Unofficial AKS Cheat Sheet
Official AKS FAQ is here
- AKS Cheat Sheet
Reference: az aks
-
Get k8s available versions
az aks get-versions --location $REGION -o table KubernetesVersion Upgrades ------------------- ------------------------ 1.12.7 None available 1.12.6 1.12.7 1.11.9 1.12.6, 1.12.7 1.11.8 1.11.9, 1.12.6, 1.12.7 1.10.13 1.11.8, 1.11.9 1.10.12 1.10.13, 1.11.8, 1.11.9 1.9.11 1.10.12, 1.10.13 1.9.10 1.9.11, 1.10.12, 1.10.13 -
Get Available VM size list for AKS
az vm list-skus --location $REGION -o table -
To configure kubectl to connect to your Kubernetes cluster
az aks get-credentials --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER_NAME
-
Open k8s Dashboard
az aks browse --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER_NAME
If you're using RBAC enabled kubernetes cluster, you need to configure Service Account and RoleBinding in order to make Dashbaord work.
# Here is a way to give full privilege (role: cluster-admin) to the Dashboard’s Service Account kubernetes-dashboard $ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: kubernetes-dashboard labels: k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: kubernetes-dashboard namespace: kube-system EOF
If you want to configure more granular privilege to the Dashboard's service account instead of giving full privilege(role: cluster-admin), please follow "Option 1: Access to Dashboard with your Service Account" in this article.
In addition, please see Kubernetes dashboard with Azure Container Service (AKS) to know about basic dashboard operations.
-
Get AKS Cluster info
az aks show --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER_NAME -o table Name Location ResourceGroup KubernetesVersion ProvisioningState Fqdn -------- ---------- --------------- ------------------- ------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------- azconlab japaneast RG_azconlab 1.12.6 Succeeded azconlab-rgazconlab-87c7c7-97ac1e80.hcp.japaneast.azmk8s.io
-
Get Node Resource Group
az aks show --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER_NAME --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv
-
Scale AKS Cluster nodes
az aks scale --name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \ --node-count $NODE_COUNT
-
Upgrade AKS Cluster version
az aks upgrade --name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \ --kubernetes-version $KUBERNETS_VERSION # Check which Kubernetes releases are available for upgrade for your AKS cluster az aks get-upgrades --name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP -o table
-
Enable Add-on
- Enable Azure Monitor for Containers
OMS_WORKSPACE_RESOURCE_ID="/subscriptions/87c7c7f9-0c9f-47d1-a856-1305a0cbfd7a/resourceGroups/DefaultResourceGroup-EJP/providers/Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/DefaultWorkspace-77c7c7f9-0c9f-47d1-a856-1305a0cbfd7a-EJP" az aks enable-addons -a monitoring \ --name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \ --workspace-resource-id $OMS_WORKSPACE_RESOURCE_ID
- Enable HTTP Application Routing
