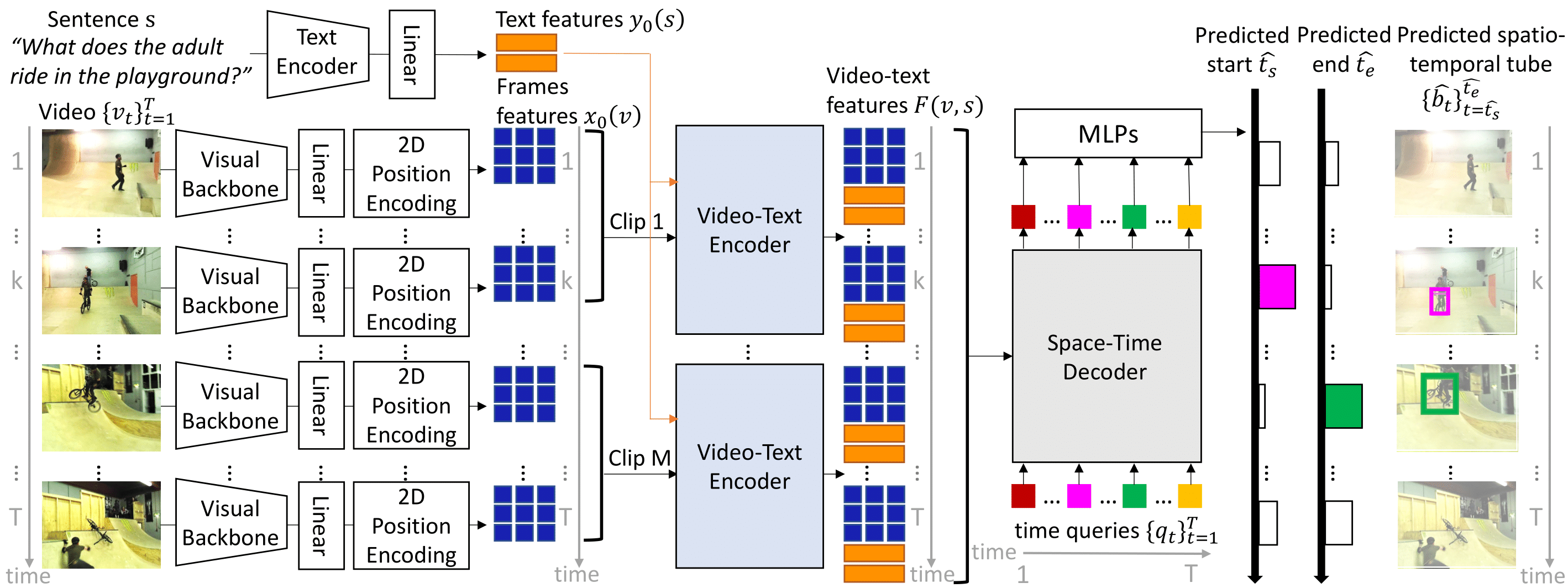
This repository provides the code for our paper. This includes:
- Software setup, data downloading and preprocessing instructions for the VidSTG, HC-STVG1 and HC-STVG2.0 datasets
- Training scripts and pretrained checkpoints
- Evaluation scripts and demo
Download FFMPEG and add it to the PATH environment variable.
The code was tested with version ffmpeg-4.2.2-amd64-static.
Then create a conda environment and install the requirements with the following commands:
conda create -n tubedetr_env python=3.8
conda activate tubedetr_env
pip install -r requirements.txt
Setup the paths where you are going to download videos and annotations in the config json files.
VidSTG: Download VidOR videos and annotations from the VidOR dataset providers.
Then download the VidSTG annotations from the VidSTG dataset providers.
The vidstg_vid_path folder should contain a folder video containing the unzipped video folders.
The vidstg_ann_path folder should contain both VidOR and VidSTG annotations.
HC-STVG: Download HC-STVG1 and HC-STVG2.0 videos and annotations from the HC-STVG dataset providers.
The hcstvg_vid_path folder should contain a folder video containing the unzipped video folders.
The hcstvg_ann_path folder should contain both HC-STVG1 and HC-STVG2.0 annotations.
To preprocess annotation files, run:
python preproc/preproc_vidstg.py
python preproc/preproc_hcstvg.py
python preproc/preproc_hcstvgv2.py
Download pretrained RoBERTa tokenizer and model weights in the TRANSFORMERS_CACHE folder.
