mustache or pug etc..
Checkout our Template package that support multiple view engines.
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
"github.com/gofiber/template/pug"
)
func main() {
// You can setup Views engine before initiation app:
app := fiber.New(fiber.Config{
Views: pug.New("./views", ".pug"),
})
// And now, you can call template `./views/home.pug` like this:
app.Get("/", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.Render("home", fiber.Map{
"title": "Homepage",
"year": 1999,
})
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}📖 Group
func middleware(c fiber.Ctx) error {
fmt.Println("Don't mind me!")
return c.Next()
}
func handler(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.SendString(c.Path())
}
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
// Root API route
api := app.Group("/api", middleware) // /api
// API v1 routes
v1 := api.Group("/v1", middleware) // /api/v1
v1.Get("/list", handler) // /api/v1/list
v1.Get("/user", handler) // /api/v1/user
// API v2 routes
v2 := api.Group("/v2", middleware) // /api/v2
v2.Get("/list", handler) // /api/v2/list
v2.Get("/user", handler) // /api/v2/user
// ...
}📖 Logger
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3/middleware/logger"
)
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Use(logger.New())
// ...
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}📖 CORS
import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3/middleware/cors"
)
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Use(cors.New())
// ...
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}Check CORS by passing any domain in Origin header:
curl -H "Origin: http://example.com" --verbose http://localhost:3000func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/", static.New("./public"))
app.Get("/demo", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.SendString("This is a demo!")
})
app.Post("/register", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.SendString("Welcome!")
})
// Last middleware to match anything
app.Use(func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.SendStatus(404)
// => 404 "Not Found"
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}📖 JSON
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/user", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.JSON(&User{"John", 20})
// => {"name":"John", "age":20}
})
app.Get("/json", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
return c.JSON(fiber.Map{
"success": true,
"message": "Hi John!",
})
// => {"success":true, "message":"Hi John!"}
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3/middleware/websocket"
)
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/ws", websocket.New(func(c *websocket.Conn) {
for {
mt, msg, err := c.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Println("read:", err)
break
}
log.Printf("recv: %s", msg)
err = c.WriteMessage(mt, msg)
if err != nil {
log.Println("write:", err)
break
}
}
}))
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
// ws://localhost:3000/ws
}import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
"github.com/valyala/fasthttp"
)
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/sse", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
c.Set("Content-Type", "text/event-stream")
c.Set("Cache-Control", "no-cache")
c.Set("Connection", "keep-alive")
c.Set("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked")
c.Context().SetBodyStreamWriter(fasthttp.StreamWriter(func(w *bufio.Writer) {
fmt.Println("WRITER")
var i int
for {
i++
msg := fmt.Sprintf("%d - the time is %v", i, time.Now())
fmt.Fprintf(w, "data: Message: %s\n\n", msg)
fmt.Println(msg)
w.Flush()
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
}
}))
return nil
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}📖 Recover
import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3/middleware/recover"
)
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Use(recover.New())
app.Get("/", func(c fiber.Ctx) error {
panic("normally this would crash your app")
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}📖 Config
import (
"log"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v3"
)
func main() {
app := fiber.New(fiber.Config{
EnableTrustedProxyCheck: true,
TrustedProxies: []string{"0.0.0.0", "1.1.1.1/30"}, // IP address or IP address range
ProxyHeader: fiber.HeaderXForwardedFor,
})
log.Fatal(app.Listen(":3000"))
}Here is a list of middleware that are included within the Fiber framework.
