1.1 Java语言的诞生和发展
1.2 Java语言的特点: 简单易学(去掉了指针、联合体、结构体),面向对象(封装、单一继承、多态),平台无关性,分布式,可靠性,安全性,支持多线程,支持网络编程,编译与解释共存
1.3 Java技术简介: Java SE,Java ME,Java EE
1.4 Java虚拟机: Java程序-----(编译)字节码-----(解释)本地机器码
1.5 Java程序种类和结构:Application,Applet,主类是Java程序执行的入口点
小程序示例:
-
编写Applet小程序:
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.JApplet; public class Main extends JApplet { public void paint(Graphics g) { g.drawString("Hello, Java",50,50); } } -
编写html文件:
<Main.html> <html> <applet code = "Main.class" width = "200" height = "120" alt = "sorry! Your Browser cannot support Java Applet!"> </applet> </html> -
打开PowerShell窗口,输入:AppletViewer ...html
2.1 Java开发工具(JDK)
2.2 Java 帮助文档
2.3 JDK的使用
3.1 数据类型:基本数据类型和引用数据类型
3.2 关键字和标识符
编码习惯:类名首字母大写、变量、方法及对象首字母小写、对于标识符,大写中间单词的首字母、对于常量,大写所有字母、包名全部小写
3.3 常量
3.4 变量
3.5 数据类型转换
字符串型数据与数值数据相互转换:
Float.parseFloat(String s) // double c = Double.parseDouble("1287.233);
数值型数据转换为字符串:
string = "" + 12.65;
数据输入方式1
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str;
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
str = buf.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
}
}
数据输入方式2
Scanner...
3.6 由键盘输入数据
3.7 运算符与表达式
5.1 数组的基本概念
在堆中创建了一个数组或对象之后,同时还在栈中定义了一个特殊的变量,让栈中的这个变量的取值等于数组或对象在堆内存中的首地址,栈中的这个变量成了数组或变量的引用变量(句柄)
5.2 一维数组
内置方法:
public static int binarySearch(X[] a,X key)
public static void sort(X[] a)
public static void sort(X[] a,int fromIndex,int toIndex)
public static X[] copyof( X[] original,int newLength)
public static boolean equals(X[] a,X[] a2)
for-each 语法
杨辉三角:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static Scanner in;
private static int[][] a;
public static void main(String[] args) {
in = new Scanner(System.in);
a = new int[11][11];
a[1][1] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i <= 10;i++) {
for(int j=1;j <= i;j++) {
a[i][j] = a[i-1][j-1] + a[i-1][j];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
5.3 多维数组
5.4 三维以上多维数组
5.5 字符串
方法:
public int length()
public boolean equals (Object anObject)
public String substring(int beginIndex)
public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
public char charAt(int index)
public int indexOf(String str)
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
public String replace(char oldChar,char newChar)
public String trim()
public String toLowerCase()
public String toUpperCase()
单词划分:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static int find (String s,String des) {
String tmp = "";
int lens = s.length();
int lend = des.length();
for ( int i=0; i < lens; i++ ) {
int j = 0, ii = i;
for ( ;j < lend; j++) {
if(s.charAt(ii++) != des.charAt(j)) break;
}
if(j == lend) {
if( ( i ==0 || s.charAt(i-1) == ' ' ) && ( i+lend == lens || s.charAt(i+lend) == ' ')) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String des = in.next();
in.nextLine();
String str = in.nextLine();
StringTokenizer ss = new StringTokenizer(str);
int cnt = 0;
while(ss.hasMoreElements()) {
String s = ss.nextToken();
if(s.equalsIgnoreCase(des)) cnt++;
}
if(cnt != 0) {
System.out.print(cnt + " ");
str = str.toLowerCase();
des = des.toLowerCase();
int pos = find(str,des);
System.out.println(pos);
} else {
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
}
6.1 类的基本概念
6.2 定义类
6.3 对象的创建与使用
6.4 参数的传递
6.5 匿名对象
7.1 类的私有成员和公有成员
注:缺省访问标识符:若在类成员的前面不加任何访问控制符,表示这个成员只能被同一个包(类库)中的类访问和调用。
7.2 方法的重载
7.3 构造方法
7.4 静态成员
7.5 对象的应用
对象赋值之后,当参数是基本参数类型的时候,则是传值方式调用;而当参数是引用变量时,则是传址方式调用。
8.1 类的继承(单继承)
Object类
equals()
toString()
instanceof
class Person {
protected String name;
protected int age;
public Person(String name,int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
protected void show() {
System.out.println("姓名:" + name + "年龄:" + age);
}
}
class Student extends Person {
private String department;
public Student(String name,int age,String dep) {
super(name,age);
department = dep;
}
protected void show() {
System.out.println("系别:" + department);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student("JiananYuan",20,"CSSE");
stu.show();
}
}
8.2 抽象类
import com.sun.org.apache.regexp.internal.REDebugCompiler;
abstract class Shape {
protected String name;
public Shape(String xm) {
name = xm;
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
}
abstract public double getArea();
abstract public double getLength();
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private final double PI = 3.14;
private double radius;
public Circle(String name,double r) {
super(name);
radius = r;
}
public double getArea() {
return PI * radius * radius;
}
public double getLength() {
return 2 * PI * radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double width,height;
public Rectangle(String name,double width,double height) {
super(name);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public double getArea() {
return width * height;
}
public double getLength() {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape rect = new Rectangle("长方形",6.5,10.3);
System.out.println(";面积: " + rect.getArea());
System.out.println(";周长: " + rect.getLength());
Shape circle = new Circle("长方形",10.2);
System.out.println(";面积: " + circle.getArea());
System.out.println(";周长: " + circle.getLength());
}
}
8.3 接口
接口数据成员都是静态的且必须初始化,方法必须全部是abstract的
不能多继承,但可多接口
8.4 内部类
class Group {
private int age;
public class Student {
String name;
public Student(String n,int a) {
name = n;
age = a;
}
public void output() {
