Don't forget to hit the ⭐ if you like this repo.
- Introduction
- Rapid Software Development
- Agile Development
- Plan-Driven and Agile Development
- Balance of Plan-Driven or Agile Development
- Comparison between Plan-Driven and Agile Development
- Agile Methods
- Agile Manifesto
- The Principles of Agile Methods
- Agile Methods Applicability
- Agile Development Techniques
- XP(Extreme Programming)
- The Extreme Programming Release Cycle
- XP and Agile Principles
- Influential XP Practices
- 1: User Stories for Specification
- 2: Refactoring
- 3: Test-First Development
- 4: Pair Programming
- Agile Project Management
- Scrum
- The Scrum Process
- Task Board
- The Scrum Sprint Cycle
- Teamwork in Scrum
- Scrum Benefits
- Example of Agile Project Management: JIRA Software
- DevOps: Agile & Learn to Operations Work
- DevOps and Tools
- Agile DevOps
- Scaling Agile Methods
- Practical Problems with Agile Methods
- Large Systems Development
- Scaling Out and Scaling Up
- Scaling Up to Large Systems
- Scaling Out to Large Companies
- Agile Methods and Software Maintenance
- Agile Maintenance
- Agile and Plan-Based Factors
- Agile and Waterfall: AgiFall
- Agile-Waterfall Hybrid
Agile methodology is a project management approach that was introduced in 2001 as an alternative to traditional, rigid project management approaches like the waterfall model. Unlike the waterfall model, which follows a sequential, linear approach to software development, agile methodology is an iterative and incremental approach that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction.
The main difference between agile and the waterfall model is that the waterfall model follows a sequential process where each phase must be completed before the next can begin. This approach can lead to delays and difficulty adapting to changes in customer needs or market conditions. In contrast, agile methodology focuses on delivering a working product in short development cycles, with frequent releases and continuous improvement. This approach allows for greater flexibility and the ability to respond quickly to changing requirements.
Agile methodology is based on the Agile Manifesto, which outlines the values and principles of the approach. The manifesto emphasizes the importance of individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. Agile methodology encourages cross-functional teams to work together and collaborate with stakeholders to deliver a high-quality product that meets customer needs.
Overall, agile methodology offers a more flexible and adaptable approach to project management and software development than traditional waterfall models. By emphasizing collaboration, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement, agile methodology can help teams deliver better products in less time while also fostering a more collaborative and engaged work environment.
Agile methodology is a project management approach that emphasizes rapid development and delivery, planning, and agile development techniques. In software development, these principles are often implemented using tools like GitHub, which is a popular code hosting and collaboration platform that allows teams to work together on software development projects.
-
Rapid development and delivery: Agile methodology focuses on delivering a working product in short development cycles, with frequent releases and continuous improvement. With GitHub, teams can work together to rapidly develop and deliver software by collaborating on code, reviewing and merging pull requests, and automating tests and deployment.
-
Plan development: Agile methodology encourages teams to plan development based on user stories, which are short descriptions of a feature or requirement from the perspective of the end-user. In GitHub, teams can create and manage user stories using issues and project boards, which help to organize and prioritize work and track progress towards milestones.
-
Agile development: Agile development techniques, such as Scrum and Kanban, are often used to implement agile methodology in software development. With GitHub, teams can use these techniques to manage and complete complex projects by organizing work into sprints, creating backlogs and prioritizing tasks, and visualizing work in progress using project boards and dashboards.
Agile development is a methodology that emphasizes iterative and incremental development, collaboration, and flexibility. Some key characteristics of agile development that aligns include:
-
Interleaved development: Agile development often involves interleaved development, where multiple features or components of a project are developed and tested concurrently. This approach helps to reduce overall development time and can allow for more efficient use of resources.
-
Series of versions: Agile development typically involves the creation of a series of versions, with each version representing a subset of the overall project requirements. These versions are often released on a regular basis, with each release incorporating feedback and improvements from previous versions.
-
Frequent delivery: Agile development places a strong emphasis on frequent delivery of working software. This helps to ensure that the project stays on track and meets customer needs, while also allowing for feedback and improvements throughout the development process.
