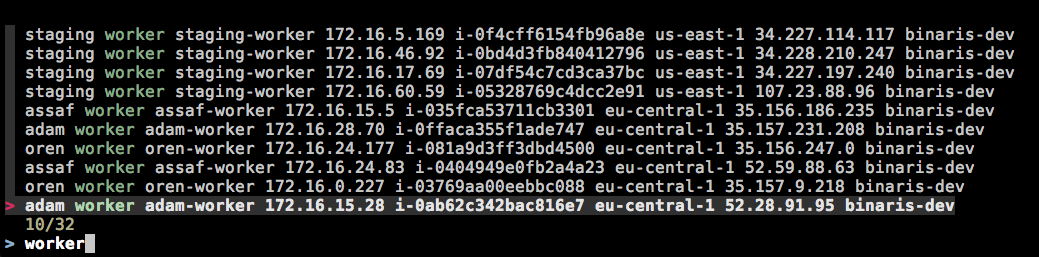
Type ec2 and you'll get an interactive fuzzy finder of all the instances in your EC2 account that have a public IP.
Narrow the search by typing the instance name, region, IP address or tag value.
ENTER to select an instance and SSH into it.
This script assumes your EC2 SSH private key exists in ~/.ssh/[key-name].pem.
Instead of calling DescribeInstance on demand (which is painfully slow), this project contains a Serverless Lambda function that fetches the entire list of instances every minute and caches it in S3.
The bucket is accessible only to the IAM group dev. Tweak this with your org's relevant group name as appropriate.
- You'll need FZF (the fuzzy finder).
- You'll also need the AWS CLI installed locally (
pip install awscli). - And of course your
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_IDenvars should be defined. - Clone this repo, and add its directory to your
$PATH. - The CLI assumes that your SSH keys exist in
~/.ssh/[KeyName].pem.
You'll see serverless installed, and permissions to manage Lambda in your AWS account.
npm install -g serverless
make deploy
You can tweak the following to suit your organization.
Look in servereless.yml for the custom object and tweak it.
- You should change the bucket name to include your organization's name. The default won't work for you, since bucket name are universal.
- Update the
BUCKETvariable in the fileec2as well.
- Update the
- You can change the IAM group name (default is
dev) that's allowed to see the list of instances this tool caches. - You can specify the list of tags that are relevant for finding instances in your account. The defaults are relevant to Binaris (
realm,service, ...), so you probably want to change this if you're not part of our team. :)
service: ec2-fzf
custom:
# Choose your bucket name here, it will be created for you.
bucket: ec2-cache.binaris.com
# Specify a list of relevant tags for finding instances (space separated)
tags: "realm service Name"
# SSH IAM Group (IAM group that should be allowed to use this tool)
group: "dev"
...
To deploy, run make deploy. It's a good idea to test locally first with make run_local.