- Commands
- How To Pass Options / Switches
- Scripting / Integration - Best Practices / Style Guide
- See Help Menu In Action
- Default Options and Switches
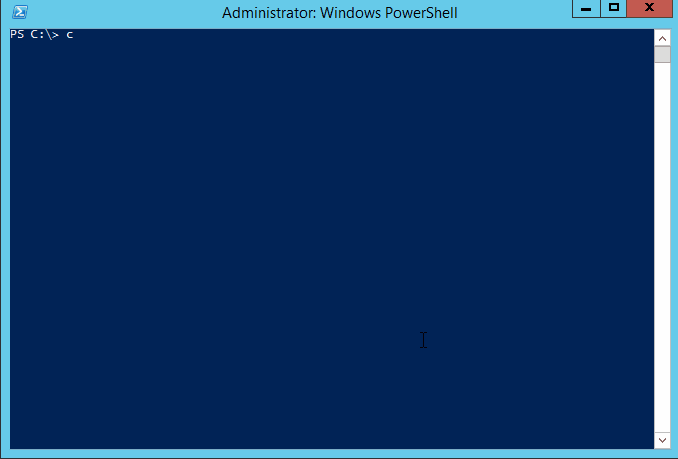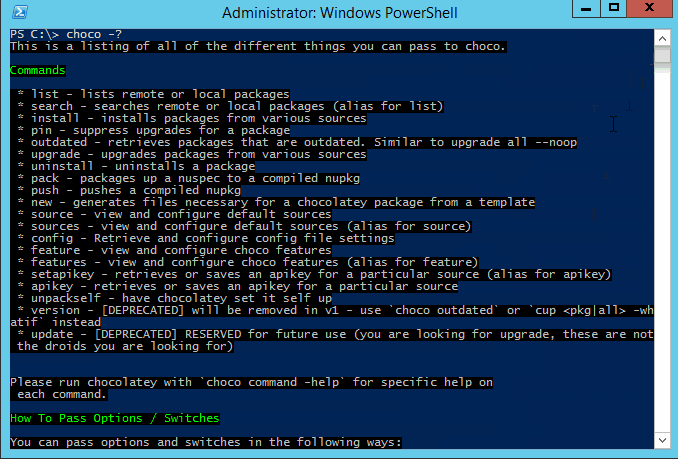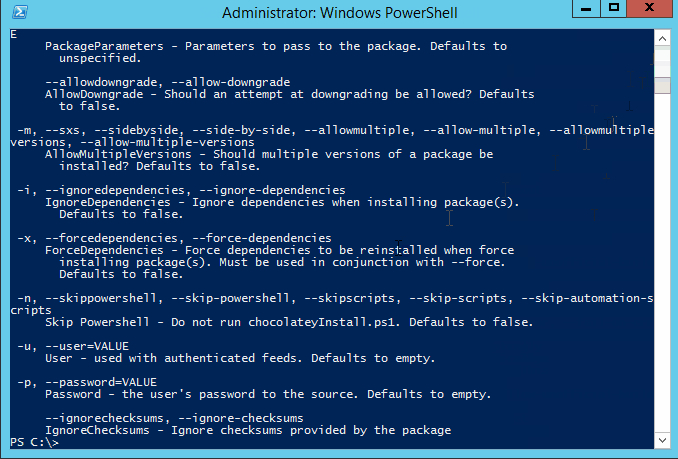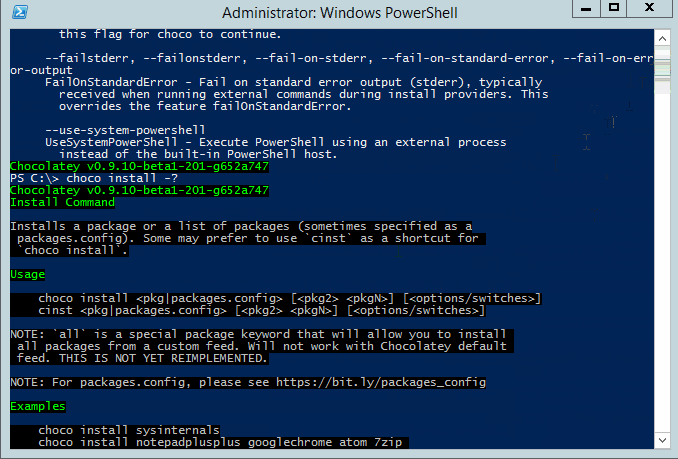
This is a listing of all of the different things you can pass to choco.