-
Extensive toolset: Agile development often involves the use of an extensive toolset to help manage the development process. This can include project management software, collaboration platforms, automated testing and deployment tools, and more.
-
Minimal documentation: Agile development places a greater emphasis on working software than on comprehensive documentation. While some documentation may be necessary, the focus is on delivering working software and incorporating feedback and improvements as quickly as possible.
All in all, the agile development methodology emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and rapid delivery of working software. By using interleaved development, creating a series of versions, delivering software frequently, using an extensive toolset, and minimizing documentation, agile development can help teams to be more productive, efficient, and responsive to changing requirements and customer needs.
Plan-driven development: Also known as the Waterfall model, it is a software development methodology that follows a sequential approach to building software products. In this methodology, the development process is divided into a series of distinct phases, and each phase must be completed before the next one begins.
Separate development stages: The phases in the plan-driven development model typically include requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. This approach requires extensive planning and documentation before development begins, with a detailed project plan that includes project scope, schedule, and budget.
Iteration: To address the inflexibility of the plan-driven approach, some organizations have adopted an iterative approach, where each phase is broken down into smaller iterations. This allows for more frequent feedback and the ability to make changes based on that feedback. However, even with an iterative approach, the plan-driven model is still characterized by a linear, sequential development process.
Advantages and disadvantages: The plan-driven approach is suitable for large, complex projects with well-defined requirements. However, it can be inflexible in the face of changing requirements, and changes made later in the development process can lead to delays and increased costs.
Example: An example of plan-driven development is the software development process used by NASA for space missions, where a detailed plan is necessary to ensure the success of the mission.
Agile development: Agile is a software development methodology that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. This approach is characterized by short development cycles, frequent feedback, and the ability to adapt to changing requirements.
Separate development stages: Agile development involves breaking down the development process into smaller, more manageable pieces that can be completed in a short amount of time. These pieces, called iterations or sprints, typically last between 1-4 weeks and include requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and deployment.
Inter-leaved: In Agile development, different development stages can be inter-leaved or performed simultaneously within an iteration, allowing for quick feedback and the ability to make changes based on that feedback. This approach allows for a more flexible and adaptable development process, which can lead to faster delivery of working software.
Advantages and disadvantages: Agile development is suitable for projects with rapidly changing requirements or uncertain scope, where flexibility and adaptability are more important than a detailed plan. However, Agile development can be more challenging to manage for large, complex projects, and the need for continuous feedback and collaboration can lead to communication and coordination challenges.
Example: An example of Agile development is the development process used by a software development team building a mobile app. The team breaks down the development process into short sprints, each focusing on a specific feature or functionality. Within each sprint, the team inter-leaves development stages, allowing for quick feedback and the ability to make changes based on that feedback.
Agile development is often implemented through various frameworks or methodologies such as Scrum, Kanban, Lean, and Extreme Programming (XP). Each methodology has its unique approach to implementing agile principles, but they all share the same values and principles.
Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile methodology that focuses on continuous feedback, continuous testing, and continuous delivery. XP was developed in the 1990s as a response to the traditional "waterfall" software development process. The XP methodology is based on a set of practices that are intended to increase software quality and reduce the time it takes to deliver working software. Here are the key practices of XP:
-
Pair Programming: Two developers work together on a single computer, continuously reviewing each other's code and providing feedback.
-
Test-Driven Development (TDD): Developers write automated tests before writing code to ensure that the code is working as intended.
-
Continuous Integration: Developers integrate their code changes frequently, usually several times a day, to detect issues early and ensure that the code is working together.
-
Refactoring: Developers improve the code continuously, making it easier to understand, maintain, and modify.
-
Simple Design: The focus is on keeping the design simple, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
-
Coding Standards: The team agrees on a set of coding standards to ensure consistency and maintainability of the codebase.
-
Planning Game: A collaborative approach to planning where the development team and the customer work together to prioritize and estimate the work to be done.
