Pharo offers many automatic refactoring tools. This tutorial presents what refactorings are, when and how to apply them and to show any possible inconvenience before using them.
Martin Fowler defines refactoring as: "... It is a disciplined technique to restructure an existing body of code, altering its internal structure without changing its external behavior" 1. This means that before carrying out any type of refactoring in the code it is important to have complete test coverage to demonstrate that the code behavior does not change during the refactoring process.
| Refactoring | Supported in |
|---|---|
| Rename | Package, Class, Method, Instance and Temporary Variable |
| Extract | Method and Temporary Variable |
| Remove | Package, Class, Method and Instance Variable |
| Copy | Class |
| Move | Class and method |
| Inline | Method and Temporary Variable |
| Push up / Push down | Method and Instance Variable |
| Replace | Method |
| Other refactorings | Class, Method, Instance and Temporary Variable |
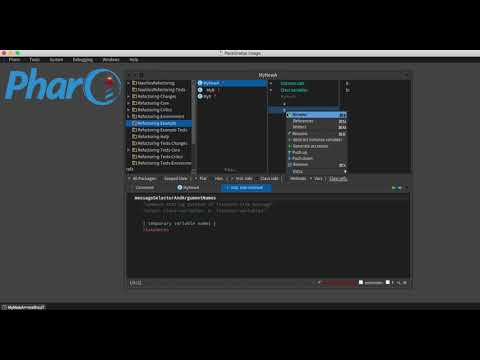
Renaming seems like a trivial refactoring however it can lead to many complications because this action can lead to involuntary changes of elements not related to the same name. The Pharo's rename tool has can minimize these errors.
- When the name is not descriptive enough.
- The name of the class / method / variable does not match what it really is.
- Something new was introduced that requires the existing code to have a new more specific name.
This refactoring can be done for classes, methods and variables.
- Select the
class / variable / method.- Press Meta+R or from the menu, select Rename.
- Fill the input of dialog with the new name and press Ok button.
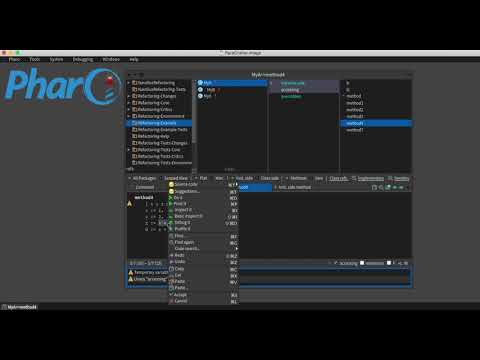
The extraction Pharo's tools allow developers to reshape their code when they have duplicate code or when they want to change the design.
Pharo can perform this refactoring to extract methods and extract temporal variables.
Example >> method
| a b c|
a := 1.
b := a + list size.
c := b + list size.Selecting list size on source code
Example >> method
| a b c d|
a := 1.
d := list size.
b := a + d.
c := b + d.
- Select the section of
source codeyou want to convert in temporary variable.- Press Meta+T or from the menu, select Source code.
- Select Extract temp option.
- Fill dialog's input with the name of the variable and press Ok button.
Example >> method
| a b c d|
a := 1.
b := 2.
c := a + b.
d := a + c.Selecting a + b on source code
Example >> method
| a b c d|
a := 1.
b := 2.
c := self add: a to: b.
d := self add: a to: c.
Example >> add: a to: b
^ a + b
- Select the section of the
source codeyou wish to extract.- Press Meta+T or from the menu, select Source code.
- Select Extract method option.
- Fill the input of dialog with the name of method and press Ok button.
Sometimes when the code is refactored it can end with code that is no longer used, or that should no longer be used. Therefore, it is necessary to eliminate all the unused code since this affects the developers who work and try to understand the source code.
This refactoring can be done for packages, classes, methods and variables.
- Select the
package / class / variable / method.- Press Meta+X
Many times we want to change or add some functionalities to our code, however this entails major changes which makes it dangerous to do it on the original class. That is why it may be necessary to copy the classes to have a backup in case you want to reverse the changes.