az aks enable-addons --addons http_application_routing \ --name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
- Enable Azure Monitor for Containers
-
Check egress IP
kubectl run -it --rm runtest --image=debian --generator=run-pod/v1 pod> apt-get update && apt-get install curl -y pod> curl -s checkip.dyndns.org
Reference: az acr
-
Create an Azure Container Registry
az acr create --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $ACR_NAME --sku Basic
SKU:
Basic,Standard,Premium,Classic -
Get ACR list
az acr list -o table
-
Get ACR Detail
az acr show -n $ACR_NAME -g $RESOURCE_GROUP # Get only ACR ID az acr show -n $ACR_NAME -g $RESOURCE_GROUP --query "id" -o tsv
-
Show ACR Repositories
# Show list of repositories az acr repository list -n $ACR_NAME -o table Result ---------------- azure-vote-back azure-vote-front testcontainer food-recognition web-front # Show the detail of a repository az acr repository show -n $ACR_NAME --repository $REPO_NAME -o table CreatedTime ImageName LastUpdateTime ManifestCount Registry TagCount ---------------------------- ------------ ---------------------------- --------------- --------------------- ---------- 2019-01-17T05:19:36.6227367Z captureorder 2019-04-05T04:50:34.8244574Z 5 myazconacr.azurecr.io 5 # Show list of tags in a repository az acr repository show-tags -n $ACR_NAME --repository $REPO_NAME -o table Result -------- 21 32 55 56 59
-
Login to ACR
az acr login --name $ACR_NAME # Alternatively login with docker command ACR_LOGIN_SERVER=$ACR_NAME.azurecr.io docker login $ACR_LKOGIN_SERVER -u $ACR_USER -p $ACR_PASSWORD
-
ACR Task - Build
You can queues a quick build, providing streamed logs for an Azure Container Registry by using az acr build
az acr build --registry $ACR_NAME --image [CONTAINER_NAME:TAG] [SOURCE_LOCATION] ## More usages are: #Queue a local context (folder), pushed to ACR when complete, with streaming logs. az acr build -t sample/hello-world:{{.Run.ID}} -r MyRegistry . # Queue a local context, pushed to ACR without streaming logs. az acr build -t sample/hello-world:{{.Run.ID}} -r MyRegistry --no-logs . # Queue a local context to validate a build is successful, without pushing to the registry using the --no-push parameter. az acr build -t sample/hello-world:{{.Run.ID}} -r MyRegistry --no-push . # Queue a local context to validate a build is successful, without pushing to the registry. Removing the -t parameter defaults to --no-push az acr build -r MyRegistry .
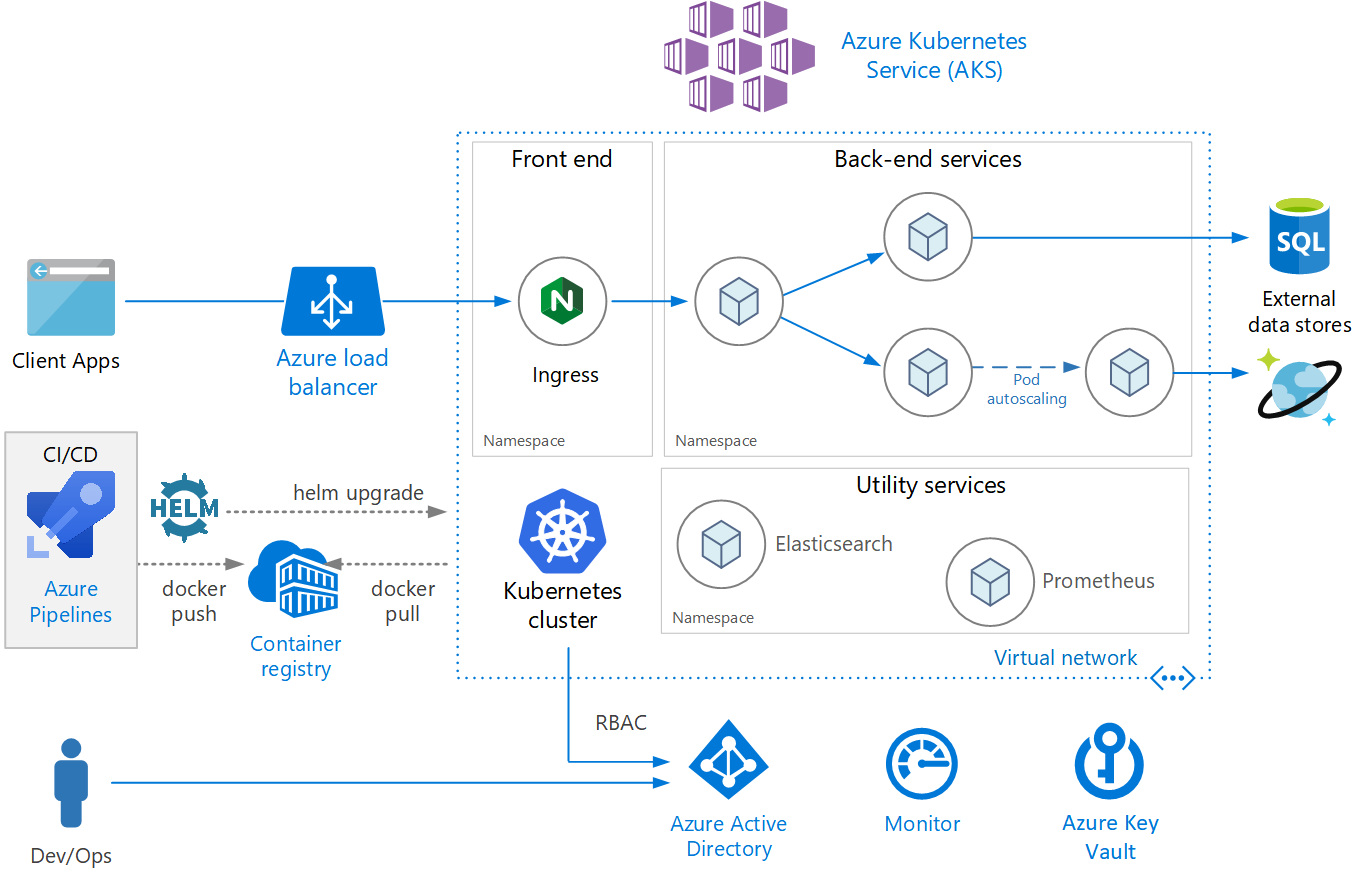
- Microservices architecture on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- https://github.com/mspnp/microservices-reference-implementation
- Building microservices on Azure
- About Service Principal
- Update Service Principal in AKS cluster
- 3 options to manage access and identity for AKS clusters
- Azure RBAC (integration with Azure AD) to control the access to AKS
from Bast pracitses for authn & authz in AKS