The XP methodology places a strong emphasis on teamwork, communication, and feedback, enabling teams to deliver high-quality software quickly and efficiently. By prioritizing customer needs, continuous testing, and continuous delivery, XP helps to ensure that the product is always aligned with customer expectations.
Example of Extreme Approuch to Iterative Development
-
New Versions may be built several times per day
-
Increments are delivered to customers every 2 weeks
-
All tests must be run for every build
-
Build is only accepted when the tests sucessfully run
-
Identify the Stakeholders The first step in choosing user stories is to identify the stakeholders who will be impacted by the software. Stakeholders can include end-users, customers, managers, and other stakeholders who have an interest in the software.
-
Brainstorm User Stories Once the stakeholders have been identified, the development team should brainstorm user stories that capture the stakeholders' requirements. User stories should be written in a simple, non-technical language and should describe the desired outcome or value to the user.
-
Prioritize User Stories Once the user stories have been identified, the team should prioritize them based on the customer's needs and the value they provide. Prioritization can be done collaboratively with the customer and the development team.
-
Estimate User Stories After prioritization, the team should estimate the effort required to complete each user story. This can be done using story points or another relative estimation technique. Estimation should be done collaboratively with the development team and should take into account the team's capacity and expertise.
-
Break Down User Stories User stories should be broken down into smaller, manageable tasks that can be completed in a single iteration. Breaking down user stories helps to identify any dependencies or technical challenges and ensures that the work is manageable for the team.
-
Validate user stories Once the user stories have been prioritized, estimated, and broken down, the team should validate them with the customer. This ensures that the user stories capture the customer's requirements and that the priorities and estimates are aligned with the customer's needs.
After all the steps above are completed, the team need to create a release plan based on the priority and dependencies of the stories.
In the development step of the Extreme Programming (XP) release cycle, the actual coding of the software takes place. This step is crucial as it involves turning the requirements and user stories into functional code. The development process in XP is characterized by several practices that are designed to ensure high-quality code that meets the needs of the customer. Some of these practices include:
I. Pair programming: In XP, developers work in pairs on the same code. This practice ensures that the code is reviewed as it is being written, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the quality of the code.
II. Continuous integration: XP emphasizes frequent integration of code changes into the main codebase. This ensures that code is tested and integrated early, reducing the risk of problems being discovered later in the development process.
III. Test-driven development: XP follows a test-driven development approach, where developers write automated tests for their code before writing the code itself. This ensures that the code meets the requirements and reduces the likelihood of introducing bugs into the codebase.
IV. Refactoring: XP encourages frequent refactoring of the codebase to keep it clean and maintainable. This ensures that the code remains easy to work with and reduces the likelihood of introducing bugs into the codebase.
Overall, the development step in the XP release cycle is focused on producing high-quality code that meets the needs of the customer while ensuring that the code remains easy to work with and maintainable.
