This document provides a high-level overview of Sourcegraph's architecture so you can understand how our systems fit together.
+This document provides a high level overview of Sourcegraph's architecture, detailing the purpose and interactions of each service in the system.
## Diagram +You can click on each component to jump to its respective code repository or subtree. Open in new tab +  -## Repository syncing +Note several omittions have been made for clarity: +- Almost every service has a link back to the frontend, from which it gathers configuration updates +- Telemetry to Sourcegraph.com +- Sourcegraph Observability, including Prometheus, Grafana, and cAdvisor +These edges are omitted for clarity. + +## Service Quick Links + +### Core Services +- [Frontend](#frontend) - Central service that serves the web UI and GraphQL API +- [Gitserver](#gitserver) - Stores and provides access to Git repositories +- [Repo-updater](#repo-updater) - Tracks repository states and synchronizes with code hosts + +### Search Infrastructure +- [Zoekt-indexserver](#zoekt-indexserver) - Creates search indices for repositories +- [Zoekt-webserver](#zoekt-webserver) - Serves search queries against the indexed repositories +- [Searcher](#searcher) - Handles non-indexed searches for repositories +- [Syntect Server](#syntect-server) - Provides syntax highlighting for code + +### Code Intelligence +- [Symbols](#symbols) - Extracts and indexes symbol information +- [Precise-code-intel-worker](#precise-code-intel-worker) - Processes code intelligence data +- [Worker](#worker) - Runs background tasks across the system + +### Data Persistence +- [Frontend DB](#frontend-db) - Primary PostgreSQL database for core data +- [Codeintel DB](#codeintel-db) - Database for code intelligence data +- [Codeinsights DB](#codeinsights-db) - Database for code insights data +- [Blob Store](#blob-store) - Object storage for large files +- [Redis](#redis) - In-memory data store for caching and sessions + +### External Components +- [Executors](#executors) - Isolated environments for compute-intensive operations +- [Code Hosts](#code-hosts) - External systems hosting repositories + +### Infrastructure +- [Observability Infrastructure](#observability-infrastructure) - Prometheus, Grafana, and cAdvisor +- [Telemetry](#telemetry) - Usage data collection +- [External Services and Dependencies](#external-services-and-dependencies) - External services Sourcegraph can use + +### Cody Architecture +- [Cody Gateway](#cody-gateway) - Routes requests to AI providers +- [Cody Context Fetcher](#cody-context-fetcher) - Provides relevant code context +- [Cody Agent](#cody-agent) - Client-side component in IDE +- [Completions API](#completions-api) - Handles code completions +- [Policy Service](#policy-service) - Enforces usage policies +- [Cody Proxy](#cody-proxy) - Load balancing between AI providers +- [Attribution Tracking](#attribution-tracking) - Tracks code origin +- [Cody Assistant](#cody-assistant) - Interactive chat interface + +## Core Services + +### Frontend + +**Purpose**: The frontend service is the central service in Sourcegraph's architecture. It serves the web application, hosts the GraphQL API, and coordinates most user interactions with Sourcegraph. + +**Importance**: This is the primary entrypoint for most Sourcegraph functionality. Without it, users cannot interact with Sourcegraph through the web UI or API. + +**Additional Details**: +- Handles user authentication and session management +- Enforces repository permissions +- Coordinates interactions between most services +- Manages the settings cascade (user, organization, and global settings) +- Implements the GraphQL API layer that powers both the web UI and external API clients +- Stateless service that can be horizontally scaled +- Organized into multiple internal packages with clear separation of concerns + +**Internal Architecture**: +- **HTTP Server**: Handles incoming HTTP requests