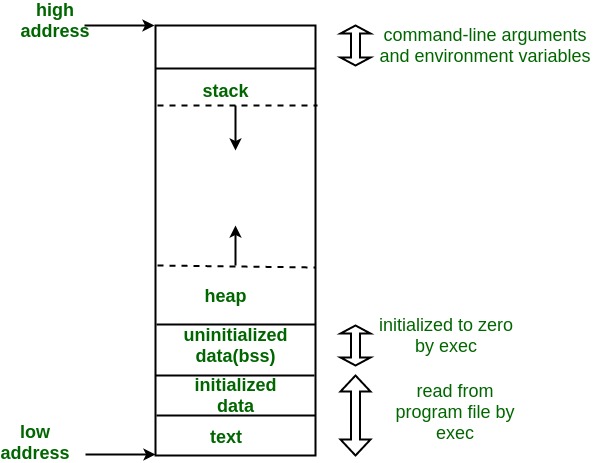
1. Text Segment/Code Segment
It contains executable instructions. Usually, the text segment is sharable so taht only a single copy needs to be in memory for frequently executed programs. Also, the text segment is often read-only, to prevent a program from modifying its instructions
2. Initialized Data Segment
Initialized data segment, usually called simply the Data Segment. It contains global variables and static variables that are initialized by the programmer. This segment can be further classified into initilized read-only area and initialized read-write area. For example the global styring char s[] = "hello world" , the pointer variable s would be stored in read-write area while the string literal "hello world" is stored in read-only area.
3. Unintialized Data Segment(bss)
It contains all global vriables and static variables that are initialized to zero or do not have explicity initialization in source code. For instance, global in j and static int j
4. Stack
Stack contains the program stack, a LIFO struture, typically located in the higher parts of memory. Every time a function is called, a Stack frame is pushed into the stack, and the "satck pointer" will be set to track the top of the stack. When the function returns, the corresponding stack frame will be popped and terminated. Memoery in Stack is managed by the system, and the system automatically allocate and deallocate the variables.
5. Heap
Heap is the segment where dynamic memory allocation usually takes place. The memory is managed by programmers manually. Programmers can use malloc, calloc, realloc to manage the heap memory, and use free to delete the data. However luckily in Swift, Heap is managed by ARC, so programmers don't need to handle memory allocation and deallocation on their behalf.
| Heap | Stack | |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Based on Linked List, Tree, Array | Stack |
| Feature | Manually handle the memory size, allocation & deallocation, etc | The system automatically handles allocating and deallocating the data, LIFO structure |
| Object | Class, Referece Type, Variable Type | Value Type, such as struct, enum, Int, function return value, local variables |
| Thread | Since it's shared and global, it may be not safe in multi-thread. | Thread-safe |
- Access Speed: stack is faster than heap
- Memory Limit: stack usually has memory size limit, but heap doesn't