As a data expert you work at a car dealership company which sells new cars of various brands and models. Your company is small and new but it has branches in several countries. Since the establishment of the company your colleagues have sold several cars to the customers. Now your boss realized your company imperatively needs a database to keep the records about the cars, salespersons, customers, and invoices. Your boss trusts you very much so he assigned you the challenge to design, create, and manage the database.
Using pen and paper (or computer software if you are skillful at creating digital diagrams), design a database to meet the minimal requirements of your boss. The minimal information to be recorded is described below:
-
Cars - e.g. the vehicle identification number (VIN), manufacturer, model, year, and color of the cars in your company's inventory.
-
Customers - e.g. the customer ID, name, phone number, email, address, city, state/province, country, and zip/postal code of the customers.
-
Salespersons - e.g. staff ID, name, and the store at your company.
-
Invoices - e.g. the invoice number, date, car, customer, and salesperson related to each car sale.
Before solving this challenge, review your lesson about database structure and design then ask yourself:
-
What entities and attributes should be included in the database?
- For each attribute, what data type is most suitable?
- Note that in MySQL typically each entity table should have an auto-increment numeric ID. The auto-increment ID is different from the customer ID or staff ID.
- Also note that some attributes are required while other ones can be blank.
-
What are the relations between these entities? Which relations are one-to-one vs one-to-many vs many-to-many?
-
How can you use foreign keys to normalize your database design?
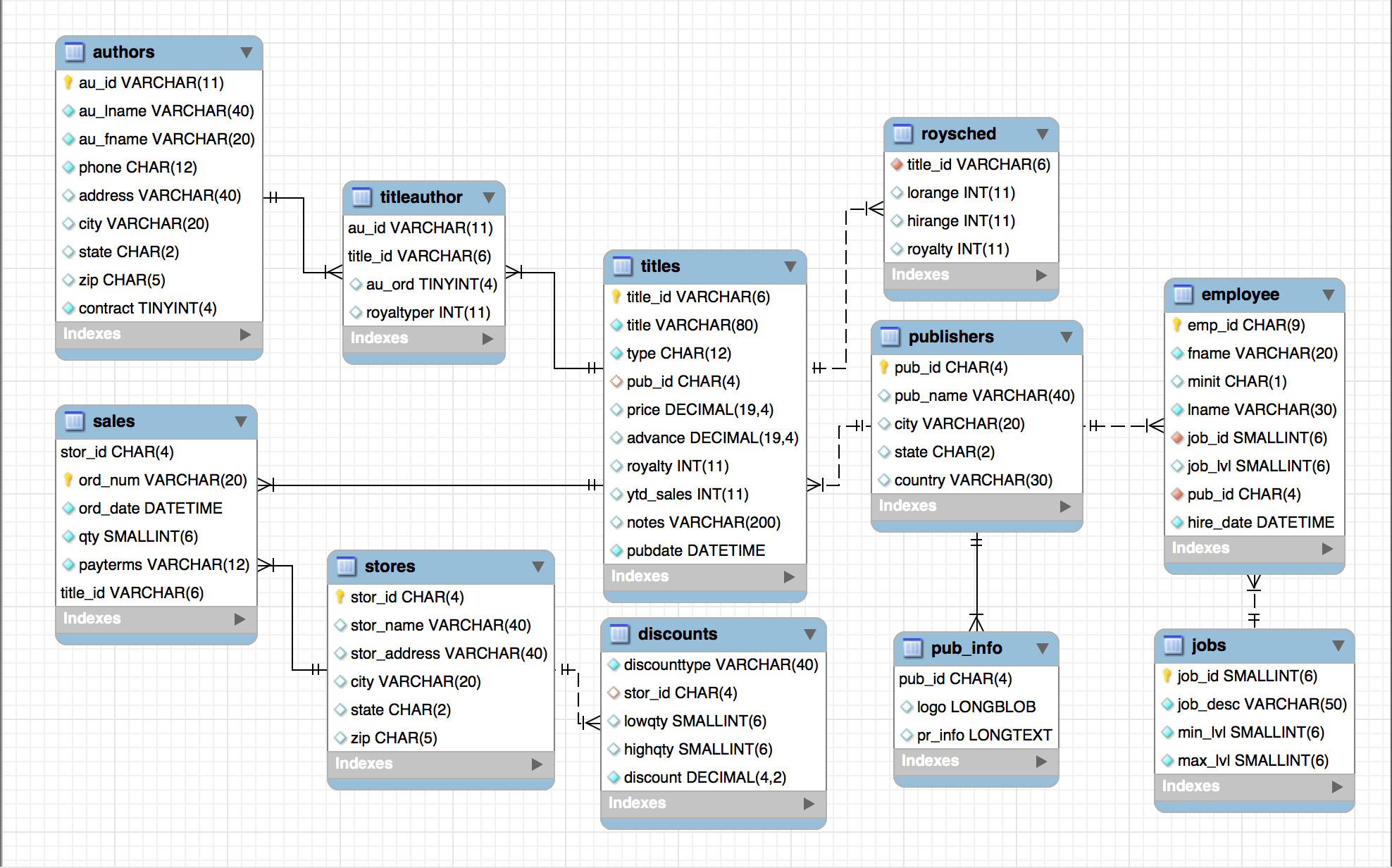
Your end product of this challenge should look something like below, though it doesn't have to be that complicated:
If you use pen and paper to create the design, take a picture with your phone and send the image to yourself. If you use software to create the database diagram, export in the image format (JPG or PNG). Either way, the image will be submitted as one of the deliverables.
