-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 56
Home
The Eclipse Graphical Editing Framework (GEF) provides framework components to create rich graphical Java client applications, integrated with the Eclipse Workbench UI or standalone, as well as Eclipse-integrated end-user tools.
The user documentation for the provided end-user tools can be accessed via the User Documentation section, while the developer documentation for the different framework components can be accessed via the Developer Documentation section.
You may also consult the Further Reading section for further additional information.
GEF provides a Graphviz DOT authoring component and a Tag Cloud renderer component, which may be used as end-user tools in an Eclipse environment. The user documentation for both end-user tools is provided in terms of a DOT User Guide and a Cloudio User Guide.


GEF is constituted of nine loosely coupled framework components, each broken down into one or more modules. Each module is technically realized through a pair of Eclipse bundle and related feature, each component accordingly through an SDK feature that bundles all module features with their respective sources, as well as a shared documentation feature.
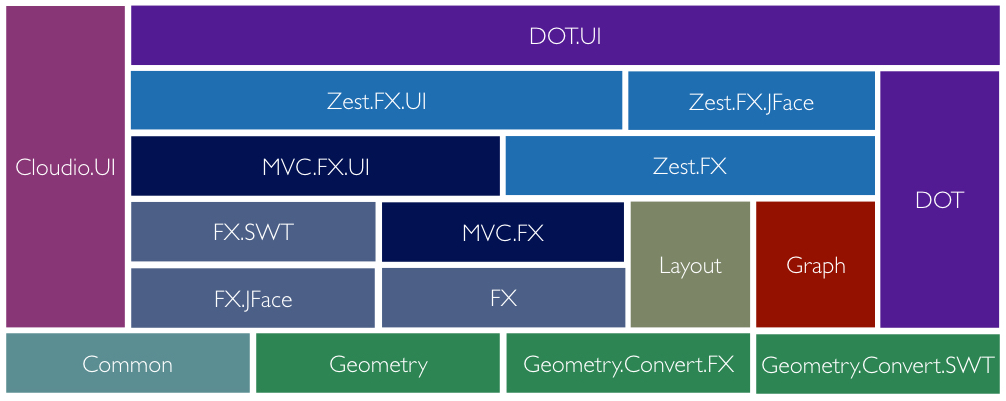
The naming of the components' modules indicate their UI-toolkit and Eclipse UI dependencies. That is, module names containing '.SWT', '.JFace', or '.FX' indicate a respective dependency to SWT, JFace, or JavaFX. Module names containing '.UI' indicate a dependency to the Eclipse UI. Please note that '.FX' is only used to indicate dependencies on the JavaFX UI toolkit and that JavaFX collections and properties are used throughout (except by Geometry and Cloudio).
-
Common - Provides basic abstractions and infrastructure used by (potentially) all other components, including an enhanced adaptable pattern and notification support.
-
Geometry (Geometry / Geometry.Convert.SWT / Geometry.Convert.FX) - Provides different abstractions (Euclidean, Projective, Planar) for 2D geometric calculations, and conversions of planar geometries (curves, shapes, poly shapes) to/from respective SWT, AWT, and JavaFX equivalents (as well as conversions between SWT and AWT geometries).
 Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed Geometry Examples.
Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed Geometry Examples.
- FX (FX / FX.SWT / FX.JFace) - Provides support for rendering Geometry-based shapes, as well as abstractions that are needed in the context of graphical editors and views, i.e. visual anchor implementations and a connection abstraction. Also enhances the JavaFX-SWT-Integration with forwarding of touch gestures and provides proper support for embedding SWT Controls via a generic adapter into a JavaFX scene graph (within the context of the JavaFX SWT integration).
 Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed FX Examples and FX SWT Examples.
Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed FX Examples and FX SWT Examples.
- Graph - Provides a simply, UI-independent data-model (Graph, Node, Edge) for representing directed graphs. Is used as data model by DOT and underlying visualization-model for Zest.
 Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed Graph Examples.
Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed Graph Examples.
- Layout - Provides layout algorithm implementations as well as a model facade to adapt layout model data for these algorithms.
 Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed Layout Examples.
Usage of API is demonstrated by undeployed Layout Examples.
- MVC (MVC / MVC.UI / MVC.FX / MVC.FX.UI) - Provides the core model-view-controller framework to build up graphical editors and views. Provides an UI toolkit independent and a JavaFX specific layer, as well as Eclipse-UI integration for both. Can be used to build standalone and Eclipse-integrated editors and views.
 Usage of API is demonstrated by a bundled MVC Logo Example, which is available as a standalone application, an Eclipse Workbench UI integrated view, as well as a JNLP-based web application.
Usage of API is demonstrated by a bundled MVC Logo Example, which is available as a standalone application, an Eclipse Workbench UI integrated view, as well as a JNLP-based web application.
- Zest (Zest.FX / Zest.FX.JFace / Zest.FX.UI) - Provides support for visualization of Graph-based models, integrating automated layout based on Layout. Internally built on FX and MVC.
 Usage of API is demonstrated by a bundled Zest Graph Example, which is available as a standalone application and an Eclipse Workbench UI integrated view, as well as undeployed Zest Examples and Zest JFace Examples.
Usage of API is demonstrated by a bundled Zest Graph Example, which is available as a standalone application and an Eclipse Workbench UI integrated view, as well as undeployed Zest Examples and Zest JFace Examples.
- DOT (DOT / DOT.UI) - Provides a basic GraphViz DOT-Editor (Xtext) as well as a Zest-based DOT-visualization.
 Usage of (still internal) API is demonstrated by undeployed DOT Examples.
Usage of (still internal) API is demonstrated by undeployed DOT Examples.
- Cloudio (Coudio.UI) - Provides support for visualizing tag clouds. Is based on SWT/JFace, integrated in the Eclipse UI, and will (at least for now) not be ported to JavaFX.
 Usage of (still internal) API is demonstrated by undeployed Cloudio UI Examples.
Usage of (still internal) API is demonstrated by undeployed Cloudio UI Examples.
Further information about the history and current plans, as well as on technical details can be inferred from the following presentations/articles/posts:
- Alexander Nyßen (2016): GEF4 Common Collections and Properties - Guava goes FX, ANy's Argument (Blog)
- Alexander Nyßen (2015): GEF4 - Sightseeing Mars, EclipseCon Europe, Ludwigsburg, 2015
- Alexander Nyßen (2015): GEF4 - Mission to Mars Accomplished!, ANy's Argument (Blog)
- Alexander Nyßen (2014): IAdaptable - GEF4's Interpretation of a Classic, ANy's Argument (Blog)
- Alexander Nyßen (2014): GEF4 - Our mission to Mars, EclipseCon Europe, Ludwigsburg, 2014
- Alexander Nyßen (2014): GEF4 - There's really something going on!, EclipseCon NA, San Francisco (CA), 2014
- Alexander Nyßen (2013): GEF4, RheinJug, Düsseldorf, 2013 , Video (German)
- Alexander Nyßen (2013): GEF4 SwtFX (Lightning Talk), EclipseCon Europe, Ludwigsburg, 2013
- Alexander Nyßen (2013): GEF4 - (Continue to) Share and Enjoy..., EclipseCon NA, Boston (MA), 2013
- Alexander Nyßen (2012): GEF4 - Share And Enjoy..., EclipseCon Europe, Ludwigsburg, 2012
- Alexander Nyßen (2012): GEF - Past, Present, and Future, EclipseCon NA, Reston (VA), 2012