An incredibly simple and lightweight tool for preparing packaging for the publishing process.
- Rock solid infrastructure. Builds on well maintained Acorn, Babel and Rollup under the hood.
- Supports multiple entries (cli, client, server, library, ...) - even multiple binary entries.
- Creates multiple output formats (ESM, CommonJS, UMD, ...)
- Exports TypeScript definitions (respects
typesdefinition inpackage.json). - Lazy JSX support (powered by a custom Rollup plugin) to keep JSX intact while bundling. Major benefit for e.g. UI components: This moves decision over JSX debug capabilities or optimization settings into the application space.
- Rebases assets to the bundled output destination. Say hello to images, web fonts, and more. It also supports assets references in CSS/SCSS.
- Includes a watch mode for live development. Very useful for developing libraries.
- New: Deep bundling allows Webpack-like bundling where content from
node_modulesin bundled as well. By default only local code is bundled. - Supports auto-executing binaries. This is super useful when dealing with development web servers for example.
- Offers builds by compressing bundles with Terser as needed (for files with
.minin their name). - Prints out generated file sizes of all bundles.
- Injects common env-variables into the build (
BUNDLE_{NAME|VERSION|TARGET}). AlsoNODE_ENVfor all UMD builds. - Executes Babel with an environment based on
NODE_ENVbut with additional data from thetarget(e.g.node,liborcli) and the outputformat(e.g.esm,cjs) - Supports JSON out of the box and inlines the serialized content into the bundle.
For Preppy itself installation is done by executing one command.
$ npm install -D preppyDepending on your transpiling needs you need Babel with the requires presets/plugins. This is nothing extra to install typically as you might have these things in-place already. Example:
$ npm install -D @babel/plugin-transform-runtime @babel/preset-env @babel/preset-typescript @babel/core
$ npm install @babel/runtime core-jsPlease note: Since Preppy v11 Node v16 is the minimum required version!
As transpiling happens via Babel you have to install the Babel Core, Plugins and Presets on your own. You also need to use a standard Babel Configuration inside your package.
Example babel.config.json:
{
"plugins": [
[
"@babel/transform-runtime",
{
"corejs": 3
}
]
],
"presets": [
[
"@babel/env",
{
"useBuiltIns": "usage",
"corejs": 3
}
],
[
"@babel/typescript",
{
"allExtensions": true,
"isTSX": true
}
]
]
}Note: env gets a lot more depth when working with Preppy. It's actually set to this: ${env}-${target}-${format} e.g. "development-browser-esm". This gives you more control e.g. more setting up targets for Browserslist.
Note: Leave out the "@babel/typescript" when you do not need TypeScript transpiling.
Note: Please disable transform-runtime for all UMD builds as UMD is better working when only clean named imports are kept external.
To keep things simple and reduce to number of dependencies, Preppy uses your local Babel configuration to transpile your code. You have to make sure that all required Babel mechanics, presets and plugins are installed locally to your project.
Preppy also support extracting TypeScript types into .d.ts files to make them usable by users of your libraries. The generated code is still transpiled by Babel. The standard typescript CLI is used for extracting the types.
These are the typical entry points looked up for by Preppy:
src/index.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}
We made the experience that this works pretty fine for most projects. If you have the need for more input files, please report back to us.