Currently this tool only applies to classes and to use it you just have to follow the following steps:
- Select
class.- Press Meta+C or from the menu, select Copy.
Move allows you to move classes and methods from one package to another, and move methods to class / instance side or even move them to another class.
- Select
class or classesthat you want to move.- Press Meta+MC or from the menu, select Refactorings and then select Move to package option.
- Select the package and press Ok button
- Select the
method or methodsto be moved.- Select Refactorings and then select Move to package option.
- Select the package and press Ok button.
- Select the
method or methodsto be moved.- Select Refactorings and then select Move to another class option.
- Select the new class for method(s) and press Ok button.
- Select the method or methods to be moved.
- Press Meta+TC, select Refactorings and then select Move to class side option.
- Select the
method or methodsto be moved.- Press Meta+TI, select Refactorings and then select Move to instance side option.
Inline refactoring allows you to reverse extract refactoring of a method or temporary variable.
Inline variables replaces the use of redundant variables with its initializer.
Example >> method
| number b |
number := anotherClass value.
b := 3 + number.Selecting number temp on source code
Example >> method
| b |
b := 3 + anotherClass value.
- Select the
temporary variablein the source code.- Press Meta+T or from the menu, select Source code.
- Select Inline temp option.
The results of inline method place methods's body in the body of the method where we select its call.
Example >> method
| a b c d|
a := 1.
b := 2.
c := self add: a to: b.
d := self add: a to: c.
Example >> add: a to: b
^ a + bSelecting self add: a to: b. on source code
Example >> method
| a b c d|
a := 1.
b := 2.
c := a + b.
d := a + c.
- Select the
call to methodin the source code.- Press Meta+T or from the menu, select** Source code**.
- Select Inline method option.
This refactoring replaces all calls to the method selected from its class by the body of its implementation, in addition to the method itself being eliminated.
- Select the
method.- From the menu, select Refactorings.
- Select Inline senders option.
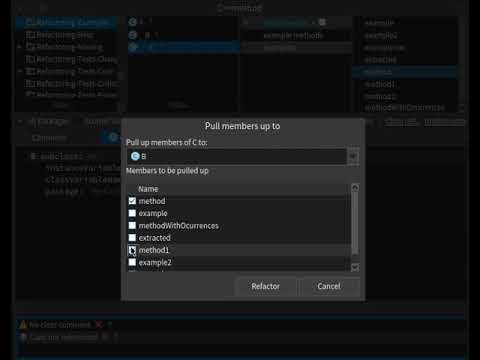
Gets rid of duplicate code. If you need to make changes to a method, it’s better to do so in a single place than have to search for all duplicates of the method in subclasses; this refactoring technique can also be used if, for some reason, a subclass redefines a superclass method but performs what’s essentially the same work.
- Select the method
- Select Meta+PU or from the menu, select Refactorings and then select Push up option.
Improves class coherence. A method is located where you expect to see it. For example if you see that a method is needed by more than one subclass, but not all of them, it may be useful to create an intermediate subclass and move the method to it. This allows avoiding the code duplication that would result from pushing a method down to all subclasses.
- Select the method
- Select Meta+PD or from the menu, select Refactorings and then select Push down option.
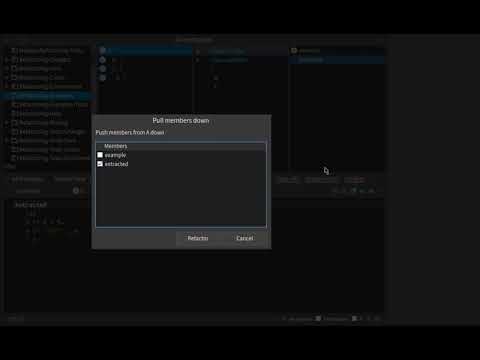
In the same way as in the methods you can perform the push up and push down refactorings on the instance variables
- Select the
variable.- From the menu select Push up option.
- Select the
variable.- From the menu select Push down option.
