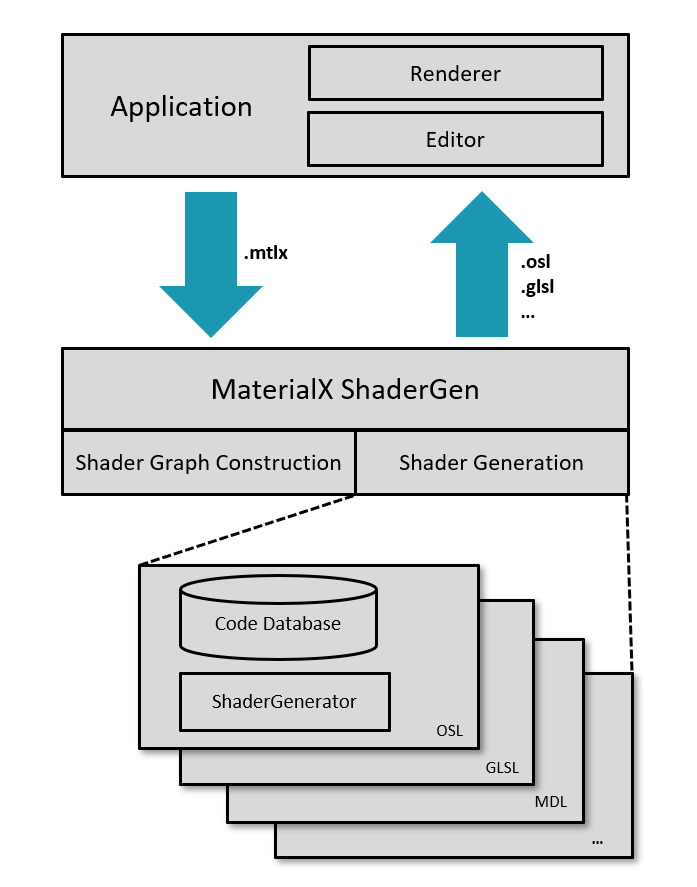
A shader generation framework is implemented as part of MaterialX. This can help applications to transform the agnostic MaterialX data description into executable shader code for a specific renderer. A library module named MaterialXGenShader contains the core shader generation features, and support for specific languages resides in separate libraries, e.g. MaterialXGenGlsl, MaterialXGenOsl.
Note that this system has no runtime and the output produced is source code, not binary executable code. The source code produced needs to be compiled by a shading language compiler before being executed by the renderer. See Figure 1 for a high level overview of the system.
Figure 1: Shader generation with multiple shader generators.
The MaterialX description is free from device specific details and all implementation details needs to be taken care of by shader generators. There is one shader generator for each supported shading language. However for each language there can also be variations needed for different renderers. For example; OpenGL renderers supporting GLSL can use forward rendering or deferred rendering, each with very different requirements for how the shaders are constructed. Another example is different renderers supporting OSL but with different sets of closures or closure parameters. Hence a separate shader generator can be defined for each language/target combination.
Class inheritance and specialization is used to create support for new languages or to customize existing language support for a new target. To add a new shader generator for a target you add a new C++ class derived from the base class ShaderGenerator, or one of the existing derived shader generator classes (GlslShaderGenerator, OslShaderGenerator, etc.), and override the methods you need to customize. You might also need to derive a new Syntax class, which is used to handle syntactical differences between different shading languages. Then you need to make sure there are implementations defined for all the nodes you want to support, standard library nodes and nodes from other libraries, by either reusing existing implementations where applicable or adding in new ones. See 1.3 Node Implementations on how that is done.
Note that a shader generator doesn’t need to be defined at the time when node definitions are added. New shader generators can be added later, and node implementations for new targets can be added for existing nodes.
There are four different methods to define the implementation of a node:
- Using an inline expression.
- Using a function written in the target language.
- Using a nodegraph that defines the operation performed by the node.
- Using a C++ class that emits code dynamically during shader generation.
