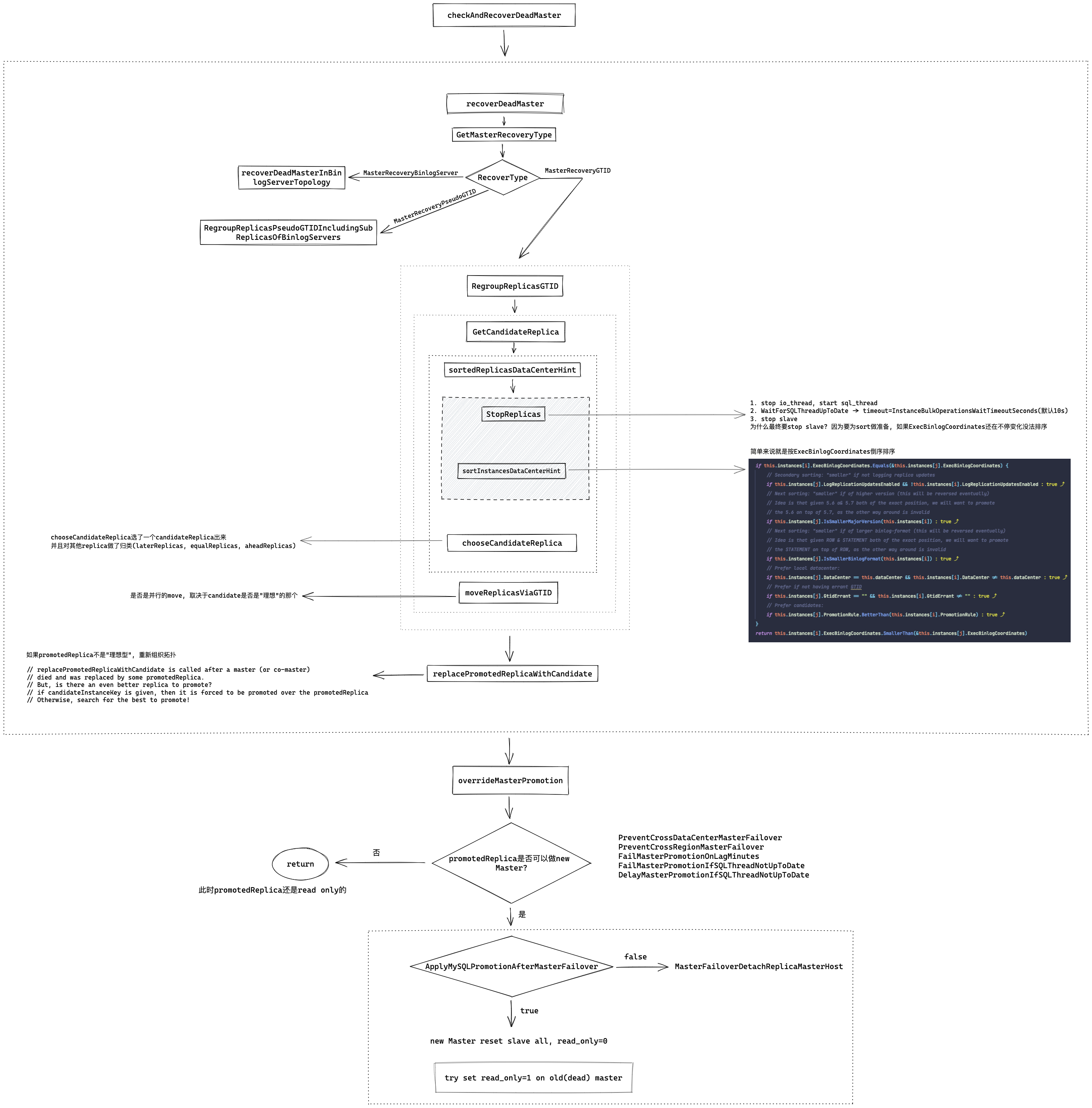
书接上文Orchestrator Failover过程源码分析-II
// RegroupReplicasGTID will choose a candidate replica of a given instance, and take its siblings using GTID
func RegroupReplicasGTID(
masterKey *InstanceKey, // 实参传进来的是 挂掉的旧主库
returnReplicaEvenOnFailureToRegroup bool, // 实参传进来的是 true
startReplicationOnCandidate bool, // 实参传进来的是 false
onCandidateReplicaChosen func(*Instance), // 实参传进来的是 nil
postponedFunctionsContainer *PostponedFunctionsContainer,
postponeAllMatchOperations func(*Instance, bool) bool, // 实参传进来的是 promotedReplicaIsIdeal 函数
)RegroupReplicasGTID will choose a candidate replica of a given instance, and take its siblings using GTID 英文简简单单一句话, 中文不知道咋翻译.. 我理解就是RegroupReplicasGTID会从目标实例(即DeadMaster)的从库中选出一个candidate出来, 然后提升他为新主库, 并接管所有的从库
要理解RegroupReplicasGTID, 还是要先看它调用的GetCandidateReplica
// GetCandidateReplica chooses the best replica to promote given a (possibly dead) master
func GetCandidateReplica(masterKey *InstanceKey, forRematchPurposes bool) (*Instance, [](*Instance), [](*Instance), [](*Instance), [](*Instance), error) {
// masterKey 实参传进来的是 挂掉的旧主库. InstanceKey结构体里只有Hostname和Port
// forRematchPurposes 实参传进来是 true
// 声明变量, 这是一个指针
var candidateReplica *Instance
aheadReplicas := [](*Instance){} // 字面量声明, 所以 aheadReplicas != nil
equalReplicas := [](*Instance){}
laterReplicas := [](*Instance){}
cannotReplicateReplicas := [](*Instance){}
dataCenterHint := ""
// 这里实际是根据Hostname和Port读取backend db database_instance表, 实例化了一个instance, 使用readInstanceRow填充了各种属性, 如is_candidate, promotion_rule等等
if master, _, _ := ReadInstance(masterKey); master != nil {
dataCenterHint = master.DataCenter
}
// 返回给定主站的副本列表,用于候选选择。
// 就是把masterKey的所有从库读出来了, 返回一个[](*Instance)
replicas, err := getReplicasForSorting(masterKey, false)
if err != nil {
// 如果有err, 这里直接return. 注意此时candidateReplica是等于nil的
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err
}
// type StopReplicationMethod string
