Rabbit MQ is a popular industrial strength open source implementation of the AMQP messaging protocol for communicating with message queue middleware that runs on all major operating systems.
Rabbit MQ is built on the robust Erlang OTP platform which is a prerequisite for installing Rabbit MQ Server, both are downloadable at:
- Download and install Erlang OTP For Windows (vR16B03)
- Run the Rabbit MQ Server Windows Installer (v3.2.3)
The windows installer will download, install and run the Rabbit MQ Server Windows Service listening for AMQP clients at the default port: 5672.
To provide better visibility of the state of the Rabbit MQ Server instance it's highly recommended to enable Rabbit MQ's Management Plugin which you can do on the command line with:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\RabbitMQ Server\rabbitmq_server-3.2.3\sbin\rabbitmq-plugins.bat" enable rabbitmq_management
To see the new changes you need to restart the RabbitMQ Windows Service which can be done on the command line with:
net stop RabbitMQ && net start RabbitMQ
Or by restarting the service from the services.msc MMC applet UI:
- Open Windows Run dialog by pressing the Windows + R key:
- Select the RabbitMQ Windows Service and click the Restart Icon:
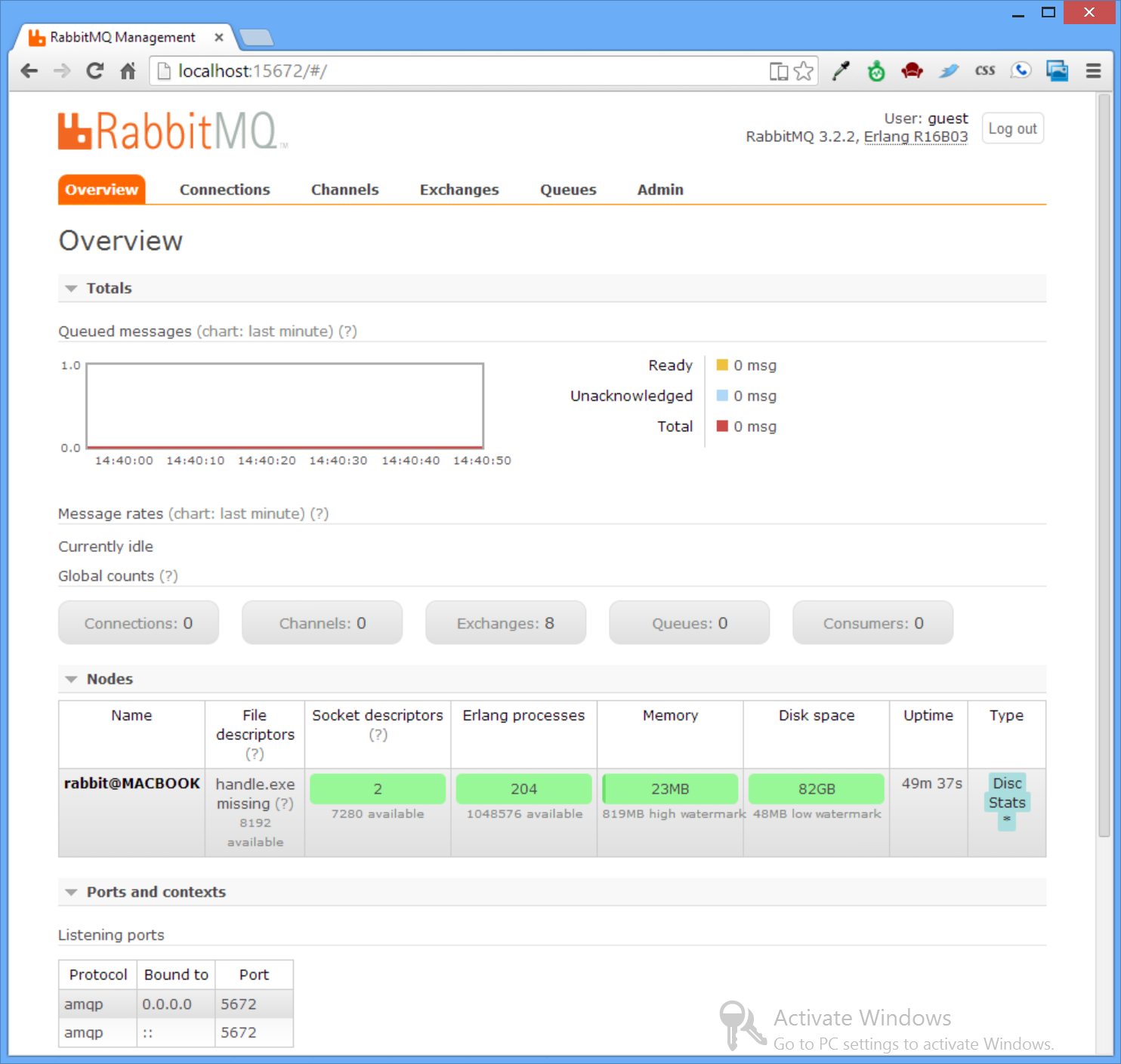
Once restarted, open the Rabbit MQ's management UI with a web browser at: http://localhost:15672 to see an overview of
the state of the Rabbit MQ server instance:
To use Rabbit MQ from .NET get Rabbit MQ's .NET client bindings from NuGet:
PM> Install-Package RabbitMQ.Client
With the package installed, we can go through a common scenario of sending and receiving durable messages with Rabbit MQ.
