Active recall planner download
This app is supported by me, for any advice please contact me on twitter.
The recall method is the method of training your brain to retrieve informations from your memory in the most efficient way.
Active recall is the idea to force your brain to recall some piece of information effictevely. More often the brain is forced to recall something during the time, stronger it will be the link to that piece of information. In a certain way it can be compared to what backpropagation is in deep-learning. Therefore, writing down questions and answering them later on force your brain to remember them.
Use Cornell Notes Method of Taking Notes and create many questions, then in revision answer those questions.
Save questions from the book and slides and answer them.
All previous methods can be used to create cards to answer them.
- howtostudy
- How my friend ranked 1st at Medical School - The Active Recall Framework
- Overview how to study Cambridge style
- Study with Me + Active Recall tips | Life as a Junior Doctor
- How I Study at Cambridge University | ACTIVE RECALL
- How I Study For Exams in Medical School Active Recall Study Strategies
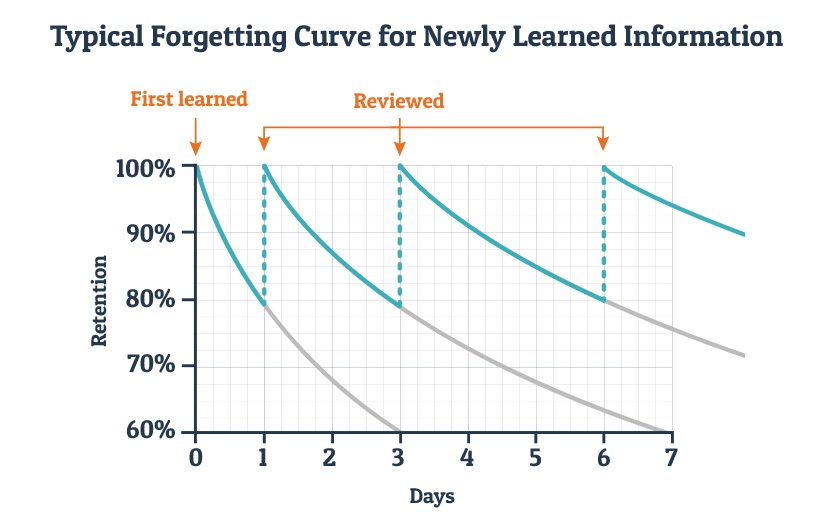
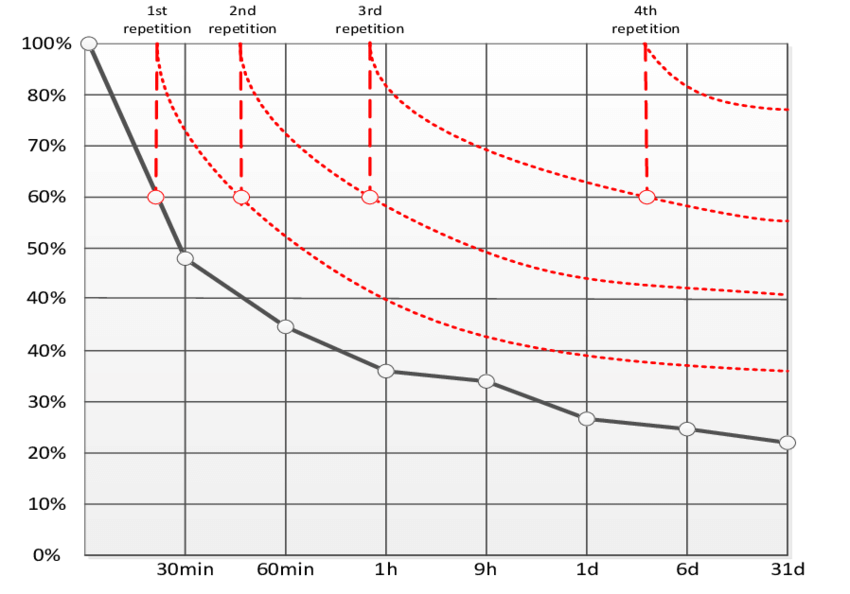
The rate of forgetting is minimised if students interact (re-read/discuss/write/engage) with their notes within 24 hours. A second repetition for a shorter period of time within a day brings recall back up to 100%. A third repetition within a week for an even shorter time brings recall back to 100%.
- Space repetition is the idea that spacing your active recall sessions your brain will implant that memories in the long-term memory side of your brain. A simple way to do it is to give two or three days distance between each topic and then try to answer again to the same questions you answered on day one.
- Longer delay between initial learning and recalling facts was associated with poorer retention rate.