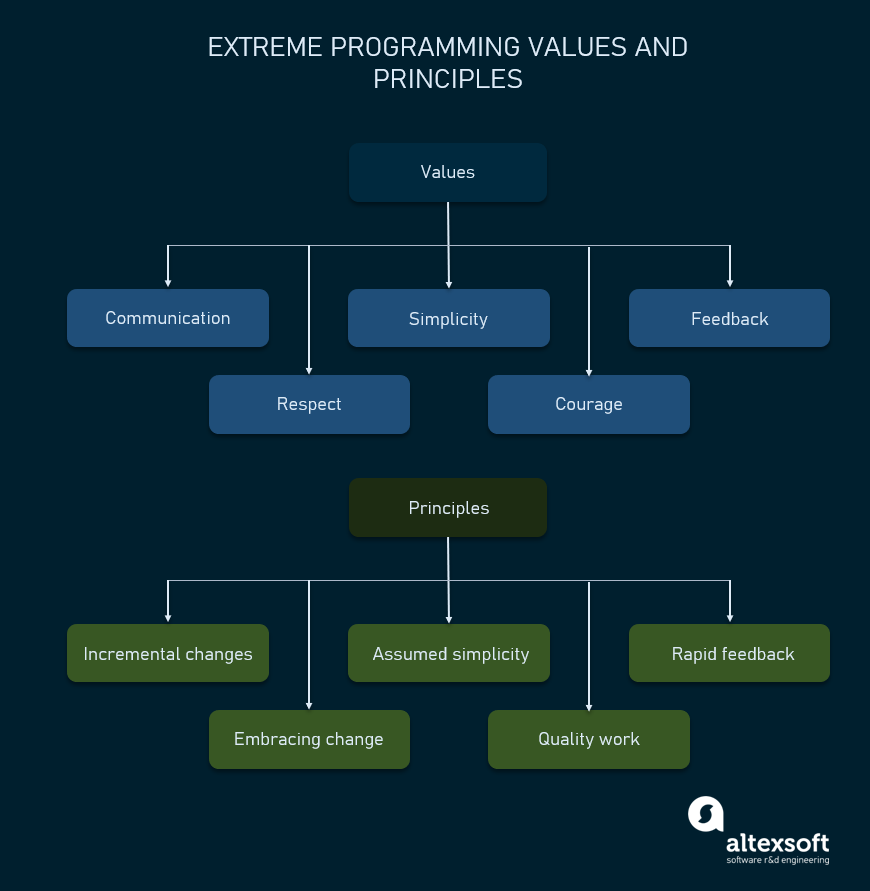
XP is based on a set of principles that align with the Agile Manifesto, which was created in 2001 as a way to promote agility and flexibility in software development.
Here are some of the key principles of XP and how they relate to the Agile Manifesto:
-
Communication: XP places a strong emphasis on communication between developers, stakeholders, and customers. This aligns with the Agile Manifesto's principle of "Individuals and interactions over processes and tools."
-
Simplicity: XP promotes simplicity in software design and development, with the goal of delivering the most valuable software with the least amount of complexity. This aligns with the Agile Manifesto's principle of "Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential."
-
Feedback: XP emphasizes the importance of frequent feedback from stakeholders, customers, and end-users. This aligns with the Agile Manifesto's principle of "Working software is the primary measure of progress."
-
Respect: XP encourages respect for everyone involved in the software development process, including developers, stakeholders, and customers. This aligns with the Agile Manifesto's principle of "Respect for people and continuous improvement."
-
Courage: XP promotes courage in the face of uncertainty and encourages developers to take risks and experiment. This aligns with the Agile Manifesto's principle of "Responding to change over following a plan."
-
Iteration: XP emphasizes delivering software in small, frequent iterations rather than in one large release. This aligns with the Agile Manifesto's principle of "Delivering working software frequently, with a preference to the shorter timescale."
Key Practice:
- User stories for specification
- Refactoring
- Test-first development
- Pair programming
Key Practice #1 – Pair Programming One of the most unique traits of XP is the practice of pair-programming, where two (and possibly more) engineers work side-by-side to develop code together. This practice involves two programmers working together on the same codebase, sharing knowledge and collaborating to improve the quality of the code. This approach is designed to optimize quality due to the built-in validation mechanism that is expected between two engineers which contribute to a single unit of code. While some organizations embrace this technique, this approach will require careful selection of partners to ensure maximum effectiveness. Culturally, there may also be a need to educate leadership folks who may not understand the value and see this as increased overhead/cost.
Key Practice #2 – Planning Game XP receives credit for introducing a different approach to planning work through planning small batches of work frequently and through a consistent schedule. This practice involves regular planning meetings where the team collaboratively decides what work to do next, based on the customer's priorities. This was a precursor to what many of us know as “Sprint Planning” or “Iteration Planning” today within Scrum or other Agile approaches. Planning iteratively and applying a popular technique called “user stories” is one of the most important aspects of XP that has trickled down to Scrum, the most popular Agile method in the world today.
Key Practice #3 – Continuous Process This practice involves regular planning meetings where the team collaboratively decides what work to do next, based on the customer's priorities.The practice of integrating code regularly and releasing the code on a cadence has been recently popularized by the movement also known as “DevOps” which originated the XP practices. Building code iteratively and releasing frequently enables the team to assess state of the product and resolve issues as early and often as possible which ultimately leads to higher overall quality in the end.
