It is a dotnet framework that helps in the development of MAS (Multi-agent systems) applied to integrative business information systems (IBIS). MAS Unity will assist in the construction, deployment and monitoring of a cluster of autonomous agents.
This repository has a sample of the application of MAS Unity. This code presents an example of an agent that performs the credit analysis after purchase. The following steps show the implementation of the sample project.
The sample project was created as a web API with ASP.NET Core, and uses the MAS Unity dependencies:
Install-Package MasUnity
Install-Package MasUnity.HostedService
Install-Package MasUnity.HealthCheck
Tutorial: Create a web API with ASP.NET Core
It's important to keep your Agent code organized and easy to maintain. This section will provide a modeling tactical approach to achieve a satisfactory maintainability level. For this, it's recommended to use a domain-model approach to approximate the Agent of own acting environment. In this sense, we propose this modeling structure:
Project/
│
├─ Use cases/
│ │
│ ├─ Agents/
│ │ │
│ │ ├─ Actions/
│ │ │ ├─ Action.cs
│ │ │ │
│ │ ├─ Knowledges/
│ │ │ ├─ Knowledge.cs
│ │ │ │
│ │ ├─ Agent.cs
│ │ ├─ Schedule.cs
│ │ │
│ ├─ Environment/
│ │ │ ├─ Environment.cs
-
Use case: is a list of actions or event steps typically defining the interactions between a Agent and a system to achieve a goal.
-
Agents: an agent is a computer system that is situated in some environment, and that is capable of autonomous action in this environment in order to meet its design objectives.
-
Actions: each agent is responsible for performing tasks to solve partial problems. MAS supports task synchronization, task allocation, task sharing, and result sharing
-
Knowledge: is an integral part of the intelligent agent and multi-agent systems paradigm. Agents possess knowledge and act based on their own knowledge, beliefs, desires, and intentions.
-
Environment: system operates in an environment which is similar to the notion of the environment of an organization and that of a multi-agent system.
Our sample simulates a purchase analysis environment. In this context, the Agent verify if the transaction is a credit card transaction. Given some conditions, this Agent should allow or deny the transaction. For this, the Agent realizes the transaction and choose de appropiated action to be executed. The following subsections ilustrates the implementation of Action, Knowledges and Agents classes in this sample.
An Action is a class that implements the Realize and Execute methods of IAction interface. How is shown in the following code:
public class AllowCreditCardTransaction : IAction
{
...
public Task<Perception> Realize(AgentContext context, CancellationToken cancellation)
{
Transaction = Queue.GetNext();
return Perception.Assertion(
("It's a credit card transaction", Transaction.IsCreditCardTransaction()),
("It's normal transaction time", AboutTransactionSchedule.ItsNormalTransactionSchedule()),
("It's a safe credit card transactions", Knowledge.IsSafeTransaction(Transaction))
);
}
public async Task<AgentResult> Execute(AgentContext context, CancellationToken cancellation)
{
await Queue.SaveAsApprovedTransaction(Transaction);
return AgentResult.Ok($"{Transaction.Id} Allowed");
}
} See all actions code in sample project.
The Knowledge class implement the interface IKnowledge. This interface is used only for injection concerns. The following code ilustrate the Knowledge implementation:
//Transactions after 20 PM
public class AboutCreditCardTransactionAfter20Pm : IKnowledge
{
public bool IsUnsafeTransaction(Transaction transaction) =>
transaction.IsCreditCardTransaction() && transaction.Value >= 2500 && transaction.ReliabilityRating <= 3;
}
//Transactions between 8AM and 20 PM
public class AboutCreditCardTransactionBetween8AmAnd20Pm : IKnowledge
{
public bool IsSafeTransaction(Transaction transaction) =>
transaction.IsCreditCardTransaction() && !IsUnsafeTransaction(transaction);
public bool IsUnsafeTransaction(Transaction transaction) =>
transaction.IsCreditCardTransaction() && transaction.Value >= 4500 && transaction.ReliabilityRating < 3;
}See all Knowledges code in sample project.
