Don't forget to hit the ⭐ if you like this repo.
- Introduction
- Rapid Software Development
- Agile Development
- Plan-Driven and Agile Development
- Balance of Plan-Driven or Agile Development
- Comparison between Plan-Driven and Agile Development
- Plan-Driven Development
- Agile Development
- Agile Methods
- Agile Manifesto
- The Principles of Agile Methods
- Agile Methods Applicability
- Agile Development Techniques
- XP(Extreme Programming)
- The Extreme Programming Release Cycle
Rapid software development (RSD) is an approach to software development that emphasizes speed and efficiency in the delivery of working software. It is characterized by short development cycles, frequent releases, and a focus on delivering value to customers quickly. RSD is often associated with agile methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban, which emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. RSD also often involves the use of rapid prototyping and iterative design, allowing developers to quickly test and refine their ideas based on feedback from customers and stakeholders. One of the key benefits of RSD is the ability to respond quickly to changing requirements and customer needs. By breaking down development into small, manageable pieces, and focusing on delivering working software as quickly as possible, RSD allows teams to be more responsive to changing market conditions and customer feedback. However, RSD can also present some challenges, such as the need for effective communication and collaboration among team members and the need for adequate testing and quality assurance to ensure that the software is stable and reliable.
Overall, rapid software development is a flexible and adaptable approach to software development that can help teams deliver high-quality software quickly and efficiently while responding to changing requirements and customer needs.
Agile development is an approach to software development that emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. It is a subset of the Agile methodology and is characterized by short development cycles, frequent releases, and a focus on delivering value to customers quickly. Agile development is based on the Agile Manifesto, which values individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. Agile development teams work closely with customers and stakeholders to understand their needs and provide frequent opportunities for feedback. The development process is typically broken down into small, manageable pieces, and work is organized into short iterations or sprints. Some common practices used in Agile development include daily stand-up meetings, regular sprint planning and review meetings, continuous integration and testing, and user stories to capture requirements. Agile development also emphasizes teamwork, communication, and collaboration, with a focus on empowering individuals and allowing them to self-organize to get work done.
Overall, Agile development provides a flexible and adaptable approach to software development that can help teams deliver high-quality software quickly and efficiently while responding to changing requirements and customer needs.
Plan-driven development and Agile development are two different approaches to software development, with different philosophies and methodologies. Plan-driven development is a traditional approach to software development that emphasizes planning and control. In this approach, a detailed plan is developed at the beginning of the project, and work proceeds according to that plan. The plan is used to define the scope of the project, the milestones to be achieved, and the resources required to complete the project. The plan is typically created by a project manager or a team of experts, and it is updated periodically as the project progresses.
Agile development, on the other hand, is an iterative and collaborative approach to software development that emphasizes flexibility and adaptability. In this approach, the project is broken down into small, manageable pieces, and work is organized into short iterations or sprints. The focus is on delivering value to the customer quickly and frequently, with a high degree of collaboration between team members and customers. In plan-driven development, the emphasis is on following a detailed plan and adhering to a strict schedule. In Agile development, the emphasis is on adapting to changing requirements and feedback from customers, with a focus on delivering working software quickly and efficiently.
Overall, plan-driven development and Agile development represent two different approaches to software development, with different strengths and weaknesses. Plan-driven development is often used in large, complex projects where detailed planning and control are necessary, while Agile development is often used in smaller, more dynamic projects where flexibility and adaptability are critical.
The balance of plan-driven and Agile development depends on the nature of the project and the needs of the stakeholders. Both plan-driven and Agile development have their strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right approach requires careful consideration of the project's requirements, goals, and constraints.
In some cases, a plan-driven approach may be more appropriate, such as when the project has a clear and well-defined scope, a fixed budget, and a strict timeline. Plan-driven approaches may also be more suitable for projects that require a high degree of predictability and control, such as safety-critical systems or complex infrastructure projects. In other cases, an Agile approach may be more appropriate, such as when the project requirements are unclear or subject to change, or when the project involves significant innovation or experimentation. Agile approaches may also be more suitable for projects that require a high degree of collaboration and communication among team members and stakeholders.
In practice, many software development projects use a hybrid approach that combines elements of both plan-driven and Agile development. For example, a project may begin with a detailed plan but use Agile methods for implementation, testing, and delivery. Alternatively, a project may use Agile methods for requirements gathering and design but then switch to a plan-driven approach for implementation and testing.