In the following sub-sections each of these methods are explained. For all methods the implementation is tied to a specific nodedef with a well defined interface of typed inputs and outputs.
Provided code generators support a very simple expression language for inlining code. This is useful for simple nodes where the operation can be expressed as a single line of code. Inlining will reduce the number of function calls and produce more compact code. The syntax to use is the same as the target shading language, with the addition of using the node’s input ports as variables wrapped in double curly brackets: {{input}}. The code generator will replace these variables with values assigned or connected to the respective inputs. Figure 2 gives an example.
Connecting the expression to the nodedef is done using an <implementation> element as seen in
Figure 2. The first option is to keep inline code in a file. The file extension is used to differentiate inline expressions from source code functions, using filename.inline. The second option is to directly embed the inlined code using sourcecode. This is the recommended approach for inlining if there the logic can fit on one line of code.
<!-- Node definition elements for node <add> -->
<nodedef name="ND_add_float" node="add">
<input name="in1" type="float" />
<input name="in2" type="float" />
<output name="out" type="float" defaultinput="in1" />
</nodedef>
<nodedef name="ND_add_color3" node="add" type="color3">
<input name="in1" type="color3" />
<input name="in2" type="color3" />
<output name="out" type="color3" defaultinput="in1" />
</nodedef>
<!-- ... more types ... -->
<!-- Implementation elements for node <add> -->
<implementation name="IM_add_float" nodedef="ND_add_float" file="mx_add.inline" />
<implementation name="IM_add_color3" nodedef="ND_add_color3" file="mx_add.inline" />
<!-- ... more types ... -->
<!-- Node definition elements for node <mix> -->
<nodedef name="ND_mix_float" node="mix">
<input name="fg" type="float" />
<input name="bg" type="float" />
<input name="mix" type="float" />
<output name="out" type="float" defaultinput="bg" />
</nodedef>
<nodedef name="ND_mix_color3" node="mix">
<input name="fg" type="color3" />
<input name="bg" type="color3" />
<input name="mix" type="color3" />
<output name="out" type="color3" defaultinput="bg" />
</nodedef>
<!-- ... more types ... -->
<!-- Implementation elements for node <mix> -->
<implementation name="IM_mix_float" nodedef="ND_mix_float" sourcecode="mix({{bg}}, {{fg}}, {{mix}})" />
<implementation name="IM_mix_color3" nodedef="ND_mix_color3" sourcecode="mix({{bg}}, {{fg}}, {{mix}})" />
<!-- ... more types ... -->// File 'mx_add.inline' contains:
{{in1}} + {{in2}}Figure 2: Inline expressions for implementing nodes <add> and <mix>. The code for <add> is stored in an additional file, while the code for <mix> is specified as part of the
<implemenentation> declaration.
For nodes that can’t be implemented by inline expressions a function definition can be used instead. The function signature should match the nodedefs interface with inputs and outputs. See Figure 3 for an example. Connecting the source code to the nodedef is done using an <implementation> element, see the MaterialX Specification for more information.
<!-- Node definition element -->
<nodedef name="ND_image_color3" node="image">
<input name="file" type="filename" value="" uniform="true" />
<input name="layer" type="string" value="" uniform="true" />
<input name="default" type="color3" value="0.0, 0.0, 0.0" />
<input name="texcoord" type="vector2" defaultgeomprop="UV0" />
<input name="uaddressmode" type="string" value="periodic" uniform="true" />
<input name="vaddressmode" type="string" value="periodic" uniform="true" />
<input name="filtertype" type="string" value="linear" uniform="true" />
<input name="framerange" type="string" value="" uniform="true" />
<input name="frameoffset" type="integer" value="0" uniform="true" />
<input name="frameendaction" type="string" value="constant" uniform="true" />
<output name="out" type="color3" default="0.0, 0.0, 0.0" />
</nodedef>
<!-- Implementation element -->
<implementation name="IM_image_color3_osl" nodedef="ND_image_color3" file="mx_image_color3.osl" target="genosl" />// File 'mx_image_color3.osl' contains:
void mx_image_color3(string file, string layer, color defaultvalue,
vector2 texcoord, string uaddressmode, string vaddressmode, string filtertype,
string framerange, int frameoffset, string frameendaction,
output color out)
{
// Sample the texture
out = texture(file, texcoord.x, texcoord.y,
"interp", filtertype,
"subimage", layer,
"missingcolor", defaultvalue,
"wrap", uaddressmode);
}Figure 3: Shading language function's implementation for node <image> in OSL.