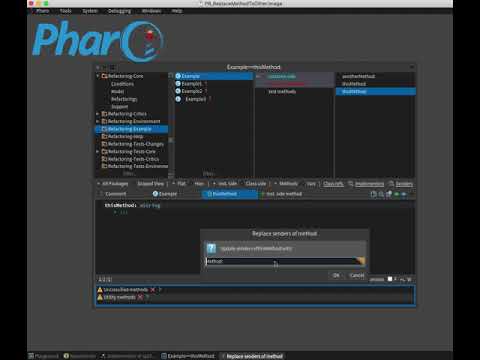
Replace senders helps us to change the senders of the selected method to the name of another method that we want, considering that the method with which we replace it must have the same number of arguments as the original.
- Select the
method.- From the menu, select Refactorings.
- Select Replace senders option.
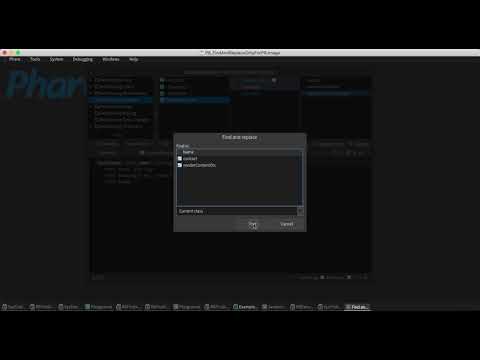
Find and replace helps us when we have duplicate code, if this refactoring consists in selecting a method and looking for the occurrences of your body in a range of methods that is selected.
Example >> textInputOn: html withName: aString andSymbol: aSymbol
html text: aString.
html textInput on: aSymbol of: self contact.
html break
Example >> renderContentOn: html
html
form: [ html text: 'Name:'.
html textInput on: #name of: self contact.
html break.
html text: 'Email address:'.
html textInput on: #emailAddress of: self contact.
html break.
html text: 'Example:'.
html textInput on: #example of: self contact.
html break]Example >> textInputOn: html withName: aString andSymbol: aSymbol
html text: aString.
html textInput on: aSymbol of: self contact.
html break
Example >> renderContentOn: html
html
form: [ self textInputOn: html withName: 'Name:' andSymbol: #name.
self textInputextInputOnt: html withName: 'Email address:' andSymbol: #emailAddress.
self textInputOn: html withName: 'Example:' andSymbol: #example ]
- Select the
method.- From the menu, select Refactorings.
- Select Find and replace option.
This refactoring generates the get and set messages of the instance variables, can be used from the class and the variables.
Object subclass: #Example
instanceVariableNames: 'a'
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'Object subclass: #Example
instanceVariableNames: 'a'
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
Example >> a
^ a
Example >> a: anObject
a := anObject
- Select the
classthat you want generate accessors.- Select Meta+GA or from the menu, select Generate accessors option.
- Select the
variable(s)that you want generate accessors.- From the menu, select Generate accessors option.
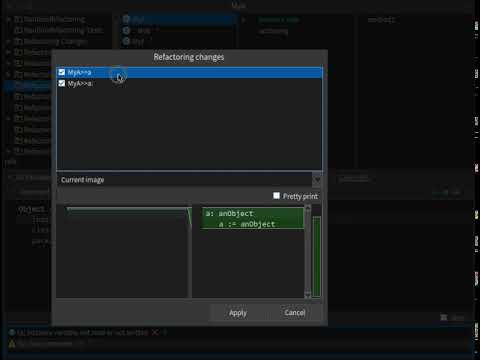
Generate a new subclass of a class.