Key Practice #4 – Coding Standards One of the most important and often forgotten practices amongst new Agile teams is the concept of coding standards. If a team of engineers do not construct a common set of rules, the end product will suffer a lack of consistency and increase the likelihood of technical debt as well as defects.
Key Practice #5 – Sustainable Pace One of the key tenets of Agile Manifesto is to respect work-life balance for teams and encourage sustainable development, which enhances morale as well as product quality. XP reinforces this value in order to maximize team effectiveness.
Key Practice #6 – Test Driven Development (TDD) Test Driven Development(TDD) is a specific practice of Test First that is commonly associated with Extreme Programming (XP). XP states that unit tests must be written prior to code, which is a practice that many organizations are not accustomed to. TDD enhances code quality because it requires a test to be written which means that code will always pass the test before it is submitted and integrated with the work from other members of the team.
A user story is a short, simple description of a feature or functionality of a software system that is written from the perspective of an end-user or customer. User stories are used in Agile software development methodologies to capture the requirements of the system and guide the development process.
User stories are typically written on index cards or sticky notes and are arranged on a physical or digital board called a "product backlog". The product backlog is a prioritized list of user stories that guides the development team in their work, with the highest priority user stories being completed first.
By using user stories, development teams can ensure that they are focused on delivering features and functionality that meet the needs of the end-user or customer, and can prioritize their work based on the value that each user story delivers. This helps to ensure that the development process is aligned with the goals of the business or organization and that the resulting software is of high quality and provides value to the end-users.
Refactoring is a software development technique that involves improving the quality and structure of existing code without changing its behavior. The goal of refactoring is to make code more readable, maintainable, and efficient, while also reducing technical debt and improving overall software design.
Refactoring involves making a series of small, incremental changes to code, rather than rewriting entire sections of the code all at once. Examples of refactoring techniques include renaming variables and methods to make their purpose clearer, breaking down large functions into smaller, more focused ones, simplifying complex logic and conditionals, and eliminating code duplication.
Refactoring is often used in Agile software development methodologies, where it is performed regularly throughout the development process to improve the quality and maintainability of the codebase. In Agile, refactoring is seen as a continuous process that is performed alongside development and testing, rather than a separate phase of the software development lifecycle.
There are several benefits to refactoring, including:
Improved code quality: Refactoring helps to improve the readability, maintainability, and efficiency of code, making it easier to understand and work with.
Reduced technical debt: By improving the quality of the codebase, refactoring helps to reduce technical debt, which is the cost of maintaining and fixing poorly written or designed code.
Better software design: Refactoring can help to identify and eliminate design flaws in the code, leading to a more robust and scalable software architecture.
Increased productivity: By making the codebase easier to work with, refactoring can increase developer productivity and reduce the time needed to add new features or fix bugs.
Overall, refactoring is an important technique for improving the quality and maintainability of software code, and is a key part of Agile software development methodologies.
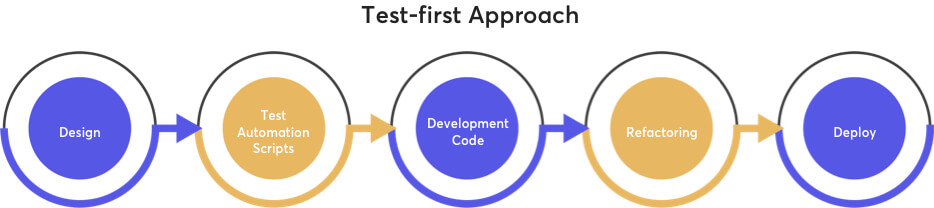
Test-First Development is an approach to writing software that involves writing a unit test for a function before writing the function. Test-First Development (TFD) is a software development approach that involves writing unit tests before writing any code. This process ensures that unit tests are written, leading to higher-quality, robust code, with fewer bugs. TFD offers several benefits, some of which are:
-
Improved code quality: TFD helps to improve the quality of code by enforcing rigorous testing and forcing the programmer to clarify the function specification. Writing tests first helps the programmer to practice specification-based testing, leading to code that meets the requirements and has fewer bugs.