using Go's standard library +- **GraphQL Engine**: Processes GraphQL queries with custom resolvers for various data types +- **Authorization Layer**: Enforces permissions across all API and UI operations +- **Request Router**: Routes user requests to appropriate internal handlers +- **Service Clients**: Contains client code for communicating with other Sourcegraph services +- **Database Layer**: Manages connections and transactions with the PostgreSQL database + +**Request Flow**: +1. User request arrives at the frontend service +2. Authentication and session validation occur +3. Permission checks are performed for the requested resource +4. The request is routed to the appropriate handler (e.g., search, repository view) +5. The handler coordinates with other services to fulfill the request +6. Results are transformed into the appropriate response format +7. Response is returned to the user + +**Interactions**: +- Serves as the central coordination point for all other services +- Stores user, repository metadata, and other core data in the frontend database +- Acts as a reverse proxy for client requests to other services +- Forwards search requests to zoekt-webserver (indexed search) and searcher (unindexed search) +- Makes API calls to gitserver for repository operations (e.g., file content, commit information) +- Requests repository metadata from repo-updater +- Retrieves code intelligence data from the codeintel database +- Enforces permissions across all accessed resources +- Provides the GraphQL API that all clients use to interact with Sourcegraph + +### Gitserver + +**Purpose**: Gitserver is a shardedable service that clones and maintains local Git repositories from code hosts, making them available to other Sourcegraph services. + +**Importance**: Without gitserver, Sourcegraph cannot access repository content, making search, code navigation, and most other features non-functional. + +**Additional Details**: +- Maintains a persistent cache of repositories, but code hosts remain the source of truth +- Performs Git operations like clone, fetch, archive, and rev-parse +- Implements custom Git operations optimized for Sourcegraph's use cases +- Uses disk-based caching strategies to optimize performance +- Handles repository cleanup and garbage collection +- Repositories can sharded across multiple gitserver instances for horizontal scaling if necessary + +**Internal Architecture**: +- **Repository Manager**: Manages the lifecycle of repositories (cloning, updating, cleaning) +- **Git Command Executor**: Executes Git commands with appropriate timeouts and resource limits +- **Request Handler**: Processes API requests for repository operations +- **Sharding Logic**: Determines which gitserver instance should host a particular repository +- **Cleanup Worker**: Periodically removes unused repositories to free up disk space + +**Repository Flow**: +1. Repository is first requested by a client (through frontend or repo-updater) +2. Gitserver checks if the repository exists locally +3. If not present, gitserver clones the repository from the code host +4. For subsequent operations, gitserver operates on the local copy +5. Periodic fetches update the repository with new commits +6. Git operations (archive, show, etc.) are performed directly on the local repository + +**Scaling Characteristics**: +- Each gitserver instance has an independent set of repositories +- New gitserver instances can be added to handle more repositories +- Repository distribution uses consistent hashing to minimize redistribution when scaling +- Performance is largely determined by disk I/O speed and available memory +- For detailed scaling information, see the [Gitserver Scaling Guide](../../../admin/deploy/scale.md#gitserver) + +**Interactions**: +- Receives repository update requests from repo-updater to clone or update repositories +- Provides repository data to almost all other services through HTTP APIs +- Serves git