-
Create a MySQL database for this lab. You can do so in the command line like this:
$ mysql -u your_username -p mysql> CREATE DATABASE lab_mysql; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec) mysql> USE lab_mysql; Database changed
Note: If you have set a password for the database user, you need to supply
-pin the MySQL connection command. Once you hit enter, MySQL will ask you to type the password. If you didn't set the password for the database user, you don't need to supply-pin the connection command. -
Now, based on the database design you created, write the SQL query to create the tables and columns. You will be using the
CREATE TABLEstatement for which you can find reference here.You can test your
CREATE TABLEstatement in either SQL command line or the database software you installed (e.g. Sequel Pro or MySQL Workbench). Remember after creating each table, you need to delete it in order to test the sameCREATE TABLEstatement again. -
After writing and testing all the statements, create a text file with the name
create.sql. At the beginning of the file, indicate which database you want to use e.g.:USE lab_mysql;
-
Then following the
USEstatement, write all yourCREATE TABLEstatements. You'll need oneCREATE TABLEstatement for each table you decide to create. Make sure to end each statement with a semicolon.
This .sql file will be one of your deliverables. A .sql file is often used by software/data engineers to automate database operations. For example, to execute all the commands in the create.sql file, you can simply execute source create.sql; in MySQL command line. Many programming languages such as Python and PHP can also execute .sql files.
The purpose of database seeding is to provide some dummy data for an empty database so that software development can be started based on the dummy data. In this challenge you will create seeding.sql which inserts dummy data rows into the tables of your new database.
You'll be using the INSERT INTO statement for this purpose. A tutorial you can refer to can be fine here.
For your convenience, we provide you some example dummy data. These dummy data may not readily work with your database depending on how you have designed your database. You may need to change them to the appropriate form.
| ID | VIN | Manufacturer | Model | Year | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3K096I98581DHSNUP | Volkswagen | Tiguan | 2019 | Blue |
| 1 | ZM8G7BEUQZ97IH46V | Peugeot | Rifter | 2019 | Red |
| 2 | RKXVNNIHLVVZOUB4M | Ford | Fusion | 2018 | White |
| 3 | HKNDGS7CU31E9Z7JW | Toyota | RAV4 | 2018 | Silver |
| 4 | DAM41UDN3CHU2WVF6 | Volvo | V60 | 2019 | Gray |
| 5 | DAM41UDN3CHU2WVF6 | Volvo | V60 Cross Country | 2019 | Gray |
| ID | Customer ID | Name | Phone | Address | City | State/Province | Country | Postal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10001 | Pablo Picasso | +34 636 17 63 82 | - | Paseo de la Chopera, 14 | Madrid | Madrid | Spain | 28045 |
| 1 | 20001 | Abraham Lincoln | +1 305 907 7086 | - | 120 SW 8th St | Miami | Florida | United States | 33130 |
| 2 | 30001 | Napoléon Bonaparte | +33 1 79 75 40 00 | - | 40 Rue du Colisée | Paris | Île-de-France | France | 75008 |
| ID | Staff ID | Name | Store |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 00001 | Petey Cruiser | Madrid |
| 1 | 00002 | Anna Sthesia | Barcelona |
| 2 | 00003 | Paul Molive | Berlin |
| 3 | 00004 | Gail Forcewind | Paris |
| 4 | 00005 | Paige Turner | Mimia |
| 5 | 00006 | Bob Frapples | Mexico City |
| 6 | 00007 | Walter Melon | Amsterdam |
| 7 | 00008 | Shonda Leer | São Paulo |
| ID | Invoice Number | Date | Car | Customer | Sales Person |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 852399038 | 22-08-2018 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| 1 | 731166526 | 31-12-2018 | 3 | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 271135104 | 22-01-2019 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
Now you find an error you need to fix in your existing data - in the Salespersons table, you mistakenly spelled Miami as Mimia for Paige Turner. Also, you received the email addresses of the three customers:
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Pablo Picasso | ppicasso@gmail.com |
| Abraham Lincoln | lincoln@us.gov |
| Napoléon Bonaparte | hello@napoleon.me |
Create update.sql to update your existing data.
In addition, you also find a duplicated car entry for VIN DAM41UDN3CHU2WVF6. You want to delete car ID #4 from the database. Create delete.sql to perform the deletion.
-
Your database structure design diagram in the form of image.
-
create.sqlandseeding.sql -
[OPTIONAL]
update.sqlanddelete.sql
-
Upon completion, add the deliverables to git, commit changes, and submit to github. Make sure you submit to your own forked repo.
cd your-code git add . git commit -m "Lab MySQL solutions" git push origin master
-
Navigate to your forked repo and create a Pull Request to the class repo.
- If you don't remember how to do this, review the lesson in the Prework titled Git Forking.
- Also your instructor and TA will provide support to you.
-
Create a pull request with title following this format:
[<lab_name>] <your_name>- For example, if the lab is lab-mysql and your name is Marc Pomar, your pull request name should be something like
[lab-mysql] Marc Pomar.
- For example, if the lab is lab-mysql and your name is Marc Pomar, your pull request name should be something like
-
If you have successfully created the pull request you are done! CONGRATS :)
MySQL Reference: Creating a Table
MySQL Reference: INSERT Syntax