Framework to easily generate complex synthetic data pipelines by visualizing and configuring the pipeline as a
computational graph. LangGraph is used as the underlying graph
configuration/execution library. Refer
to LangGraph examples to get a sense of the different
kinds of computational graph which can be configured.
SyGra Framework is created to generate synthetic data. As it is a complex process to define the flow, this design simplifies the synthetic data generation process. SyGra platform will support the following:
- Defining the seed data configuration
- Define a task, which involves graph node configuration, flow between nodes and conditions between the node
- Define the output location to dump the generated data
Seed data can be pulled from either Huggingface or file system. Once the seed data is loaded, SyGra platform allows datagen users to write any data processing using the data transformation module. When the data is ready, users can define the data flow with various types of nodes. A node can also be a subgraph defined in another yaml file.
Each node can be defined with preprocessing, post processing, and LLM prompt with model parameters. Prompts can use seed data as python template keys.
Edges define the flow between nodes, which can be conditional or non-conditional, with support for parallel and one-to-many flows.
At the end, generated data is collected in the graph state for a specific record, processed further to generate the final dictionary to be written to the configured data sink.
Pick how you want to use SyGra:
-
Framework → Run end-to-end pipelines from YAML graphs + CLI tooling and project scaffolding. (Start here:
Installation) -
Library → Import SyGra in your own Python app/notebook; call APIs directly. (Start here:
SyGra Library)
TL;DR – Framework Setup
See full steps in Installation.
git clone git@github.com:ServiceNow/SyGra.git
cd SyGra
poetry run python main.py --task examples.glaive_code_assistant --num_records=1TL;DR – Library Setup
See full steps in Sygra Library.
pip install sygra import sygra
workflow = sygra.Workflow("tasks/examples/glaive_code_assistant")
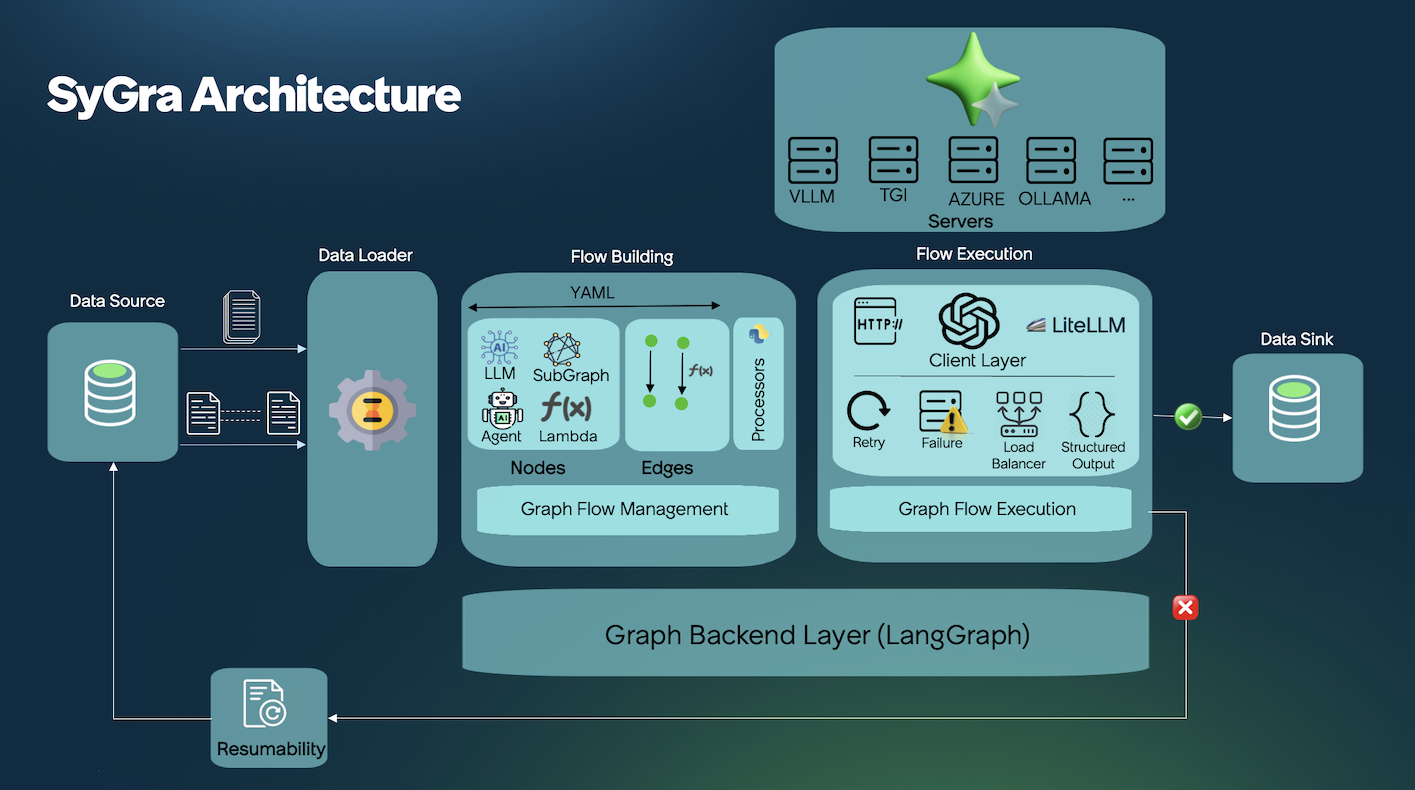
workflow.run(num_records=1)The SyGra architecture is composed of multiple components. The following diagrams illustrate the four primary components and their associated modules.
