参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!
题目描述:
给定一个由 1(陆地)和 0(水)组成的矩阵,岛屿指的是由水平或垂直方向上相邻的陆地单元格组成的区域,且完全被水域单元格包围。孤岛是那些位于矩阵内部、所有单元格都不接触边缘的岛屿。
现在你需要将所有孤岛“沉没”,即将孤岛中的所有陆地单元格(1)转变为水域单元格(0)。
输入描述:
第一行包含两个整数 N, M,表示矩阵的行数和列数。
之后 N 行,每行包含 M 个数字,数字为 1 或者 0,表示岛屿的单元格。
输出描述
输出将孤岛“沉没”之后的岛屿矩阵。
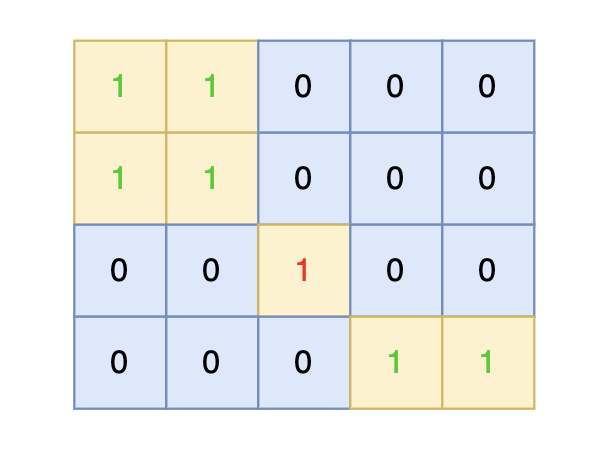
输入示例:
4 5
1 1 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
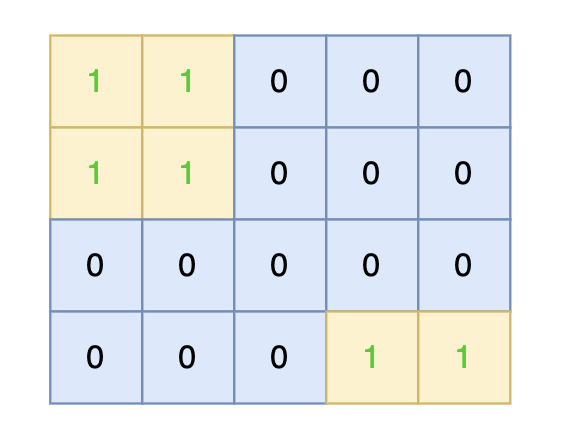
输出示例:
1 1 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
提示信息:
将孤岛沉没:
数据范围:
1 <= M, N <= 50
这道题目和0101.孤岛的总面积正好反过来了,0101.孤岛的总面积是求 地图中间的空格数,而本题是要把地图中间的 1 都改成 0 。
那么两题在思路上也是差不多的。
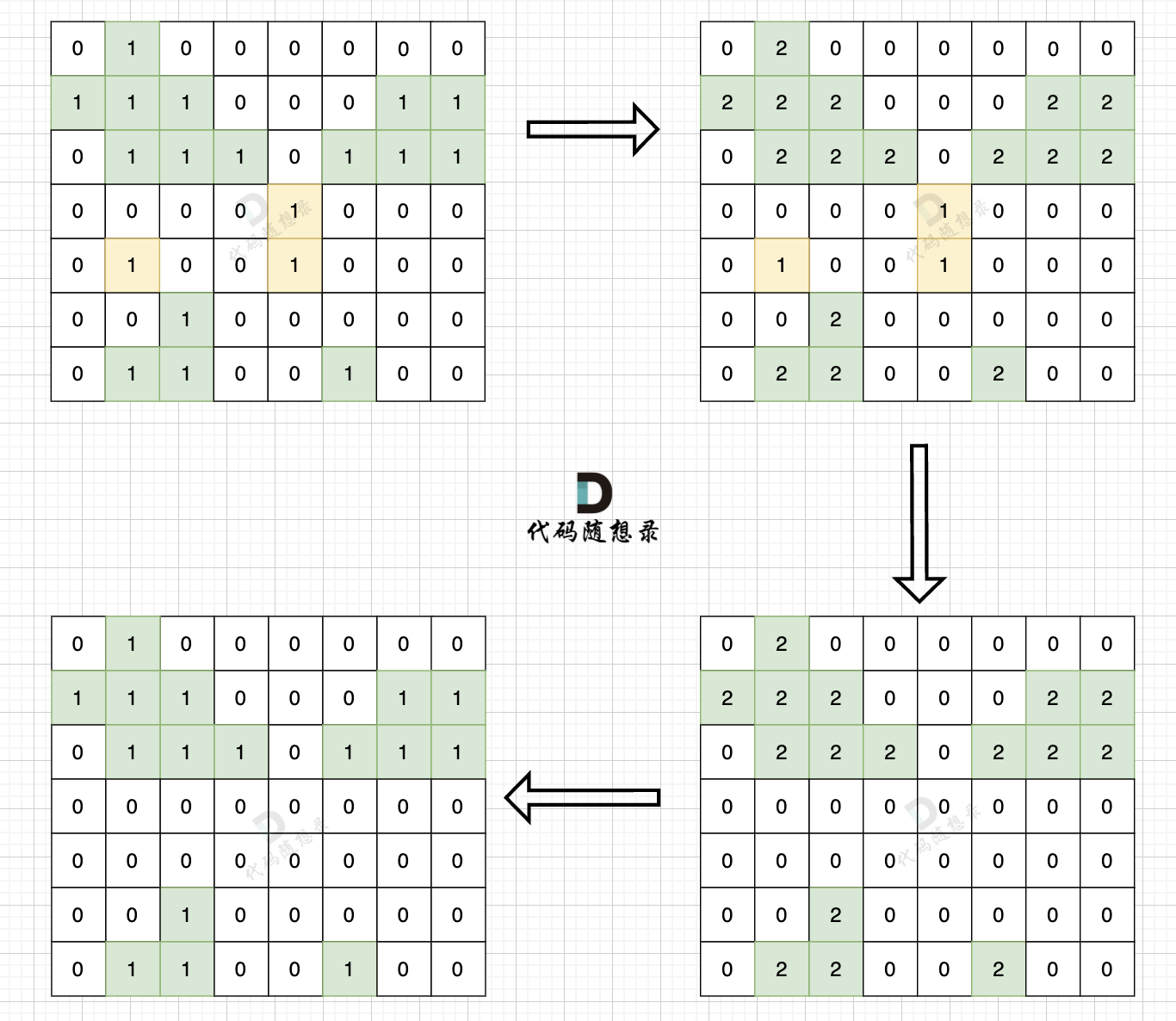
思路依然是从地图周边出发,将周边空格相邻的陆地都做上标记,然后在遍历一遍地图,遇到 陆地 且没做过标记的,那么都是地图中间的 陆地 ,全部改成水域就行。
有的录友可能想,我在定义一个 visited 二维数组,单独标记周边的陆地,然后遍历地图的时候同时对 数组board 和 数组visited 进行判断,决定 陆地是否变成水域。
这样做其实就有点麻烦了,不用额外定义空间了,标记周边的陆地,可以直接改陆地为其他特殊值作为标记。
步骤一:深搜或者广搜将地图周边的 1 (陆地)全部改成 2 (特殊标记)
步骤二:将水域中间 1 (陆地)全部改成 水域(0)
步骤三:将之前标记的 2 改为 1 (陆地)
如图:
整体C++代码如下,以下使用dfs实现,其实遍历方式dfs,bfs都是可以的。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; // 保存四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) {
grid[x][y] = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 向四个方向遍历
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
// 超过边界
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue;
// 不符合条件,不继续遍历
if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 0 || grid[nextx][nexty] == 2) continue;
dfs (grid, nextx, nexty);
}
return;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> grid[i][j];
}
}
// 步骤一:
// 从左侧边,和右侧边 向中间遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) dfs(grid, i, 0);
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) dfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
// 从上边和下边 向中间遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) dfs(grid, 0, j);
if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) dfs(grid, n - 1, j);
}
// 步骤二、步骤三
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) grid[i][j] = 0;
if (grid[i][j] == 2) grid[i][j] = 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cout << grid[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
// 创建readline接口
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
// 创建异步迭代器
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
let graph // 地图
let N, M // 地图大小
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
// 读取输入,初始化地图
const initGraph = async () => {
let line = await readline();
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
line = await readline()
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
graph[i][j] = line[j]