The Agent class might inherit a PoractiveAgent (wich demands a schedule) or a ReactiveAgent (wich execution depends of a directily call). Both parent classes demands the implementation of RegisterActions method. The following code ilustrate the Agent implementation:
public class CreditRiskAgent: ProactiveAgent
{
private readonly IAgentServiceScope _scope;
public CreditRiskAgent(IAgentServiceScope scope, CreditRiskAgentSchedule schedule) : base(schedule)
{
_scope = scope;
}
protected override IEnumerable<IAction> RegisterActions()
{
yield return _scope.GetService<AllowCreditCardTransaction>();
yield return _scope.GetService<DenyCreditCardTransaction>();
yield return _scope.GetService<DenyCreditCardTransactionAfter20Pm>();
}
}The following code ilustrate the configutration of five instances of MAS Unity Agents in Asp.net application
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.ConfigureMasUnity((option) =>
{
option.AddAgent<CreditRiskAgent>(5)
.WithSchedule<CreditRiskAgentSchedule>()
.WithEnvironment<PendingTransactions>()
.WithKnowledge<AboutCreditCardTransactionAfter20Pm>()
.WithKnowledge<AboutCreditCardTransactionBetween8AmAnd20Pm>()
.WithAction<AllowCreditCardTransaction>()
.WithAction<DenyCreditCardTransaction>()
.WithAction<DenyCreditCardTransactionAfter20Pm>()
.WithHealtCheck()
.Build();
});
}
} See all code in sample project
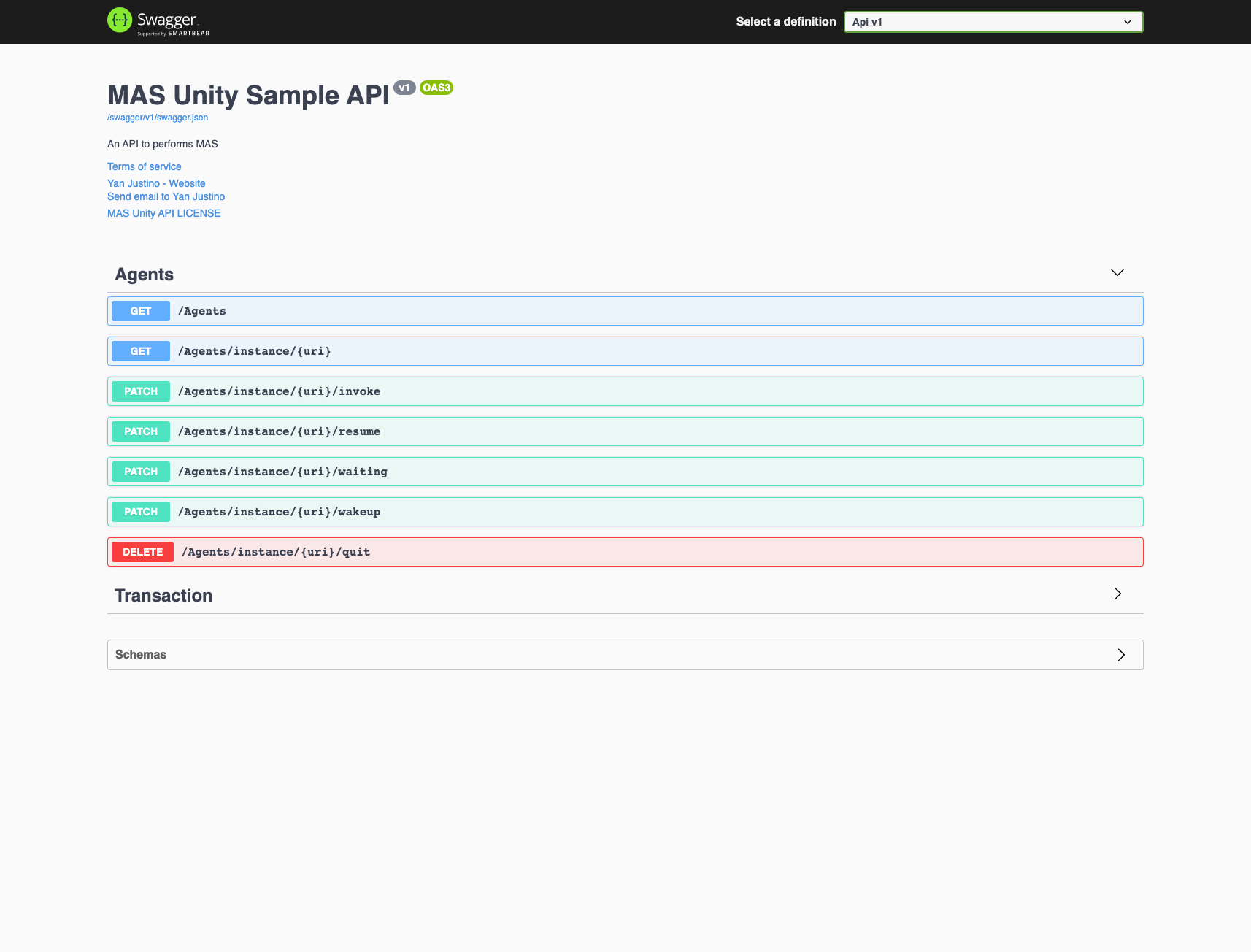
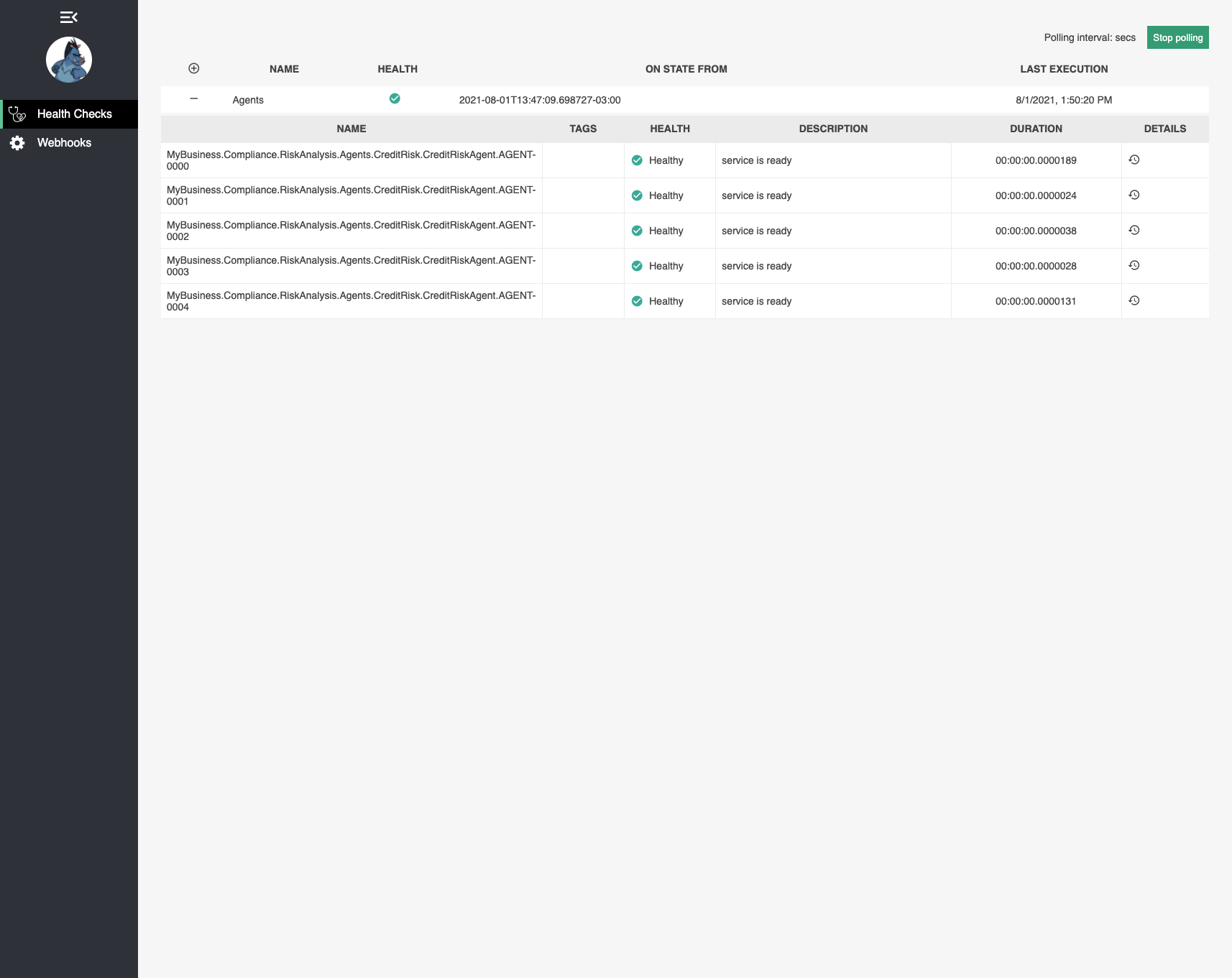
see this code to understand how to configure Health Check and Open API for your Agents.
When you configure your agente using the method .WithHealtCheck(), it's possible monitoring the health of each agent instance.
MAS Unity provides a controller to manipulate the Agent instance execution.