As of the release of brainreg version 1.0.0, brainreg-napari is now a part of brainreg.
If you are looking to install the brainglobe-napari plugin, please install brainreg with it's optional napari dependency as detailed in the installation instructions on the website or repository.
Before you update, you should also remove the old brainreg-napari package from your environment using either
python -m pip uninstall brainreg-napari # If you installed via pip
conda remove brainreg-napari # If you installed via condaYou can find the old documentation and installation instructions below, but please note this version of the package should be considered unmaintained.
Napari plugin to run brainreg, developed by Stephen Lenzi.
pip install brainreg-napariDocumentation and tutorials for the plugin can be found here.
For segmentation of bulk structures in 3D space (e.g. injection sites, Neuropixels probes), please see brainreg-segment.
This software is at a very early stage, and was written with our data in mind. Over time we hope to support other data types/formats. If you have any issues, please get in touch on the forum or by raising an issue.
brainreg is an update to amap (itself a port of the original Java software) to include multiple registration backends, and to support the many atlases provided by bg-atlasapi.
The aim of brainreg is to register the template brain (e.g. from the Allen Reference Atlas) to the sample image. Once this is complete, any other image in the template space can be aligned with the sample (such as region annotations, for segmentation of the sample image). The template to sample transformation can also be inverted, allowing sample images to be aligned in a common coordinate space.
To do this, the template and sample images are filtered, and then registered in a three step process (reorientation, affine registration, and freeform registration.) The resulting transform from template to standard space is then applied to the atlas.
Full details of the process are in the
original aMAP paper.
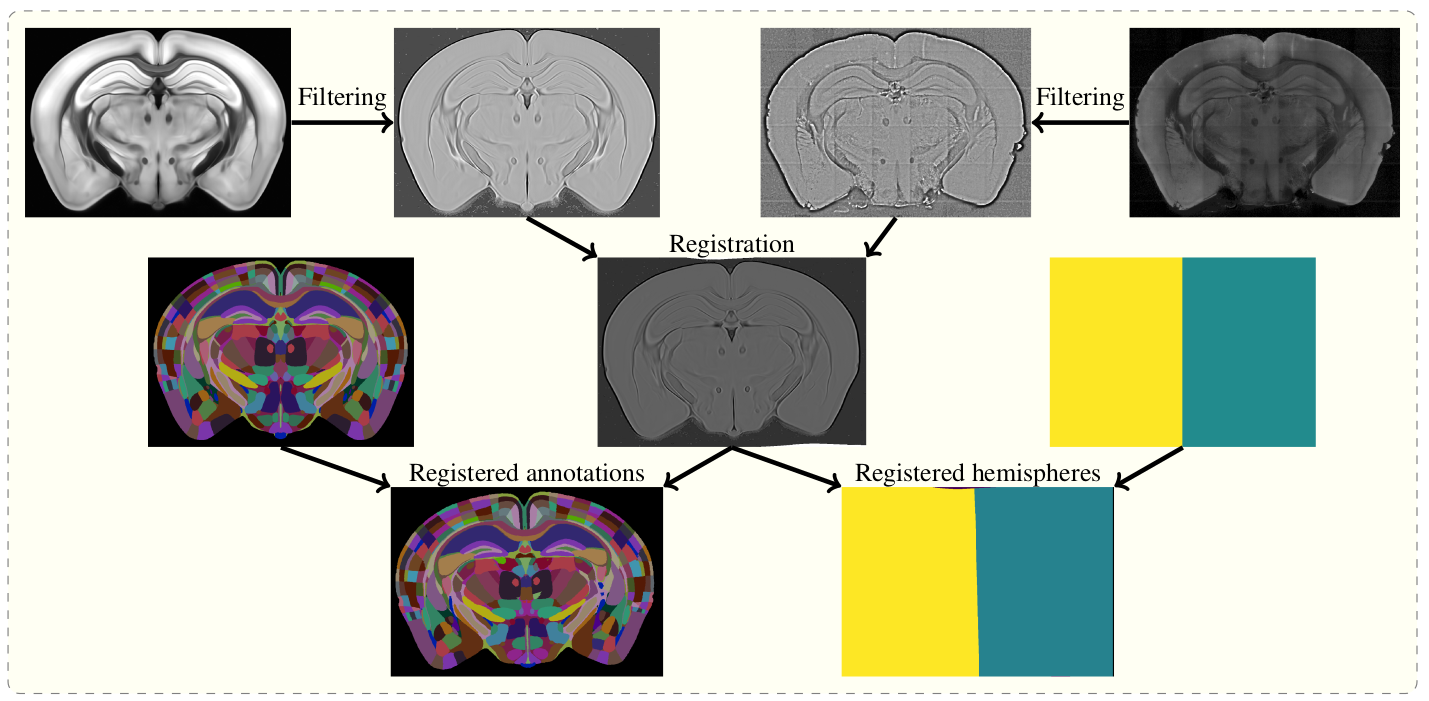 Overview of the registration process
Overview of the registration process
Contributions to brainreg-napari are more than welcome. Please see the developers guide.
If you find brainreg useful, and use it in your research, please let us know and also cite the paper:
Tyson, A. L., Vélez-Fort, M., Rousseau, C. V., Cossell, L., Tsitoura, C., Lenzi, S. C., Obenhaus, H. A., Claudi, F., Branco, T., Margrie, T. W. (2022). Accurate determination of marker location within whole-brain microscopy images. Scientific Reports, 12, 867 doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04676-9
Please also cite aMAP (the original pipeline from which this software is based):
Niedworok, C.J., Brown, A.P.Y., Jorge Cardoso, M., Osten, P., Ourselin, S., Modat, M. and Margrie, T.W., (2016). AMAP is a validated pipeline for registration and segmentation of high-resolution mouse brain data. Nature Communications. 7, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11879
Lastly, if you can, please cite the BrainGlobe Atlas API that provided the atlas:
Claudi, F., Petrucco, L., Tyson, A. L., Branco, T., Margrie, T. W. and Portugues, R. (2020). BrainGlobe Atlas API: a common interface for neuroanatomical atlases. Journal of Open Source Software, 5(54), 2668, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02668
Don't forget to cite the developers of the atlas that you used (e.g. the Allen Brain Atlas)!