As an alternative to defining source code, there is also an option to reference a nodegraph as the implementation of a nodedef. The only requirement is that the nodegraph and nodedef have matching inputs and outputs.
This is useful for creating a compound for a set of nodes performing some common operation. It can then be referenced as a node inside other nodegraphs. It is also useful for creating compatibility graphs for unknown nodes. If a node is created by some third party, and its implementation is unknown or proprietary, a compatibility graph can be created using known nodes and be referenced as a stand-in implementation. Linking a nodegraph to a nodedef is done by simply setting a nodedef attribute on the nodegraph definition. See Figure 4 for an example.
<nodedef name="ND_checker_float" node="checker">
<input name="texcoord" type="vector2" defaultgeomprop="UV0" />
<input name="uvtiling" type="vector2" value="8.0, 8.0" />
<output name="out" type="float" />
</nodedef>
<nodegraph name="IM_checker_float" nodedef="ND_checker_float">
<multiply name="mult1" type="vector2">
<input name="in1" type="vector2" interfacename="texcoord" />
<input name="in2" type="vector2" interfacename="uvtiling" />
</multiply>
<floor name="floor1" type="vector2">
<input name="in" type="vector2" nodename="mult1" />
</floor>
<dotproduct name="dotproduct1" type="float">
<input name="in1" type="vector2" nodename="floor1" />
<input name="in2" type="vector2" value="1, 1" />
</dotproduct>
<modulo name="modulo1" type="float">
<input name="in1" type="float" nodename="dotproduct1" />
<input name="in2" type="float" value="2" />
</modulo>
<output name="out" type="float" nodename="modulo1" />
</nodegraph>Figure 4: Checker node implementation using a nodegraph.
In some situations static source code is not enough to implement a node. The code might need to be customized depending on parameters set on the node. Or for a hardware render target vertex streams or uniform inputs might need to be created in order to supply the data needed for the node implementation.
In this case, a C++ class can be added to handle the implementation of the node. The class should be derived from the base class ShaderNodeImpl. It should specify what target it is for by overriding getTarget(). It then needs to be registered for a ShaderGenerator by calling ShaderGenerator::registerImplementation(). See Figure 5 for an example.
When a ShaderNodeImpl class is used for a nodedef the corresponding <implementation> element doesn’t need a file attribute, since no static source code is used. The <implementation> element will then act only as a declaration that there exists an implementation for the nodedef for a particular target.
Note that by using a ShaderNodeImpl class for your node's implementation it is no longer data driven, as in the other three methods above. So it's recommended to use this only when inline expressions or static source code functions are not enough to handle the implementation of a node.
/// Implementation of ’foo' node for OSL
class FooOsl : public ShaderNodeImpl
{
public:
static ShaderNodeImplPtr create() { return std::make_shared<FooOsl>(); }
const string& getTarget() const override { return OslShaderGenerator::TARGET; }
void emitFunctionDefinition(const ShaderNode& node, GenContext& context,
ShaderStage& stage) const override
{
// Emit function definition if needed for the node
}
void emitFunctionCall(const ShaderNode& node, GenContext& context,
ShaderStage& stage) const override
{
// Emit function call, or inline shader code, for the node
}
};OslShaderGenerator::OslShaderGenerator() :
ShaderGenerator(std::make_shared<OslSyntax>())
{
...
// Register foo implementation for nodedefs it should be used for
registerImplementation("IM_foo_color2_osl", FooOsl::create);
registerImplementation("IM_foo_color3_osl", FooOsl::create);
registerImplementation("IM_foo_color4_osl", FooOsl::create);
...