1. Developer authenticates with Azure AD(AAD). 2. AAD token issuance endpoint issues the access token. 3. The developer performs an action using the AAD token, such as kubectl create pod 4. k8s validates the token with AAD and fetches the developer's group memberships. 5. k8s RBAC and cluster policies are applied. 6. Developer's request is successful or not based on previous validation of AAD group membership and k8s RBAC and policies. - Kubernetes RBAC
- Using RBAC Authorization@k8s.io
- Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, ClusterRoleBindings
- Pod Identities
- Use managed identities for Pods in AKS to access to Azure resources
- Managed Identities let you automatically request access to services through Azure AD. You don't manually define credentials for pods, instead they request an access token in real time (See azure doc)
- Use Pod Identities(Managed Identity)
- Use managed identities for Pods in AKS to access to Azure resources
- Azure RBAC (integration with Azure AD) to control the access to AKS
- cluster security and upgrades
- Securing access to the API server, limiting container access, and managing upgrades and node reboots.
- Container image management and security
- Securing the image and runtimes, using trusted registries, and automated builds on base image updates..
- Pod security
- Securing access to resources, limiting credential exposure, and using pod identities and Azure Key Vault
- KeyVault with FlexVol@Github page
- Data Volume Options (Azure Managed)
Azure Disk(Dynamic / Static): can be used to create a Kubernetes DataDisk resource- Disks can use (1) Azure Premium storage (2) Azure Standard storage
- Read/write many: No (only available to a single node)
Azure Files(Dynamic / Static): can be used to mount an SMB 3.0 share backed by an Azure Storage account to pods- Files can use (1) Azure Standard storage and (2) Azure Premium storage ( NOTE: Azure Files support premium storage in AKS clusters that run Kubernetes 1.13 or higher)
- Read/write many: Yes
- Other Key points
- Both support
Windows Server container - Both use
Azure Storage Service Encryption (SSE)by default that encrypts data at rest. Disks cannot currently be encrypted using Azure Disk Encryption at the AKS node level. - Performance benchmark: see this
- Both support
- Other data volume options
- Azure Netapp Files: Managed NFS service on Azure (see Setup manual)
- Best practices: Storage and Backup
- kubenet (default policy)
- az aks create --network-plugin option:
kubenet - see also @k8s.io
- az aks create --network-plugin option:
- Azure CNI
- az aks create --network-plugin option:
azure
- az aks create --network-plugin option:
- Kubernetes version:
1.12+ - Network Policy Recipes
- Network policy Options in AKS
-
Azure Network Policies- the Azure CNI sets up a bridge in the VM host for intra-node networking. The filtering rules are applied when the packets pass through the bridge
- az aks create --network-plugin
azure
-
Calico Network Policies- the Azure CNI sets up local kernel routes for the intra-node traffic. The policies are applied on the pod’s network interface.
