UpDown Meter graphs network activity for a specific network adapter. It is deliberately designed to consume trace memory and processor time, so it can run as long as the system runs, providing an overview of how the connection is being used.
When UpDown Meter is first run we see a prompt to choose a network adapter.
To select an adapter, open the settings menu by clicking the button in the lower-right of the toolbox ( ) or choose the settings option from the tray icon menu. Once an adapter has been selected and confirmed by clicking the [OK] or [Apply] buttons, the graph updates to show a scrolling image that updates once per second, as shown below.
) or choose the settings option from the tray icon menu. Once an adapter has been selected and confirmed by clicking the [OK] or [Apply] buttons, the graph updates to show a scrolling image that updates once per second, as shown below.
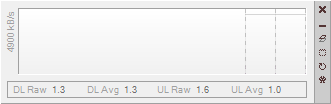
Each block divided by a dashed vertical line represents a unit of 30 seconds, so this graph is showing the last 61 seconds of network activity. Since the graph appears empty, either there is no activity or our graph is calibrated incorrectly. Once the graph has been calibrated it might look something like the following.
The graph scrolls from right to left, so the newest information is displayed on the right. Red indicates downloaded data whilst green represents uploaded data. Yellow represents uploaded or downloaded data, depending on which is lesser at that point in time—it sounds weird but it's actually quite visually intuitive!
Reading from the left, the graph above shows we started downloading data at full speed for about 80 seconds. Then, we stopped downloading and uploaded data at full speed for about 60 seconds (our upload capacity is approximately a quarter of our download capacity). Next, we started downloading at full speed whilst simultaneously continuing our upload for two minutes. During this period, we observe that our connection is unable to reach maximum download speed whilst also uploading at full speed. This is fairly normal because the data upload chokes our ACK packets, restricting the ability to pump download packets simultaneously as efficiently. This is confirmed by the last 30 seconds where we stop our upload and see the download return to full speed again.
The scale of the graph is shown in kilobytes per second on the left of the graph. This can be changed by modifying the actual speed value in network settings. By default the actual speed is the same as the reported speed, which is the theoretical maximum speed reported by the adapter's device driver, but is usually much higher than the actual speed of a typical internet connection so we must calibrate it to a more realistic value.
To calibrate the speed of an internet connection we must apply full load to the connection to test its capacity. The easiest way to do this is visit a benchmarking site such as [Speedtest.net](http://www.speedtest.net). After performing the test, return to the *actual speed* setting and modify the value until the upload or download bar (whichever is taller) just touches the horizontal bar across the top of the graph, as shown on the right.Remember: clicking the [Apply] button allows us to apply our new settings without closing the settings window, allowing us to prototype different settings quickly. This is the easiest way to calibrate the graph until an automatic calibration feature is added.
The animated tray icon shows constantly updated meters of the current network usage whilst the connection is active. When the connection is dormant, the application logo is displayed instead. The meters use the same scale as the main graph.
If using a version of windows that usually hides tray icons it is recommended to reconfigure this icon to be always shown for at-a-glance monitoring.
When moving the graph towards the edge of any screen, it automatically snaps to the edges to make it easier to position at the sides of the screen.
When always-on-top mode is enabled, the graph is always displayed above all other windows whilst it is visible. The graph can still be minimized.
The graph can be toggled between opaque and semi-transparent states.
See the latest release to download the Windows installer (.exe), compiled binaries (.zip) or source code. It is recommended to use the installer. The installer ensures all requirements are met, downloading and installing any missing dependencies, and automatically overwrites any previously installed version.
UpDown Meter requires .NET Framework 4.5.1, which ships with Windows 8.1 and later, but can be installed on earlier versions of Windows. The installer will automatically install .NET Framework if needed.
Everyone is welcome to contribute anything, from ideas to issues to graphics to documentation to code!
Compiling the code is as easy as cloning the source in Visual Studio and clicking start. In older versions of Visual Studio, it may be necessary to manually restore NuGet packages after cloning.