- [[list|CommandsList]] - lists remote or local packages
- [[search|CommandsSearch]] - searches remote or local packages (alias for list)
- [[info|CommandsInfo]] - retrieves package information. Shorthand for choco search pkgname --exact --verbose
- [[install|CommandsInstall]] - installs packages from various sources
- [[pin|CommandsPin]] - suppress upgrades for a package
- [[outdated|CommandsOutdated]] - retrieves packages that are outdated. Similar to upgrade all --noop
- [[upgrade|CommandsUpgrade]] - upgrades packages from various sources
- [[uninstall|CommandsUninstall]] - uninstalls a package
- [[pack|CommandsPack]] - packages up a nuspec to a compiled nupkg
- [[push|CommandsPush]] - pushes a compiled nupkg
- [[new|CommandsNew]] - generates files necessary for a chocolatey package from a template
- [[sources|CommandsSources]] - view and configure default sources (alias for source)
- [[source|CommandsSource]] - view and configure default sources
- [[config|CommandsConfig]] - Retrieve and configure config file settings
- [[feature|CommandsFeature]] - view and configure choco features
- [[features|CommandsFeatures]] - view and configure choco features (alias for feature)
- [[setapikey|CommandsSetapikey]] - retrieves or saves an apikey for a particular source (alias for apikey)
- [[apikey|CommandsApikey]] - retrieves or saves an apikey for a particular source
- [[unpackself|CommandsUnpackself]] - have chocolatey set itself up
- [[version|CommandsVersion]] - [DEPRECATED] will be removed in v1 - use [[
choco outdated|Commandsoutdated]] orcup <pkg|all> -whatifinstead - [[update|CommandsUpdate]] - [DEPRECATED] RESERVED for future use (you are looking for upgrade, these are not the droids you are looking for)
- [[support|CommandsSupport]] - provides support information
- [[download|CommandsDownload]] - downloads packages - optionally internalizing all remote resources
- [[synchronize|CommandsSynchronize]] - synchronizes against system installed software - generates missing packages
- [[sync|CommandsSync]] - synchronizes against system installed software - generates missing packages
- [[optimize|CommandsOptimize]] - optimizes installation, reducing space usage
Please run chocolatey with choco command -help for specific help on
each command.
You can pass options and switches in the following ways:
- Unless stated otherwise, an option/switch should only be passed one time. Otherwise you may find weird/non-supported behavior.
-,/, or--(one character switches should not use--)- Option Bundling / Bundled Options: One character switches can be
bundled. e.g.
-d(debug),-f(force),-v(verbose), and-y(confirm yes) can be bundled as-dfvy. - NOTE: If
debugorverboseare bundled with local options (not the global ones above), some logging may not show up until after the local options are parsed. - Use Equals: You can also include or not include an equals sign
=between options and values. - Quote Values: When you need to quote an entire argument, such as
when using spaces, please use a combination of double quotes and
apostrophes (
"'value'"). In cmd.exe you can just use double quotes ("value") but in powershell.exe you should use backticks (`"value`") or apostrophes ('value'). Using the combination allows for both shells to work without issue, except for when the next section applies. - Pass quotes in arguments: When you need to pass quoted values to
to something like a native installer, you are in for a world of fun. In
cmd.exe you must pass it like this:
-ia "/yo=""Spaces spaces""". In PowerShell.exe, you must pass it like this:-ia '/yo=""Spaces spaces""'. No other combination will work. In PowerShell.exe if you are on version v3+, you can try--%before-iato just pass the args through as is, which means it should not require any special workarounds. - Periods in PowerShell: If you need to pass a period as part of a value or a path, PowerShell doesn't always handle it well. Please quote those values using "Quote Values" section above.
- Options and switches apply to all items passed, so if you are
installing multiple packages, and you use
--version=1.0.0, choco is going to look for and try to install version 1.0.0 of every package passed. So please split out multiple package calls when wanting to pass specific options.