- see [the difference between the two](the Azure CNI sets up local kernel routes for the intra-node traffic. The policies are applied on the pod’s network interface.)
- az aks create --network-plugin
azure&& --network-policycalico
-
- Service: type=
LoadBalancer(NOTClusterIPnorNodePort) - Default: External Load balancer
- Static IP to LB (see azure doc)
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: servicename spec: loadBalancerIP: 41.222.222.66 type: LoadBalancer
- Internal Load balancer - Only accessible from the same VNET
- Annotation for Internal LB
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: servicename annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal: "true" spec: type: LoadBalancer ...
- You can specify IP address for LB:
loadBalancerIP:XX.XX.XX.XX - You can specify a subnet for LB with special annotation
annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal: "true" service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal-subnet: "apps-subnet"
- Annotation for Internal LB
- Ingress Controllers provided by Azure (Not nginx ingress or others)
- TLS Termination Configfuration
- Ingress for Internal VNET by using a service with Internal LB
- Static IP for egress traffic
- See azure doc
- Default: egress IP from AKS is randomly assigned
Once a Kubernetes service of type LoadBalancer is created, agent nodes are added to an Azure Load Balancer pool. For outbound flow, Azure translates it to the first public IP address configured on the load balancer. This public IP address is only valid for the lifespan of that resource. If you delete the Kubernetes LoadBalancer service, the associated load balancer and IP address are also deleted.
- Procedures
-
- Create static IP in AKS node resource Group
-
- Create a service with the static IP ( put the static IP to the
loadBalancerIPproperty)
- Create a service with the static IP ( put the static IP to the
-
- Kubernetes +1.12.x:
CoreDNS - Kubernetes < 1.12.x:
kube-dns
- Manually scale Pods
kubectl scale --replicas=$NUM deployment/$DEPLOY_NAME
- Manually scale AKS nodes
az aks scale --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER _NAME --node-count $NUM
- Autoscale Pods (see kubectl autoscale)
# If CPU utilization exceeds 50%, the autoscaler increases the pods up to a maximum of 10 instances. A minimum of 3 instances is then defined for the deployment kubectl autoscale deployment $DEPLOY_NAME --cpu-percent=50 --min=3 --max=10 # To see the status of the autoscaler kubectl get hpa
- Autoscale Cluster (Nodes)
- Configure AKS Cluster Autoscaler (preview)
- Scale across AKS and ACI using Virtual Node
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/container-service-quotas
- Default limit
- max clusters per subscription:
100 - max nodes per cluster:
100 - max pods per node setting for AKS
- Basic networking with Kubenet:
110 - Advanced networking with Azure CNI:
30( NOTE: you can change the limit for Azure CLI or Resource Manager template deployments up to110)
- Basic networking with Kubenet:
- max clusters per subscription:
- Region availability
- Provisioned Infrastructure
- Supported k8s versions
az aks get-versions --location $REGION -o table
- Business continuity and Disaster recovery in AKS
- Backup
- Azure Managed Storage (Azure Disk / Files)
- k8s apps and Persistent volumes: Velero(formerly Heptio Ark)
- Official troubleshooting Guide @k8s.io
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/troubleshooting
- Kubernetes Troubleshooting @Github
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/kube-advisor-tool
- SSH login to k8s nodes
API Server: Because AKS is free, no cost is available to reimburse, so AKS has no formal SLA. However, AKS seeks to maintain availability ofat least 99.5 percentfor the Kubernetes API server ( From SLA for AKS )Agent nodes (VMs): See Virtual Machines SLAAzure Storage(in case you use it for data volumes): See SLA for Storage Account
- Authentications
- VNET & Firewall Rule
- ACR Task - Automate OS and framework patching
- Repo & Tag Locking
- Helm Chart Repositories