- In a final test 1 week later, the group that learned at expanding time intervals performed significantly better than the group learning with steady intervals
- The Most Powerful Way to Remember What You Study
- How to Study for Exams - Spaced Repetition | Evidence-based revision tips
- My Study Method + Revision Tools - Cambridge junior doctor
- How To Revise | Scientifically Proven Revision Techniques (for English, History, Law and more)
- Cornell Note Taking System
- How better note taking can improve your memory
- Cornell Notes Method of Taking Notes
- How To Make Notes From Lectures - Active Recall
- The Essay Memorisation Framework
- The Cornell Note-taking System(questions+bullet points answers)
- Write questions rather than notes
- The Best Digital Note Taking Tablet for Students? | The reMarkable Review
- whats-the-most-effective-way-to-take-notes
-
scoping the subject/topic: syllabus -> slides -> book chapters
- this should not take more than 1 hour if done the same day or even better if you do it the day before the starting of the study cycle.
- writing down all words and topic that you do not know the meaning
- writing down questions about the subject on a piece of paper Cornell style link 1, link 2
- usually at the end of the chapters there are a set of questions
- check for questions in the slides
- for each topic of the syllabus you should at the least know to desribe to someone that does not know anything about the subject "what is". Feynman Technique
-
Active recall sourcesource 2, source 3
- for each word write down nodes of everything associated with that you remember about
- answer the questions in bullet point on the right side of your notebook (Cornell Notes Method of Taking Notes).
-
space repetition source
-
create a spreadhsheet: topic, date repetition 1, date repetition 2, ...
- use colors to determine which topic is easier and which is worst
-
This sequence is for 1 block == 1 slide of study.(study block b1=50m), (block-revision b1r=30m), (block-exercises b1e=50m)
- First day
- [b1] -> [Break 15 min] -> [b1r] -> [Break 30 m] -> [b1e] -> [Break 1 h 30m] -> [b1r]
- ------------------- Recall it the next evening ------------------
- [b1r] -> [Break 15 min] -> [b1e] -> [Break 45 m] -> [explain each topic to "people"]
- ------------------- Skip 1 day ----------------------------------
- [b1r] -> [Break 15 min] -> [b1e] -> [Break 45 m] -> [explain each topic to "people"]
- ------------------- Skip 2 days ---------------------------------
- [b1r] -> [Break 15 min] -> [b1e] -> [Break 45 m] -> [explain each topic to "people"]
- ------------------- Skip 22 days --------------------------------
- [b1r] -> [Break 15 min] -> [b1e] -> [Break 45 m] -> [explain each topic to "people"]
- First day
-
at the end of each new evening spend 10 minute thinking about what you learned that day.
-
-
revision
- start from the last chapter and move backwards
- write down on a paper or excel file each topic you are not familiar with
- 3 LIES Students Believe (That Hold Them Back)
- Why Advice is Holding You Back
- PERSONALITY-based Study Tips | Tools for Better Grades
- Study Techniques - The Good, Bad, & Useless
- YOU'RE STUDYING WRONG - Here's Why
- How to Stay Focused While Studying | Medical School Secrets
- Procrastination – 7 Steps to Cure
- How to Study Effectively and Efficiency as a Pre-Med and Medical Student
- Stop Procrastinating and Be Productive - How to Study When You Don't Want To
- Pre-Med Study Strategies - What I Wish I Knew in College (Tips from Medical School)
- POMODORO TECHNIQUE - My Favorite Tool to Improve Studying and Productivity
- Finals Week! - 6 Study Tips & Tricks
- Learn Anything in Four Steps With the Feynman Technique
- 1939-spitzer
- Retrieval Practice Produces More Learning than Elaborative Studying with Concept Mapping
- Science Brief - A powerful way to improve learning and memory
- Improving Students' Learning With Effective Learning Techniques: Promising Directions From Cognitive and Educational Psychology.
- Make-Stick-Science-Successful-Learning
- Effective Study Techniques
- THE JOURNAL OFEDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY VolumeXXXDecember, 1939 Number 9 STUDIES IN RETENTION
- Improving Students' Learning With Effective Learning Techniques: Promising Directions From Cognitive and Educational Psychology.
- A powerful way to improve learning and memory
- Test-Enhanced LearningTaking Memory Tests Improves Long-Term Retention
- Test-Enhanced Learning in the Classroom:Long-Term Improvements From Quizzing
- The Value of Applied Research: Retrieval Practice Improves Classroom Learning and Recommendations from a Teacher, a Principal, and a Scientist
- podcast 385 make stick
- The Super Mario Effect - Tricking Your Brain into Learning More | Mark Rober | TEDxPenn