// const (
// NoStopReplication StopReplicationMethod = "NoStopReplication"
// StopReplicationNormal = "StopReplicationNormal"
// StopReplicationNice = "StopReplicationNice"
// )
stopReplicationMethod := NoStopReplication
// forRematchPurposes 实参传进来是 true
if forRematchPurposes {
stopReplicationMethod = StopReplicationNice // 所以 stopReplicationMethod 是 StopReplicationNice
}
// 传入了所有的从库, StopReplicationNice, 和 主库的数据中心
// 返回根据 exec coordinates 排序的从库列表
replicas = sortedReplicasDataCenterHint(replicas, stopReplicationMethod, dataCenterHint)
if len(replicas) == 0 {
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, fmt.Errorf("No replicas found for %+v", *masterKey)
}
candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err = chooseCandidateReplica(replicas)
if err != nil {
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err
}
if candidateReplica != nil {
mostUpToDateReplica := replicas[0]
if candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates.SmallerThan(&mostUpToDateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates) {
log.Warningf("GetCandidateReplica: chosen replica: %+v is behind most-up-to-date replica: %+v", candidateReplica.Key, mostUpToDateReplica.Key)
}
}
log.Debugf("GetCandidateReplica: candidate: %+v, ahead: %d, equal: %d, late: %d, break: %d", candidateReplica.Key, len(aheadReplicas), len(equalReplicas), len(laterReplicas), len(cannotReplicateReplicas))
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, nil
}GetCandidateReplica首先根据masterKey(只包含Hostname和Port)查询Backend DB的database_instance表生成了一个master"对象"
然后从Backend DB中查询出master的所有的从库, 返回一个包含所有从库*Instance 的切片replicas
注意 如果在"获取"从库的过程中出现error, 则GetCandidateReplica会终止直接return. 而此时candidateReplica是等于nil的
接着调用sortedReplicasDataCenterHint对replicas进行排序. 接下来先展开说一下这个函数
// sortedReplicas returns the list of replicas of some master, sorted by exec coordinates
// (most up-to-date replica first).