data to frontend for repository browsing and file viewing +- Supplies repository content to searcher for unindexed searches +- Provides repository archives to zoekt-indexserver for index creation +- Communicates directly with code hosts for clone and fetch operations +- Executes git commands on behalf of other services +- Implements efficient caching to reduce load on code hosts + +### Repo-updater + +**Purpose**: The repo-updater service is responsible for keeping repositories in gitserver up-to-date and syncing repository metadata from code hosts. + +**Importance**: Critical for ensuring Sourcegraph has current information about repositories and respects code host rate limits. + +**Additional Details**: +- Singleton service that orchestrates repository updates +- Handles code host API rate limiting and scheduling +- Also responsible for permission syncing from code hosts +- Manages external service connections (GitHub, GitLab, etc.) +- Implements intelligent scheduling algorithms to prioritize updates +- Handles authentication and authorization with various code host APIs +- Maintains an in-memory queue of pending updates + +**Internal Architecture**: +- **External Service Manager**: Manages connections to code hosts and other external services +- **Repository Syncer**: Synchronizes repository metadata with code hosts +- **Permissions Syncer**: Synchronizes repository permissions from code hosts +- **Update Scheduler**: Schedules repository updates based on priority and last update time +- **Rate Limiter**: Enforces API rate limits for each code host +- **Metrics Collector**: Tracks sync status, errors, and performance metrics + +**Operational Flow**: +1. External services (code hosts) are configured in Sourcegraph +2. Repo-updater periodically polls each external service for repository information +3. New repositories are added to the database and existing ones are updated +4. Repository update operations are scheduled based on priority and last update time +5. Update requests are sent to gitserver instances based on the schedule +6. Repository permissions are synced from the code host to Sourcegraph's database +7. Metadata about repositories (e.g., fork status, visibility) is kept up to date + +**Failure Handling**: +- Implements exponential backoff for failed API requests +- Continues functioning even if some code hosts are temporarily unavailable +- Retries failed operations with appropriate delays +- Can recover state after service restarts + +**Interactions**: +- Makes API calls to code hosts to fetch repository metadata and permissions +- Instructs gitserver to clone, update, or remove repositories as needed +- Stores repository metadata in the frontend database +- Provides repository listings and metadata to frontend +- Implements rate limiting for code host API requests +- Synchronizes repository permissions from code hosts +- Maintains repository sync schedules based on activity patterns +- Validates external service configurations (GitHub, GitLab, etc.) +- Handles webhooks from code hosts for immediate updates when available + +## Search Infrastructure + +### Zoekt-indexserver + +**Purpose**: Creates and maintains the search index for repositories' default branches. + +**Importance**: Enables fast, indexed code search across repositories, which is a core functionality of Sourcegraph. + +**Additional Details**: +- Uses a trigram index for efficient substring matching +- Indexes default branches by default, but capable of indexing additional branches +- Horizontally scalable for large codebases +- Optimized for handling large repositories and codebases +- Builds specialized indices for different types of searches (content, symbols, etc.) +- Performs incremental updates when repositories change + +**Technical Implementation**: +- **Trigram Indexing**: Breaks down text into 3-character sequences for efficient substring searching +- **Sharded Index Design**: Splits large indices into manageable