| title | tags | categories | date | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
动手DIY一个underscorejs库及underscorejs源码分析1 |
|
前端技术 |
2016-10-25 17:00:00 -0700 |
Underscore 是一个 JavaScript 工具库,它提供一整套函数编程的实用功能。他弥补了 jQuery 没有实现的功能,同时又是Backbone 必不可少的部分。
underscore.js源码加上注释也就1千多行,用underscore.js作为阅读源码的开始是一个不错的开始,当然阅读源码的同时,手也不能停下来。下面我会写几篇博客,一边分析源码,一边根据源码重新DIY一份(_underscore.js),基于版本:1.8.3。
underscore.js分为集合(Collections)、数组(Arrays)、函数(Functions)、对象(Objects)、工具函数(Utility)五大部分。
所有代码挂在我的github上。
<script src="underscore.js"></script>
<!-- <script src="../DIY/1/_underscore.js"></script> -->
<script>
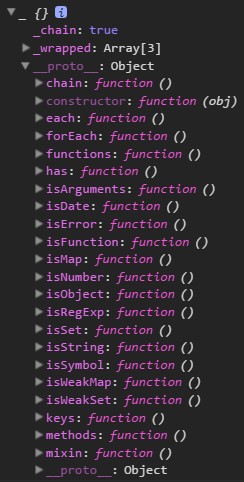
console.info(_);
console.info(_.prototype);
/**
* 数组处理
*/
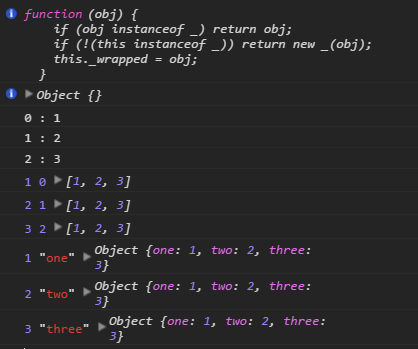
_.each([1, 2, 3], function(ele,idx) {
console.log(idx + " : " +ele);
});
_.each([1, 2, 3], console.log);
_.each({one: 1, two: 2, three: 3}, console.log);
</script>
打印结果:
 展开
展开console.info(_.prototype);打印的结果
+ Object
//... ...
- ()each:
- ()escape:
- ()every:
- ()extend:
//... ...
__proto__: Object
(function(){
}()) //在浏览器上是window(self),服务器上是global
var root = typeof self == 'object' && self.self === self && self ||
typeof global == 'object' && global.global === global && global ||
this;
//形式:_([1, 2, 3]).each(function(ele) {});会执行下面的
var _ = function(obj) {
if (obj instanceof _) return obj;
if (!(this instanceof _)) return new _(obj);
this._wrapped = obj; //存放数据
};
//形式:_.each([1, 2, 3], function(ele, idx) { });不会执行上面的函数,而是直接通过全局的_,寻找定义在_或者其原型上的方法
root._ = _;为了压缩我们把常用的方法/属性独立写成变量
var ArrayProto = Array.prototype,
ObjProto = Object.prototype;
var push = ArrayProto.push,
toString = ObjProto.toString,
hasOwnProperty = ObjProto.hasOwnProperty;
var nativeIsArray = Array.isArray,
nativeKeys = Object.keys; //判断是不是对象/函数
_.isObject = function(obj) {
var type = typeof obj;
return type === 'function' || type === 'object' && !!obj;
};
//属性中是否有key
var property = function(key) {
return function(obj) {
return obj == null ? void 0 : obj[key];
};
};
var MAX_ARRAY_INDEX = Math.pow(2, 53) - 1;
var getLength = property('length');
var isArrayLike = function(collection) {
var length = getLength(collection);
return typeof length == 'number' && length >= 0 && length <= MAX_ARRAY_INDEX;
}; var optimizeCb = function(func, context, argCount) {
//void 0 === undefined 返回ture
if (context === void 0) return func;
return function() {
return func.apply(context, arguments);
};
};一个简单的版本属性
_.VERSION = '0.0.1';_.each需要_.keys
_.each = _.forEach = function(obj, iteratee, context) {
iteratee = optimizeCb(iteratee, context);
var i, length;
if (isArrayLike(obj)) {//类数组
for (i = 0, length = obj.length; i < length; i++) {
iteratee(obj[i], i, obj); //(element, index, list)
}
} else {