Download pretrained ResNet-101 model weights in the TORCH_HOME folder.
Download MDETR pretrained model weights with ResNet-101 backbone in the current folder.
VidSTG To train on VidSTG, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=NUM_GPUS --use_env main.py --ema \
--load=pretrained_resnet101_checkpoint.pth --combine_datasets=vidstg --combine_datasets_val=vidstg \
--dataset_config config/vidstg.json --output-dir=OUTPUT_DIR
HC-STVG2.0 To train on HC-STVG2.0, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=NUM_GPUS --use_env main.py --ema \
--load=pretrained_resnet101_checkpoint.pth --combine_datasets=hcstvg --combine_datasets_val=hcstvg \
--v2 --dataset_config config/hcstvg.json --epochs=20 --output-dir=OUTPUT_DIR
HC-STVG1 To train on HC-STVG1, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=NUM_GPUS --use_env main.py --ema \
--load=pretrained_resnet101_checkpoint.pth --combine_datasets=hcstvg --combine_datasets_val=hcstvg \
--dataset_config config/hcstvg.json --epochs=40 --eval_skip=40 --output-dir=OUTPUT_DIR
Baselines
- To remove time encoding, add
--no_time_embed. - To remove the temporal self-attention in the space-time decoder, add
--no_tsa. - To train from ImageNet initialization, pass an empty string to the argument
--loadand add--sted_loss_coef=5 --lr=2e-5 --text_encoder_lr=2e-5 --epochs=20 --lr_drop=20for VidSTG or--epochs=70 --lr_drop=70 --text_encoder_lr=1e-5for HC-STVG1. - To train with a randomly initalized temporal self-attention, add
--rd_init_tsa. - To train with a different spatial resolution (e.g. res=352) or temporal stride (e.g. k=4), add
--resolution=224or--stride=5. - To train with the slow-only variant, add
--no_fast. - To train with alternative designs for the fast branch, add
--fast=VARIANT.
| Training data | parameters | url | VidSTG test declarative sentences (vIoU/vIoU@0.3/vIoU@0.5) | VidSTG test interrogative sentences (vIoU/vIoU@0.3/vIoU@0.5) | HC-STVG1 test (vIoU/vIoU@0.3/vIoU@0.5) | HC-STVG2.0 val (vIoU/vIoU@0.3/vIoU@0.5) | size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDETR init + VidSTG | k=4 res=352 | Drive | 30.4/42.5/28.2 | 25.7/35.7/23.2 | 3.0GB | ||
| MDETR init + VidSTG | k=2 res=224 | Drive | 29.0/40.4/78.3 | 24.6/33.6/21.6 | 3.0GB | ||
| ImageNet init + VidSTG | k=4 res=352 | Drive | 22.0/29.7/18.1 | 19.6/26.1/14.9 | 3.0GB | ||
| MDETR init + HC-STVG2.0 | k=4 res=352 | Drive | 36.4/58.8/30.6 | 3.0GB | |||
| MDETR init + HC-STVG2.0 | k=2 res=224 | Drive | 35.8/56.7/29.6 | 3.0GB | |||
| MDETR init + HC-STVG1 | k=4 res=352 | Drive | 32.4/49.8/23.5 | 3.0GB | |||
| ImageNet init + HC-STVG1 | k=4 res=352 | Drive | 21.2/31.6/12.2 | 3.0GB |
For evaluation only, simply run the same commands as for training with --resume=CHECKPOINT --eval.
For this to be done on the test set, add --test (in this case predictions and attention weights are also saved).
You can also use a pretrained model to infer a spatio-temporal tube on a video of your choice (VIDEO_PATH with potential START and END timestamps) given the natural language query of your choice (CAPTION) with the following command:
python demo_stvg.py --load=CHECKPOINT --caption_example CAPTION --video_example VIDEO_PATH --start_example=START --end_example=END --output-dir OUTPUT_PATH
Note that we also host an online demo at this link, the code of which is available at server_stvg.py and server_stvg.html.
This codebase is built on the MDETR codebase. The code for video spatial data augmentation is inspired by torch_videovision.
If you found this work useful, consider giving this repository a star and citing our paper as followed:
@inproceedings{yang2022tubedetr,
author = {Antoine Yang and Antoine Miech and Josef Sivic and Ivan Laptev and Cordelia Schmid},
title = {TubeDETR: Spatio-Temporal Video Grounding With Transformers},
booktitle = {CVPR},
year = {2022}}


