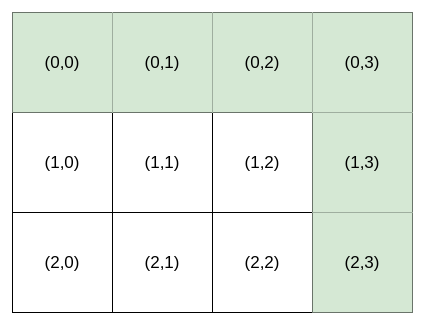
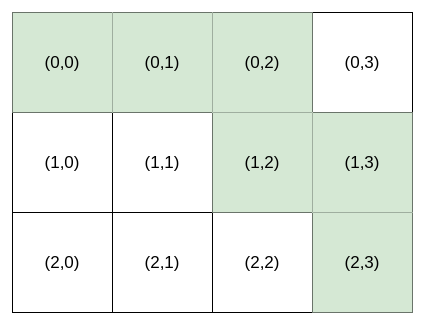
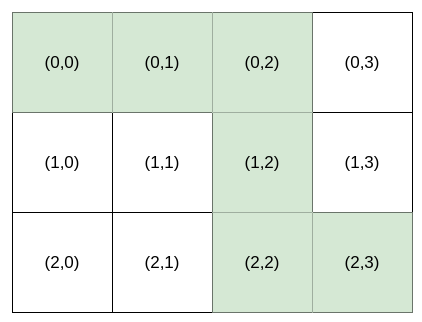
Bob 站在单元格 (0, 0) ,想要前往目的地 destination :(row, column) 。他只能向 右 或向 下 走。你可以为 Bob 提供导航 指令 来帮助他到达目的地 destination 。
指令 用字符串表示,其中每个字符:
'H',意味着水平向右移动'V',意味着竖直向下移动
能够为 Bob 导航到目的地 destination 的指令可以有多种,例如,如果目的地 destination 是 (2, 3),"HHHVV" 和 "HVHVH" 都是有效 指令 。
然而,Bob 很挑剔。因为他的幸运数字是 k,他想要遵循 按字典序排列后的第 k 条最小指令 的导航前往目的地 destination 。k 的编号 从 1 开始 。
给你一个整数数组 destination 和一个整数 k ,请你返回可以为 Bob 提供前往目的地 destination 导航的 按字典序排列后的第 k 条最小指令 。
示例 1:
输入:destination = [2,3], k = 1 输出:"HHHVV" 解释:能前往 (2, 3) 的所有导航指令 按字典序排列后 如下所示: ["HHHVV", "HHVHV", "HHVVH", "HVHHV", "HVHVH", "HVVHH", "VHHHV", "VHHVH", "VHVHH", "VVHHH"].
示例 2:
输入:destination = [2,3], k = 2 输出:"HHVHV"
示例 3:
输入:destination = [2,3], k = 3 输出:"HHVVH"
提示:
destination.length == 21 <= row, column <= 151 <= k <= nCr(row + column, row),其中nCr(a, b)表示组合数,即从a个物品中选b个物品的不同方案数。
根据题目描述我们可以知道,最终的路径是由 'V' 和 'H' 组成的,且按字典序排列后的第
我们首先考虑字典序的最高位,即最左边的字符。如果高位字符是 'V',那么所有以 'H' 开头的路径的字典序都比它小,而以 'H' 开头的路径总数为
如果 'V',我们将 'H',我们将
注意,如果 'V',因为剩下的字符都是 'V'。
问题可以转换为求解
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def kthSmallestPath(self, destination: List[int], k: int) -> str:
v, h = destination
ans = []
for _ in range(h + v):
if h == 0:
ans.append("V")
else:
x = comb(h + v - 1, h - 1)
if k > x:
ans.append("V")
v -= 1
k -= x
else:
ans.append("H")
h -= 1
return "".join(ans)class Solution {
public String kthSmallestPath(int[] destination, int k) {
int v = destination[0], h = destination[1];
int n = v + h;
int[][] c = new int[n + 1][h + 1];
c[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
c[i][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= h; ++j) {
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = n; i > 0; --i) {
if (h == 0) {
ans.append('V');
} else {
int x = c[v + h - 1][h - 1];
if (k > x) {
ans.append('V');
k -= x;
--v;
} else {
ans.append('H');
--h;
}
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}class Solution {
public:
string kthSmallestPath(vector<int>& destination, int k) {
int v = destination[0], h = destination[1];
int n = v + h;
int c[n + 1][h + 1];
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
c[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
c[i][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= h; ++j) {
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
string ans;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (h == 0) {
ans.push_back('V');
} else {
int x = c[v + h - 1][h - 1];
if (k > x) {
ans.push_back('V');
--v;
k -= x;
} else {
ans.push_back('H');
--h;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func kthSmallestPath(destination []int, k int) string {
v, h := destination[0], destination[1]
n := v + h
c := make([][]int, n+1)
for i := range c {
c[i] = make([]int, h+1)
c[i][0] = 1
}
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= h; j++ {
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j] + c[i-1][j-1]
}
}
ans := []byte{}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if h == 0 {
ans = append(ans, 'V')
} else {
x := c[v+h-1][h-1]
if k > x {
ans = append(ans, 'V')
k -= x
v--
} else {
ans = append(ans, 'H')
h--
}
}
}
return string(ans)
}