- Related projects
- References
- Supported flow direction encodings
- Installing on Windows from MSVC binaries
- Installing on Windows from MinGW GCC binaries
- Building on Windows using MSVC
- Building on Windows using MinGW GCC
- Building on Linux
- Testing MSVC binaries on Windows using TX data
- Testing MinGW GCC binaries on Windows using TX data
- Benchmark results of MSVC vs. MinGW GCC vs. WSL GCC vs. Linux GCC binaries using CONUS data
- Benchmark results
MIDAS is the core C library and executables, and is required for all Python, R, and QGIS interfaces. The following projects are thin wrappers or interfaces to MIDAS's shared library (executables for the QGIS plugin). I designed the QGIS plugin to use subprocesses to isolate long-running or error-prone operations from the main QGIS process.
- MIDASFlow: Python package
- MIDASFlow-R: R package
- MIDAS-QGIS: QGIS plugin
- MEFA (Flow Accumulation): Huidae Cho, July 2023. Memory-Efficient Flow Accumulation Using a Look-Around Approach and Its OpenMP Parallelization. Environmental Modelling & Software 167, 105771. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105771. Author's Version.
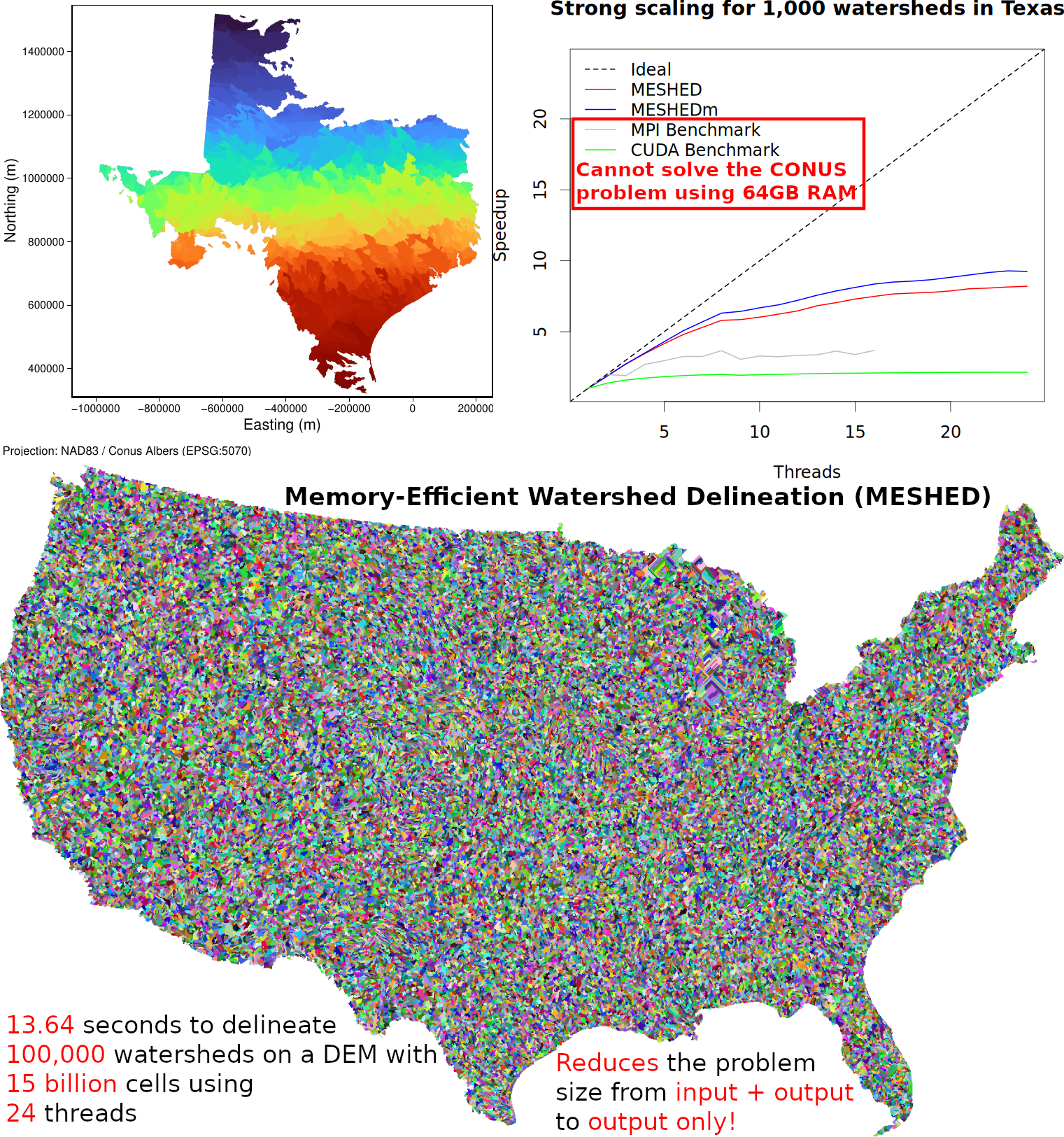
- MESHED (Watershed Delineation): Huidae Cho, January 2025. Avoid Backtracking and Burn Your Inputs: CONUS-Scale Watershed Delineation Using OpenMP. Environmental Modelling & Software 183, 106244. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2024.106244. Author's Version.