When writing scripts, such as PowerShell scripts passing options and switches, there are some best practices to follow to ensure that you don't run into issues later. This also applies to integrations that are calling Chocolatey and parsing output. Chocolatey uses PowerShell, but it is an exe, so it cannot return PowerShell objects.
Following these practices ensures both readability of your scripts AND compatibility across different versions and editions of Chocolatey. Following this guide will ensure your experience is not frustrating based on choco not receiving things you think you are passing to it.
- For consistency, always use
choco, notchoco.exe. Never use shortcut commands likecinstorcup. - Always have the command as the first argument to
choco. e.g. [[choco install|Commandsinstall]], where [[install|Commandsinstall]] is the command. - If there is a subcommand, ensure that is the second argument. e.g.
choco source list, wheresourceis the command and [[list|Commandslist]] is the subcommand. - Typically the subject comes next. If installing packages, the
subject would be the package names, e.g.
choco install pkg1 pkg2. - Never use 'nupkg' or point directly to a nupkg file UNLESS using
'choco push'. Use the source folder instead, e.g.
choco install <package id> --source="'c:\folder\with\package'"instead ofchoco install DoNotDoThis.1.0.nupkgorchoco install DoNotDoThis --source="'c:\folder\with\package\DoNotDoThis.1.0.nupkg'". - Switches and parameters are called simply options. Options come
after the subject. e.g.
choco install pkg1 --debug --verbose. - Never use the force option (
--force/-f) in scripts (or really otherwise as a default mode of use). Force is an override on Chocolatey behavior. If you are wondering why Chocolatey isn't doing something like the documentation says it should, it's likely because you are using force. Stop. - Always use full option name. If the short option is
-n, and the full option is--name, use--name. The only acceptable short option for use in scripts is-y. Find option names in help docs online or throughchoco -?/choco [Command Name] -?. - For scripts that are running automated, always use
-y. Do note that even with-ypassed, some things / state issues detected will temporarily stop for input - the key here is temporarily. They will continue without requiring any action after the temporary timeout (typically 30 seconds). - Full option names are prepended with two dashes, e.g.
--or--debug --verbose --ignore-proxy. - When setting a value to an option, always put an equals (
=) between the name and the setting, e.g.--source="'local'". - When setting a value to an option, always surround the value
properly with double quotes bookending apostrophes, e.g.
--source="'internal_server'". - If you are building PowerShell scripts, you can most likely just
simply use apostrophes surrounding option values, e.g.
--source='internal_server'. - Prefer upgrade to install in scripts. You can't [[
install|Commandsinstall]] to a newer version of something, but you can [[choco upgrade|Commandsupgrade]] which will do both upgrade or install (unless switched off explicitly). - If you are sharing the script with others, pass
--sourceto be explicit about where the package is coming from. Use full link and not source name ('https://chocolatey.org/api/v2' versus 'chocolatey'). - If parsing output, you might want to use
--limit-output/-rto get output in a more machine parseable format. NOTE: Not all commands handle return of information in an easily digestible output. - Use exit codes to determine status. Chocolatey exits with 0 when
everything worked appropriately and other exits codes like 1 when
things error. There are package specific exit codes that are
recommended to be used and reboot indicating exit codes as well. To
check exit code when using PowerShell, immediately call
$exitCode = $LASTEXITCODEto get the value choco exited with.
Here's an example following bad practices (line breaks added for readability):
choco install pkg1 -y -params '/Option:Value /Option2:value with spaces' --c4b-option 'Yaass' --option-that-is-new 'dude upgrade'
Now here is that example written with best practices (again line breaks added for readability - there are not line continuations for choco):
choco upgrade pkg1 -y --source="'https://chocolatey.org/api/v2'" --package-parameters="'/Option:Value /Option2:value with spaces'" --c4b-option="'Yaass'" --option-that-is-new="'dude upgrade'"
Note the differences between the two:
- Which is more self-documenting?
- Which will allow for the newest version of something installed or upgraded to (which allows for more environmental consistency on packages and versions)?
- Which may throw an error on a badly passed option?
- Which will throw errors on unknown option values? See explanation below.
Chocolatey ignores options it doesn't understand, but it can only
ignore option values if they are tied to the option with an
equals sign ('='). Note those last two options in the examples above?