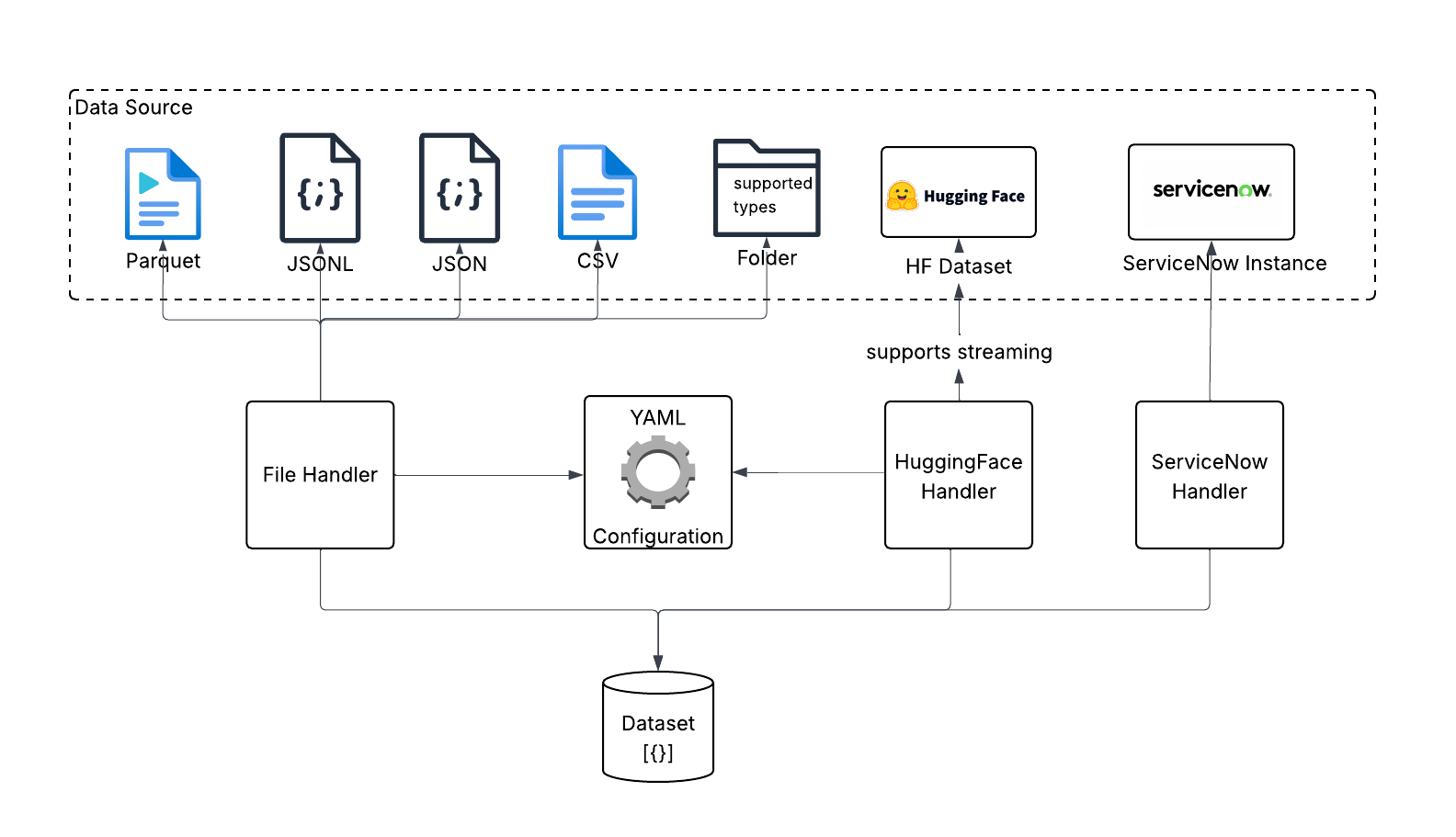
Data handler is used for reading and writing the data. Currently, it supports file handler with various file types and huggingface handler. When reading data from huggingface, it can read the whole dataset and process, or it can stream chunk of data.