shards +- **Content Extraction**: Extracts content from various file formats before indexing +- **Symbol Extraction**: Uses language-specific parsers to extract and index symbols +- **Custom Compression**: Employs specialized compression techniques for code content + +**Indexing Process**: +1. Receives a request to index a repository +2. Retrieves the latest content from gitserver +3. Analyzes repository content and extracts text and metadata +4. Breaks content into trigrams and other searchable units +5. Builds an optimized index structure with various lookup tables +6. Compresses the index and writes it to disk +7. Signals zoekt-webserver that a new index is available + +**Performance Characteristics**: +- CPU-intensive during index creation +- Memory usage scales with repository size and complexity +- Disk I/O intensive when writing indices +- Can be scaled horizontally by adding more instances and sharding repositories + +**Interactions**: +- Gets repository content from gitserver +- Creates indexes consumed by zoekt-webserver +- Coordinates with frontend to determine which repositories to index +- Emits metrics about indexing performance and coverage + +### Zoekt-webserver + +**Purpose**: Serves search requests against the trigram search index created by zoekt-indexserver. + +**Importance**: Provides the fast, indexed search capability that makes Sourcegraph search powerful. + +**Additional Details**: +- Highly optimized for low-latency searches +- Includes ranking algorithms for result relevance +- Implements sophisticated query parsing and execution +- Supports various search modifiers and operators +- Memory-maps index files for fast access +- Horizontally scalable to handle large search loads + +**Technical Implementation**: +- **In-Memory Index**: Keeps critical parts of the index in memory for fast access +- **Query Parser**: Parses complex search queries into executable search plans +- **Search Executor**: Executes search plans against the index with parallelism +- **Result Ranker**: Ranks search results by relevance using several signals +- **Result Limiter**: Enforces result limits and timeouts to ensure responsiveness + +**Search Execution Flow**: +1. Receives a query from frontend via the API +2. Parses the query into a structured search plan +3. Identifies which index shards need to be searched +4. Executes the search in parallel across relevant shards +5. Collects and ranks the results by relevance +6. Applies post-processing filters (e.g., case sensitivity, regexp matching) +7. Returns the formatted results to the caller + +**Performance Optimizations**: +- Uses memory mapping for fast index access +- Implements concurrent search execution +- Employs early termination strategies for large result sets +- Caches frequent queries and partial results +- Prioritizes interactive search performance + +**Interactions**: +- Receives search queries from frontend through HTTP API calls +- Utilizes index files created by zoekt-indexserver stored on disk +- Performs parallel searches across multiple index shards +- Returns ranked and formatted search results to frontend +- Communicates index status to frontend for search scoping decisions +- Provides detailed metrics about search performance and throughput +- Coordinates with other zoekt-webserver instances for multi-shard searches + +### Searcher + +**Purpose**: Performs non-indexed, on-demand searches for content not covered by zoekt. + +**Importance**: Provides search capability for non-default branches and unindexed repositories, ensuring comprehensive search coverage. + +**Additional Details**: +- Used for searching branches other than the default branch +- Performs structural search (non-regex pattern matching) +- Slower than zoekt but more flexible +- Processes repositories on demand rather than pre-indexing +- Supports advanced search patterns including regular expressions +- Implements a local file cache to improve performance