Ultimately, the balance of plan-driven and Agile development will depend on the specific needs of the project and the stakeholders involved. It is important to carefully consider the trade-offs and benefits of each approach and choose the approach that is best suited to achieving the project's goals.
- Emphasizes planning and control
- Detailed plan is developed at the beginning of the project
- Focus on following the plan and adhering to a strict schedule
- Works best when the project has a clear and well-defined scope, fixed budget, and strict timeline
- Focus on predictive approach
- Requires a lot of documentation and up-front planning
- Changes to the plan are costly and require extensive review and approval
- Emphasizes specialization and division of labor
- Generally follows a waterfall or V-model approach
- Quality is measured by adherence to the plan and specifications
- Emphasizes flexibility and adaptability
- Project is broken down into small, manageable pieces
- Focus on delivering value to the customer quickly and frequently
- Works best when the project requirements are unclear or subject to change
- Focus on adaptive approach
- Requires less documentation and up-front planning
- Changes are expected and can be accommodated easily
- Emphasizes collaboration and communication among team members and customers
- Generally follows an iterative and incremental approach, such as Scrum or Kanban
- Quality is measured by the working software and customer satisfaction
Overall, Plan-Driven development emphasizes planning and control, while Agile development emphasizes flexibility and adaptability. Plan-Driven development is best suited for projects with a clear and well-defined scope, while Agile development is best suited for projects with changing requirements or a high degree of innovation.
Agile methods are a set of practices and values used in Agile methodology, which is an iterative and collaborative approach to project management. Agile methods are designed to help teams deliver high quality products quickly and efficiently, while continuously adapting to changing requirements and feedback from customers.
Some common Agile methods include Scrum, Kanban, and Lean. Scrum is a framework for managing and completing complex projects, with a focus on delivering a potentially shippable product increment at the end of each sprint. Kanban is a visual workflow management system that emphasizes continuous delivery and improvement. Lean is a set of principles and practices that emphasizes delivering value to customers while minimizing waste.
Agile methods typically involve breaking a project down into small, manageable pieces and organizing work into short iterations or sprints. Teams work closely with customers and stakeholders to understand their needs and provide frequent opportunities for feedback. Agile methods also emphasize teamwork, communication, and collaboration, with a focus on empowering individuals and allowing them to self organize to get work done.
Overall, Agile methods provide a flexible and adaptable approach to project management, allowing teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and customer needs while delivering high-quality products on time and within budget.
The Agile Manifesto is a set of guiding values and principles for Agile software development. It was created by a group of software developers in 2001 as a response to the limitations of traditional, plan-driven development methods. The manifesto consists of four values and twelve principles that prioritize customer collaboration, working software, and flexibility over rigid plans and processes. The four values of the Agile Manifesto are:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
These values emphasize the importance of collaboration, communication, and adaptability in software development. They prioritize delivering value to the customer quickly and efficiently, and encourage a focus on working software over extensive documentation or planning.
The twelve principles of the Agile Manifesto expand upon these values, outlining specific guidelines for Agile development. These principles include: welcoming changing requirements, delivering working software frequently, building projects around motivated individuals, face-to-face communication, sustainable development, continuous attention to technical excellence and good design, simplicity, self-organizing teams, regular reflections and adaptations, and responding to change quickly.
Overall, the Agile Manifesto represents a shift away from traditional, plan-driven development methods and towards a more collaborative and adaptable approach to software development. It has had a significant impact on the software development industry, influencing the development of Agile methodologies such as Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming.
The Principles of Agile Methods are a set of guidelines that support the Agile Manifesto and describe how to implement Agile software development in practice. These principles were developed by the creators of the Agile Manifesto and are intended to help teams work more collaboratively and deliver value to customers quickly and efficiently. The principles are:
- Customer satisfaction through early and continuous software delivery: Agile development prioritizes delivering working software frequently to get feedback from the customer and ensure that their needs are being met.
- Accommodate changing requirements throughout the development process: Agile development embraces change and recognizes that requirements may change over time. It encourages teams to be flexible and adaptable to changing circumstances.
- Deliver working software frequently, with a preference to the shorter timescale: Agile development emphasizes delivering small, working increments of software frequently, rather than waiting until the end of the development cycle to deliver a large, complex product.
