drop trait用于在值超出范围时释放档案或网路连线等资源。
drop trait用于释放Box <T>指向的堆上的空间。
drop trait用于实现drop()方法,方法该对self进行可变参照。
下面来看一个简单的例子:
struct Example
{
a : i32,
}
impl Drop for Example
{
fn drop(&mut self)
{
println!("Dropping the instance of Example with data : {}", self.a);
}
}
fn main()
{
let a1 = Example{a : 10};
let b1 = Example{a: 20};
println!("Instances of Example type are created");
}执行上面的示例程序码,得到以下结果 -
Instances of Example type are created
Dropping the instance of Example with data : 20
Dropping the instance of Example with data : 10程式程式码说明
- 在类型
Example上实现了Drop trait,并在Drop trait的实现中定义了drop()方法。 - 在
main()函式中,建立了式样的范例,Example并且在main()函式的范围,范例远处了。 - 当范例移出作用域时,铁锈会隐式呼叫
drop()方法来删除Example类型范例。首先,删除范例b1,然后删除范例a1。
注意:无需显式呼叫
drop()方法。因此,可以说当超出范围时,锈蚀隐式呼叫drop()方法。
有时,有必要在范围结束之前删除该值。如果想提前删除该值,则使用std::mem::drop函式来删除该值。
下面来看一个手动删除值的简单例子:
struct Example
{
a : String,
}
impl Drop for Example
{
fn drop(&mut self)
{
println!("Dropping the instance of Example with data : {}", self.a);
}
}
fn main()
{
let a1 = Example{a : String::from("Hello")};
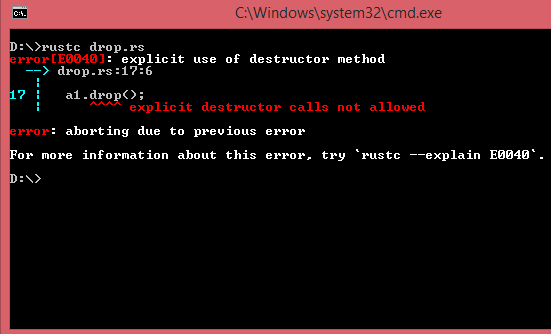
a1.drop();
let b1 = Example{a: String::from("World")};
println!("Instances of Example type are created");
}执行上面的示例程序码,得到以下结果 -
在上面的例子中,呼叫手动drop()方法。防锈编译器丢掷一个错误,显不允许式呼叫drop()方法。显不是式呼叫drop()方法,呼叫而是std::mem::drop函式在值超出范围之前删除它。
std::mem::drop的函式语法与Drop trait中定义的drop()。函式不同std::mem::drop。函式包含作为引数传递的值,值该在超出范围之前将被删除
下面来看一个简单的例子:
struct Example
{
a : String,
}
impl Drop for Example
{
fn drop(&mut self)
{
println!("Dropping the instance of Example with data : {}", self.a);
}
}
fn main()
{
let a1 = Example{a : String::from("Hello")};
drop(a1);
let b1 = Example{a: String::from("World")};
println!("Instances of Example type are created");
}执行上面的示例程序码,得到以下结果——
Dropping the instance of Example with data : Hello
Instances of Example type are created
Dropping the instance of Example with data : World在上面的例子中,通过在drop(a1)式中将例子a1作为引数传来的例子a1。