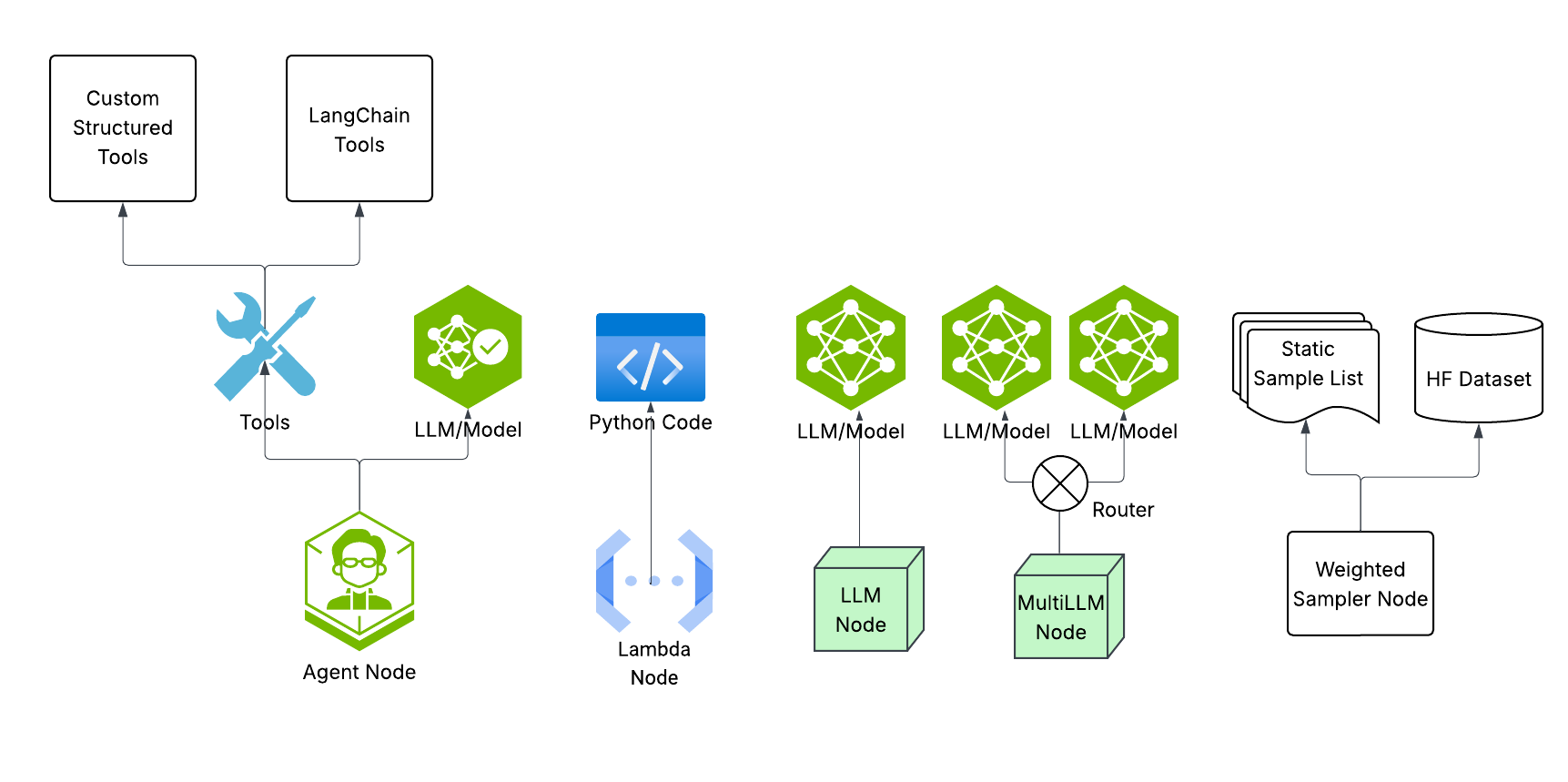
This module is responsible for building various kind of nodes like LLM node, Multi-LLM node, Lambda node, Agent node etc. Each node is defined for various task, for example multi-llm node is used to load-balance the data among various inference point running same model.