var keys = _.keys(obj);
for (var i = 0, length = keys.length; i < length; i++) {
iteratee(obj[keys[i]], keys[i], obj); //(value, key, list)
}
}
return obj; //返回obj方便链式调用
};_.keys
_.keys = function(obj) {
//不是对象/函数,返回空数组
if (!_.isObject(obj)) return [];
//使用ES5中的方法,返回属性(数组)
if (nativeKeys) return nativeKeys(obj);
var keys = [];
for (var key in obj)
if (_.has(obj, key)) keys.push(key);
//兼容IE< 9 暂时省略
// if (hasEnumBug) collectNonEnumProps(obj, keys);
return keys;
};_.has
_.has = function(obj, key) {
return obj != null && hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key);
};_.prototype的打印结果是:
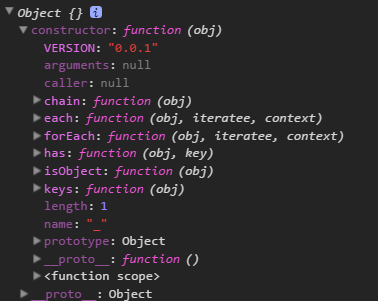
console.logo(_.prototype);不在其原型中(其实我们定义_.** 也并没有放到原型中)如果不放到原型中,第5部分不能成功调用。
需要使用的工具类
_.each(['Arguments', 'Function', 'String', 'Number', 'Date', 'RegExp', 'Error', 'Symbol', 'Map', 'WeakMap', 'Set', 'WeakSet'], function(name) {
_['is' + name] = function(obj) {
return toString.call(obj) === '[object ' + name + ']';
};
});
// IE 11 (#1621), Safari 8 (#1929), and PhantomJS (#2236).
var nodelist = root.document && root.document.childNodes;
if (typeof /./ != 'function' && typeof Int8Array != 'object' && typeof nodelist != 'function') {
_.isFunction = function(obj) {
return typeof obj == 'function' || false;
};
}
_.functions = _.methods = function(obj) {
var names = [];
for (var key in obj) {
if (_.isFunction(obj[key])) names.push(key);
}
return names.sort();
};混入,并且执行混入
_.mixin = function(obj) {
_.each(_.functions(obj), function(name) {
var func = _[name] = obj[name];
_.prototype[name] = function() {
var args = [this._wrapped]; //_ 保存的数据obj
push.apply(args, arguments);
//原型方法中的数据和args合并到一个数组中
return chainResult(this, func.apply(_, args));
//见第`4`部分
//将_.prototype[name]的this指向 _ 【func.apply(_,args)已经
//将func的this指向了 _ ,并且传了参数】,返回带链式的obj,即是 _
};
});
return _;
};
_.mixin(_);将_.*形式的方法放入到原型中
对于_(obj).*的方法,已经将数据([this._wrapped])传入到函数中(var func = _[name] = obj[name])。当然包括原型中的方法。
_mixin是支持用户自己扩展方法的。如:
_.mixin({
capitalize: function(string) {
return string.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + string.substring(1).toLowerCase();
}
});
_("fabio").capitalize();
=> "Fabio" _.chain = function(obj) {
var instance = _(obj);
instance._chain = true;
return instance;
};使用:
_.chain(arr)
.each(function(ele) {
console.log(ele);
})//可以继续链式 var chainResult = function(instance, obj) {
return instance._chain ? _(obj).chain() : obj;
};使用形式如下:
_([1, 2, 3]).each(function(n) {
console.log(n * 2);
});我们看到第2.2部分初始化的代码
var _ = function(obj) {
console.log(this);
if (obj instanceof _) return obj;
if (!(this instanceof _)) return new _(obj);
this._wrapped = obj; //存放数据
};执行的逻辑会是
- 1.
if (!(this instanceof _)) return new _(obj);再次调用构造函数,这个时候的this从window已经指向了_; - 2.