| Middleware | Description |
|---|---|
| adaptor | Converter for net/http handlers to/from Fiber request handlers. |
| basicauth | Provides HTTP basic authentication. It calls the next handler for valid credentials and 401 Unauthorized for missing or invalid credentials. |
| cache | Intercept and cache HTTP responses. |
| compress | Compression middleware for Fiber, with support for deflate, gzip, brotli and zstd. |
| cors | Enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) with various options. |
| csrf | Protect from CSRF exploits. |
| earlydata | Adds support for TLS 1.3's early data ("0-RTT") feature. |
| encryptcookie | Encrypt middleware which encrypts cookie values. |
| envvar | Expose environment variables with providing an optional config. |
| etag | Allows for caches to be more efficient and save bandwidth, as a web server does not need to resend a full response if the content has not changed. |
| expvar | Serves via its HTTP server runtime exposed variants in the JSON format. |
| favicon | Ignore favicon from logs or serve from memory if a file path is provided. |
| healthcheck | Liveness and Readiness probes for Fiber. |
| helmet | Helps secure your apps by setting various HTTP headers. |
| idempotency | Allows for fault-tolerant APIs where duplicate requests do not erroneously cause the same action performed multiple times on the server-side. |
| keyauth | Adds support for key based authentication. |
| limiter | Adds Rate-limiting support to Fiber. Use to limit repeated requests to public APIs and/or endpoints such as password reset. |
| logger | HTTP request/response logger. |
| pprof | Serves runtime profiling data in pprof format. |
| proxy | Allows you to proxy requests to multiple servers. |
| recover | Recovers from panics anywhere in the stack chain and handles the control to the centralized ErrorHandler. |
| redirect | Redirect middleware. |
| requestid | Adds a request ID to every request. |
| rewrite | Rewrites the URL path based on provided rules. It can be helpful for backward compatibility or just creating cleaner and more descriptive links. |
| session | Session middleware. NOTE: This middleware uses our Storage package. |
| skip | Skip middleware that skips a wrapped handler if a predicate is true. |
| static | Static middleware for Fiber that serves static files such as images, CSS, and JavaScript. |
| timeout | Adds a max time for a request and forwards to ErrorHandler if it is exceeded. |
List of externally hosted middleware modules and maintained by the Fiber team.
| Middleware | Description |
|---|---|
| contrib | Third party middlewares |
| storage | Premade storage drivers that implement the Storage interface, designed to be used with various Fiber middlewares. |
| template | This package contains 9 template engines that can be used with Fiber v3 Go version 1.22 or higher is required. |
For more articles, middlewares, examples or tools check our awesome list.
If you want to say Thank You and/or support the active development of Fiber:
- Add a GitHub Star to the project.
- Tweet about the project on your 𝕏 (Twitter).
- Write a review or tutorial on Medium, Dev.to or personal blog.
- Support the project by donating a cup of coffee.
To ensure your contributions are ready for a Pull Request, please use the following Makefile commands. These tools help maintain code quality, consistency.
- make help: Display available commands.
- make audit: Conduct quality checks.
- make benchmark: Benchmark code performance.
- make coverage: Generate test coverage report.
- make format: Automatically format code.
- make lint: Run lint checks.
- make test: Execute all tests.
- make tidy: Tidy dependencies.
Run these commands to ensure your code adheres to project standards and best practices.
Fiber is an open source project that runs on donations to pay the bills e.g. our domain name, gitbook, netlify and serverless hosting. If you want to support Fiber, you can ☕ buy a coffee here.
| User | Donation | |
|---|---|---|
| @destari | ☕ x 10 | |
| @dembygenesis | ☕ x 5 | |
| @thomasvvugt | ☕ x 5 | |
| @hendratommy | ☕ x 5 | |
| @ekaputra07 | ☕ x 5 | |
| @jorgefuertes | ☕ x 5 | |
| @candidosales | ☕ x 5 | |
| @l0nax | ☕ x 3 | |
| @bihe | ☕ x 3 | |
| @justdave | ☕ x 3 | |
| @koddr | ☕ x 1 | |
| @lapolinar | ☕ x 1 | |
| @diegowifi | ☕ x 1 | |
| @ssimk0 | ☕ x 1 | |
| @raymayemir | ☕ x 1 | |
| @melkorm | ☕ x 1 | |
| @marvinjwendt | ☕ x 1 | |
| @toishy | ☕ x 1 |
Copyright (c) 2019-present Fenny and Contributors. Fiber is free and open-source software licensed under the MIT License. Official logo was created by Vic Shóstak and distributed under Creative Commons license (CC BY-SA 4.0 International).