- MELFP (Longest Flow Path): Huidae Cho, September 2025. Loop Then Task: Hybridizing OpenMP Parallelism to Improve Load Balancing and Memory Efficiency in Continental-Scale Longest Flow Path Computation. Environmental Modelling & Software 193, 106630. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2025.106630. Author's Version.
Predefined flow direction encodings in GeoTIFF: power2 (default, r.terraflow, ArcGIS), taudem (d8flowdir), 45degree (r.watershed), degree




Custom flow direction encoding is also possible by passing -e E,SE,S,SW,W,NW,N,NE (e.g., 1,8,7,6,5,4,3,2 for taudem).
- Install Git for Windows
- Install Miniconda
curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe
mkdir C:\opt
Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe /S /D=C:\opt\miniconda
C:\opt\miniconda\condabin\conda.bat init- Setup Conda for MIDAS run
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --set channel_priority strict
conda create -n midas_msvc libgdal
conda activate midas_msvc- Download the source code and binaries
cd \opt
git clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git- Run MIDAS (add
C:\opt\midas\windows\msvctoPATH)
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\opt\midas\windows\msvc
mefa- Install Git for Windows
- Install Miniconda
curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe
mkdir C:\opt
Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe /S /D=C:\opt\miniconda
C:\opt\miniconda\condabin\conda.bat init- Setup Conda for MIDAS run
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --set channel_priority strict
conda create -n midas_mingw libgcc libgdal
conda activate midas_mingw- Download the source code and binaries
cd \opt
git clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git- Run MIDAS (add
C:\opt\midas\windows\mingwtoPATH)
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\opt\midas\windows\mingw
mefa- Install Visual Studio Community Edition. Select these two components:
- MSVC v143 - VS 2022 C++ x64/x86 build tools (Latest)
- Windows 11 SDK (10.0.26100.0)
- Install Git for Windows
- Install Miniconda
curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe
mkdir C:\opt
Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe /S /D=C:\opt\miniconda
C:\opt\miniconda\condabin\conda.bat init- Start Developer Command Prompt for VS 2022
- Setup Conda for MIDAS build
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --set channel_priority strict
conda create -n midas cmake libgdal
conda activate midas- Download the source code
cd \opt
git clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git
cd midas/src- Build MIDAS
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. > cmake.log 2>&1
msbuild midas.sln -p:Configuration=Release > msbuild.log 2>&1- Run MIDAS (add
C:\opt\midas\src\build\disttoPATH)
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\opt\midas\src\build\dist
mefa- Install Git for Windows
- Install Miniconda
curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe
mkdir C:\opt
Miniconda3-latest-Windows-x86_64.exe /S /D=C:\opt\miniconda
C:\opt\miniconda\condabin\conda.bat init- Setup Conda for MIDAS build
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --set channel_priority strict
conda create -n midas_mingw cmake make gcc binutils libgdal
conda activate midas_mingw- Download the source code
cd \opt
git clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git
cd midas/src- Build MIDAS
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -G "MinGW Makefiles" > cmake.log 2>&1
make > make.log 2>&1- Run MIDAS (add
C:\opt\midas\src\build\disttoPATH)
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\opt\midas\src\build\dist
mefa- Install Miniconda
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
chmod a+x Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
mkdir ~/opt
./Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -b -u -p ~/opt/miniconda
~/opt/miniconda/bin/conda init
. ~/.bashrc- Setup Conda for MIDAS build
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --set channel_priority strict
conda create -n midas git cmake make gcc gdal
conda activate midas- Download the source code
cd ~/opt
git clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git
cd midas/src- Build MIDAS
mkdir build
cd build
# LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CONDA_PREFIX/lib and -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=$CONDA_PREFIX to avoid system libraries
(
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CONDA_PREFIX/lib \
cmake .. \
-DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=$CONDA_PREFIX \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$HOME/usr/local &&
cmake --build . &&
cmake --install .
) &> build.log- Run MIDAS (add
$HOME/usr/local/bintoPATH)
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/usr/local/bin"
mefagit clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git
cd midas\windows\test
pretest.bat
test_msvc.bat
git clone https://github.com/HuidaeCho/midas.git
cd midas\windows\test
pretest.bat
test_mingw.bat
System specifications
- System model and OS
- ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 11
- Windows 11 for MSVC and MinGW
- WSL Linux 5.15.167.4-microsoft-standard-WSL2 for WSL GCC
- ThinkPad X1 Yoga Gen 8 (identical hardware specifications)
- Slackware CURRENT Linux 6.12.17 for Linux GCC
- ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 11
- CPU: Intel Core i7-1370P @ 5.20 GHz
- Cores: 14
- Logical processors: 20
- Memory: 64 GiB
MSVC
> melfp.exe inputs\fdr.tif inputs\outlets515152.shp cat msvc.gpkg lfpid -c msvc.csv
No output vector layers specified; Not creating msvc.gpkg
Using 20 threads...