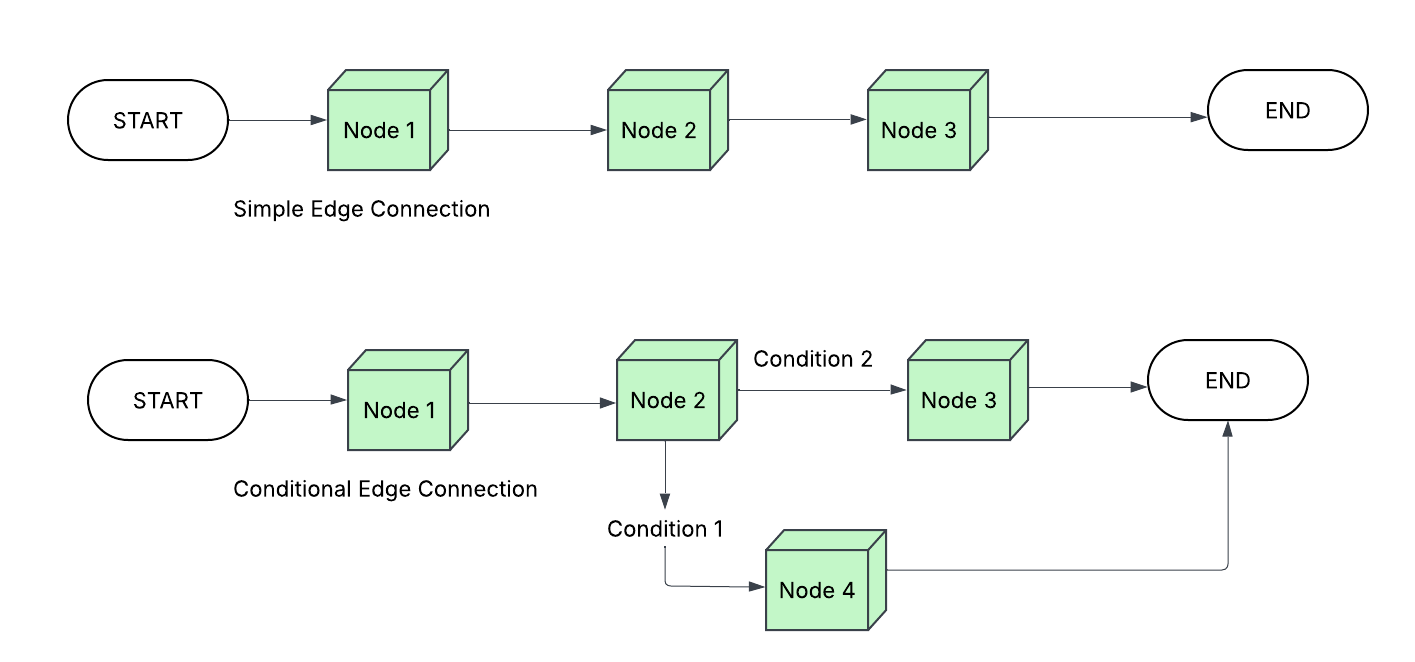
Once node are built, we can connect them with simple edge or conditional edge. Conditional edge uses python code to decide the path. Conditional edge helps implimenting if-else flow as well as loops in the graph.