}Figure 5: C++ class for dynamic code generation.
This section outlines the steps taken in general to produce a shader from the MaterialX description. The ShaderGenerator base class and its supporting classes will handle this for you, but it’s good to know the steps involved if custom changes are needed to support a new target.
Shader generation supports generating a shader starting from either an output element or a shaderref element in a material. The output can be an output port on a nodegraph or an output element inserted anywhere in a node network. A shader is generated by calling your shader generator class with either of these element types as input. The given element and all dependencies upstream will be translated into a single monolithic shader in the target shading language.
// Generate a shader starting from the given element, translating
// the element and all dependencies upstream into shader code.
ShaderPtr ShaderGenerator::generate(const string& name,
ElementPtr element,
GenContext& context)The shader generation process can be divided into initialization and code generation. The initialization consists of a number of steps:
- Create an optimized version of the graph as a tree with the given input element as root, and with only the used dependencies connected upstream. This involves removing unused paths in the graph, converting constant nodes to constant values, and adding in any default nodes for ports that are unconnected but have default connections specified. Removal of unused paths typically involves constant folding and pruning of conditional branches that will never be taken. Since the resulting shader in the end will be compiled by a shading language compiler, and receive a lot of additional optimizations, we don’t need to do too much work in this optimization step. However, a few graph level optimizations can make the resulting shader a lot smaller and save time and memory during shader compilation. It will also produce more readable source code which is good for debugging purposes. This optimization step is also a good place to do other custom optimizations needed by a particular target. For example simplification of the graph, which could involve substituting expensive nodes with approximate nodes, identification of common subgraphs that can be merged, etc.
- The nodes are sorted in topological order. Since a node can be referenced by many other nodes in the graph we need an ordering of the nodes so that nodes that have a dependency on other nodes come after all dependent nodes. This step also makes sure there are no cyclic dependencies in the graph.
- The stages for the shader are created. For a HW shader this is normally a vertex stage and a pixel stage, but other stages can be added as needed. At the minumum a single pixel stage is required, so even shaders that has no concept of multiple stages, like OSL, needs to have a single pixel stage created.
- The shader stages interface of uniforms and varyings are established. This consists of the graph interface ports that are in use, as well as internal ports that have been published to the interface (an example of the latter is for a hardware shader generator where image texture filenames get converted to texture samplers which needs to be published in order to be bound by the target application). Each node in the graph is also called for a chance to create any uniforms or varyings needed by its implementation.
- Information about scope is tracked for each node. This information is needed to handle branching by conditional nodes. For example, if a node is used only by a particular branch on a varying conditional we want to calculate this node only inside that scope, when that corresponding branch is taken. A node can be used in global scope, in a single conditional scope or by multiple conditional scopes.
The output from the initialization step is a new graph representation constructed using the classes ShaderNode, ShaderInput, ShaderOutput, ShaderGraph, etc. This is a graph representation optimized for shader generation with quick access and traversal of nodes and ports, as well as caching of extra information needed by shader generation.
After initialization the code generation steps are handled by the ShaderGenerator class and derived classes. This part is specific to the particular generator being used, but in general it consists of the following steps:
- Typedefs are emitted as specified by the Syntax class.
- Function definitions are emitted for all the atomic nodes that have shading
language functions for their implementations. For nodes using dynamic code generation their
ShaderNodeImplinstances are called to generate the functions. For nodes that are implemented by graphs a function definition representing the graph computation is emitted. - The shader signature is emitted with all uniforms set to default values. The shader uniforms can later be accessed on the returned
Shaderinstance in order for applications to be able to bind values to them. - The function calls for all nodes are emitted, in the right dependency order, propagating output results from upstream nodes as inputs to downstream nodes. Inline expressions are emitted instead of functions calls for nodes that use this.
- The final shader output is produced and assigned to the shader output variable.
