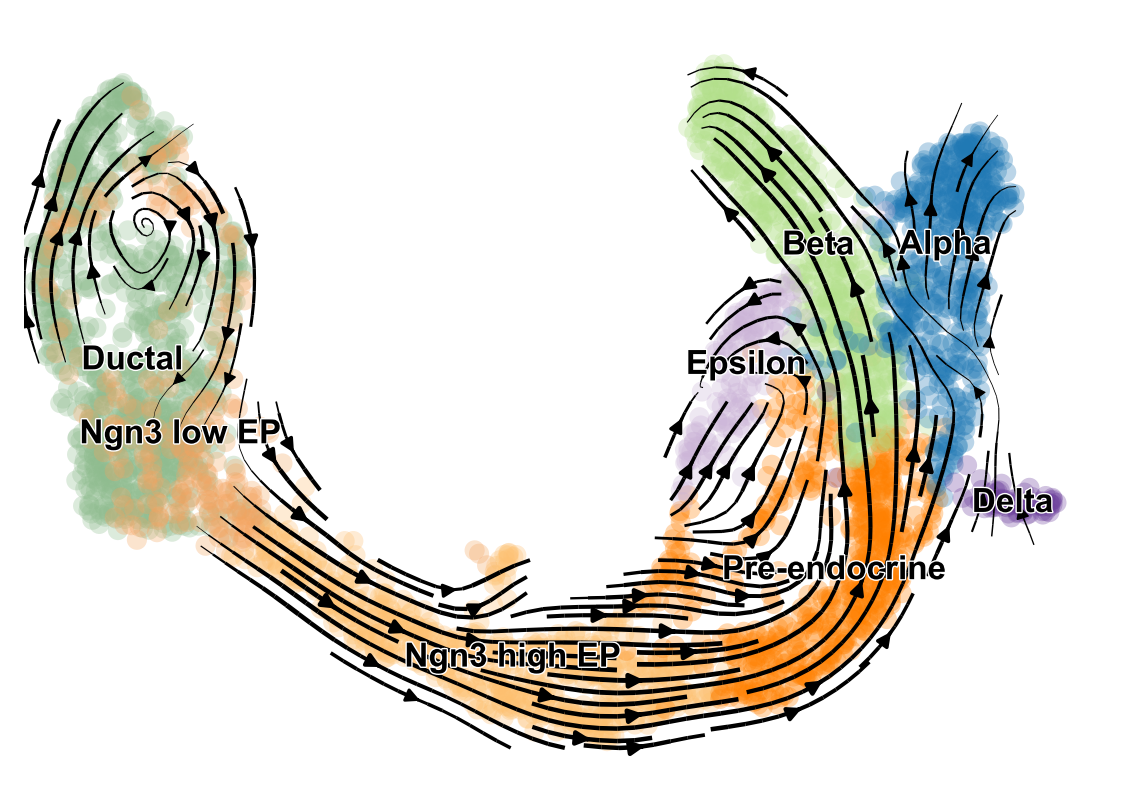
scVelo is a scalable toolkit for RNA velocity analysis in single cells, based on Bergen et al. (Nature Biotech, 2020).
RNA velocity enables the recovery of directed dynamic information by leveraging splicing kinetics. scVelo generalizes the concept of RNA velocity (La Manno et al., Nature, 2018) by relaxing previously made assumptions with a stochastic and a dynamical model that solves the full transcriptional dynamics. It thereby adapts RNA velocity to widely varying specifications such as non-stationary populations.
scVelo is compatible with scanpy and hosts efficient implementations of all RNA velocity models.
- estimate RNA velocity to study cellular dynamics.
- identify putative driver genes and regimes of regulatory changes.
- infer a latent time to reconstruct the temporal sequence of transcriptomic events.
- estimate reaction rates of transcription, splicing and degradation.
- use statistical tests, e.g., to detect different kinetics regimes.
scVelo has, for instance, recently been used to study immune response in COVID-19 patients and dynamic processes in human lung regeneration. Find out more in this list of application examples.
- Feb/2021: scVelo goes multi-core
- Dec/2020: Cover of Nature Biotechnology
- Nov/2020: Talk at Single Cell Biology
- Oct/2020: Helmholtz Best Paper Award
- Oct/2020: Map cell fates with CellRank
- Sep/2020: Talk at Single Cell Omics
- Aug/2020: scVelo out in Nature Biotech
Bergen et al. (2020), Generalizing RNA velocity to transient cell states through dynamical modeling, Nature Biotech.
Found a bug or would like to see a feature implemented? Feel free to submit an issue. Have a question or would like to start a new discussion? Head over to GitHub discussions. In either case, you can also always send us an email. Your help to improve scVelo is highly appreciated. For further information visit scvelo.org.