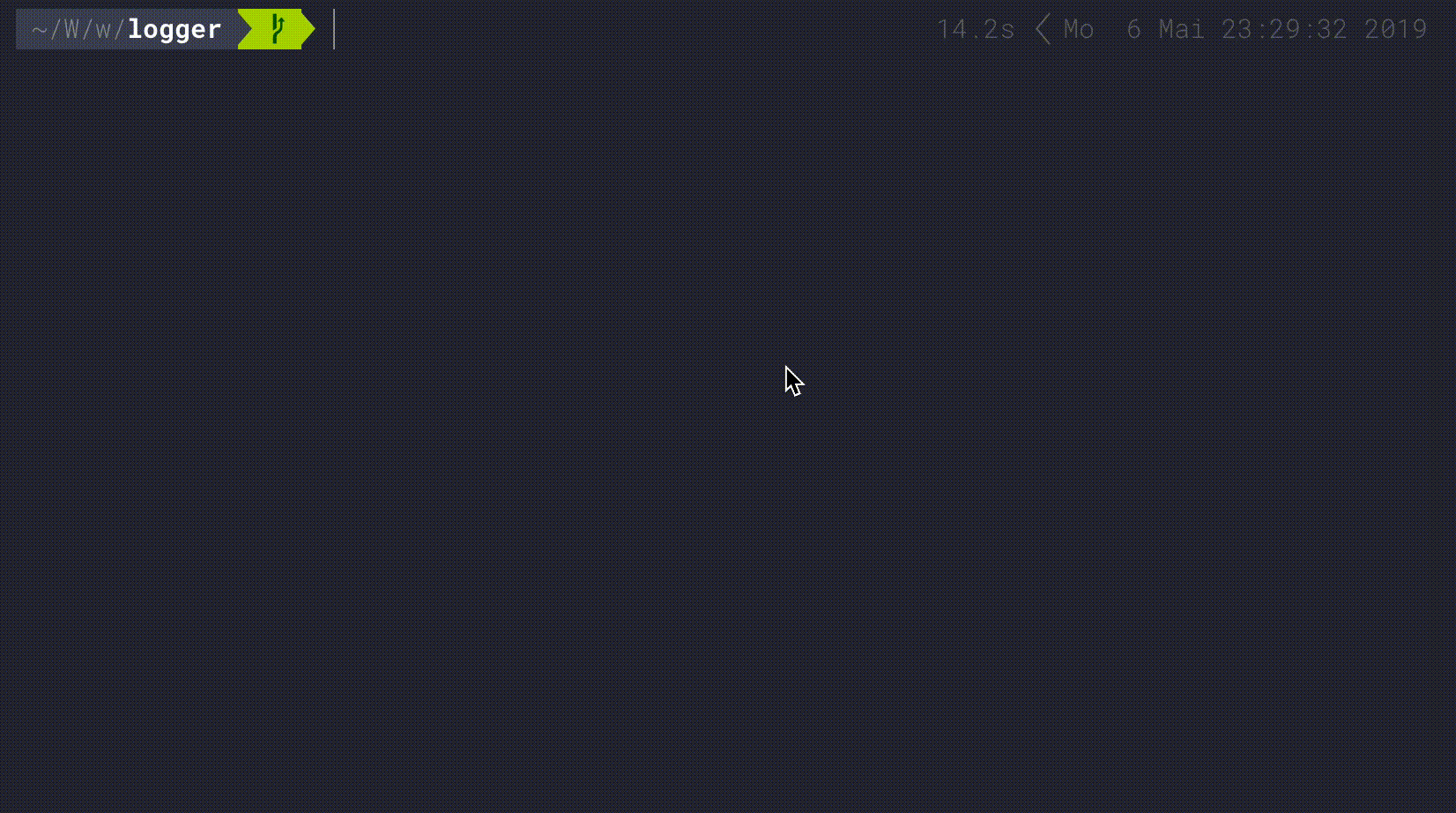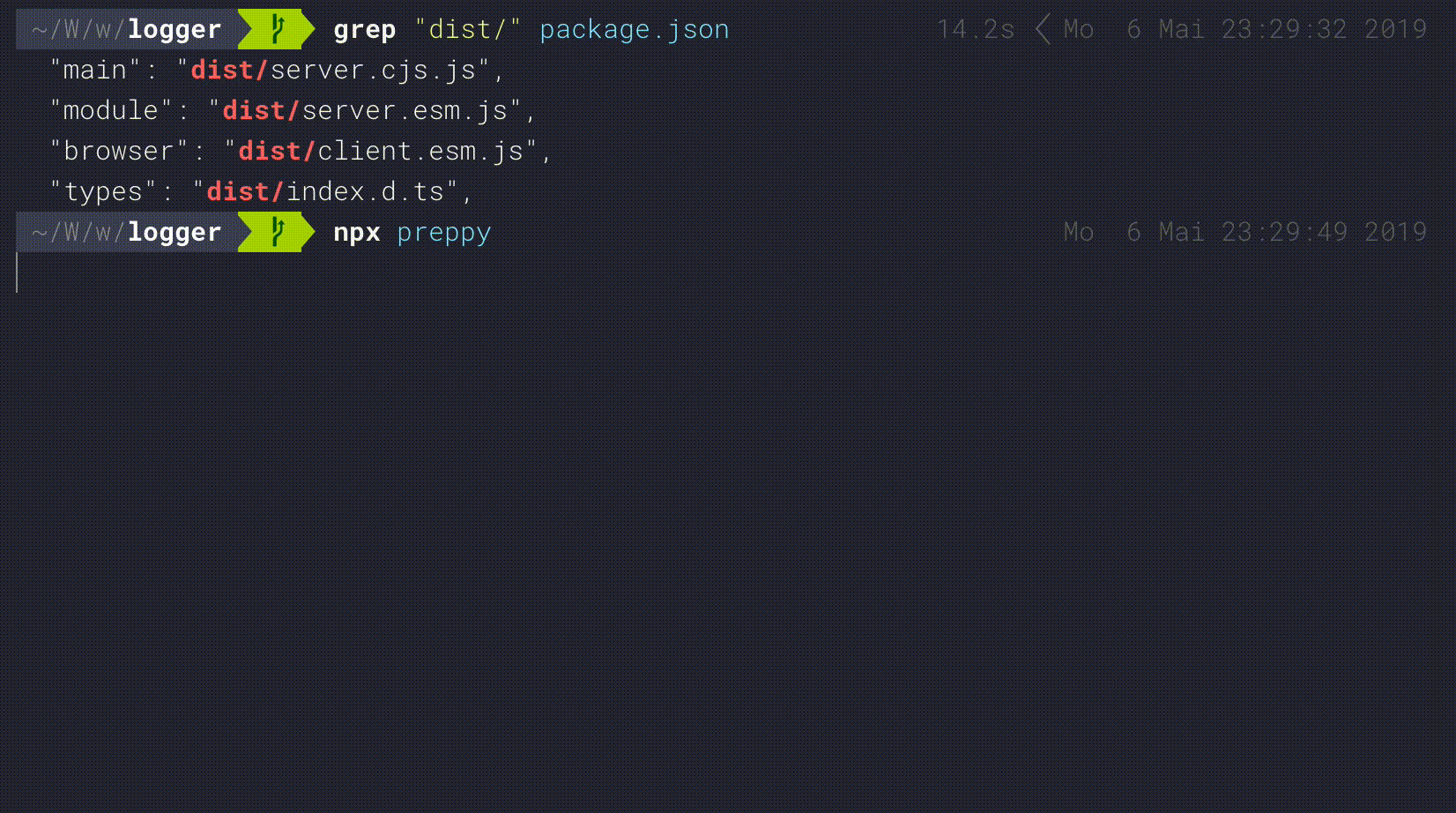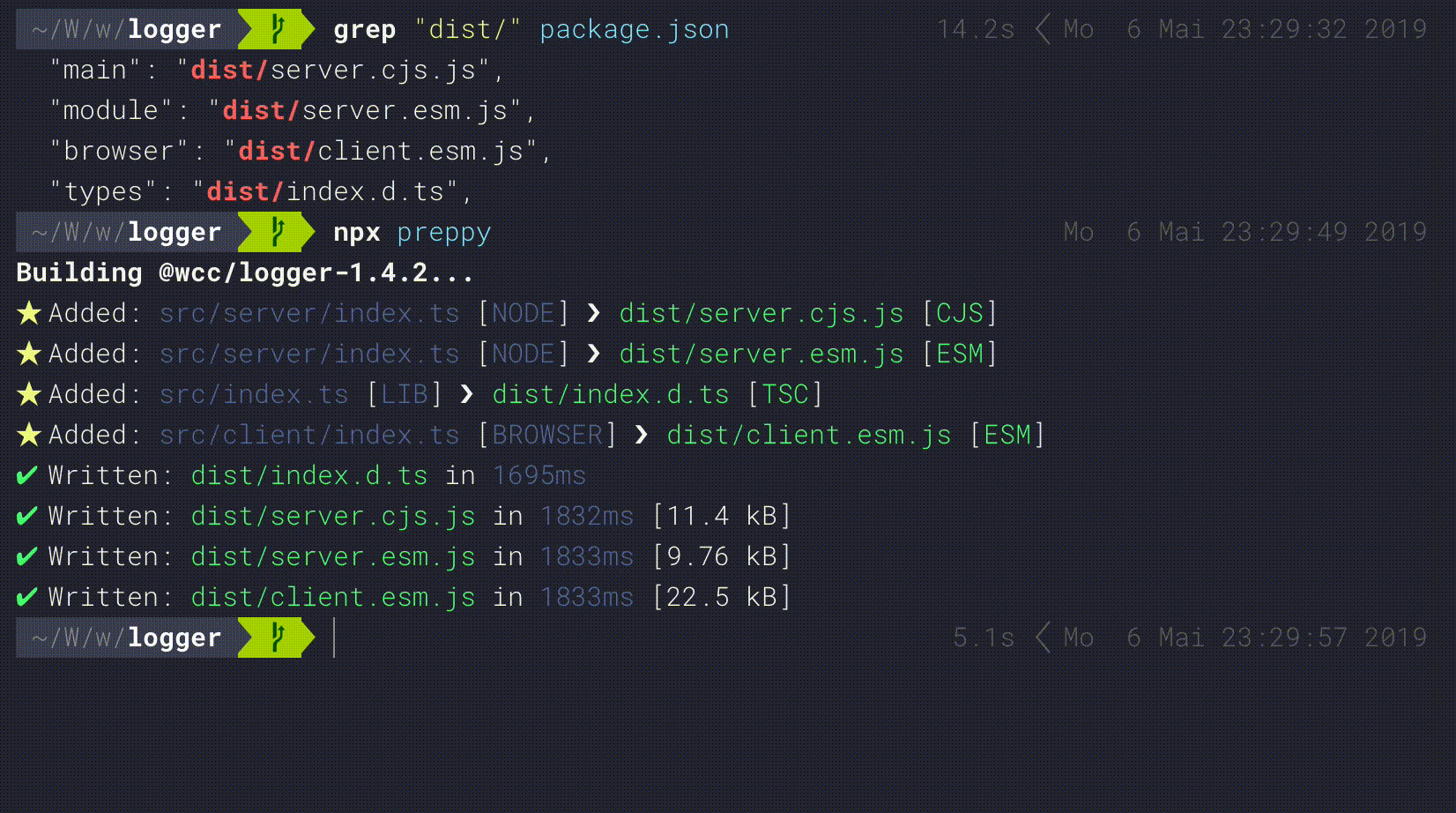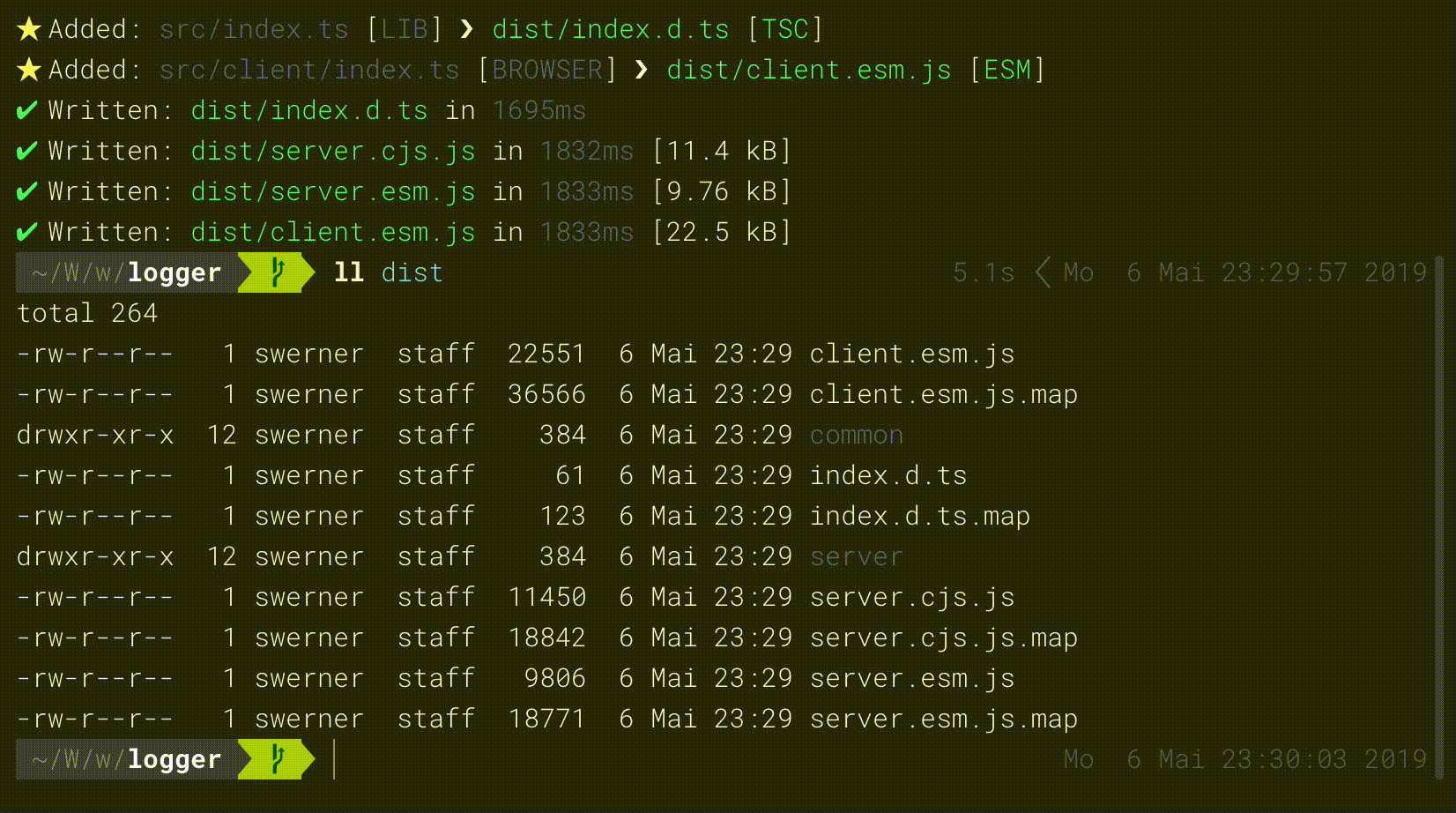
Preppy produces exports of your sources depending on the entries of your packages package.json. It supports building for ESM, CommonJS and UMD. Just add the relevant entries to the package configuration.
- CommonJS:
main - EcmaScript Modules (ESM):
module: New module standard for optimal tree shaking of bundlers. - Universal Module Definition (UMD):
umd+unpkgfor delivering a minified bundle to the CDN.
Basic Example:
{
"name": "mypackage",
"main": "lib/index.cjs.js",
"module": "lib/index.esm.js",
"unpkg": "lib/index.umd.min.js"
}For exporting types with TypeScript you should add a types entry to your package.json as well:
{
"name": "mypackage",
"main": "lib/index.cjs.js",
"module": "lib/index.esm.js",
"unpkg": "lib/index.umd.min.js",
"types": "lib/index.d.ts"
}Additionally Preppy is capable in generating for binary targets e.g. CLI tools. Not just one, but each of the one listed in the bin section of your package.json.