Note that if a single monolithic shader for the whole graph is not appropriate for your system the generator can be called on output elements at any point in your graph, and generate code for sub-parts. It is then up to the application to decide where to split the graph, and to assemble the shader code for sub-parts after all have been generated.
Creation of multiple shader stages is supported. This is needed in order to generate separate code for multiple stages on hardware render targets. A pixel stage must always be created by all targets, even for shading languages like OSL that natively doensn't have a concept of stages. The stage is where the generated shader code is stored as well as all uniforms, inputs and outputs for the shader. This is handled by the ShaderStage class, and the data can be retrieved from it when generation is completed.
One or more ShaderStage instances are created and stored on the Shader class. In addition to the pixel stage, hardware generators always specify a vertex stage. If additional stages are needed they can be added as well. When creating shader input variables you specify which stage the variable should be used in, see 1.7 for more information on shader variable creation.
Node implementations using static source code (function or inline expressions) are always emitted to the pixel stage. Controlling the vertex stage, or other stages, is not supported using static source code. In order to do that you must use dynamic code generation with a custom ShaderNodeImpl sub-class for your node. You are then able to control how it affects all stages separately. Inside emitFunctionDefinition and emitFunctionCall you can add separate sections for each stage using begin/end shader stage macros. Figure 6 shows how the texcoord node for GLSL is emitting different code into the vertex and pixel stages.
When generating a shader from a node graph or shaderref the inputs and parameters on those elements will be published as shader uniforms on the resulting shader. A listing of the created uniforms can be read from the produced Shader and ShaderStage instances. The shader uniforms can then be presented to the user and have their values set by the application.
Adding new uniforms, input and outputs to a shader stage is done by first creating a VariableBlock to store them. There are some predefined identifiers for commonly used variable blocks. For uniforms there are e.g. one named HW::PUBLIC_UNIFORMS and another named HW::PRIVATE_UNIFORMS. Public is used for uniforms to be published to the user, as described above, and private is used for uniforms needed by node implementations but set by the application and not published. For hardware targets there are also specific variable blocks called connector blocks which are used to send data from one stage to another, connecting the stages. A connector block named HW::VERTEX_DATA is used for sending data from the vertex stage to the pixel stage. Variable block creation and handling can be customized as needed by each shader generator target.
All variable blocks can be queried and accessed by the application from the ShaderStage instances after generation.
Figure 6 shows how creation of shader inputs and connector variables are done for a node implementation that requires this.
// Implementation of 'texcoord' node for GLSL
class TexCoordGlsl : public ShaderNodeImpl
{
public:
static ShaderNodeImplPtr create()
{
return std::make_shared<TexCoordGlsl>();
}
void TexCoordNodeGlsl::createVariables(const ShaderNode& node, GenContext&,
Shader& shader) const
{
const ShaderOutput* output = node.getOutput();
const ShaderInput* indexInput = node.getInput(INDEX);
const string index = indexInput ? indexInput->getValue()->getValueString() : "0";
ShaderStage& vs = shader.getStage(Stage::VERTEX);
ShaderStage& ps = shader.getStage(Stage::PIXEL);
addStageInput(HW::VERTEX_INPUTS, output->getType(), "i_texcoord_" + index, vs);
addStageConnector(HW::VERTEX_DATA, output->getType(), "texcoord_" + index, vs, ps);
}
void TexCoordNodeGlsl::emitFunctionCall(const ShaderNode& node,
GenContext& context,
ShaderStage& stage) const
{
const ShaderGenerator& shadergen = context.getShaderGenerator();
const ShaderInput* indexInput = node.getInput(INDEX);
const string index = indexInput ? indexInput->getValue()->getValueString() : "0";
const string variable = "texcoord_" + index;
DEFINE_SHADER_STAGE(stage, Stage::VERTEX)
{
VariableBlock& vertexData = stage.getOutputBlock(HW::VERTEX_DATA);
const string prefix = vertexData.getInstance() + ".";
ShaderPort* texcoord = vertexData[variable];
if (!texcoord->isEmitted())
{
shadergen.emitLine(prefix + texcoord->getVariable() + " = i_" + variable, stage);
texcoord->setEmitted();
}
}
DEFINE_SHADER_STAGE(stage, Stage::PIXEL)
{
VariableBlock& vertexData = stage.getInputBlock(HW::VERTEX_DATA);
const string prefix = vertexData.getInstance() + ".";
ShaderPort* texcoord = vertexData[variable];
shadergen.emitLineBegin(stage);
shadergen.emitOutput(node.getOutput(), true, false, context, stage);
shadergen.emitString(" = " + prefix + texcoord->getVariable(), stage);
shadergen.emitLineEnd(stage);
}
}
};Figure 6: Implementation of node texcoord in GLSL. Using a ShaderNodeImpl sub-class in order to control shader variable creation and code generation into separate shader stages.