for repeated searches + +**Technical Implementation**: +- **Archive Fetcher**: Retrieves repository archives from gitserver +- **Archive Extractor**: Extracts repository contents to temporary storage +- **Search Executor**: Runs search patterns against repository contents +- **Pattern Matcher**: Implements various pattern matching algorithms (regex, exact, structural) +- **Cache Manager**: Manages a local cache of recently searched repositories + +**Search Process**: +1. Receives a search request for a specific repository and revision +2. Checks if the repository is already in the local cache +3. If not cached, requests an archive from gitserver +4. Extracts the archive to a temporary location +5. Executes the search pattern against the extracted files +6. Applies filters (file path, language, etc.) +7. Formats and returns the matching results +8. Optionally caches the repository for future searches + +**Performance Considerations**: +- Uses streaming to return results as they're found +- Implements timeouts to prevent long-running searches +- Caches recently searched repositories to avoid repeated downloads +- Applies heuristics to optimize search patterns before execution +- Can be scaled horizontally to handle more concurrent searches + +**Interactions**: +- Receives search requests from frontend through HTTP API calls +- Requests repository archives from gitserver for each search query +- Maintains a local cache of recently searched repositories +- Returns search results to frontend as they are found (streaming) +- Handles multiple concurrent search requests with appropriate limits +- Coordinates timeout handling with frontend for long-running searches +- Reports detailed metrics about search performance and cache efficiency +- Implements fallback search when zoekt indexing is incomplete or unavailable + +### Syntect Server + +**Purpose**: Provides syntax highlighting for code in any language displayed in Sourcegraph. + +**Importance**: Enhances readability of code in search results, repository browsing, and other code views. + +**Additional Details**: +- Based on the Rust Syntect library +- Supports hundreds of programming languages and file formats +- Optimized for high throughput and low latency + +**Interactions**: +- Receives highlighting requests from frontend +- Used by search UI and repository browsing + +## Code Intelligence + +### Symbols + +**Purpose**: Extracts and indexes symbol information (functions, classes, etc.) from code for fast symbol search. + +**Importance**: Enables symbol search and contributes to basic code navigation features. + +**Additional Details**: +- Language-agnostic symbol extraction using regular expressions +- Complements precise code intelligence for languages without dedicated indexers + +**Interactions**: +- Gets repository content from gitserver +- Serves symbol search requests from frontend + +### Precise-code-intel-worker + +**Purpose**: Processes and converts uploaded LSIF/SCIP code intelligence data into queryable indexes. + +**Importance**: Enables precise code navigation (go-to-definition, find references) across repositories. + +**Additional Details**: +- Handles processing of upload records in a queue +- Converts LSIF/SCIP data into an optimized index format + +**Interactions**: +- Stores processed data in the codeintel database +- Accesses uploads from blob storage + +### Worker + +**Purpose**: A service for executing background jobs including batch changes processing, code insights computations, and other asynchronous tasks. + +**Importance**: Handles long-running operations that would otherwise block user interactions. + +**Additional Details**: +- Implements a work queue for distributed processing +- Handles retries and error recovery +- Used for executing various background jobs based on configuration + +**Interactions**: +- Communicates with frontend for job coordination +- Accesses various databases depending on the job type +- Interacts with gitserver for repository operations + +## Data Persistence + +### Frontend DB + +**Purpose**: Primary PostgreSQL database that stores user data, repository metadata, configuration, and other core application data. + +**Importance**: Stores critical data needed for almost all Sourcegraph operations. + +**Additional Details**: +- Contains user accounts, repository metadata, and configuration +- Used for transactional operations across the application +- Stores settings, user accounts, repository metadata, and more +- Employs database migrations for schema evolution +- Configured with specific optimizations for Sourcegraph's workload + +**Schema Structure**: +- **Users and Authentication**: Tables for users, organizations, credentials +- **Repository Metadata**: Tables for repositories, external services, permissions +- **Configuration**: Settings cascade for different scopes (global, org, user) +- **API Metadata**: API tokens, client information, usage tracking +- **Search Metadata**: Saved searches, search statistics, search contexts +- **Various Feature Data**: Batch changes, code monitoring, notebooks, etc. + +**Data Access Patterns**: +- High read-to-write ratio for most tables +- Transactional integrity for critical operations +- Heavy use of indexes for performance optimization +- PostgreSQL-specific features (e.g., jsonb for settings, array types, etc.) +- Connection pooling to handle concurrent requests efficiently + +**Scaling Characteristics**: +- Vertical scaling for most deployments (larger DB instance) +- Performance typically determined by index efficiency and query patterns +- Read replicas can be configured for large-scale deployments +- Designed to support thousands of repositories and users + +**Interactions**: +- Primary database for the frontend service +- Used by repo-updater for external service and repository metadata +- Stores permissions data for authorization checks +- Referenced by nearly all services for configuration and settings + +### Codeintel DB + +**Purpose**: PostgreSQL database dedicated to storing code intelligence data. + +**Importance**: Enables precise code navigation features by storing symbol relationships. + +**Additional Details**: +- Stores processed LSIF/SCIP data in an optimized format +- Separated from frontend DB for performance and scaling reasons + +**Interactions**: +- Used by precise-code-intel-worker for writing processed data +- Queried by frontend for code navigation requests + +### Codeinsights DB + +**Purpose**: PostgreSQL database that stores code insights data and time series information. + +**Importance**: Persists data for code insights dashboards and historical trend analysis. + +**Additional Details**: +- Stores time series data for tracking code metrics over time +- Separated from other databases for performance and scaling reasons + +**Interactions**: +- Written to by worker service when computing insights +- Queried by frontend when rendering code insights dashboards + +### Blob Store + +**Purpose**: Object storage service for large binary data like LSIF/SCIP uploads and other artifacts. + +**Importance**: Provides scalable storage for large data files that would be inefficient to store in PostgreSQL. + +**Additional Details**: +- Can be configured to use cloud storage (S3, GCS) or local disk +- Used primarily for code intelligence uploads and other large artifacts + +**Interactions**: +- Stores raw LSIF/SCIP uploads before processing +- Accessed by precise-code-intel-worker during processing + +### Redis + +**Purpose**: In-memory data store used for caching, rate limiting, and other ephemeral data. + +**Importance**: Improves performance by caching frequently accessed data and supporting distributed locking. + +**Additional Details**: +- Used for session data, caching, and rate limiting +- Supports pub/sub mechanisms used by some services + +**Interactions**: +- Used by frontend for caching and session management +- Used