// This function assumes given `replicas` argument is indeed a list of instances all replicating
// from the same master (the result of `getReplicasForSorting()` is appropriate)
func sortedReplicasDataCenterHint(replicas [](*Instance), stopReplicationMethod StopReplicationMethod, dataCenterHint string) [](*Instance) {
if len(replicas) <= 1 { // 如果只有一个从库, 直接返回
return replicas
}
// InstanceBulkOperationsWaitTimeoutSeconds 默认10s
// 先 StopReplicationNicely 超时10s, 如果超时了也只是记了日志. 然后StopReplication
// 然后 sortInstancesDataCenterHint. 这要看NewInstancesSorterByExec的Less方法如何实现. 简单说就是ExecBinlogCoordinates大的放前面, 如果ExecBinlogCoordinates一样, Datacenter和DeadMaster一样的放前面
replicas = StopReplicas(replicas, stopReplicationMethod, time.Duration(config.Config.InstanceBulkOperationsWaitTimeoutSeconds)*time.Second)
replicas = RemoveNilInstances(replicas)
sortInstancesDataCenterHint(replicas, dataCenterHint)
for _, replica := range replicas {
log.Debugf("- sorted replica: %+v %+v", replica.Key, replica.ExecBinlogCoordinates)
}
return replicas
}从注释可以看出sortedReplicas会返回一个按exec coordinates排序的从库列表(most up-to-date first) sortedReplicasDataCenterHint先调用StopReplicas, StopReplicas做了几件事:
对于本例, stopReplicationMethod是StopReplicationNice
- 并行的在所有从库执行StopReplicationNicely.
StopReplicationNicely会先
stop slave io_thread,start slave sql_thread, 然后对所有非延迟从库WaitForSQLThreadUpToDate, 最多等待InstanceBulkOperationsWaitTimeoutSeconds秒(也就是默认10s)如果超过InstanceBulkOperationsWaitTimeoutSeconds秒, SQL_THREAD还是没有应用完所有日志, 也不等了.
等待超时不会引发异常
- StopReplicationNicely执行完成后, 执行StopReplication. 实际就是执行stop slave
对比MHA
MHA其实会在Dead Master Shutdown Phase 停所有从库io_thread
MasterFailover.pm
sub do_master_failover {
...
$log->info("* Phase 2: Dead Master Shutdown Phase..\n");
$log->info();
force_shutdown($dead_master);
$log->info("* Phase 2: Dead Master Shutdown Phase completed.\n");
...
}
sub force_shutdown($) {
...
my $slave_io_stopper = new Parallel::ForkManager( $#alive_slaves + 1 );
my $stop_io_failed = 0;
$slave_io_stopper->run_on_start(
sub {
my ( $pid, $target ) = @_;
}
);
$slave_io_stopper->run_on_finish(
sub {
my ( $pid, $exit_code, $target ) = @_;
return if ( $target->{ignore_fail} );
$stop_io_failed = 1 if ($exit_code);
}
);
foreach my $target (@alive_slaves) {
$slave_io_stopper->start($target) and next;
eval {
$SIG{INT} = $SIG{HUP} = $SIG{QUIT} = $SIG{TERM} = "DEFAULT";
my $rc = $target->stop_io_thread();
$slave_io_stopper->finish($rc);
};
if ($@) {
$log->error($@);
undef $@;
$slave_io_stopper->finish(1);
}
$slave_io_stopper->finish(0);
}这是很合理的, 只要开始Failover了, 就说明MHA认为主库已经挂了, 那么停io_thread再根据Master_Log_File和Read_Master_Log_Pos选latest slave是没问题的
ServerManager.pm
sub identify_latest_slaves($$) {
my $self = shift;
my $find_oldest = shift;
$find_oldest = 0 unless ($find_oldest);
my $log = $self->{logger};
my @slaves = $self->get_alive_slaves();
my @latest = ();