Creating shader variables and binding values to them needs to be done in agreement with the shader generator side and application side. The application must know what a variable is for in order to bind meaningful data to it. One way of handling this is by using semantics. All shader variables created can be assigned a semantic if that is used by the target application. Shader generation does not impose a specific set of semantics to use, so for languages and applications that use this any semantics can be used. For languages that do not use semantics a variable naming convention needs to be used instead.
Built-in shader generators and accompanying node implementations have a naming convention for shader variables. A custom shader generator that derives from and takes advantage of built-in features should preferably use the same convention. Uniform variables are prefixed with u_ and vertex inputs with i_ . For languages not using semantics, Figure 7 shows the naming used for variables (inputs and uniforms) with predefined binding rules:
App data input variables
| NAME | TYPE | BINDING |
|---|---|---|
| i_position | vec3 | Vertex position in object space. |
| i_normal | vec3 | Vertex normal in object space. |
| i_tangent | vec3 | Vertex tangent in object space. |
| i_bitangent | vec3 | Vertex bitangent in object space. |
| i_texcoord_N | vec2 | Vertex texture coord for N:th uv set. |
| i_color_N | vec4 | Vertex color for N:th color set. |
Uniform variables
| NAME | TYPE | BINDING |
|---|---|---|
| u_worldMatrix | mat4 | World transform. |
| u_worldInverseMatrix | mat4 | World transform, inverted. |
| u_worldTransposeMatrix | mat4 | World transform, transposed. |
| u_worldInverseTransposeMatrix | mat4 | World transform, inverted, transposed. |
| u_viewMatrix | mat4 | View transform. |
| u_viewInverseMatrix | mat4 | View transform, inverted. |
| u_viewTransposeMatrix | mat4 | View transform, transposed. |
| u_viewInverseTransposeMatrix | mat4 | View transform, inverted, transposed. |
| u_projectionMatrix | mat4 | Projection transform. |
| u_projectionInverseMatrix | mat4 | Projection transform, inverted. |
| u_projectionTransposeMatrix | mat4 | Projection transform, transposed. |
| u_projectionInverseTransposeMatrix | mat4 | Projection transform, inverted, transposed. |
| u_worldViewMatrix | mat4 | World-view transform. |
| u_viewProjectionMatrix | mat4 | View-projection transform. |
| u_worldViewProjectionMatrix | mat4 | World-view-projection transform. |
| u_viewPosition | vec3 | World-space position of the viewer. |
| u_viewDirection | vec3 | World-space direction of the viewer. |
| u_frame | float | The current frame number as defined by the host application. |
| u_time | float | The current time in seconds. |
| u_geomprop_<name> | <type> | A named property of given <type> where <name> is the name of the variable on the geometry. |
| u_numActiveLightSources | int | The number of currently active light sources. Note that in shader this is clamped against the maximum allowed number of light sources. |
| u_lightData[] | struct | Array of struct LightData holding parameters for active light sources. The LightData struct is built dynamically depending on requirements for bound light shaders. |
| u_<unitType>UnitTarget[] | integer | An attribute indicating the target unit for a given unit type definition (<unitType>). |
Figure 7: Listing of predefined variables with their binding rules.