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyB
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'</pre>Selecting the MyA class
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyB
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyC
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
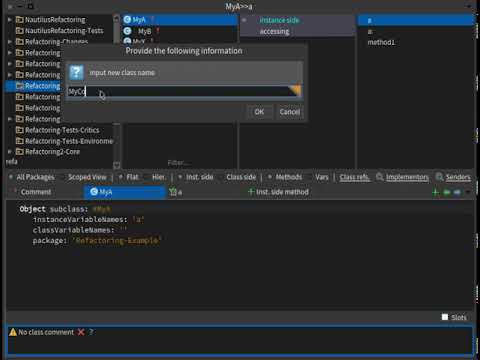
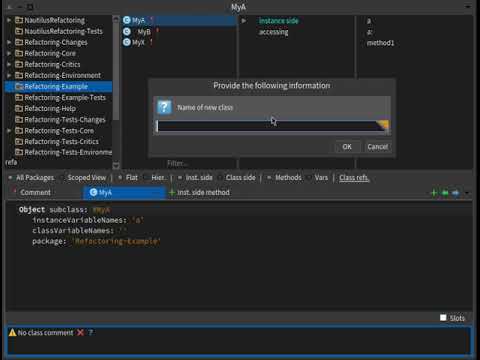
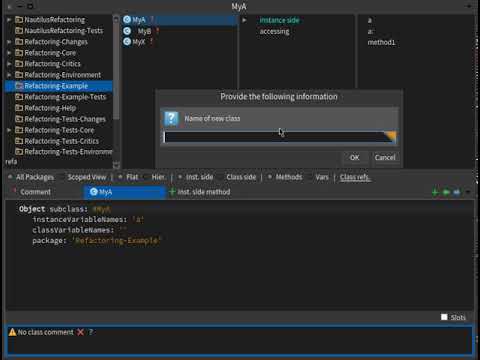
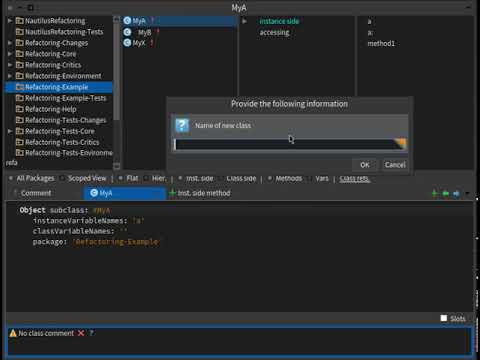
- Select
class.- From the menu, select Refactorings and then select New subclass option.
- Fill the dialog's input with new class's name.
Generate a new subclass of a class between the class and its subclasses. This refactoring is useful when we have to specialize some classes.
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyB
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'Selecting the MyA class
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyC
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyC subclass: #MyB
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
- Select
class.- From the menu, select Refactorings and then select Insert subclass option.
- Fill the dialog's input with new class's name.
Generate a new superclass of a class between the class and its superclass. This refactoring is useful when we must generalize to avoid the redundancy of the classes.
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyB
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'Selecting the MyB class
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA subclass: #MyC
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyC subclass: #MyB
instanceVariableNames: ''
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
- Select
class.- From the menu, select Refactorings and then select Insert subclass option.
- Fill the dialog's input with new class's name.
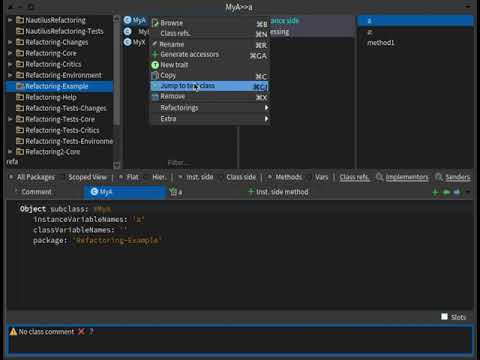
This seems trivial, however this command offers us a shortcut to automatically create a class for our tests or go to tests class.
- Select
class.- Press Meta+GJ or from the menu, select Jump to test class.
This refactoring generate accessors methods if they don't exist and replace every direct access to class variables with accessor methods.
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: 'a'
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
MyA >> method
|result|
a := self initializeVariable.
result := a value.Selecting the a variable
Object subclass: #MyA
instanceVariableNames: 'a'
classVariableNames: ''
package: 'Refactoring-Example'
Example >> a
^ a
Example >> a: anObject
a := anObject
MyA >> method
|result|
self a: self initializeVariable.
result := self a value.
- Select
variable.- From the menu, select Abstract instance variables option.
[1] Martin Fowler, Refactoring - Improving the Design of Existing Code