foreach (@slaves) {
my $a = $latest[0]{Master_Log_File};
my $b = $latest[0]{Read_Master_Log_Pos};
if (
!$find_oldest
&& (
( !$a && !defined($b) )
|| ( $_->{Master_Log_File} gt $latest[0]{Master_Log_File} )
|| ( ( $_->{Master_Log_File} ge $latest[0]{Master_Log_File} )
&& $_->{Read_Master_Log_Pos} > $latest[0]{Read_Master_Log_Pos} )
)
)
{
@latest = ();
push( @latest, $_ );
}
elsif (
$find_oldest
&& (
( !$a && !defined($b) )
|| ( $_->{Master_Log_File} lt $latest[0]{Master_Log_File} )
|| ( ( $_->{Master_Log_File} le $latest[0]{Master_Log_File} )
&& $_->{Read_Master_Log_Pos} < $latest[0]{Read_Master_Log_Pos} )
)
)
{
@latest = ();
push( @latest, $_ );
}
elsif ( ( $_->{Master_Log_File} eq $latest[0]{Master_Log_File} )
&& ( $_->{Read_Master_Log_Pos} == $latest[0]{Read_Master_Log_Pos} ) )
{
push( @latest, $_ );
}
}
foreach (@latest) {
$_->{latest} = 1 if ( !$find_oldest );
$_->{oldest} = 1 if ($find_oldest);
}
$log->info(
sprintf(
"The %s binary log file/position on all slaves is" . " %s:%d\n",
$find_oldest ? "oldest" : "latest", $latest[0]{Master_Log_File},
$latest[0]{Read_Master_Log_Pos}
)
);
if ( $latest[0]{Retrieved_Gtid_Set} ) {
$log->info(
sprintf( "Retrieved Gtid Set: %s", $latest[0]{Retrieved_Gtid_Set} ) );
}
if ($find_oldest) {
$self->set_oldest_slaves( \@latest );
}
else {
$self->set_latest_slaves( \@latest );
}
}
orchestrator是根据ExecBinlogCoordinates比较出latest slave
ExecBinlogCoordinates 是应用binlog坐标的意思 对应show slave status中的
- Relay_Master_Log_File
- Exec_Master_Log_Pos 表示sql_thread已经应用了主库哪个binlog哪个位置的日志.
然而若想不丢数据, 则应该根据ReadBinlogCoordinates比较出latest slave, 也就是MHA的实现方式, 即
- Master_Log_File
- Read_Master_Log_Pos 使用ExecBinlogCoordinates选Latest Slave是可能丢数据的(即使开了半同步), 可以通过tc命令轻松复现orc这种选latest slave导致的丢数据问题.
具体模拟方法见#1312 我修改了NewInstancesSorterByExec的Less的方法, 改为使用ReadBinlogCoordinates选择latest slave, 解决了上述问题.
那么最准确的方式是要等所有slave sql_thread跑完. orchestrator虽然调用了WaitForSQLThreadUpToDate, 但只等待了10s(超时).
随后运行sortInstancesDataCenterHint函数
// sortInstances shuffles given list of instances according to some logic
func sortInstancesDataCenterHint(instances [](*Instance), dataCenterHint string) {
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(NewInstancesSorterByExec(instances, dataCenterHint)))
}这里做了个Reverse排序, 具体如何排序的, 要看NewInstancesSorterByExec的Less方法
关于sort.Reverse
type reverse struct { // This embedded Interface permits Reverse to use the methods of // another Interface implementation. Interface }> // Less returns the opposite of the embedded implementation's Less method. func (r reverse) Less(i, j int) bool { return r.Interface.Less(j, i) }> // Reverse returns the reverse order for data. func Reverse(data Interface) Interface { return &reverse{data} }sort.Reverse返回的是一个*reverse. reverse结构体就一个匿名字段Interface reverse实现了Less方法, 他本质就是使用Interface.Less, 只不过调换了参数顺序 所以Reverse()虽然返回的是初始数据,但是改变了数据的Less()方法, 在排序时调用这个就会产生逆排序的效果.