by repo-updater for coordination and caching + +## External Components + +### Executors + +**Purpose**: Isolated environments for running compute-intensive operations like Batch Changes and Code Insights computations. + +**Importance**: Enables secure, scalable execution of user-provided code and resource-intensive operations. + +**Additional Details**: +- Runs as separate infrastructure from the main Sourcegraph instance +- Provides isolated sandboxed environments +- Horizontally scalable based on compute needs + +**Interactions**: +- Receives jobs from the main Sourcegraph instance +- Returns results to the worker service + +### Code Hosts + +**Purpose**: External systems (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, etc.) that host the repositories Sourcegraph interacts with. -At its core, Sourcegraph maintains a persistent cache of all repositories that are connected to it. It is persistent because this data is critical for Sourcegraph to function. Still, it is ultimately a cache because the code host is the source of truth, and our cache is eventually consistent. +**Importance**: Source of truth for all code and repository metadata synchronized to Sourcegraph. -- `gitserver` is the sharded service that stores repositories and makes them accessible to other Sourcegraph services -- `repo-updater` is the singleton service responsible for ensuring all repositories in gitserver are as up-to-date as possible while respecting code host rate limits. It is also responsible for syncing repository metadata from the code host that is stored in the repo table of our Postgres database +**Additional Details**: +- Sourcegraph maintains connections to these systems via API tokens +- Rate limits and permissions from code hosts must be respected -## Permission syncing +**Interactions**: +- Repo-updater syncs repository metadata and permissions from code hosts +- Gitserver clones and fetches repositories from code hosts +- Batch Changes creates and updates changesets (PRs/MRs) on code hosts -Repository permissions are mirrored from code hosts to Sourcegraph by default. This builds the foundation of Sourcegraph authorization for repositories to ensure users see consistent content on code hosts. Currently, the background permissions syncer resides in the repo-updater. +## Observability Infrastructure -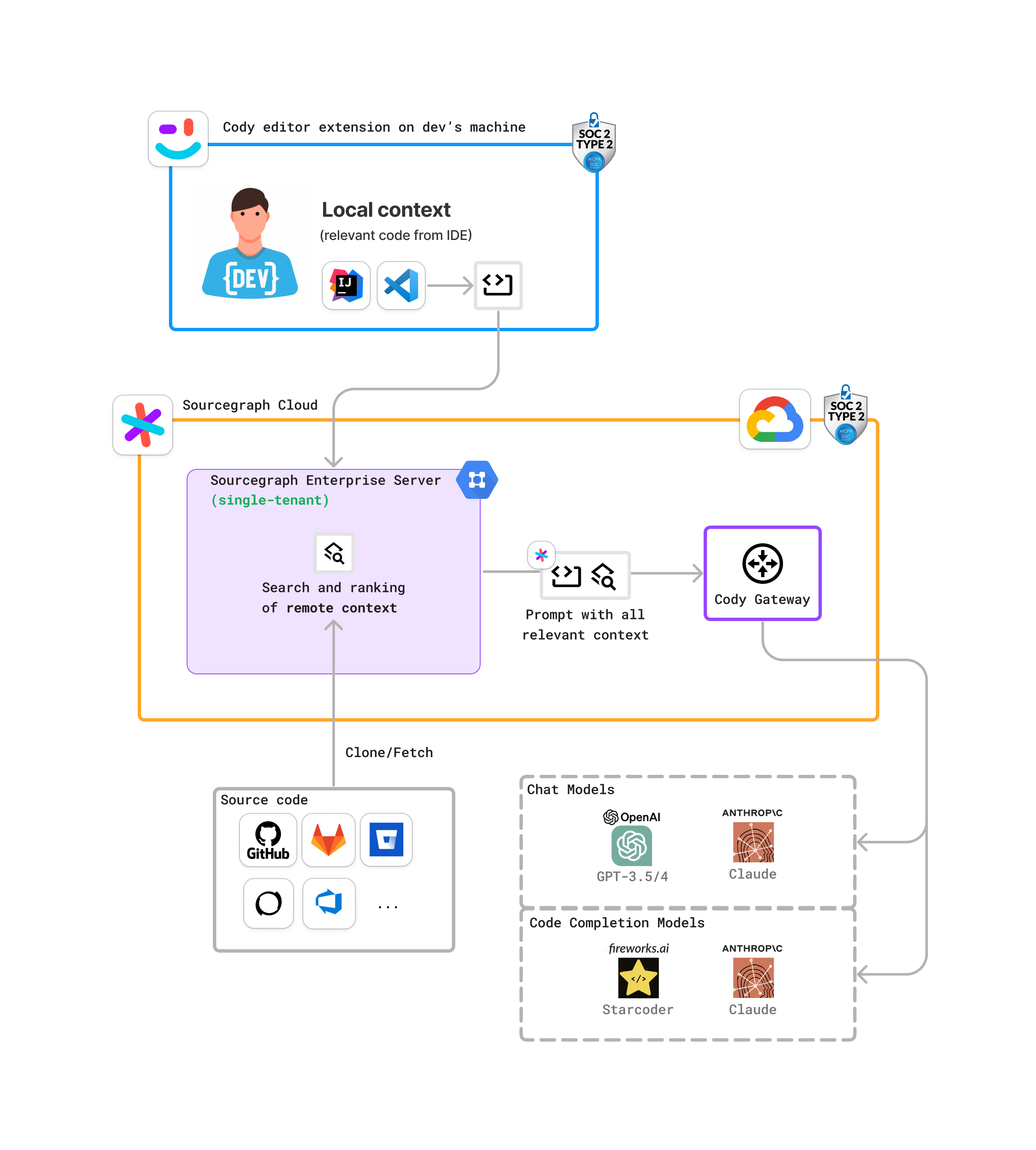 +**Blob Storage**:
+- **Purpose**: Stores large binary objects such as LSIF/SCIP uploads and other artifacts
+- **Default Implementation**: MinIO (S3-compatible)
+- **Cloud Alternatives**: Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage
-### Sourcegraph Enterprise Server (self-hosted) on Amazon Bedrock
+### Distributed Tracing
-This is an example of a more complex deployment that uses Sourcegraph Enterprise Server (self-hosted) and Amazon Bedrock.
+**Jaeger**:
+- **Purpose**: Provides end-to-end distributed tracing for debugging and monitoring
+- **Usage**: Optional component for advanced debugging and performance analysis
+- **Cloud Alternatives**: AWS X-Ray, Google Cloud Trace, Azure Monitor
-
+**Blob Storage**:
+- **Purpose**: Stores large binary objects such as LSIF/SCIP uploads and other artifacts
+- **Default Implementation**: MinIO (S3-compatible)
+- **Cloud Alternatives**: Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage
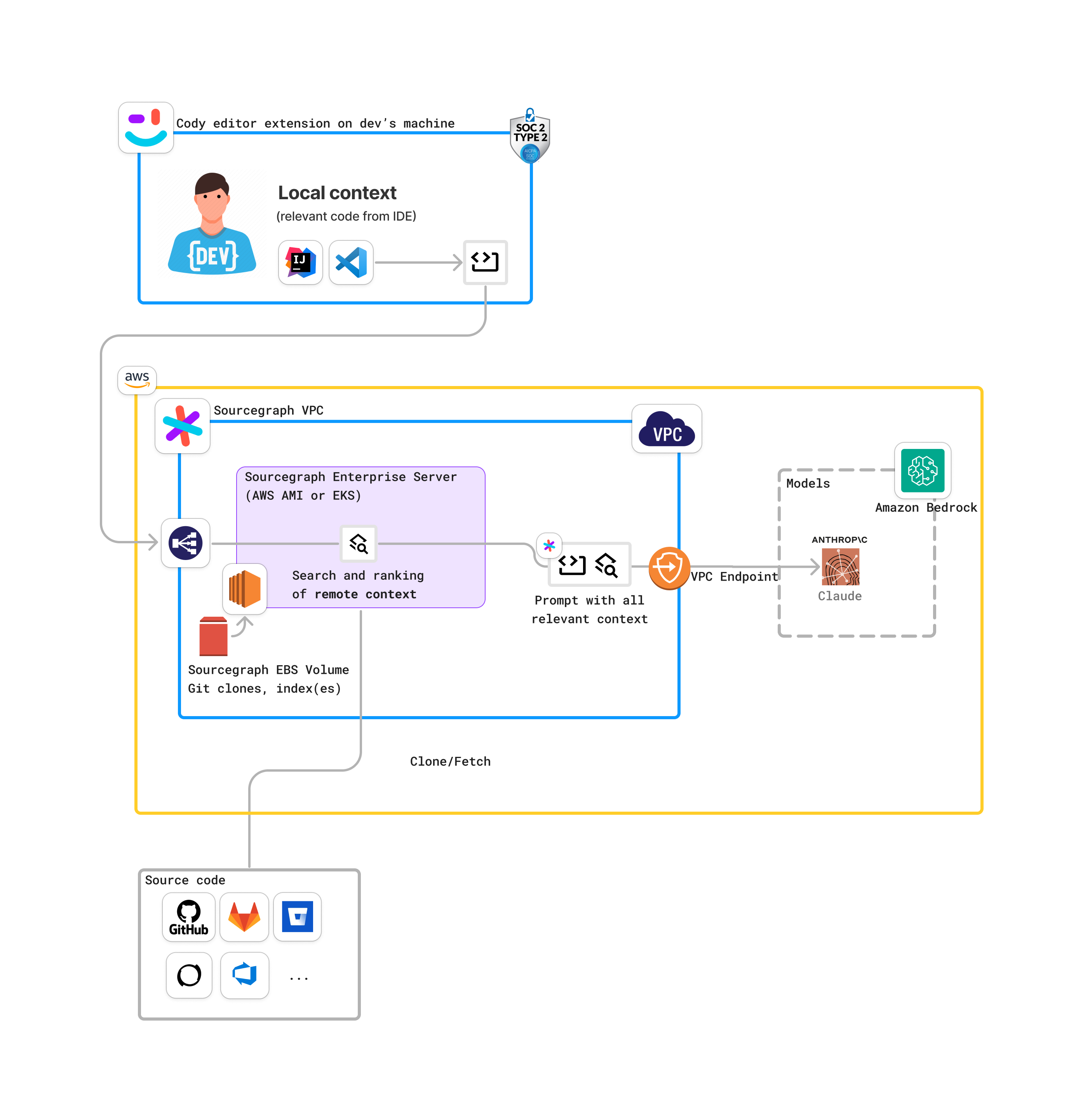
-### Sourcegraph Enterprise Server (self-hosted) on Amazon Bedrock
+### Distributed Tracing
-This is an example of a more complex deployment that uses Sourcegraph Enterprise Server (self-hosted) and Amazon Bedrock.
+**Jaeger**:
+- **Purpose**: Provides end-to-end distributed tracing for debugging and monitoring
+- **Usage**: Optional component for advanced debugging and performance analysis
+- **Cloud Alternatives**: AWS X-Ray, Google Cloud Trace, Azure Monitor
- +### External Code Hosts
-### Data flow
+Sourcegraph connects to various code hosts to synchronize repositories and metadata.