- Collaboration between business stakeholders and developers throughout the project: Agile development encourages collaboration between all stakeholders involved in the project, including business stakeholders, developers, and testers, to ensure that everyone is working towards a common goal.
- Supportive and trustful team environment: Agile development emphasizes building a supportive and trustful team environment, where team members are empowered to make decisions and work together to achieve common goals.
- Enable face-to-face interactions: Agile development encourages face-to-face interactions between team members, including business stakeholders, developers, and testers, to facilitate communication and collaboration.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress: Agile development prioritizes delivering working software as the primary measure of progress, rather than relying on metrics such as lines of code or hours worked.
- Sustainable development: Agile development prioritizes sustainable development practices, including a focus on technical excellence, continuous improvement, and regular feedback.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design: Agile development emphasizes the importance of technical excellence and good design, including practices such as automated testing, refactoring, and continuous integration.
- Simplicity: Agile development encourages teams to keep things simple and avoid unnecessary complexity, both in the software they develop and in their development processes.
- Self-organizing teams: Agile development encourages self-organizing teams, where team members are empowered to make decisions and work collaboratively towards common goals.
- Regular reflections and adaptations to improve efficiency: Agile development emphasizes regular reflection and adaptation to improve efficiency, including practices such as retrospectives and continuous improvement cycles.
Overall, the Principles of Agile Methods provide a framework for implementing Agile development in practice, and emphasize the importance of collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement in software development.
Agile methods are applicable in a wide variety of software development contexts, including:
- Rapidly changing environments: Agile methods are well-suited to environments where requirements are likely to change frequently, as they are designed to be flexible and adaptable.
- Complex projects: Agile methods can be effective in complex projects where traditional plan-driven approaches may struggle to cope with uncertainty and changing requirements.
- Small teams: Agile methods are particularly effective for small teams that require a high degree of collaboration and communication to deliver value to the customer.
- Innovative projects: Agile methods are well-suited to innovative projects where experimentation and exploration are required to develop new ideas and solutions.
- Customer-focused development: Agile methods prioritize delivering value to the customer and seek to involve the customer in the development process as much as possible.
- Continuous improvement: Agile methods emphasize continuous improvement and encourage teams to reflect on their processes and make changes to improve efficiency and quality.
- Software maintenance: Agile methods can be effective in software maintenance contexts, where small changes or enhancements need to be made frequently to existing software.
Overall, Agile methods are most applicable in contexts where flexibility, collaboration, and customer focus are key priorities, and where traditional plan-driven approaches may struggle to cope with uncertainty and change. However, it is important to note that not all software development contexts are well-suited to Agile methods, and it is important to carefully consider the requirements of each project when selecting a development approach.
Agile development is an approach to software development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and rapid iteration. Extreme Programming (XP), DSDM, FDD, RUP, Kanban, Crystal, and Scrum are all software development methodologies with different approaches and techniques.
- XP (Extreme Programming)is an Agile software development methodology that focuses on rapid feedback, continuous testing and integration, and customer involvement to produce high-quality software efficiently.
- DSDM (Dynamic Systems Development Method) is an Agile software development methodology that emphasizes frequent delivery of working software, active user involvement, and prioritization of requirements based on business value to ensure that the final product meets the customer's needs.
- FDD (Feature-Driven Development) is an Agile software development methodology that focuses on creating and delivering high-quality software features in a timely and efficient manner.
- RUP (Rational Unified Process) is a comprehensive software development process framework that emphasizes iterative development, risk management, and architecture-centric approach.
- Kanban is a visual system for managing workflow. Kanban boards display the status of work items, and the team limits the amount of work in progress to improve efficiency.
- Crystal is a family of Agile software development methodologies that emphasizes teamwork, communication, and simplicity, with a focus on tailoring the process to the needs of the project based on its size, criticality, and priorities.
- Scrum is a framework for managing and completing complex projects. Scrum emphasizes self-organizing teams and a flexible, iterative approach to development.
A very influential agile method, developed in the late 1990s, that introduced a range of agile development techniques. Extreme Programming (XP) also takes an ‘extreme’ approach to iterative development: o New versions may be built several times per day -To ensure that the code is always working and can be delivered quickly. This practice is known as continuous integration. Continuous integration is important in XP because it helps to catch errors early and ensures that the code is always in a releasable state. By integrating code changes frequently, XP teams can detect and fix errors quickly, reducing the risk of costly delays and rework later in the development process.
o Increments are delivered to customers every 2 weeks -This is part of the practice known as "iterative and incremental development". Iterative and incremental development in XP involves breaking down the development process into small, manageable iterations or sprints. Each iteration is focused on delivering a working increment of the software that can be demonstrated to stakeholders and customers for feedback. By delivering increments of working software every 2 weeks, XP teams can ensure that they are building the right product for the customer and that the software meets their needs. This frequent feedback helps to reduce the risk of building software that doesn't meet the customer's expectations or requirements, which can result in costly rework later in the development process.
o All tests must be run for every build and the build is only accepted if tests run successfully -This practice is known as "test-driven development" or TDD. TDD in XP involves writing tests for a specific piece of functionality before writing the code to implement it. The tests are run frequently and automatically as part of the build process to ensure that the code works as expected and meets the requirements. The goal of XP is to produce software that meets the needs of the customer while maximizing the value of the development effort. It emphasizes close collaboration between the development team and the customer to ensure that the software meets the customer's needs and is delivered on time and within budget.
Please create an Issue for any improvements, suggestions or errors in the content.
You can also contact me using Linkedin for any other queries or feedback.
Scaling Agile methods refers to the process of applying Agile principles and practices to larger and more complex projects that involve multiple teams and stakeholders. Here are some tips for scaling Agile methods:
- Adopt a framework: There are several frameworks available for scaling Agile, such as Scrum of Scrums, SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework), LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum), Nexus, etc. Choose a framework that aligns with your organization's needs and goals.
- Create cross-functional teams: To scale Agile, it is essential to have cross-functional teams that include representatives from various departments or areas of expertise. This allows for better collaboration, improved communication, and shared ownership of the project.
- Establish a shared vision: To ensure that all teams are working towards the same goal, it is important to establish a shared vision for the project. This will help to align everyone's efforts and ensure that they are working towards a common purpose.
- Focus on communication: Communication is essential in Agile, but it becomes even more critical when scaling Agile. Encourage open and transparent communication channels between teams, stakeholders, and customers
- Implement Agile practices: Scaling Agile requires a consistent approach to Agile practices, such as daily stand-ups, retrospectives, and sprint planning sessions. These practices help teams stay focused, prioritize work, and deliver value to customers.
- Invest in training and coaching: Scaling Agile can be challenging, so it is essential to invest in training and coaching for teams and stakeholders. This will help to ensure that everyone understands Agile principles and practices and can work effectively in an Agile environment
- Continuously improve: Agile is an iterative process, so it is important to continuously evaluate and improve the way you scale Agile. Encourage teams to regularly review their processes and identify areas for improvement
o Large systems development refers to the process of designing, building, and implementing software systems that are complex and often require collaboration among multiple teams or organizations. These systems typically have a large number of components and interactions, and require careful planning and management to ensure that they are delivered on time and within budget.
o Large systems development involves several stages, including requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and deployment. During the requirements gathering phase, stakeholders and end-users are consulted to identify the features and functionalities that the system should have. In the design phase, the architecture and overall structure of the system are defined, often using modeling tools to visualize and communicate the design to stakeholder
o In summary, large systems development is a complex process that requires careful planning, design, implementation, testing, and deployment, as well as effective management and coordination. It is a challenging but rewarding field that plays a critical role in enabling organizations to leverage technology to improve their operations and achieve their goals.
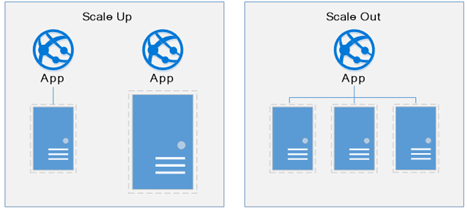
Scaling out and scaling up are two approaches used to increase the capacity of a system to handle more load or to meet higher performance demands.
Scaling out refers to adding more nodes or servers to a distributed system to handle more traffic or requests. This approach involves adding more hardware resources to distribute the workload across a larger number of machines. This can be achieved by adding more servers to a load-balanced cluster, or by deploying additional instances of a service in a cloud environment. Scaling out can be cost-effective, as it allows for more granular control over resource allocation, and can help to avoid a single point of failure.
Scaling up on the other hand, involves increasing the capacity of a single server or machine to handle more traffic or requests. This approach involves adding more resources to a single machine, such as increasing CPU or memory capacity, or upgrading to a more powerful server. Scaling up can be more expensive than scaling out, as it requires purchasing more powerful hardware, but it can be useful when a system is reaching the limit of what it can handle with its existing resources.
Both scaling out and scaling up can be effective ways to increase the capacity of a system, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs of the system and the resources available. A combination of both approaches can also be used to achieve the desired level of performance and scalability
Scaling up to a large system can be a complex and challenging task, but it is essential for organizations that want to grow and expand their operations. Here are some general tips that can help you scale up a large system:
- Plan ahead: Before scaling up, you need to have a clear plan in place. This should include identifying potential bottlenecks and risks, as well as establishing metrics for success.
- Optimize performance: To scale up a large system, you need to optimize its performance. This can involve improving hardware resources, optimizing software and databases, and using techniques like load balancing to distribute traffic evenly across multiple servers
- Automate processes: Automation can help streamline processes and reduce the risk of errors. This includes automating deployment, testing, and monitoring processes.
- Focus on security: As your system grows, so does the risk of security breaches. Make sure to implement appropriate security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Scaling out to large companies can be a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Here are some general tips to consider:
- Understand the needs of your customers: Large companies have different needs than small businesses, and it's important to understand their requirements in order to tailor your products or services to meet their needs.
- Build a strong team: Scaling to a large company requires a strong team that can handle the increased workload and demands of a larger customer base. Make sure to hire experienced professionals who are committed to your company's goals
- Develop scalable systems: Your systems need to be able to handle the increased volume of customers and transactions. This may require investing in technology and infrastructure to support your growth
- Monitor and measure your progress: Keep track of key metrics to measure your progress and identify areas for improvement. This will help you make data-driven decisions as you continue to scale your busines
Agile and plan-based approaches are two different methodologies used in software development. Agile development emphasizes flexibility and adaptability, while plan-based approaches rely on detailed planning and documentation. Both approaches have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which approach to use depends on the specific needs of the project.
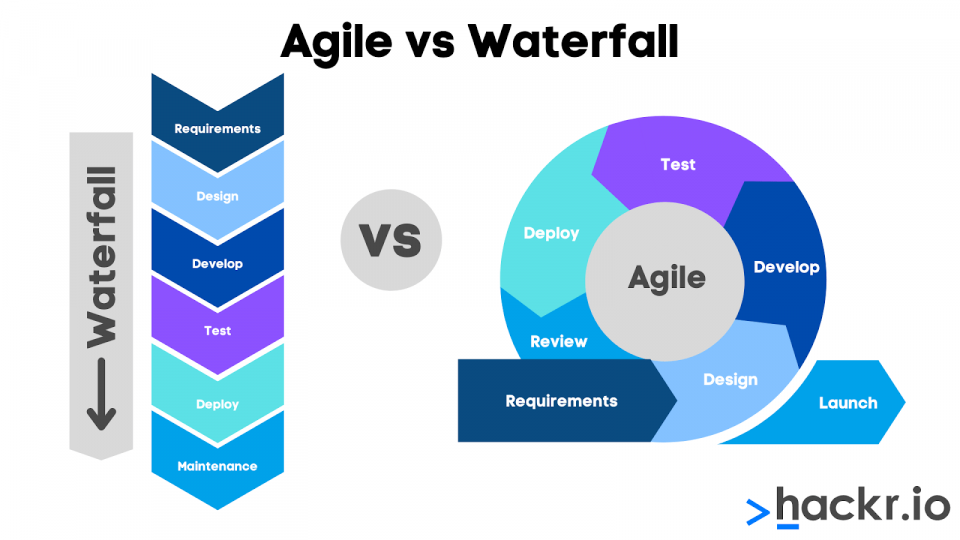
o Agile and Waterfall are two different software development methodologies that have been used for many years. Agile is an iterative and flexible approach that prioritizes collaboration and communication between team members and customers. Waterfall, on the other hand, is a linear approach that involves a sequential process of planning, development, testing, and deployment.
o Agile and Waterfall have different strengths and weaknesses, and each methodology is better suited to certain types of projects. Some organizations have attempted to combine elements of both methodologies to create a hybrid approach that takes advantage of the strengths of each methodology while minimizing their weaknesses
Overall, the success of any hybrid approach will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific needs of the project, the skillset and experience of the development team, and the preferences of the organization's stakeholders.