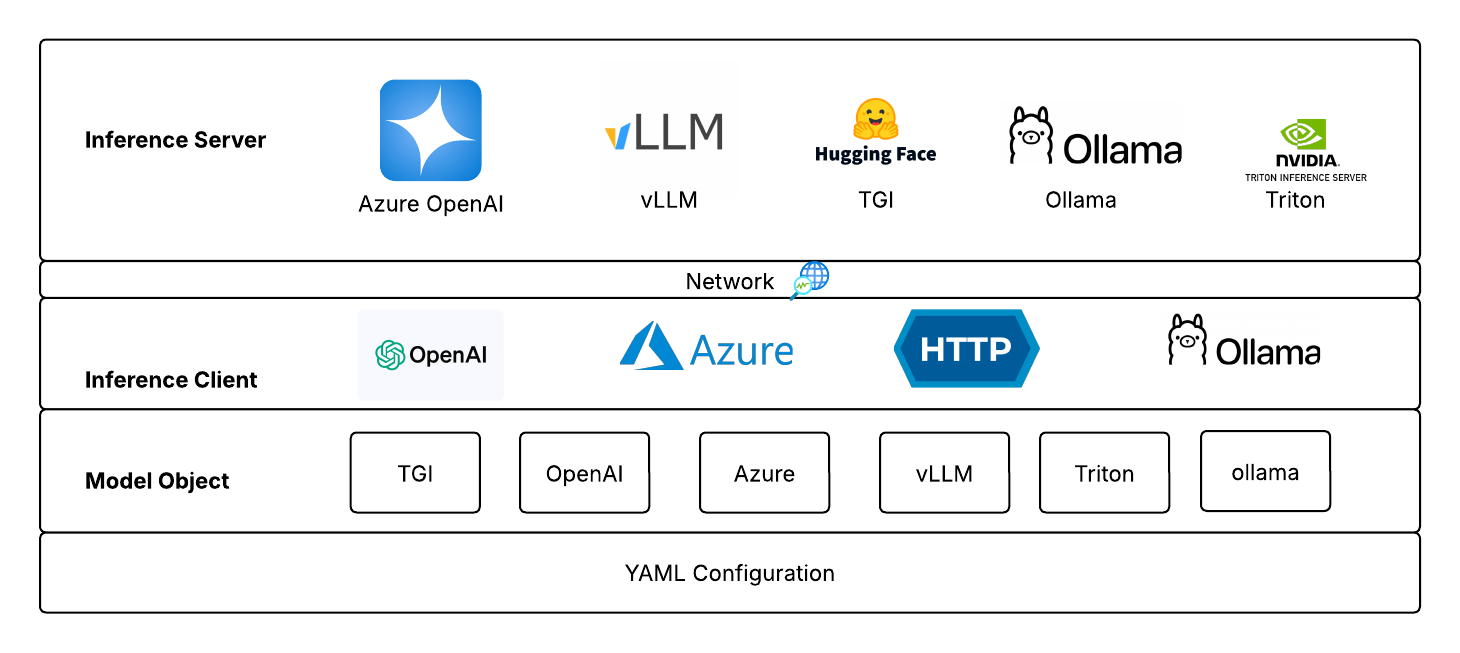
SyGra doesn't support inference within the framework, but it supports various clients, which helps connecting with different kind of servers. For example, openai client is being supported by Huggingface TGI, vLLM server and Azure services. However, model configuration does not allow to change clients, but it can be configured in models code.
SyGra supports extendability and ease of implementation—most tasks are defined as graph configuration YAML files. Each task consists of two major components: a graph configuration and Python code to define conditions and processors. YAML contains various parts:
- Data configuration : Configure file or huggingface as source and sink for the task.
- Data transformation : Configuration to transform the data into the format it can be used in the graph.
- Node configuration : Configure nodes and corresponding properties, preprocessor and post processor.
- Edge configuration : Connect the nodes configured above with or without conditions.
- Output configuration : Configuration for data tranformation before writing the data into sink.
A node is defined by the node module, supporting types like LLM call, multiple LLM call, lambda node, and sampler node.
LLM-based nodes require a model configured in models.yaml and runtime parameters. Sampler nodes pick random samples from static YAML lists. For custom node types, you can implement new nodes in the platform.
As of now, LLM inference is supported for TGI, vLLM, Azure, Azure OpenAI, Ollama and Triton compatible servers. Model deployment is external and configured in models.yaml.
To contact us, please send us an email!
The package is licensed by ServiceNow, Inc. under the Apache 2.0 license. See LICENSE for more details.
Questions?
Open an issue or start a discussion! Contributions are welcome.