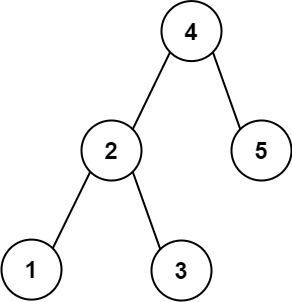
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个目标值 target ,请在该二叉搜索树中找到最接近目标值 target 的数值。如果有多个答案,返回最小的那个。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,5,1,3], target = 3.714286 输出:4
示例 2:
输入:root = [1], target = 4.428571 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 104]内 0 <= Node.val <= 109-109 <= target <= 109
我们用一个变量
接下来,进行中序遍历,每次计算当前节点与目标值
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: float) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
dfs(root.left)
nonlocal ans, mi
t = abs(root.val - target)
if t < mi:
mi = t
ans = root.val
dfs(root.right)
ans, mi = root.val, inf
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans;
private double target;
private double mi = Double.MAX_VALUE;
public int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
this.target = target;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
double t = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (t < mi) {
mi = t;
ans = root.val;
}
dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int closestValue(TreeNode* root, double target) {
int ans = root->val;
double mi = INT_MAX;
function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root->left);
double t = abs(root->val - target);
if (t < mi) {
mi = t;
ans = root->val;
}
dfs(root->right);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func closestValue(root *TreeNode, target float64) int {
ans := root.Val
mi := math.MaxFloat64
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Left)
t := math.Abs(float64(root.Val) - target)
if t < mi {
mi = t
ans = root.Val
}
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} target
* @return {number}
*/
var closestValue = function (root, target) {
let mi = Infinity;
let ans = root.val;
const dfs = root => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
const t = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (t < mi) {
mi = t;
ans = root.val;
}
dfs(root.right);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
};与方法一类似,我们用一个变量
接下来,进行二分查找,每次计算当前节点与目标值
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: float) -> int:
ans, mi = root.val, inf
while root:
t = abs(root.val - target)
if t < mi or (t == mi and root.val < ans):
mi = t
ans = root.val
if root.val > target:
root = root.left
else:
root = root.right
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
int ans = root.val;
double mi = Double.MAX_VALUE;
while (root != null) {
double t = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (t < mi || (t == mi && root.val < ans)) {
mi = t;
ans = root.val;
}
if (root.val > target) {
root = root.left;
} else {
root = root.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int closestValue(TreeNode* root, double target) {
int ans = root->val;
double mi = INT_MAX;
while (root) {
double t = abs(root->val - target);
if (t < mi || (t == mi && root->val < ans)) {
mi = t;
ans = root->val;
}
if (root->val > target) {
root = root->left;
} else {
root = root->right;
}
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func closestValue(root *TreeNode, target float64) int {
ans := root.Val
mi := math.MaxFloat64
for root != nil {
t := math.Abs(float64(root.Val) - target)
if t < mi || (t == mi && root.Val < ans) {
mi = t
ans = root.Val
}
if float64(root.Val) > target {
root = root.Left
} else {
root = root.Right
}
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} target
* @return {number}
*/
var closestValue = function (root, target) {
let ans = root.val;
let mi = Number.MAX_VALUE;
while (root) {
const t = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (t < mi || (t === mi && root.val < ans)) {
mi = t;
ans = root.val;
}
if (root.val > target) {
root = root.left;
} else {
root = root.right;
}
}
return ans;
};