NewInstancesSorterByExec的Less方法
func (this *InstancesSorterByExec) Less(i, j int) bool {
// Returning "true" in this function means [i] is "smaller" than [j],
// which will lead to [j] be a better candidate for promotion
// Sh*t happens. We just might get nil while attempting to discover/recover if this.instances[i] == nil {
return false
}
if this.instances[j] == nil {
return true
}
if this.instances[i].ExecBinlogCoordinates.Equals(&this.instances[j].ExecBinlogCoordinates) {
// Secondary sorting: "smaller" if not logging replica updates
if this.instances[j].LogReplicationUpdatesEnabled && !this.instances[i].LogReplicationUpdatesEnabled {
return true
}
// Next sorting: "smaller" if of higher version (this will be reversed eventually)
// Idea is that given 5.6 a& 5.7 both of the exact position, we will want to promote
// the 5.6 on top of 5.7, as the other way around is invalid
if this.instances[j].IsSmallerMajorVersion(this.instances[i]) {
return true
}
// Next sorting: "smaller" if of larger binlog-format (this will be reversed eventually)
// Idea is that given ROW & STATEMENT both of the exact position, we will want to promote
// the STATEMENT on top of ROW, as the other way around is invalid
if this.instances[j].IsSmallerBinlogFormat(this.instances[i]) {
return true
}
// Prefer local datacenter:
if this.instances[j].DataCenter == this.dataCenter && this.instances[i].DataCenter != this.dataCenter {
return true
}
// Prefer if not having errant GTID
if this.instances[j].GtidErrant == "" && this.instances[i].GtidErrant != "" {
return true
}
// Prefer candidates:
if this.instances[j].PromotionRule.BetterThan(this.instances[i].PromotionRule) {
return true
}
} return this.instances[i].ExecBinlogCoordinates.SmallerThan(&this.instances[j].ExecBinlogCoordinates)
}简单来说, 就是根据ExecBinlogCoordinates比较, 如果ExecBinlogCoordinates相同在比DataCenter, DataCenter与DeadMaster一样的为"大"
instance.ExecBinlogCoordinates.LogFile = m.GetString("Relay_Master_Log_File")
instance.ExecBinlogCoordinates.LogPos = m.GetInt64("Exec_Master_Log_Pos")
那么至此sortInstancesDataCenterHint干了啥也就清楚了, 就是排了个序, 把most up-to-date从库放在最前面, 如果两个从库ExecBinlogCoordinates一样, 则从库所在数据中心和主库一样的放前面
首要条件是ExecBinlogCoordinates. PromotionRule的"好坏"只是最次要的排序条件(因为他在最后一个if里). ExecBinlogCoordinates相同时, 排序优先级是:
- LogReplicationUpdatesEnabled
- SmallerMajorVersion
- SmallerBinlogFormat
- same DataCenter with dead master
- GtidErrant == ""
- PromotionRule
接下来GetCandidateReplica会调用chooseCandidateReplica, 初步选一个candidate, chooseCandidateReplica接收的参数就是刚刚sortedReplicasDataCenterHint返回的排序后的replicas切片
// chooseCandidateReplica
func chooseCandidateReplica(replicas [](*Instance)) (candidateReplica *Instance, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas [](*Instance), err error) {
if len(replicas) == 0 {
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, fmt.Errorf("No replicas found given in chooseCandidateReplica")
}
// 返回在给定实例中发现的主要(最常见)的Major版本
// 比如replicas里有三个实例, 5.6.30, 5.7.32, 5.7.26. 那priorityMajorVersion就是5.7
priorityMajorVersion, _ := getPriorityMajorVersionForCandidate(replicas)
// 返回在给定实例中发现的主要(最常见)binlog格式
// 比如replicas里有三个实例, mixed, row, row. 那么priorityBinlogFormat是row
priorityBinlogFormat, _ := getPriorityBinlogFormatForCandidate(replicas)
for _, replica := range replicas {
replica := replica
if isGenerallyValidAsCandidateReplica(replica) && // 做一些简单的检测, 比如IsLastCheckValid, LogBinEnabled, LogReplicationUpdatesEnabled(前三个都应该为true), IsBinlogServer(应为false)
!IsBannedFromBeingCandidateReplica(replica) && // 是否被参数 PromotionIgnoreHostnameFilters 匹配, 希望不匹配
!IsSmallerMajorVersion(priorityMajorVersion, replica.MajorVersionString()) && // 希望 replica 版本 <= priorityMajorVersion. 更希望高版本做低版本从库. 那比如最常见版本是5.6, 然后有一个replica是5.7, 他是那个most up-to-date的从库, 到这里一比较, 他就不符合条件, 就被pass了
!IsSmallerBinlogFormat(priorityBinlogFormat, replica.Binlog_format) { // 希望比如priorityBinlogFormat row, 那replica是mixed或statement
// this is the one
candidateReplica = replica
break
}
}
// 不用想那么多, 以我们的场景, 不存在Major版本不同的, Binlog_format也都是row
// 那只要这个从库没什么"毛病", 也没在PromotionIgnoreHostnameFilters中, 那基本上replicas[0]就是candidateReplica
// 如果上面的所有replica都不符合条件, candidateReplica就=nil, 就会进入这个if
if candidateReplica == nil {
// Unable to find a candidate that will master others.