If you roll off of a commercial edition or someone with older version
attempts to run the badly crafted script --c4b-option 'Yaass' --option-that-is-new 'dude upgrade', they are likely to see errors on
'Yaass' and 'dude upgrade' because they are not explicitly tied to the
option they are written after. Now compare that to the other script.
Choco will ignore --c4b-option="'Yaass'" and
--option-that-is-new="'dude upgrade'" as a whole when it doesn't
register the options. This means that your script doesn't error.
Following these scripting best practices will ensure your scripts work everywhere they are used and with newer versions of Chocolatey.
NOTE: Options and switches apply to all items passed, so if you are
running a command like install that allows installing multiple
packages, and you use --version=1.0.0, it is going to look for and
try to install version 1.0.0 of every package passed. So please split
out multiple package calls when wanting to pass specific options.
-?, --help, -h
Prints out the help menu.
-d, --debug
Debug - Show debug messaging.
-v, --verbose
Verbose - Show verbose messaging. Very verbose messaging, avoid using
under normal circumstances.
--trace
Trace - Show trace messaging. Very, very verbose trace messaging. Avoid
except when needing super low-level .NET Framework debugging. Available
in 0.10.4+.
--nocolor, --no-color
No Color - Do not show colorization in logging output. This overrides
the feature 'logWithoutColor', set to 'False'. Available in 0.10.9+.
--acceptlicense, --accept-license
AcceptLicense - Accept license dialogs automatically. Reserved for
future use.
-y, --yes, --confirm
Confirm all prompts - Chooses affirmative answer instead of prompting.
Implies --accept-license
-f, --force
Force - force the behavior. Do not use force during normal operation -
it subverts some of the smart behavior for commands.
--noop, --whatif, --what-if
NoOp / WhatIf - Don't actually do anything.
-r, --limitoutput, --limit-output
LimitOutput - Limit the output to essential information
--timeout, --execution-timeout=VALUE
CommandExecutionTimeout (in seconds) - The time to allow a command to
finish before timing out. Overrides the default execution timeout in the
configuration of 2700 seconds. '0' for infinite starting in 0.10.4.
-c, --cache, --cachelocation, --cache-location=VALUE
CacheLocation - Location for download cache, defaults to %TEMP% or value
in chocolatey.config file.
--allowunofficial, --allow-unofficial, --allowunofficialbuild, --allow-unofficial-build
AllowUnofficialBuild - When not using the official build you must set
this flag for choco to continue.
--failstderr, --failonstderr, --fail-on-stderr, --fail-on-standard-error, --fail-on-error-output
FailOnStandardError - Fail on standard error output (stderr), typically
received when running external commands during install providers. This
overrides the feature failOnStandardError.
--use-system-powershell
UseSystemPowerShell - Execute PowerShell using an external process
instead of the built-in PowerShell host. Should only be used when
internal host is failing. Available in 0.9.10+.
--no-progress
Do Not Show Progress - Do not show download progress percentages.
Available in 0.10.4+.
--proxy=VALUE
Proxy Location - Explicit proxy location. Overrides the default proxy
location of ''. Available for config settings in 0.9.9.9+, this CLI
option available in 0.10.4+.
--proxy-user=VALUE
Proxy User Name - Explicit proxy user (optional). Requires explicity
proxy (`--proxy` or config setting). Overrides the default proxy user of
'123'. Available for config settings in 0.9.9.9+, this CLI option
available in 0.10.4+.
--proxy-password=VALUE
Proxy Password - Explicit proxy password (optional) to be used with
username. Requires explicity proxy (`--proxy` or config setting) and
user name. Overrides the default proxy password (encrypted in settings
if set). Available for config settings in 0.9.9.9+, this CLI option
available in 0.10.4+.
--proxy-bypass-list=VALUE
ProxyBypassList - Comma separated list of regex locations to bypass on
proxy. Requires explicity proxy (`--proxy` or config setting). Overrides
the default proxy bypass list of ''. Available in 0.10.4+.
--proxy-bypass-on-local
Proxy Bypass On Local - Bypass proxy for local connections. Requires
explicity proxy (`--proxy` or config setting). Overrides the default
proxy bypass on local setting of 'True'. Available in 0.10.4+.
--log-file=VALUE
Log File to output to in addition to regular loggers. Available in 0.1-
0.8+.
NOTE: This documentation has been automatically generated from choco -h.