See RabbitMqTests.cs in this repo, for runnable samples of this walkthru below:
Firstly, you will need to register the type of Exchange and Queue before you can use them. To create a durable work queue, create a durable "direct" exchange and bind a durable queue to it, e.g:
const string ExchangeName = "test.exchange";
const string QueueName = "test.queue";
using (IConnection conn = rabbitMqFactory.CreateConnection())
using (IModel channel = conn.CreateModel())
{
channel.ExchangeDeclare(ExchangeName, "direct", durable:true, autoDelete:false, arguments:null);
channel.QueueDeclare(QueueName, durable:true, exclusive:false, autoDelete:false,arguments:null);
channel.QueueBind(QueueName, ExchangeName, routingKey: QueueName);
}In this example we'll also reuse the QueueName for the routing key which will enable directly sending messages to a specific queue.
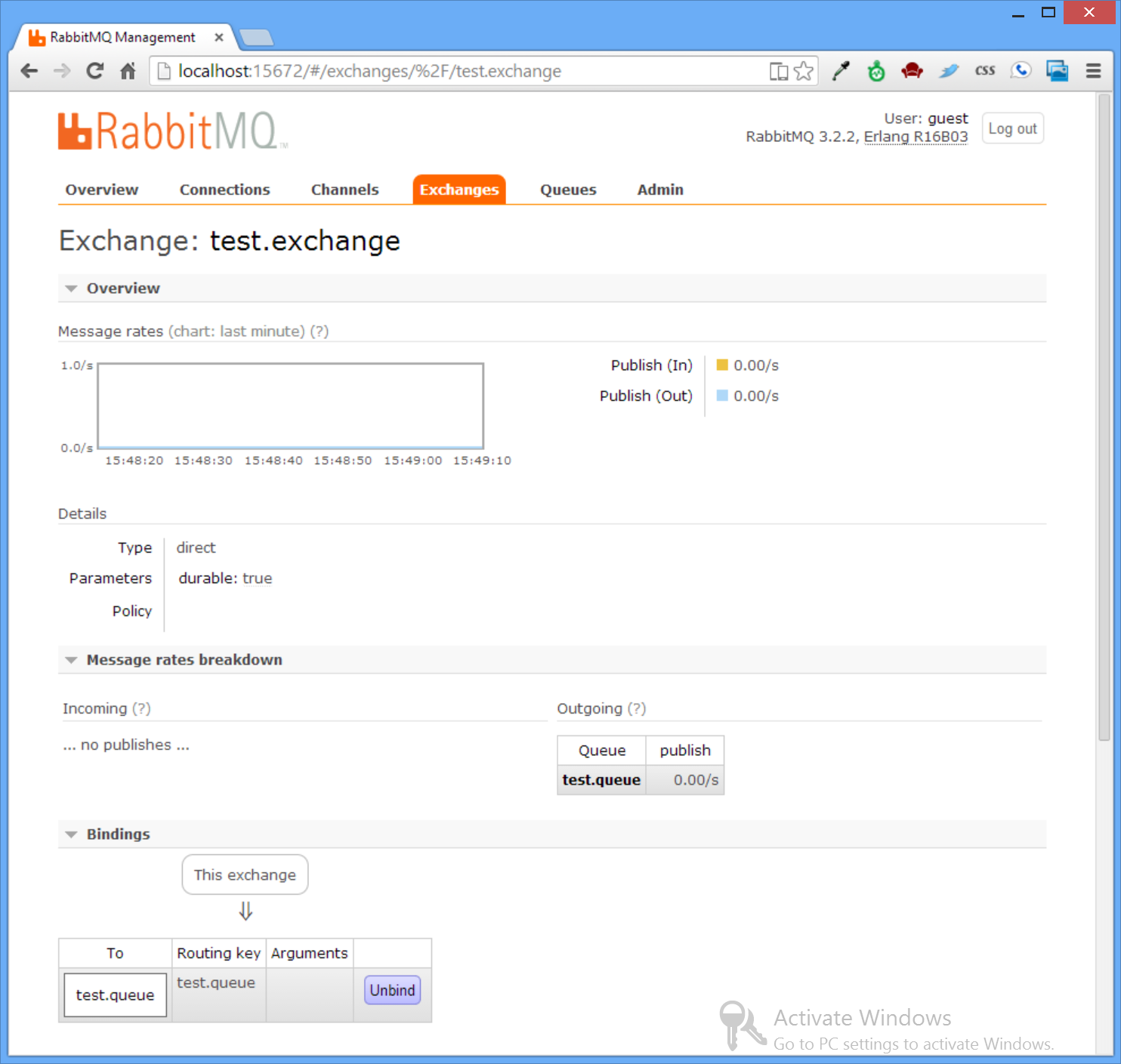
The registration code only needs to be run once to register and configure the Exchange and Queue we'll be using in the remaining examples. Once run, go back to the Management UI to see the new test.exchange Exchange with a binding to the newly created test.queue:
Once the exchange and queue is setup we can start publishing messages to it.
Rabbit MQ lets you send messages with any arbitrary byte[] body, for text messages you should send them as UTF8 bytes.
To ensure the message is persistent across Rabbit MQ Server starts you will want to mark the message as persistent as seen below:
var props = channel.CreateBasicProperties();
props.SetPersistent(true);
var msgBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello, World!");
