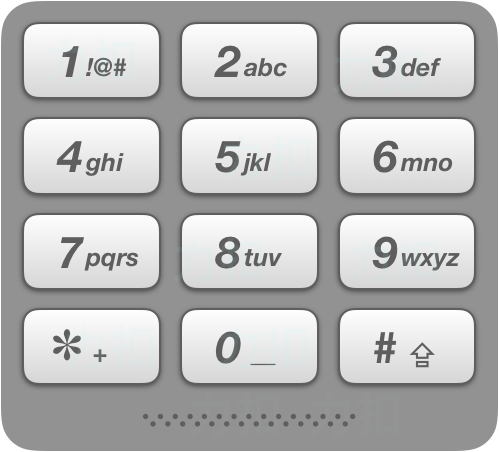
在老式手机上,用户通过数字键盘输入,手机将提供与这些数字相匹配的单词列表。每个数字映射到0至4个字母。给定一个数字序列,实现一个算法来返回匹配单词的列表。你会得到一张含有有效单词的列表。映射如下图所示:
示例 1:
输入: num = "8733", words = ["tree", "used"] 输出: ["tree", "used"]
示例 2:
输入: num = "2", words = ["a", "b", "c", "d"] 输出: ["a", "b", "c"]
提示:
num.length <= 1000words.length <= 500words[i].length == num.lengthnum中不会出现 0, 1 这两个数字
我们考虑一种正向的解法,遍历字符串
我们不妨考虑逆向的解法,遍历给定的单词列表,对于每个单词
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def getValidT9Words(self, num: str, words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
def check(w: str) -> bool:
return all(d[c] == num[i] for i, c in enumerate(w))
d = {c: d for c, d in zip(ascii_lowercase, "22233344455566677778889999")}
return [w for w in words if check(w)]class Solution {
public List<String> getValidT9Words(String num, String[] words) {
String s = "22233344455566677778889999";
int[] d = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
d[i] = s.charAt(i);
}
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int n = num.length();
for (String w : words) {
boolean ok = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[w.charAt(i) - 'a'] != num.charAt(i)) {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
ans.add(w);
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<string> getValidT9Words(string num, vector<string>& words) {
string s = "22233344455566677778889999";
int d[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
d[i] = s[i];
}
vector<string> ans;
int n = num.size();
for (auto& w : words) {
bool ok = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[w[i] - 'a'] != num[i]) {
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
ans.emplace_back(w);
}
}
return ans;
}
};func getValidT9Words(num string, words []string) (ans []string) {
s := "22233344455566677778889999"
d := [26]rune{}
for i, c := range s {
d[i] = c
}
for _, w := range words {
ok := true
for i, c := range w {
if d[c-'a'] != rune(num[i]) {
ok = false
break
}
}
if ok {
ans = append(ans, w)
}
}
return
}function getValidT9Words(num: string, words: string[]): string[] {
const s = '22233344455566677778889999';
const d: string[] = Array(26);
for (let i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
d[i] = s[i];
}
const ans: string[] = [];
const n = num.length;
for (const w of words) {
let ok = true;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[w[i].charCodeAt(0) - 97] !== num[i]) {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
ans.push(w);
}
}
return ans;
}class Solution:
def getValidT9Words(self, num: str, words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
trans = str.maketrans(ascii_lowercase, "22233344455566677778889999")
return [w for w in words if w.translate(trans) == num]