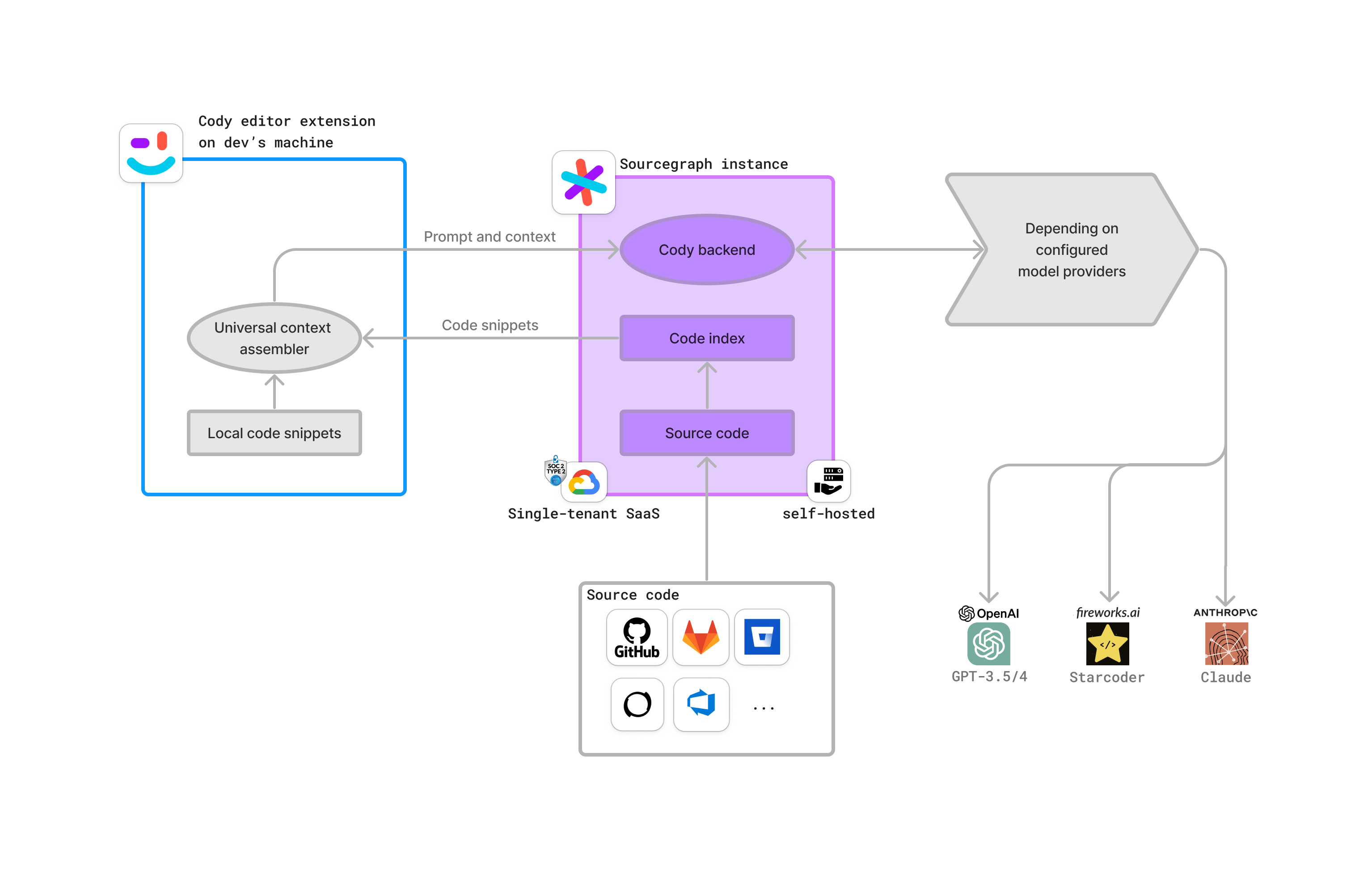
-The following diagram describes the data flow between the different components of Cody Enterprise.
+## Additional Resources
-
+### External Code Hosts
-### Data flow
+Sourcegraph connects to various code hosts to synchronize repositories and metadata.
-The following diagram describes the data flow between the different components of Cody Enterprise.
+## Additional Resources
- +- [Life of a repository](life-of-a-repository.md) - Detailed explanation of repository syncing
+- [Life of a search query](life-of-a-search-query.md) - How search requests flow through the system
+- [Monitoring architecture](https://handbook.sourcegraph.com/engineering/observability/monitoring_architecture) - How Sourcegraph's observability system works
+- [Life of a ping](life-of-a-ping.md) - How usage data is collected
+- [Background permissions syncing](../../../admin/repo/permissions.md#background-permissions-syncing) - Details on permission synchronization
+- [Using external services with Sourcegraph](../../../admin/external_services/index.md) - How to configure external services
+- [Life of a repository](life-of-a-repository.md) - Detailed explanation of repository syncing
+- [Life of a search query](life-of-a-search-query.md) - How search requests flow through the system
+- [Monitoring architecture](https://handbook.sourcegraph.com/engineering/observability/monitoring_architecture) - How Sourcegraph's observability system works
+- [Life of a ping](life-of-a-ping.md) - How usage data is collected
+- [Background permissions syncing](../../../admin/repo/permissions.md#background-permissions-syncing) - Details on permission synchronization
+- [Using external services with Sourcegraph](../../../admin/external_services/index.md) - How to configure external services