-
Reduced debugging time: TFD reduces debugging time as programmers get instant feedback on whether the function is working or not. If the function fails to pass the test, the benefits of unit testing in helping the programmer to quickly diagnose and fix the problem are instantly available. The test-debug cycle is rapid.
-
Faster development time: TFD helps to reduce overall development time as the programmer writes more code (the unit tests) which speeds up the overall development process. The existing unit tests also serve as a safety net when modifying an existing function for which unit tests already exist.
-
Improved psychological benefits: TFD offers psychological benefits to programmers as they work on the project, creating little tests and then writing code that passes those tests, leading to a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction every time a new test passes. This process leads to more visible and regular successes, reducing the hours of frustration debugging a new function in the context of a complex program, with few visible results.
In summary, TFD is an effective approach to software development that offers several benefits to programmers and organizations alike. By enforcing rigorous testing, clarifying function specification, reducing debugging time, improving code quality, reducing overall development time, and offering psychological benefits, TFD helps to ensure that software is of high quality and meets the requirements of end-users or customers.
Pair programming is a software development technique where two programmers collaborate and work together at a single workstation. The process involves two roles: the driver, who is responsible for writing code, and the observer or navigator, who reviews each line of code as it is typed in. The two programmers frequently switch roles to maintain an equal share of work and knowledge.
The observer plays a crucial role in the pair programming process. Along with reviewing the code, the observer also considers the "strategic" direction of the work, offering ideas for improvements and identifying potential future problems to address. This frees the driver to focus solely on the "tactical" aspects of completing the current task while using the observer as a safety net and guide.
Pair programming has become a popular practice in software development due to its ability to improve code quality, reduce errors and bugs, and enhance communication between team members. It also fosters a collaborative and supportive work environment, leading to increased job satisfaction and team cohesion. By combining the strengths and knowledge of two programmers, pair programming helps to produce high-quality code and improve overall project outcomes.
Agile project management is an iterative and flexible approach to managing software development projects. It emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and customer satisfaction. In contrast to traditional plan-driven project management methods, agile project management focuses on delivering working software in incremental iterations.
Key points to keep in mind about agile project management:
-
Agile project management is designed to be responsive to changing customer needs and priorities. This is in contrast to plan-driven project management, which is based on a detailed plan that is created at the start of the project and followed throughout.
-
Agile project management emphasizes collaboration between developers, project managers, and customers. This helps ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
-
Agile project management typically involves working in short iterations or sprints. Each sprint focuses on delivering a specific set of features or functionality.
-
Agile project management prioritizes working software over comprehensive documentation. This means that developers focus on creating code that works and is tested, rather than spending time on extensive documentation.
-
Agile project management encourages continuous improvement and learning. This means that project teams should regularly reflect on their processes and look for ways to improve.
Overall, agile project management is a flexible and adaptable approach to software development that can help software project managers deliver high-quality software in a timely and efficient manner.
