| slug | id | title | date | comments | tags | description | references | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
49-facebook-tao |
49-facebook-tao |
How Facebook Scale its Social Graph Store? TAO |
2018-09-18 22:50 |
true |
|
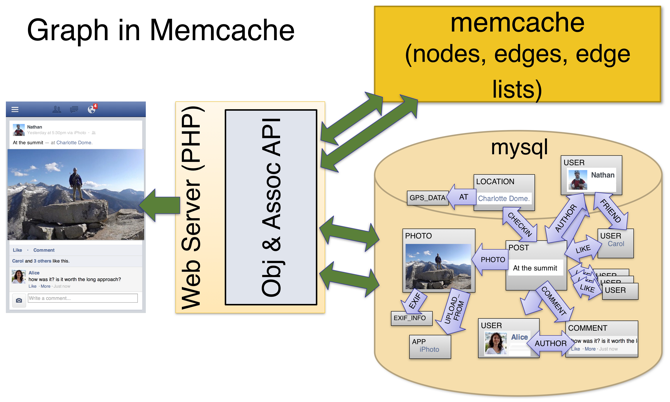
Before Tao, Facebook used the cache-aside pattern to scale its social graph store. There were three problems: list update operation is inefficient; clients have to manage cache and hard to offer read-after-write consistency. With Tao, these problems are solved. |
Before TAO, use cache-aside pattern
Social graph data is stored in MySQL and cached in Memcached
3 problems:
- list update operation in Memcached is inefficient. cannot append but update the whole list.
- clients have to manage cache
- Hard to offer ==read-after-write consistency==
To solve those problems, we have 3 goals:
- online data graph service that is efficiency at scale
- optimize for read (its read-to-write ratio is 500:1)
- low read latency
- high read availability (eventual consistency)
- timeliness of writes (read-after-write)
- Objects (e.g. user, location, comment) with unique IDs
- Associations (e.g. tagged, like, author) between two IDs
- Both have key-value data as well as a time field
-
Efficiency at scale and reduce read latency
- graph-specific caching
- a standalone cache layer between the stateless service layer and the DB layer (aka Functional Decomposition)
- subdivide data centers (aka Horizontal Data Partitioning)
-
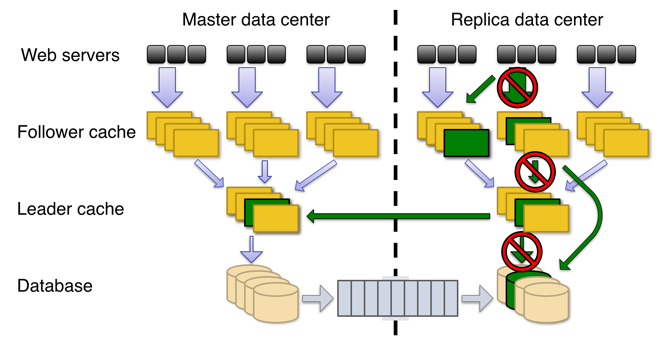
Write timeliness
- write-through cache
- follower/leader cache to solve thundering herd problem
- async replication
-
Read availability
- Read Failover to alternate data sources
- MySQL databases → durability
- Leader cache → coordinates writes to each object
- Follower caches → serve reads but not writes. forward all writes to leader.
Read failover