给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
- 结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
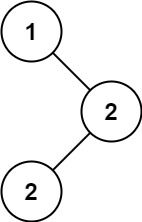
输入:root = [1,null,2,2] 输出:[2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
nonlocal mx, prev, ans, cnt
dfs(root.left)
cnt = cnt + 1 if prev == root.val else 1
if cnt > mx:
ans = [root.val]
mx = cnt
elif cnt == mx:
ans.append(root.val)
prev = root.val
dfs(root.right)
prev = None
mx = cnt = 0
ans = []
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int mx;
private int cnt;
private TreeNode prev;
private List<Integer> res;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root);
int[] ans = new int[res.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i) {
ans[i] = res.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
cnt = prev != null && prev.val == root.val ? cnt + 1 : 1;
if (cnt > mx) {
res = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(root.val));
mx = cnt;
} else if (cnt == mx) {
res.add(root.val);
}
prev = root;
dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* prev;
int mx, cnt;
vector<int> ans;
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
dfs(root->left);
cnt = prev != nullptr && prev->val == root->val ? cnt + 1 : 1;
if (cnt > mx) {
ans.clear();
ans.push_back(root->val);
mx = cnt;
} else if (cnt == mx)
ans.push_back(root->val);
prev = root;
dfs(root->right);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findMode(root *TreeNode) []int {
mx, cnt := 0, 0
var prev *TreeNode
var ans []int
var dfs func(root *TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Left)
if prev != nil && prev.Val == root.Val {
cnt++
} else {
cnt = 1
}
if cnt > mx {
ans = []int{root.Val}
mx = cnt
} else if cnt == mx {
ans = append(ans, root.Val)
}
prev = root
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}public class Solution {
private int mx;
private int cnt;
private TreeNode prev;
private List<int> res;
public int[] FindMode(TreeNode root) {
res = new List<int>();
Dfs(root);
int[] ans = new int[res.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < res.Count; ++i) {
ans[i] = res[i];
}
return ans;
}
private void Dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Dfs(root.left);
cnt = prev != null && prev.val == root.val ? cnt + 1 : 1;
if (cnt > mx) {
res = new List<int>(new int[] { root.val });
mx = cnt;
} else if (cnt == mx) {
res.Add(root.val);
}
prev = root;
Dfs(root.right);
}
}