The following example generates a mycli binary which is generated from the matching source file.
Binaries are generally generated from one of these source files:
src/{name}.{js|ts}src/cli/{name}.{js|ts}src/cli.{js|ts}src/cli/index.{js|ts}
Example Configuration:
{
"name": "mycli",
"bin": {
"mycli": "bin/mycli"
}
}Preppy also has some support for building universal libraries. While for most projects it's completely feasible to have one library for both NodeJS and browsers (or only for one of these), others might want (slightly) different packages to browsers and NodeJS.
The only difference here is that you have to define a new browser definition inside your package.json. Also
the input fields differ from the one of the normal libraries or binaries:
src/client.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}src/browser.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}src/client/index.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}src/browser/index.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}
For the NodeJS part you can use any of the following entries:
src/node.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}src/server.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}src/node/index.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}src/server/index.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}
Example Configuration:
{
"name": "mylib",
"browser": "lib/browser.esm.js",
"unpkg": "lib/browser.umd.js",
"main": "lib/node.cjs.js",
"module": "lib/node.esm.js"
}Note: The bundle under browser is a ESM bundle which is ideally used by bundlers like Webpack or Parcel.
Note: When any of these files exists, we use prefer it over the normal library for the unpkg entry in package.json as well.
Preppy injects these environment values into your code base:
process.env.BUNDLE_NAME: Extractednamefield frompackage.json.process.env.BUNDLE_VERSION: Extractedversionfield frompackage.json.process.env.BUNDLE_TARGET: One of the supported targets. Eithernode,browser,liborcli.process.env.BUNDLE_ENV: Environment name. Typical values aredevelopment,productionandtest. Use this instead ofNODE_ENVto inject the current value at bundle time.
These values are injected into your code base by replacing the original instance.
For UMD bundles we also replace:
process.env.NODE_ENV: Same asBUNDLE_ENV- mainly replaced as this is a pretty common standard field which can't be resolved in browsers.
Notes:
- It only works correctly when you use the whole identifier.
- In verbose mode we are logging the environment settings configured.
This is a special mode for Preppy. Where it normally targets build steps for libraries this
so-called deep mode compares to default behavior of Parcel or Webpack. It inlines code which is defined in node_modules as much as possible. The logic uses information from the package.json file and only bundles dependencies which are defined in devDependencies and not in dependencies. All this combined with the tree-shaking capabilities of the underlying Rollup results into monolithic easy to deploy code with minimal external runtime dependencies. To enable deep mode pass the --deep flag on the CLI.
Note: Using this functionality may require a bit of trial and error with the dependencies or devDependecies listed in the package.json. There are a few packages that cause warnings and errors when processed with Preppy's Rollup engine. In these cases, these packages usually need to be kept external and remain as a entry oin dependencies. From experience, this problem mostly affects packages that have been implemented very close to infrastructural properties of NodeJS.
Preppy comes with a binary which can be called from within your scripts section
in the package.json file.
"scripts": {
"prepare": "preppy"
}There is also some amount of parameters you can use if the auto detection of your library does not work out correctly.
Usage
$ preppy
Options
--entry-lib Entry file for Library (universal) target [auto]
--entry-browser Entry file for Browser target [auto]
--entry-node Entry file for NodeJS target [auto]
--entry-cli Entry file for CLI target [auto]
--root The root folder of your project [auto]
--output Override output folder (and package.json entries) [auto]
--watch Keeps running and rebuilds on any change [false]
--limit Limits the current build scope to files matching [null]
--deep Produces a deep bundle which includes dependencies inline [false]
--exec Executes the generated binary after creation [false]
--notify Enables notifications (useful when used in watch mode) [false]
--no-sourcemap Disables creation of a source map file during processing [false]
-v, --verbose Verbose output mode [false]
-q, --quiet Quiet output mode [false]
Apache License; Version 2.0, January 2004
Copyright 2016-2022
Sebastian Software GmbH