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 从(x,y)开始深度优先遍历地图
* @param {*} graph 地图
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
* @return {*}
*/
const dfs = (graph, x, y) => {
if (graph[x][y] !== 1) return
graph[x][y] = 2 // 标记为非孤岛陆地
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nextx = x + dir[i][0]
let nexty = y + dir[i][1]
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue
dfs(graph, nextx, nexty)
}
}
(async function () {
// 读取输入,初始化地图
await initGraph()
// 遍历地图左右两边
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (graph[i][0] === 1) dfs(graph, i, 0)
if (graph[i][M - 1] === 1) dfs(graph, i, M - 1)
}
// 遍历地图上下两边
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (graph[0][j] === 1) dfs(graph, 0, j)
if (graph[N - 1][j] === 1) dfs(graph, N - 1, j)
}
// 遍历地图,将孤岛沉没,即将陆地1标记为0;将非孤岛陆地2标记为1
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] === 1) graph[i][j] = 0
else if (graph[i][j] === 2) graph[i][j] = 1
}
console.log(graph[i].join(' '));
}
})()const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
// 创建readline接口
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
// 创建异步迭代器
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
let graph // 地图
let N, M // 地图大小
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
// 读取输入,初始化地图
const initGraph = async () => {
let line = await readline();
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
line = await readline()
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
graph[i][j] = line[j]
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 从(x,y)开始广度优先遍历地图
* @param {*} graph 地图
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
* @return {*}
*/
const bfs = (graph, x, y) => {
let queue = []
queue.push([x, y])
graph[x][y] = 2 // 标记为非孤岛陆地
while (queue.length) {
let [xx, yy] = queue.shift()
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nextx = xx + dir[i][0]
let nexty = yy + dir[i][1]
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue
if (graph[nextx][nexty] === 1) bfs(graph, nextx, nexty)
}
}
}
(async function () {
// 读取输入,初始化地图
await initGraph()
// 遍历地图左右两边
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (graph[i][0] === 1) bfs(graph, i, 0)
if (graph[i][M - 1] === 1) bfs(graph, i, M - 1)
}
// 遍历地图上下两边
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (graph[0][j] === 1) bfs(graph, 0, j)
if (graph[N - 1][j] === 1) bfs(graph, N - 1, j)
}
// 遍历地图,将孤岛沉没,即将陆地1标记为0;将非孤岛陆地2标记为1
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] === 1) graph[i][j] = 0
else if (graph[i][j] === 2) graph[i][j] = 1
}
console.log(graph[i].join(' '));
}
})()