// Instead, pick a (single) replica which is not banned.
for _, replica := range replicas {
replica := replica
if !IsBannedFromBeingCandidateReplica(replica) { // 选出第一个not banned的
// this is the one
candidateReplica = replica
break
}
}
// 如果选出了一个 not banned
if candidateReplica != nil {
// 把candidateReplica从 replicas里移除
replicas = RemoveInstance(replicas, &candidateReplica.Key)
}
return candidateReplica, replicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, fmt.Errorf("chooseCandidateReplica: no candidate replica found")
}
// 能走到这里, 说明第一次循环就找到candidateReplica了
// 把candidateReplica从 replicas里移除
replicas = RemoveInstance(replicas, &candidateReplica.Key)
// 迭代replicas
for _, replica := range replicas {
replica := replica
// 如果这个实例不能做 candidateReplica 的从库, 就把它放到 cannotReplicateReplicas切片里
if canReplicate, err := replica.CanReplicateFrom(candidateReplica); !canReplicate {
// lost due to inability to replicate
cannotReplicateReplicas = append(cannotReplicateReplicas, replica)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("chooseCandidateReplica(): error checking CanReplicateFrom(). replica: %v; error: %v", replica.Key, err)
}
// 如果这个实例 ExecBinlogCoordinates SmallerThan candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates, 放到laterReplicas
} else if replica.ExecBinlogCoordinates.SmallerThan(&candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates) {
laterReplicas = append(laterReplicas, replica)
// 如果这个实例 ExecBinlogCoordinates == candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates, 放到 equalReplicas
} else if replica.ExecBinlogCoordinates.Equals(&candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates) {
equalReplicas = append(equalReplicas, replica)
// 佛足额, 说明这个实例 ExecBinlogCoordinates > candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates, 放到 aheadReplicas
} else {
// lost due to being more advanced/ahead of chosen replica.
aheadReplicas = append(aheadReplicas, replica)
}
}
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err
}chooseCandidateReplica选了一个candidateReplica出来
并且对其他replica做了归类(laterReplicas, equalReplicas, aheadReplicas)
CanReplicateFrom的具体逻辑请看CanReplicateFrom
从代码可以看出orchestrator并不会以0数据丢失为最优先级选择candidate
// 返回在给定实例中发现的主要(最常见)的Major版本
// 比如replicas里有三个实例, 5.6.30, 5.7.32, 5.7.26. 那priorityMajorVersion就是5.7
priorityMajorVersion, _ := getPriorityMajorVersionForCandidate(replicas)
// 返回在给定实例中发现的主要(最常见)binlog格式
// 比如replicas里有三个实例, mixed, row, row. 那么priorityBinlogFormat是row
priorityBinlogFormat, _ := getPriorityBinlogFormatForCandidate(replicas)
for _, replica := range replicas {
replica := replica
if isGenerallyValidAsCandidateReplica(replica) && // 做一些简单的检测, 比如IsLastCheckValid, LogBinEnabled, LogReplicationUpdatesEnabled(前三个都应该为true), IsBinlogServer(应为false)
!IsBannedFromBeingCandidateReplica(replica) && // 是否被参数 PromotionIgnoreHostnameFilters 匹配, 希望不匹配
!IsSmallerMajorVersion(priorityMajorVersion, replica.MajorVersionString()) && // 希望 replica 版本 <= priorityMajorVersion. 更希望高版本做低版本从库. 那比如最常见版本是5.6, 然后有一个replica是5.7, 他是那个most up-to-date的从库, 到这里一比较, 他就不符合条件, 就被pass了
!IsSmallerBinlogFormat(priorityBinlogFormat, replica.Binlog_format) { // 希望比如priorityBinlogFormat row, 那replica是mixed或statement
// this is the one
candidateReplica = replica
break
}
}上述代码中的replicas是sortInstancesDataCenterHint返回的, 按ExecBinlogCoordinates从大到小排序的切片(即ExecBinlogCoordinates最大的index是0)
但是最终candidateReplica是否是replicas[0], 取决于其MajorVersion和BinlogFormat(当然还有isGenerallyValidAsCandidateReplica和IsBannedFromBeingCandidateReplica)
在Discussion: recovering a dead master中也有如下描述: Find the best replica to promote.
- 一种天真的方法是选择最新的副本, 但这可能并不总是正确的选择
A naive approach would be to pick the most up-to-date replica, but that may not always be the right choice.