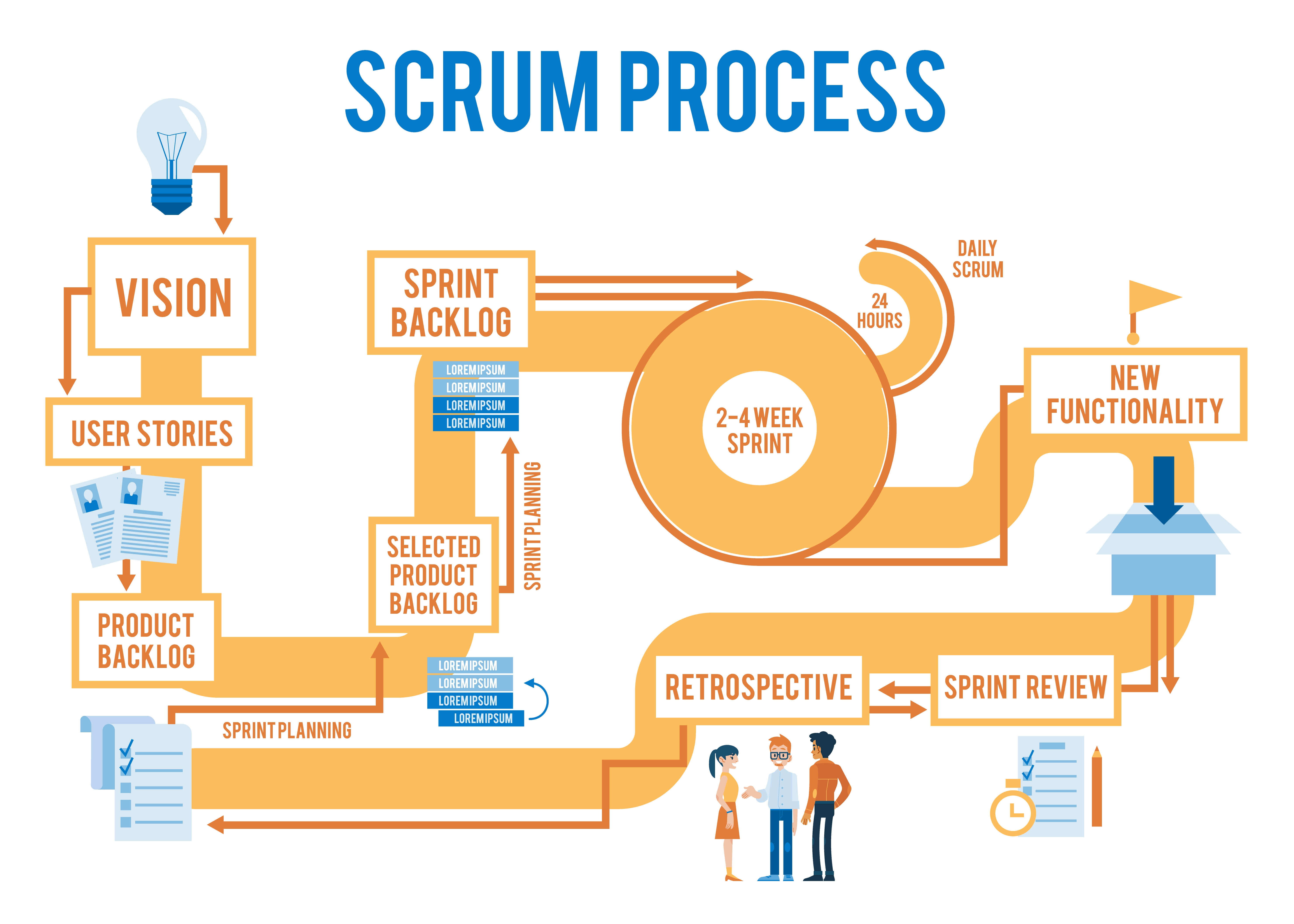
Scrum is a popular framework for managing iterative development in agile software development. It is a lightweight process that helps teams deliver high-quality software in a flexible and adaptive way. Scrum is based on a series of sprint cycles that allow teams to focus on delivering small, incremental improvements to the product.
Key points to keep in mind about agile project management:
-
Scrum is based on a series of sprint cycles. Each sprint typically lasts two to four weeks and focuses on delivering a small set of features or functionality.
-
Scrum teams are self-organizing and cross-functional. This means that they are responsible for managing their own work and have all the skills necessary to deliver a working product.
-
The Scrum framework includes several roles, including the product owner, the Scrum master, and the development team. Each role has specific responsibilities and works together to deliver the product.
-
Scrum emphasizes frequent communication and collaboration between team members. This helps ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals and that any issues are addressed quickly.
-
At the end of each sprint, the team holds a sprint review meeting to demonstrate the work they have completed and gather feedback from stakeholders.
-
The final sprint in a Scrum project is the sprint where the product is completed and released. This sprint is known as the "sprint 0" or the "release sprint".
