Card Fraud is a challenging problem that causes significant economic losses to businesses. The primary goal of this project is to build an machine learning model that detects card fraud detection based on transactions records. From a data point of view this is particularly challenging due to the lack of data (no many datasets available and occurrence is highly unbalanced) and patterns shift over time.
A secondary goal of this project is to familiarize me with the with the latest technology in adjacent areas of machine learning such as Data Engineering, Hyperparameter optimisation, MLOps.
-
Perform data transformation and feature engineering using PySpark.
-
Produce a binary classification model with a minor class (fraud) recall over 60% and a total f1 score over 80%
-
Use MLFlow to manage the life cycle of an ML model from parameters logging to model registry
- PySpark - Data and Feature Engineering.
- CatBoost - Gradient Booting Decision Trees
- MLFlow - Different MLOps activities. From creating experiments, recoding model parameters and metrics to model registry,
The data set was downloaded from The Fraud Detection Handbook GitHub. This is a simulated dataset Yann-Aël Le Borgne. In summary, it a dataset formed by 1,744,667 records. Each record represents a single transaction containing information from the user, the terminal used for the transaction and the amount.
This dataset presents many challenges due to its business nature.
-
The datasets is highly imbalanced as less tha 1% of the transactions are fraudulent.
-
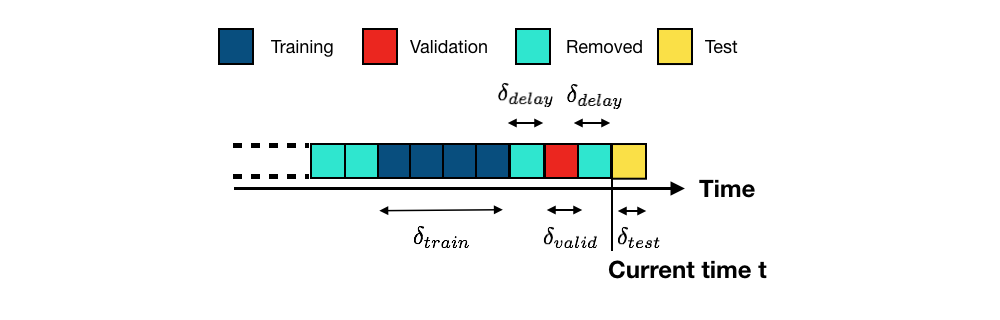
Data Shift. The behavioural patterns change over time. The patterns observed in a period (e.g. year) may not translate in future periods. Moreover, we need to consider that there is a business process to validate transactions. Therefore, there is a window of time between the latest transaction received and the . For more details please, read Fraud Detection Handbook. Chapter 5.2
-
Over / Under sampling. As less than 1% of the transactions are fraudulent I used imblearn to oversample (with SMOTE) the minority class and randomly undersample the majority class; so the training dataset is balanced.
-
Feature engineering.
- Time features. Based on the transaction timestamp we can determined if the transaction was conducted on weekends or night.
- User profiles. For each customer I computed the total number and the average number of transaction in the last 1, 7 or 30 days before the new transaction. This inform use on whether in some customer habits. We use rolling windows as customer behaviours may change over time
- Payment terminal Fraud risk. Similar to customers, I computed the total and average number of transaction conducted on a given terminal. Additionally I computed the number of previous fraudulent transaction in different time windows. The logic is that once a terminal has been compromised, it is more likely to generate more fraudulent transactions transactions.
- Catboost was the best performing model, although performance was very similar between Gradient Bosting Decision Trees model (XGBoots, LightGBM).
- Importance of Hyperparameter tunning. Much better performance in for the minor class by using hyperparameter tunning increasing recall of the minor class from 0.6 to almost 0.7 without a major impact on other metrics. It is true that False Positive rate has increased slightly but as discussed below this is acceptable
I decided that recall was the most interesting metric from a business perspective. Assuming that predicted fraudulent detections would be further reviewed by an SME. We want to reduce as much as possible False Negative (undetected fraudulent transaction), while False Positive (legit transactions flagged as fraudulent) are less critical.
- Explore if Deep Neural Networks provide a better performance.
- Review the Data split strategy.
- Test how to deploy a registered model using MLFlow and use it. MLFlow was generated on the necessary artifacts (model.pkl, env.yaml)
References :
[1] Reproducible Machine Learning for Credit Card Fraud Detection - Practical Handbook
[2] https://deepnote.com/@deepnote/Detecting-credit-card-fraud-using-TensorFlow-and-Keras-9848c5e4-f0a5-4c88-987d-d3b1c171d1be