-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 12
Protocol Communication
Security is at the core of DSA. Inter-node connections in DSA are typically initiated by the Responder to the Requester. This achieves deployment flexibility as an added benefit allows for nodes on a LAN to establish secure, full-duplex connections to nodes on a WAN.
There are 3 inter-node connection types in DSA:
- Requester - Requester is able to browse and interact with the model of a Responder
- Responder - Responder is able to expose its model structure, stream model updates and receive commands from Requesters
- Requester + Responder - A DSBroker implements this pattern in an effort to route requests and responses between connected nodes
Currently there are 3 forms of transport channel bindings:
- HTTP
- WebSocket
- Socket
A Test Case of the handshake algorithm
The Handshake is based on ECDH with the NIST recommended curve P-256, also known as secp256r1.
All Base64 encoded strings used in DSLink handshake are url and filename safe Base64 alphabet rfc-4648 with no padding
The request uses an HTTP POST method to perform the request. A json request data is posted to the server's connection end point:
{
"publicKey":"BEACGownMzthVjNFT7Ry-RPX395kPSoUqhQ_H_vz0dZzs5RYoVJKA16XZhdYd__ksJP0DOlwQXAvoDjSMWAhkg4",
"zone":"default",
"isRequester":true,
"isResponder":true,
"version":"1.0.1"
}Query parameters:
- dsId
- A unique string of 43-128 characters, the last 43 characters are url safe Base64 encoded SHA256 hash of the public-key binary
- example: "link-dataflow-s-R9RKdvC2VNkfRwpNDMMpmT_YWVbhPLfbIc-7g4cpc"
Json parameters:
- publicKey
- Base64 of a ECDH public key ECPoint encoded in X9.63 (uncompressed)
- isRequester
- Indicates if the client is a requester
- isResponder
- Indicates if the client is a responder
- version
- version of DSA protocol
- zone (optional)
- Designates the quarantine zone the client wants to be in.
This is an example configuration of a DSA node.
{
"dsId":"broker-dsa-FEuG-dsvoy3Mfh-DY4ZLqxWdcjA9mky2MyCd0DmqTMw",
"publicKey":"BG4OYopcM2q09amKRKsc8N99ns5dybnBYG4Fi8bQVf6fKjyT_KRlPMJCs-3zvnSbBCXzS5fZfi88JuiLYwJY0gc",
"wsUri":"/ws",
"httpUri":"/http",
"tempKey":"BARngwlfjwD7goZHCh_4iWsP0e3JszsvOtovn1UyPnqZLlSOyoUH1v_Lop0oUFClpVhlzsWAAqur6S8apZaBe4I",
"salt":"0x205",
"saltS": "1x218",
"saltL": "2x221",
"updateInterval":200
}When client connect to server's connection end point, sever should return its configuration JSON in the http response body
- dsId
- dsId of the server
- publicKey
- Base64 of a ECDH public key ECPoint encoded in X9.63 (uncompressed)
- wsUri
- An endpoint for web socket connection
- Absolute URI to a different host or port is not allowed
- Requires a query parameter of "auth"
- SHA256 (UTF8Bytes (salt) + SharedSecret) ("+" here means concatenating of byte buffer)
- The salt is already provided within the JSON response
- httpUri
- An endpoint for http connection
- Absolute URI to a different host or port is not allowed
- See HTTP Queries
- salt
- A salt string to protect connection from replay attack on websocket connection
- Server should make sure that the salt is never reused unless connection is reset and nonce is regenerated
- saltS
- salt string for http short polling
- saltL
- salt string for http long polling
- tempKey
- a one time public key for the ECDH
- Base64 of a ECDH public key ECPoint encoded in X9.63 (uncompressed)
- updateInterval
- Only affects the responder
- When specified, a responder shouldn't send stream updates to server more often than the minimum interval in milliseconds, value subscriptions in the responder should be cached.
- If a value subscription update is already cached then it should update the cache with the new value to prevent useless updates or updating an incorrect value.
- This value only affects the time between 2 updates of same stream.
- If the responder does not respect the interval the requestor may close the connection due to flooding.

After receiving server configuration, client should send authentication data in http query string on every connection, this must also be done for websockets, however, a salt wont be returned.
The client must send the following url parameters:
- dsId
- dsId of the client
- auth
- Authentication string encoded in Base64 to prove client is a valid owner of the dsId and publicKey
- SHA256 (UTF8Bytes (salt) + SharedSecret ) ("+" here means concatenating of byte buffer)
- SharedSecret is the result of a standard ECDH with client's private key and server's one time public key: tempKey
The server sends the following headers:
- salt
- The server creates a new salt every time for the client to hash the decrypted nonce bytes.
- This is used for sending another query when creating the "auth" token.
WebSocket connection is very similar to HTTP mode except authentication only needs to be done once.
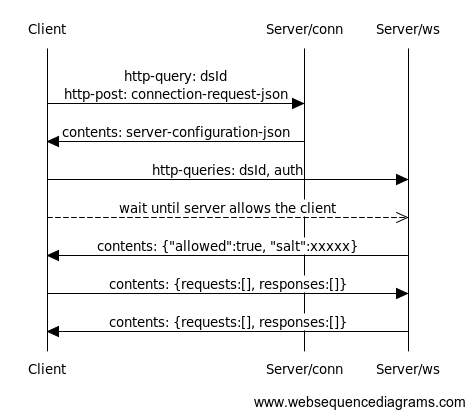
when in websocket mode, both client and server need to make sure a message is sent to other side at least once every 60 seconds, (because of network latency can cause message delay on other side, 30 ~ 45 seconds is suggested value for a minimal interval)
if no message is received in 60 seconds, websocket should be considered disconnected and a re-connection is needed
Protocol
◌ Design
◌ Initializing Connection
◌ Node API
◌ Methods
◌ Broker
◌ Broker Discovery
◌ Configs
◌ Value Types
◌ Tokens
◌ Quality of Service
DSLink Manager
◌ dslink.json
◌ Startup Command
SDK Development
◌ Implementation Guide
DSA Server
◌ Installation
◌ Update Server
◌ Server Configuration
◌ CLI Tools
◌ DSA Permission Basics
◌ DSA Permission Model
◌ Permission List for the Root
◌ Authentication
◌ OpenID Connect
◌ Password Hasher
◌ DGLux Server SSL (HTTPS)
◌ Docker
◌ Audit
◌ Data Node
◌ Install NGINX with DSA Server
◌ Configure Ubuntu Linux to auto start DSA server
◌ Troubleshooting