- 最新的副本可能没有必要的配置来充当其他副本的主节点(例如, binlog 格式、MySQL 版本控制、复制过滤器等). 一味地推广最新的副本可能会丢失副本容量 It may so happen that the most up-to-date replica will not have the necessary configuration to act as master to other replicas (e.g. binlog format, MySQL versioning, replication filters and more). By blindly promoting the most up-to-date replica one may lose replica capacity.
orchestrator尝试提升将保留最多服务容量的副本.orchestratorattempts to promote a replica that will retain the most serving capacity.
- 提升所述副本, 接管其同级
Promote said replica, taking over its siblings.
- Bring siblings up to date
- 可能的话, 做第二阶段选举提升; 如果可能的话, 用户可能已经标记了要提升的特定服务器(见
register-candidate命令)
Possibly, do a 2nd phase promotion; the user may have tagged specific servers to be promoted if possible (see
register-candidatecommand).
但针对我们的场景, 同一个集群不存在Major版本不同实例, Binlog_format也都是row 那只要这个从库没什么"毛病", 也没在PromotionIgnoreHostnameFilters中, 那基本上replicas[0]就是candidateReplica
那么继续看GetCandidateReplica剩下的代码
candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err = chooseCandidateReplica(replicas)
if err != nil { // 如果chooseCandidateReplica走到 if candidateReplica == nil { ,就会进入这个if
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err
}
if candidateReplica != nil {
mostUpToDateReplica := replicas[0]
// 这是有可能的
// 比如最常见版本是5.6, 然后有一个replica是5.7, 他是那个most up-to-date的从库, 但它比priorityMajorVersion大. 他就不适合做candidate
if candidateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates.SmallerThan(&mostUpToDateReplica.ExecBinlogCoordinates) {
log.Warningf("GetCandidateReplica: chosen replica: %+v is behind most-up-to-date replica: %+v", candidateReplica.Key, mostUpToDateReplica.Key)
}
}
log.Debugf("GetCandidateReplica: candidate: %+v, ahead: %d, equal: %d, late: %d, break: %d", candidateReplica.Key, len(aheadReplicas), len(equalReplicas), len(laterReplicas), len(cannotReplicateReplicas))
return candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, nil
}// RegroupReplicasGTID will choose a candidate replica of a given instance, and take its siblings using GTID
func RegroupReplicasGTID(
masterKey *InstanceKey, // 实参传进来的是 挂掉的旧主库
returnReplicaEvenOnFailureToRegroup bool, // 实参传进来的是 true
startReplicationOnCandidate bool, // 实参传进来的是 false
onCandidateReplicaChosen func(*Instance), // 实参传进来的是 nil
postponedFunctionsContainer *PostponedFunctionsContainer,
postponeAllMatchOperations func(*Instance, bool) bool, // 实参传进来的是 promotedReplicaIsIdeal 函数
) (
lostReplicas [](*Instance),
movedReplicas [](*Instance),
cannotReplicateReplicas [](*Instance),
candidateReplica *Instance,
err error,
) {
var emptyReplicas [](*Instance)
var unmovedReplicas [](*Instance)
// candidateReplica有可能==nil
candidateReplica, aheadReplicas, equalReplicas, laterReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, err := GetCandidateReplica(masterKey, true)
// 如果chooseCandidateReplica走到 if candidateReplica == nil { ,就会进入这个if
// Unable to find a candidate that will master others.
// Instead, pick a (single) replica which is not banned.
if err != nil {
// returnReplicaEvenOnFailureToRegroup实参传进来的是 true
if !returnReplicaEvenOnFailureToRegroup {
candidateReplica = nil
}
return emptyReplicas, emptyReplicas, emptyReplicas, candidateReplica, err
}
// onCandidateReplicaChosen实参传进来的是 nil
if onCandidateReplicaChosen != nil {
onCandidateReplicaChosen(candidateReplica) // 所以走不到这里
}
// equalReplicas 和 laterReplicas 都可以做candidateReplica的从库, 所以放到replicasToMove里
replicasToMove := append(equalReplicas, laterReplicas...)
hasBestPromotionRule := true
if candidateReplica != nil {
// 迭代replicasToMove
for _, replica := range replicasToMove {
// 比较PromotionRule. 判断candidateReplica是不是用户prefer的
if replica.PromotionRule.BetterThan(candidateReplica.PromotionRule) {
hasBestPromotionRule = false
}
}
}
moveGTIDFunc := func() error {
log.Debugf("RegroupReplicasGTID: working on %d replicas", len(replicasToMove))
// moves a list of replicas under another instance via GTID, returning those replicas
// that could not be moved (do not use GTID or had GTID errors)
movedReplicas, unmovedReplicas, err, _ = moveReplicasViaGTID(replicasToMove, candidateReplica, postponedFunctionsContainer)
unmovedReplicas = append(unmovedReplicas, aheadReplicas...)