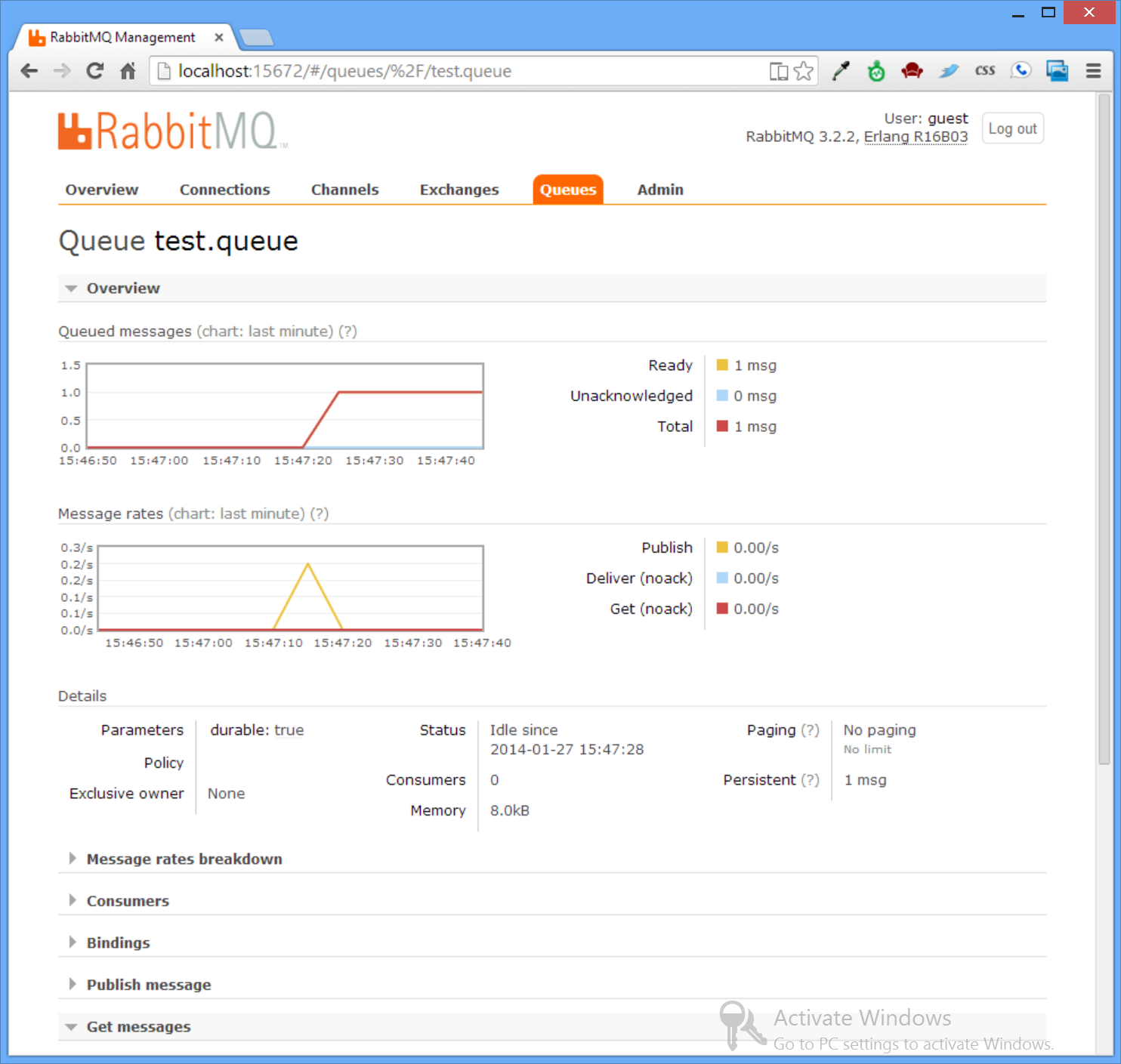
channel.BasicPublish(ExchangeName, routingKey:QueueName, basicProperties:props, body:msgBody);The routing key will ensure that a copy of the message is delievered to the test.queue which you can see in the Admin UI:
There are a couple of different ways you can read published messages from the queue, the most straightforward way is to use BasicGet:
BasicGetResult msgResponse = channel.BasicGet(QueueName, noAck:true);
var msgBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(msgResponse.Body);
msgBody //Hello, World!The noAck:true flag tells Rabbit MQ to immediately remove the message from the queue.
Another popular use-case is to only send acknowledgement (and remove it from the queue) after you've successfully accepted the message,
which can be done with a separate call to BasicAck:
BasicGetResult msgResponse = channel.BasicGet(QueueName, noAck:false);
//process message ...
channel.BasicAck(msgResponse.DeliveryTag, multiple:false);An alternate way to consume messages is via a push-based event subscription.
You can use the built-in QueueingBasicConsumer to provide a simplified programming model by allowing you to block on a
Shared Queue until a message is received, e.g:
var consumer = new QueueingBasicConsumer(channel);
channel.BasicConsume(QueueName, noAck:true, consumer:consumer);
var msgResponse = consumer.Queue.Dequeue(); //blocking
var msgBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(msgResponse.Body);
msgBody //Hello, World!The Shared Queue will block until it receives a message or the channel it's assigned to is closed which causes it to throw
an EndOfStreamException. With this, you can setup a long-running background thread to continually process multiple messages
in an infinite loop until the Queue is closed.
The sample below shows an example of this in action which publishes 5 messages on a separate thread before closing the channel the subscription is bound to causing an EndOfStreamException to be thrown, ending the subscription and exiting the loop:
using (IConnection conn = rabbitMqFactory.CreateConnection())
using (IModel channel = conn.CreateModel())
{
var consumer = new QueueingBasicConsumer(channel);
channel.BasicConsume(QueueName, noAck: true, consumer: consumer);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => {
var now = DateTime.UtcNow;
while (DateTime.UtcNow - now < TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5))
{
var props = channel.CreateBasicProperties();
props.SetPersistent(true);
var msgBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello, World!");
channel.BasicPublish(ExchangeName, routingKey:QueueName, basicProperties:props,
body:msgBody);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
channel.Close();
});
while (true)
{
try
{
var msgResponse = consumer.Queue.Dequeue(); //blocking
var msgBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(msgResponse.Body);
Console.WriteLine("Received Message: " + msgBody);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
catch (EndOfStreamException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Channel was closed, Exiting...");
break;
}
}
}The complete source of these examples are available in the stand-alone RabbitMqTests.cs.