Reading flow direction raster <inputs\fdr.tif>...
Input time for flow direction: 9198000 microsec
Reading outlets <inputs\outlets515152.shp>...
Input time for outlets: 17007000 microsec
Number of cells: 14998630400
Number of outlets: 515152
Tracing stack size for loop-then-task: 3072
Finding longest flow paths...
Computation time for longest flow paths: 622248000 microsec
Number of longest flow paths found: 521946
Writing longest flow path head coordinates <msvc.csv>...
Output time for longest flow path head coordinates: 1980000 microsec
Total elapsed time: 657635000 microsec
- Computation time: 622.248000 sec
- I/O time: 35.387000 sec
- Total time: 657.635000 sec
MinGW GCC
> melfp.exe inputs\fdr.tif inputs\outlets515152.shp cat mingw.gpkg lfpid -c mingw.csv
No output vector layers specified; Not creating mingw.gpkg
Using 20 threads...
Reading flow direction raster <inputs\fdr.tif>...
Input time for flow direction: 6823994 microsec
Reading outlets <inputs\outlets515152.shp>...
Input time for outlets: 16805443 microsec
Number of cells: 14998630400
Number of outlets: 515152
Tracing stack size for loop-then-task: 3072
Finding longest flow paths...
Computation time for longest flow paths: 120324302 microsec
Number of longest flow paths found: 521946
Writing longest flow path head coordinates <mingw.csv>...
Output time for longest flow path head coordinates: 2097205 microsec
Total elapsed time: 153459228 microsec
- Computation time: 120.324302 sec
- I/O time: 33.13493 sec
- Total time: 153.459228 sec
WSL GCC
$ melfp inputs/fdr.tif inputs/outlets515152.shp cat wsl.gpkg lfpid -c wsl.csv
No output vector layers specified; Not creating wsl.gpkg
Using 20 threads...
Reading flow direction raster <inputs/fdr.tif>...
Input time for flow direction: 7537860 microsec
Reading outlets <inputs/outlets515152.shp>...
Input time for outlets: 223358 microsec
Number of cells: 14998630400
Number of outlets: 515152
Tracing stack size for loop-then-task: 3072
Finding longest flow paths...
Computation time for longest flow paths: 38734223 microsec
Number of longest flow paths found: 521946
Writing longest flow path head coordinates <wsl.csv>...
Output time for longest flow path head coordinates: 426007 microsec
Total elapsed time: 47034415 microsec
- Computation time: 38.734223 sec
- I/O time: 8.300192 sec
- Total time: 47.034415 sec
Linux GCC
$ melfp inputs/fdr.tif inputs/outlets515152.shp cat linux.gpkg lfpid -c linux.csv
No output vector layers specified; Not creating linux.gpkg
Using 20 threads...
Reading flow direction raster <inputs/fdr.tif>...
Input time for flow direction: 1310629 microsec
Reading outlets <inputs/outlets515152.shp>...
Input time for outlets: 174350 microsec
Number of cells: 14998630400
Number of outlets: 515152
Tracing stack size for loop-then-task: 3072
Finding longest flow paths...
Computation time for longest flow paths: 21766454 microsec
Number of longest flow paths found: 521946
Writing longest flow path head coordinates <linux.csv>...
Output time for longest flow path head coordinates: 398142 microsec
Total elapsed time: 24136021 microsec
- Computation time: 21.766454 sec
- I/O time: 2.369567 sec
- Total time: 24.136021 sec
Computation time ranking
- Linux GCC: fastest baseline
- WSL GCC: 1.78x slower than Linux GCC
- MinGW GCC: 5.53x slower than Linux GCC
- MSVC: 28.59x slower than Linux GCC
Based on these results, Linux offers the best performance and should be used if possible. If you must use Windows, prefer WSL for better performance. If WSL is not available, MinGW GCC binaries provide the most reasonable performance among native Windows options.
System specifications
- CPU: Intel Core i9-12900 @ 2.40GHz
- Cores: 16
- Logical processors: 24
- Memory: 64 GiB
- OS: Windows 11
Citation
- Huidae Cho, July 2023. Memory-Efficient Flow Accumulation Using a Look-Aroun d Approach and Its OpenMP Parallelization. Environmental Modelling & Software 167, 105771. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105771.
System specifications
- CPU: Intel Core i9-12900 @ 2.40GHz
- Cores: 16
- Logical processors: 24
- Memory: 64 GiB
- OS: Windows 11
- Downstream flow length (computation time only)
- Texas results
- 8.2 s (24 threads)
- 19.6 s (1 thread)
- CONUS results
- 4.7 m (24 threads)
- 7.3 m (1 thread)
- Texas results
- Downstream flow length (computation time only)
- OS: Linux 6.6.30
- Downstream flow length (computation time only)
- Texas results
- 9.4 s (24 threads)
- 20.0 s (1 thread)
- CONUS results
- 2.0 m (24 threads)
- 4.0 m (1 thread)
- Texas results
- Downstream flow length (computation time only)