return log.Errore(err)
}
// 这个 postponeAllMatchOperations 就是 recoverDeadMaster中定义的 promotedReplicaIsIdeal
// 做一些判断, 但基本上就是看 hasBestPromotionRule 和 candidateReplica的promotion rule是不是MustNotPromoteRule. 如果candidateReplica就是理想的, 那moveGTIDFunc就放到异步推迟执行
if postponedFunctionsContainer != nil && postponeAllMatchOperations != nil && postponeAllMatchOperations(candidateReplica, hasBestPromotionRule) {
postponedFunctionsContainer.AddPostponedFunction(moveGTIDFunc, fmt.Sprintf("regroup-replicas-gtid %+v", candidateReplica.Key))
} else {
// 否则同步执行
err = moveGTIDFunc()
}
// 我没太看懂上面那个if else, 除了canidateReplica恰好是prefer的那个时多输出一个日志义务外, 和else时有啥区别吗?
if startReplicationOnCandidate { // 实参传进来的是 false. 在DeadMaster场景, 这里不能传true, 因为StartReplication会调用MaybeEnableSemiSyncReplica, 而后者需要连接 old master
// 但是old master已经挂了所以肯定连不上, 于是这里出现error直接return了, 后面真正的start slave是没机会执行的
StartReplication(&candidateReplica.Key)
}
log.Debugf("RegroupReplicasGTID: done")
AuditOperation("regroup-replicas-gtid", masterKey, fmt.Sprintf("regrouped replicas of %+v via GTID; promoted %+v", *masterKey, candidateReplica.Key))
return unmovedReplicas, movedReplicas, cannotReplicateReplicas, candidateReplica, err
}所以 RegroupReplicasGTID
- 选了个candidateReplica出来, 并给其他replica归了类 这个candidateReplica不一定是最终的主库, 只是它的ExecBinlogCoordinates大
- 通过moveReplicasViaGTID, 将其他的replica(除了aheadReplicas和cannotReplicateReplicas)都change master到了candidateReplica
至此RegroupReplicasGTID工作完成了, 剩下的工作可以交换给recoverDeadMaster了, 就是recoverDeadMaster 主要做了几件事中的最后两步操作
recoverDeadMaster 主要做了几件事
- GetMasterRecoveryType, 确定到底用什么方式恢复, 是基于GTID? PseudoGTID? 还是BinlogServer?
- 重组拓扑, 我们的案例是使用RegroupReplicasGTID. 但这里有一个问题, 可能现在我们的新主库并不是我们"期望"的实例, 就是说之所以选他做主库可能是因为他有最全的日志. 但不是我们设置的prefer的 所以通过一个闭包promotedReplicaIsIdeal去做了判断和标记
- 如果存在lostReplicas, 并且开启了DetachLostReplicasAfterMasterFailover, 那么会并行的对所有lostReplicas执行DetachReplicaMasterHost. 其实就是执行change master to master_host='// {host}'
- 如果当前选举的new master不是我们prefer的实例, 重组拓扑, 用prefer做新主库
根据Orchestrator Failover过程源码分析-II 没有在recoverDeadMaster和checkAndRecoverDeadMaster中看到任何代码执行了start slave sql_thread
那在checkAndRecoverDeadMaster执行到这里时, 不是肯定会超时吗
if config.Config.DelayMasterPromotionIfSQLThreadNotUpToDate && !promotedReplica.SQLThreadUpToDate() {
AuditTopologyRecovery(topologyRecovery, fmt.Sprintf("DelayMasterPromotionIfSQLThreadNotUpToDate: waiting for SQL thread on %+v", promotedReplica.Key))
if _, err := inst.WaitForSQLThreadUpToDate(&promotedReplica.Key, 0, 0); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("DelayMasterPromotionIfSQLThreadNotUpToDate error: %+v", err)
}
AuditTopologyRecovery(topologyRecovery, fmt.Sprintf("DelayMasterPromotionIfSQLThreadNotUpToDate: SQL thread caught up on %+v", promotedReplica.Key))
}