this._wrapped = obj; //存放数据
var previousUnderscore = root._;
_.noConflict = function() {
root._ = previousUnderscore;
return this;
};使用:
var $$ = _.noConflict();//previousUnderscore
$$.each([1, 2, 3], function(ele, idx) {
console.info(idx + " : " + ele);
});全部代码贴在这里,可以在我的github查看具体的所有代码
/**
* DIY 一个underscore库1
*/
(function() {
//在浏览器上是window(self),服务器上是global
var root = typeof self == 'object' && self.self === self && self ||
typeof global == 'object' && global.global === global && global ||
this;
var previousUnderscore = root._;
var _ = function(obj) {
console.log(this);
if (obj instanceof _) return obj;
if (!(this instanceof _)) return new _(obj);
this._wrapped = obj; //存放数据
};
root._ = _;
var ArrayProto = Array.prototype,
ObjProto = Object.prototype;
var push = ArrayProto.push,
toString = ObjProto.toString,
hasOwnProperty = ObjProto.hasOwnProperty;
var nativeIsArray = Array.isArray,
nativeKeys = Object.keys;
//判断是不是对象/函数
_.isObject = function(obj) {
var type = typeof obj;
return type === 'function' || type === 'object' && !!obj;
};
var optimizeCb = function(func, context, argCount) {
//void 0 === undefined 返回ture
if (context === void 0) return func;
return function() {
return func.apply(context, arguments);
};
};
_.VERSION = '0.0.1';
var property = function(key) {
return function(obj) {
return obj == null ? void 0 : obj[key];
};
};
var MAX_ARRAY_INDEX = Math.pow(2, 53) - 1;
var getLength = property('length');
var isArrayLike = function(collection) {
var length = getLength(collection);
return typeof length == 'number' && length >= 0 && length <= MAX_ARRAY_INDEX;
};
_.each = _.forEach = function(obj, iteratee, context) {
iteratee = optimizeCb(iteratee, context);
var i, length;
if (isArrayLike(obj)) {
for (i = 0, length = obj.length; i < length; i++) {
iteratee(obj[i], i, obj); //(element, index, list)
}
} else {
var keys = _.keys(obj);
for (i = 0, length = keys.length; i < length; i++) {
iteratee(obj[keys[i]], keys[i], obj); //(value, key, list)
}
}
return obj; //返回obj方便链式调用
};
_.keys = function(obj) {
//不是对象/函数,返回空数组
if (!_.isObject(obj)) return [];
//使用ES5中的方法,返回属性(数组)
if (nativeKeys) return nativeKeys(obj);
var keys = [];
for (var key in obj)
if (_.has(obj, key)) keys.push(key);
//兼容IE< 9
};
_.has = function(obj, key) {
return obj != null && hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key);
};
/*链式*/
_.chain = function(obj) {
var instance = _(obj);
instance._chain = true;
return instance;
};
/*
_.chain(arr)
.each(function(ele) {
console.log(ele);
})
*/
var chainResult = function(instance, obj) {
return instance._chain ? _(obj).chain() : obj;
};
/**
* 方法放入原型中
*/
_.each(['Arguments', 'Function', 'String', 'Number', 'Date', 'RegExp', 'Error', 'Symbol', 'Map', 'WeakMap', 'Set', 'WeakSet'], function(name) {
_['is' + name] = function(obj) {
return toString.call(obj) === '[object ' + name + ']';
};
});
// IE 11 (#1621), Safari 8 (#1929), and PhantomJS (#2236).
var nodelist = root.document && root.document.childNodes;
if (typeof /./ != 'function' && typeof Int8Array != 'object' && typeof nodelist != 'function') {
_.isFunction = function(obj) {
return typeof obj == 'function' || false;
};
}
_.functions = _.methods = function(obj) {
var names = [];
for (var key in obj) {
if (_.isFunction(obj[key])) names.push(key);
}
return names.sort();
};
_.mixin = function(obj) {
_.each(_.functions(obj), function(name) {
var func = _[name] = obj[name];
_.prototype[name] = function() {
var args = [this._wrapped]; //_ 保存的数据obj
push.apply(args, arguments);
//原型方法中的数据和args合并到一个数组中
return chainResult(this, func.apply(_, args));
//将_.prototype[name]的this指向 _ (func.apply(_,args)已经
//将func的this指向了 _ ,并且传了参数),返回带链式的obj,即是 _
};
});
return _;
};
_.mixin(_);
/**
* 避免冲突
*/
_.noConflict = function() {
root._ = previousUnderscore;
return this;
};
}());参考阅读: