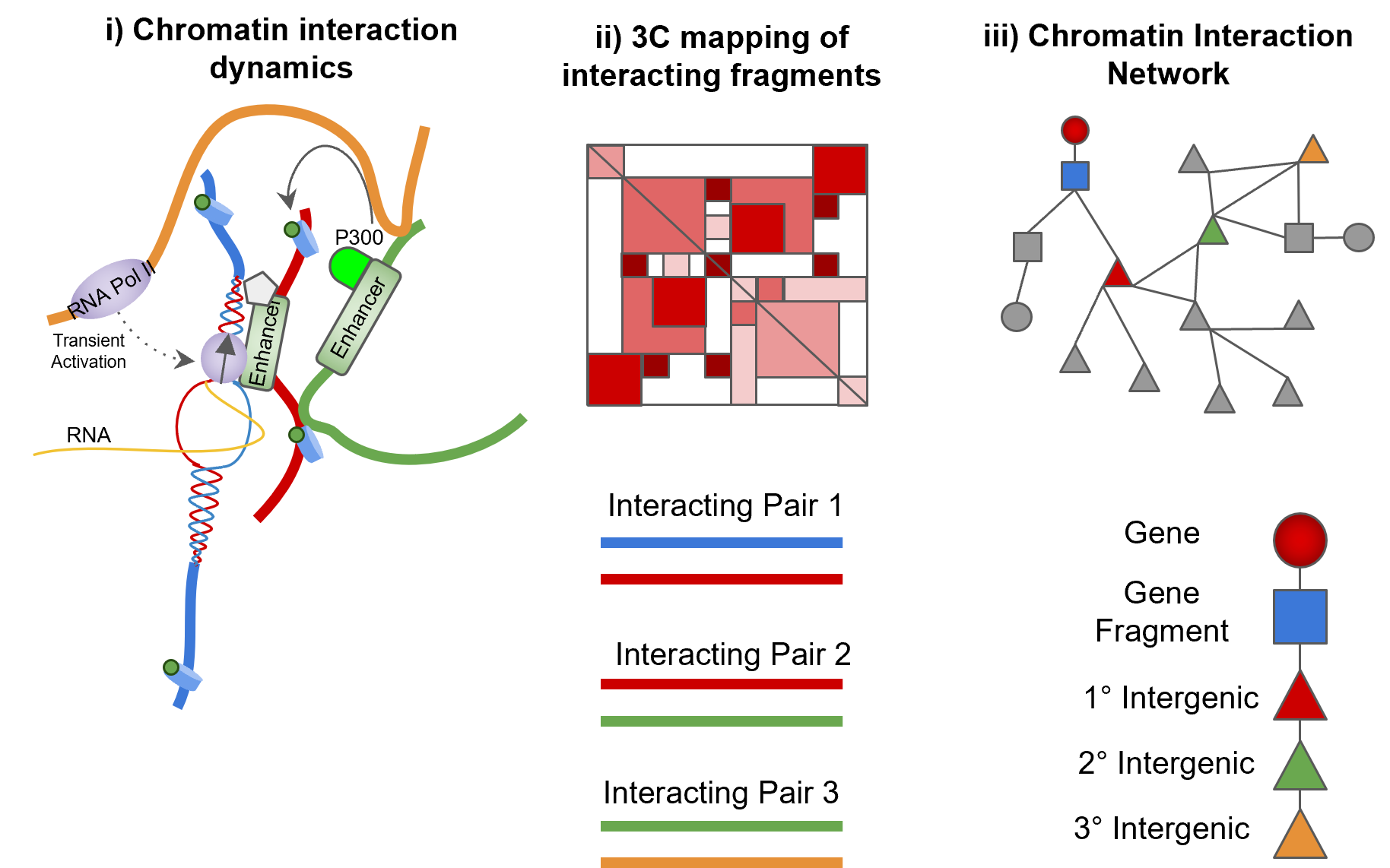
Signals pertaining to transcriptional activation are transferred from enhancers found in intergenic loci to genes in the form of transcription factors, cofactors, and various transcriptional machinery such as RNA Pol II. How and where this information is transmitted to and from is central for decoding the regulatory landscape of any gene and identifying enhancers. Esearch3D is an unsupervised algorithm designed to predict enhancer regions from 3C data. It works by reverse engineering the flow of regulatory information from enhancers to genes. Using this approach we were able to identify intergenic regulatory enhancers using solely gene expression and 3D genomic data.
Esearch3D models chromosome conformation capture (3C) data as chromatin interaction network (CIN) and then exploits graph-theory algorithms to integrate RNA-seq data to calculate an imputed activity score (IAS) for intergenic regions. We also provide a visualisation tool to allow an easy interpretation of the results.
- It uses the expression levels of genes and a chromatin interaction network to impute the activity score of enhancers represented as nodes
- It reverse engineers the flow of regulatory information modeled by enhancers that act to increase the rate of transcription of their target genes
- It leverages the relationship between the 3D organisation of chromatin and global gene expression
- It represents a novel enhancer associated feature that can be used to predict enhancers
- It provides a graphical user interface to interact with the network composed by genes, enhancers and intergenic loci associated to their imputed activity score
- It includes a parallelised version of a network-based algorithm called random walk with restart that works on sparse matrices to reduce the system usage
Maninder Heer*, Luca Giudice*, Claudia Mengoni, Rosalba Giugno^, Daniel Rico^, Esearch3D: propagating gene expression in chromatin networks to illuminate active enhancers, Nucleic Acids Research, 2023;, gkad229, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad229
*equal contribution ^co-senior authors
Esearch3D is available on R, you can install it with:
install.packages("devtools")
install.packages("htmltools", version="0.5.2", type="source")
devtools::install_github(
repo="InfOmics/Esearch3D",
ref = "main",
dependencies = "Depends",
upgrade = "always",
quiet = T
# type = "binary" # usable only in Windows OS
)The following vignettes are available:
- Vignette for IAS score computation on mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) DNaseI capture Hi-C dataset
- Vignette for IAS score computation and enhancer classification on mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) DNaseI capture Hi-C dataset
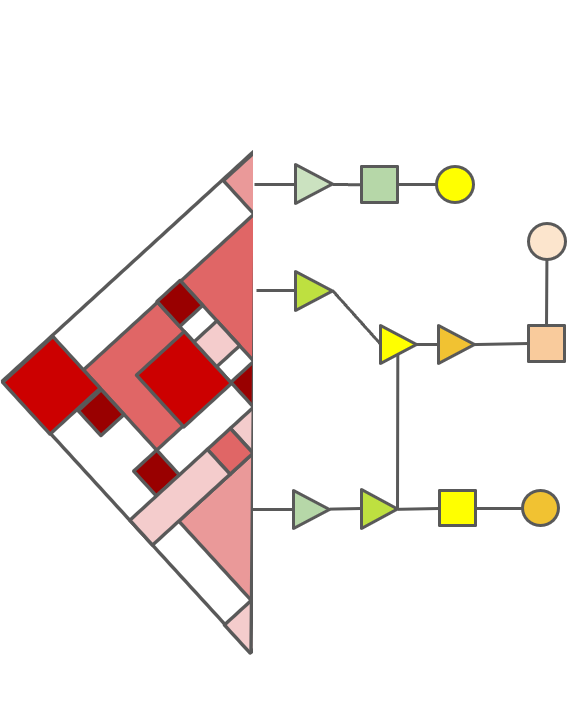
- Enhancers are localised to genes in 3D space and can influence the regulation of promoters directly and indirectly.
- 3C can capture chromatin interactions but only in a pairwise manner.
- Representation of chromatin fragments as nodes in a network and their interactions as edges preserves the global structure of interacting chromatin.
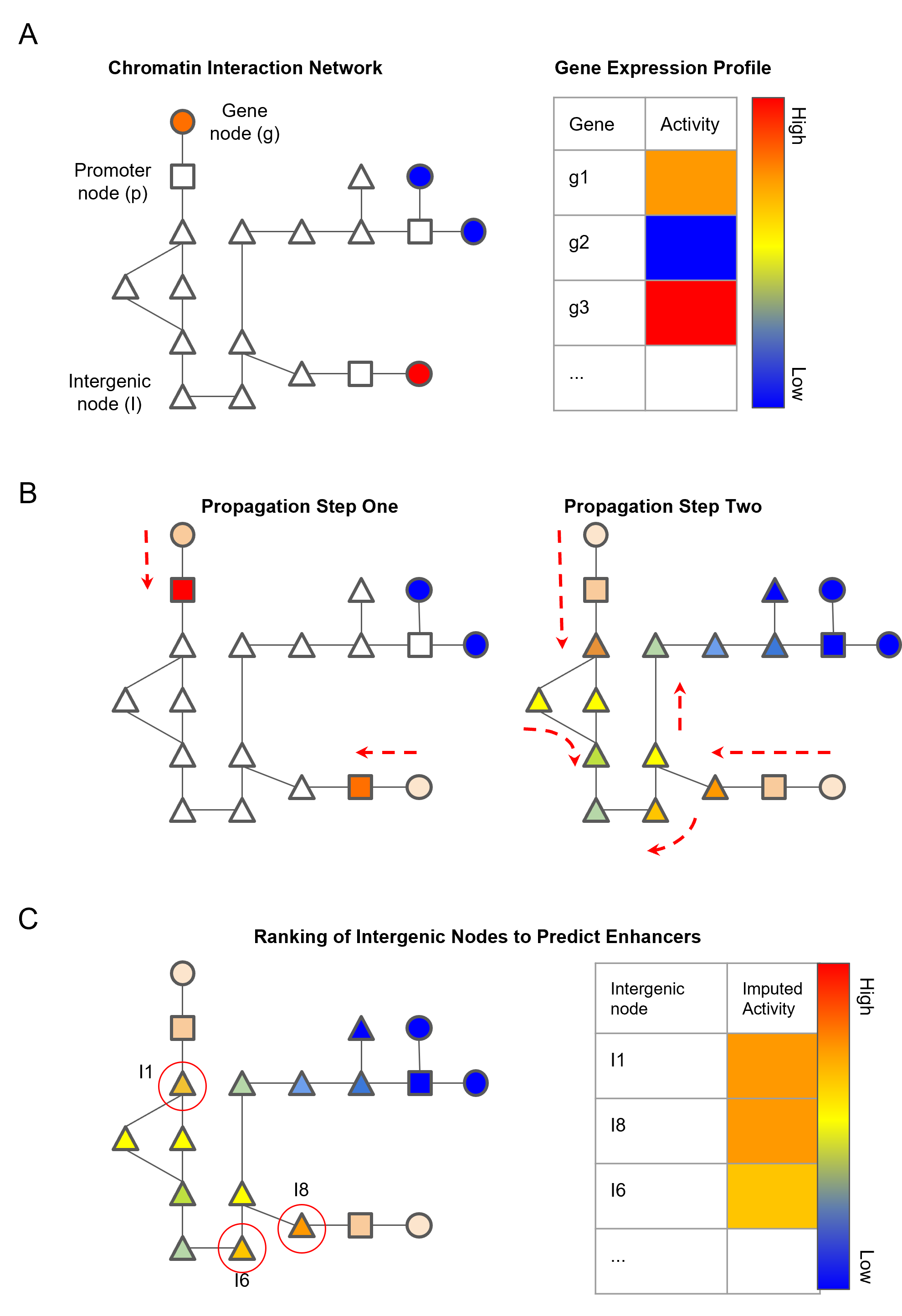
Schematic diagram of the network propagation used to impute activity values at intergenic nodes:
- A. Genes are mapped to nodes representing genic chromatin fragments. Each gene has an associated gene activity value determined by RNA-seq data.
- B. Gene activity is propagated from gene nodes to genic chromatin nodes in propagation step one. Activity scores are then imputed in intergenic chromatin nodes by propagating the scores from genic chromatin nodes.
- C. Ranking of non-genic nodes by the imputed activity score to identify high confidence enhancer nodes.
It takes just a few lines of code to run ESearch3D with the sample data provided:
library(Esearch3D)
#Load and set up the example data ----
data("wg_data_l")
#1) A two column dataframe representing the gene - fragment interaction network
gf_net = wg_data_ll$gf_net
#2) A two column dataframe representing the fragment-fragment interaction network
ff_net = wg_data_l$ff_net
#3) A matrix containing the starting values of the nodes (gene node scores are given by the RNA-seq values while fragments have a starting value of 0)
input_m = wg_data_l$input_m
#4) A list of genes to annotate to the chromatin fragments
ann_net_b=wg_data_l$ann_net_b
#Two step propagation -----
#Propagation over the gene-fragment network
gf_prop = rwr_OVprop(g=gf_net,
input_m = input_m,
no_cores = 2,
r = 0.1)
#Propagation over the gene-fragment-fragment network
ff_prop=rwr_OVprop(g=ff_net,
input_m = gf_prop,
no_cores = 2,
r = 0.8)
#Create an annotated igraph object
net=create_net2plot(gf_net,
input_m,
gf_prop,
ann_net_b,
frag_pattern = "frag",
ff_net,
ff_prop)
#Start the GUI
start_GUI(net, ann_net_b)The GUI allows the user to explore the network following the network-based propagation of gene expression from genic nodes to intergenic nodes. The user can investigate the imputed activity scores (IAS) and their 3D-genetic neighborhood. The visualised network can be downloaded and further analysed in Cytoscape.
- Select a node ID and the desired distance from a selected node: Allows to visualise the neighbourhood of a node of interest
- Scale colours: Allows the user to scale the colors of the visualised nodes to the selected neighbourhood
- Select by propagation ranges: Only show the nodes with a value that falls between a specific range
- Download html file: Allows the user to download the network as an html file the network created with the GUI
- Download GML file: Allows the user to download the network and its features as a GML file that can be opened in Cytoscape.
The following image shows you an example of how to interact with the GUI and its functionalities