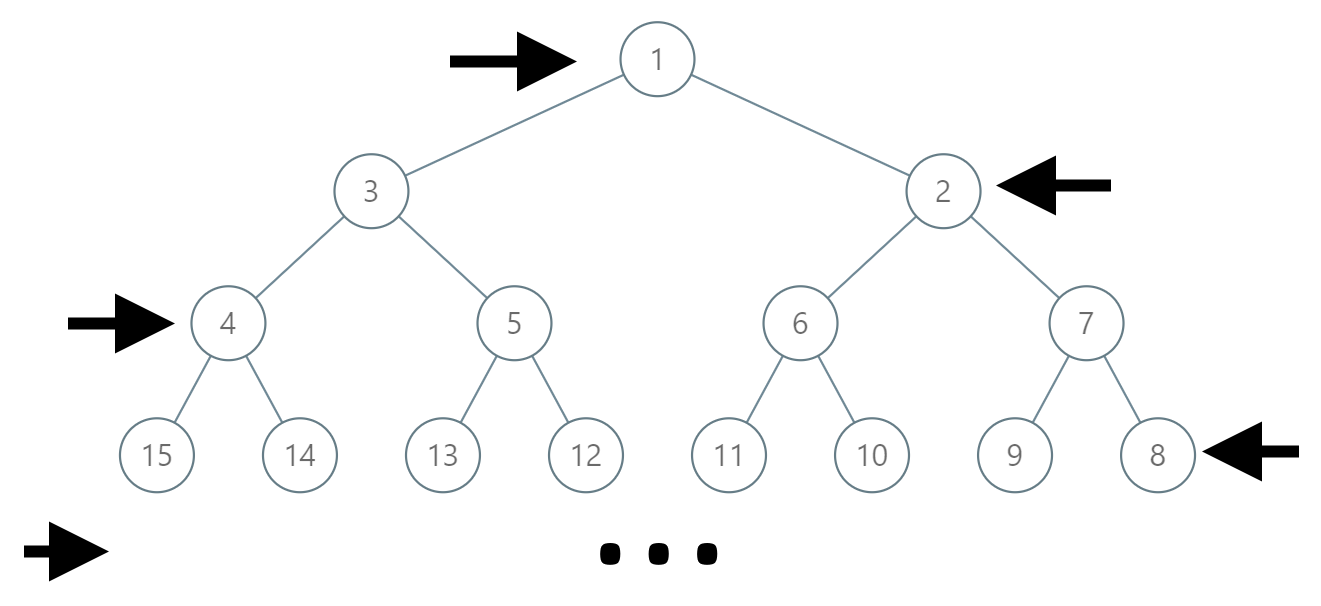
In an infinite binary tree where every node has two children, the nodes are labelled in row order.
In the odd numbered rows (ie., the first, third, fifth,...), the labelling is left to right, while in the even numbered rows (second, fourth, sixth,...), the labelling is right to left.
Given the label of a node in this tree, return the labels in the path from the root of the tree to the node with that label.
Example 1:
Input: label = 14 Output: [1,3,4,14]
Example 2:
Input: label = 26 Output: [1,2,6,10,26]
Constraints:
1 <= label <= 10^6
For a complete binary tree, the number of nodes in the $i$th row is
Finally, we need to reverse the path, because the problem requires the path from the root node to node
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def pathInZigZagTree(self, label: int) -> List[int]:
x = i = 1
while (x << 1) <= label:
x <<= 1
i += 1
ans = [0] * i
while i:
ans[i - 1] = label
label = ((1 << (i - 1)) + (1 << i) - 1 - label) >> 1
i -= 1
return ansclass Solution {
public List<Integer> pathInZigZagTree(int label) {
int x = 1, i = 1;
while ((x << 1) <= label) {
x <<= 1;
++i;
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (; i > 0; --i) {
ans.add(label);
label = ((1 << (i - 1)) + (1 << i) - 1 - label) >> 1;
}
Collections.reverse(ans);
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> pathInZigZagTree(int label) {
int x = 1, i = 1;
while ((x << 1) <= label) {
x <<= 1;
++i;
}
vector<int> ans;
for (; i > 0; --i) {
ans.push_back(label);
label = ((1 << (i - 1)) + (1 << i) - 1 - label) >> 1;
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;
}
};func pathInZigZagTree(label int) (ans []int) {
x, i := 1, 1
for x<<1 <= label {
x <<= 1
i++
}
for ; i > 0; i-- {
ans = append(ans, label)
label = ((1 << (i - 1)) + (1 << i) - 1 - label) >> 1
}
for i, j := 0, len(ans)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
ans[i], ans[j] = ans[j], ans[i]
}
return
}