Overall, Scrum is a flexible and adaptable framework that can help teams manage iterative development in a way that is efficient and effective. By focusing on delivering small, incremental improvements to the product, Scrum helps teams stay focused and on track, ultimately leading to a successful product that wraps up the project.
Scrum is a popular agile framework for managing complex projects. It emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation to deliver high-quality software in an iterative and incremental manner. The Scrum process consists of roles, events, artifacts, and rules that work together to facilitate efficient project management and continuous improvement.
A task board is a visual tool used in agile project management to track the progress of work and improve team communication. It is a physical or digital board that displays the status of tasks in various stages of completion, allowing team members to quickly see what needs to be done and who is responsible for it. The task board is a key component of agile project management and can help teams stay organized and focused on delivering high-quality software in an efficient and effective manner.
The sprint cycle is a time-boxed iteration in which the team works to deliver a potentially releasable increment of the product.
- The sprint cycle begins with a selection phase in which the team chooses items from the product backlog to work on during the sprint.
- During the sprint cycle, the team is isolated from the customer and the organization, allowing them to focus on completing the work.
- The Scrum Master is responsible for facilitating the sprint cycle and ensuring that the team stays on track and overcomes any obstacles.
- At the end of the sprint cycle, the work is reviewed and presented to stakeholders, providing a clear view of the team's progress and - accomplishments.
In Scrum, a popular Agile framework, teamwork plays a critical role in project success. The team works together to complete tasks and deliver high-quality software in an iterative and incremental manner. The Scrum Master facilitates the team's collaboration by ensuring that everyone is aligned with the project goals and objectives. Additionally, the whole team attends short daily meetings called stand-ups or daily scrums, which provide an opportunity for team members to synchronize their work and discuss any impediments. By working together as a cohesive unit, the team can achieve better results and deliver value to the customer.
- Scrum helps teams deliver high-quality software in an iterative and incremental manner.
- It promotes transparency, inspection, and adaptation, allowing for continuous improvement throughout the project.
- Scrum enables teams to stay focused on delivering value to the customer by prioritizing work based on business value.
- It encourages collaboration and teamwork, which can lead to better results and a more enjoyable work environment.
- Scrum allows for flexibility and adaptability in response to changing requirements or market conditions.
- It provides a framework for managing complex projects in a structured and efficient manner.
- Scrum can lead to increased productivity and faster time-to-market for software products.
JIRA Software is a popular project management tool used in Agile software development. It is designed to help teams plan, track, and release software products in an iterative and incremental manner. JIRA provides a variety of features and functionalities that support Agile practices such as Scrum and Kanban, including the ability to create and manage product backlogs, track sprint progress, and visualize team workflows.
DevOps is a methodology that combines Agile and Lean principles with operations. It streamlines the development lifecycle, breaks down silos between teams, and creates a culture of collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement. By integrating operations into development, it enables faster and more reliable delivery of high-quality software products. Ultimately, DevOps delivers value to customers and the business by ensuring a more efficient and effective software development process.
DevOps is a software development methodology that emphasizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams, with a focus on automating repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and reliability. To support these goals, a series of tools have emerged in recent years to help DevOps teams manage their workflows, including tools for continuous integration and delivery, containerization, configuration management, and monitoring. By using these tools, DevOps teams can automate manual processes, reduce errors, and improve overall productivity. The result is a more efficient and effective software development process that delivers high-quality software products quickly and reliably.
Agile DevOps is an approach to software development that combines Agile methodologies with DevOps practices. It involves breaking down silos between development and operations teams and creating a culture of collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement. Agile DevOps aims to deliver high-quality software products more quickly and reliably by integrating Agile practices such as Scrum and Kanban with DevOps tools and processes. This approach emphasizes the importance of collaboration, automation, and feedback throughout the entire software development lifecycle, from planning and development to testing, deployment, and monitoring. The result is a more efficient and effective software development process that delivers value to customers and the business.
Please create an Issue for any improvements, suggestions or errors in the content.
You can also contact me using Linkedin for any other queries or feedback.