System.out.println("姓名:" + this.name + ";年龄:" + age);
}
}
public void output() {
Student stu = new Student("QAQ",24);
stu.output();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Group g = new Group();
g.output();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
(
new Inner() {
void setName(String n) {
name = n;
System.out.println(name);
}
}
).setName("Li Hua");
}
static class Inner {
String name;
}
}
8.5 包
import sun.util.resources.cldr.aa.CalendarData_aa_ER;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar today = Calendar.getInstance();
int y = today.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int m = today.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int d = today.get(Calendar.DATE);
System.out.println("今天是" + y + "年" + (m+1) + "月" + d + "日");
System.out.println((new Random()).nextFloat());
}
}
8.6 Java语言的垃圾回收
9.1 异常处理的基本概念
9.2 异常处理类
9.3 异常的处理
基本格式:try - catch - finally
import jdk.nashorn.internal.runtime.arrays.ArrayIndex;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
int i;
int[] a = {1,2,3,4};
for(i=0;i<5;i++) {
try {
System.out.println(a[i]/i);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到了数组下标越界异常");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("异常类名称是:" + e);
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("捕获" + e.getMessage() + "异常!");
}
finally {
System.exit(1);
}
}
System.out.println("继续...");
}
}
9.4 抛出异常
- 抛出异常的方法与调用方法处理异常
例子1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5, b = 0;
try {
if(b == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException();
} else {
System.out.println(a/b);
}
} catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
例子2
import java.text.NumberFormat;
import java.util.jar.JarOutputStream;
public class Main {
public static double multi(int n) {
if(n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("求负数阶乘异常");
double s = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) s *= i;
return s;
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
try {
int m = Integer.parseInt(agrs[0]);
System.out.println(multi(m));
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("命令行没有提供参数");
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("应该输入一个整数");
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
} finally {
System.out.println("end");
}
}
}
例子3
import java.text.NumberFormat;
public class Main {
static void check(String str1) throws NullPointerException {
if(str1.length() > 2) {
str1 = null;
System.out.println(str1.length());
}
char ch;
for(int i=0;i<str1.length();i++) {
ch = str1.charAt(i);
if(!Character.isDigit(ch)) {
throw new NumberFormatException();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws Exception {
int num;
try {
check(agrs[0]);
num = Integer.parseInt(agrs[0]);
if(num > 60) {
System.out.println("pass");
} else {
System.out.println("failed");
}
} catch(NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("null pointer exception occurred");
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("format of data wrong");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("no argument in cmd");
}
}
}
9.5 自定义异常类
class CircleException extends Exception {
double radius;
CircleException(double r) {
radius = r;
}
public String toString() {
return "半径r = " + radius + "不是一个正数";
}
}
class Circle {
private double radius;
public void setRadius(double r) throws CircleException {
if(r < 0) throw new CircleException(r);
else radius = r;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("圆面积:" + Math.PI * radius * radius);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws CircleException{
Circle cir = new Circle();
cir.setRadius(-2);
cir.show();
}
}
通过本章的讨论,可以看出对异常的处理不外乎两种方式:
-
在方法内使用try - catch 语句来处理方法本身所产生的异常
-
在方法声明的头部使用throws语句或在方法内使用throw语句将它送往上一层调用机构去处理。
10.1 Java语言的输入输出类库
10.2 使用Input和OutputStream流类
-
文件输入输出
import java.io.*; class Main { public static void main(String[] agrs) { FileInputStream fin; FileOutputStream fout; char ch; int data; try { fin = new FileInputStream(FileDescriptor.in); fout = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Jianan Yuan\\Desktop\\test.txt"); System.out.println("输入,按 # 结束"); while((ch = (char)fin.read()) != '#') { fout.write(ch); } fin.close(); fout.close(); System.out.println(); fin = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Jianan Yuan\\Desktop\\test.txt"); fout = new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out); while(fin.available() > 0) { data = fin.read(); fout.write(data); } fin.close(); fout.close(); } catch(FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println( "文件没找到"); } catch(IOException e) { System.out.println("文件异常"); } } }
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Jianan Yuan\\Music\\Delacey - Dream It Possible.mp3");
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Jianan Yuan\\Desktop\\copy.wav");
System.out.println("size = " + fin.available());
byte[] b = new byte[fin.available()];
fin.read(b);
fout.write(b);
fin.close();
fout.close();
}
}
-
顺序输入流
-
管道输入输出流
-
过滤输入输出流
注意DataOutputStream和DataInputStream的灵活使用
- 标准输入输出
10.3 使用Reader和Writer
-
FileReader
-
FileWriter
-
BufferedReader
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Main { public static void main(String[] agrs) { String thisLine; int cnt = 0; try { BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\Jianan Yuan\\Desktop\\test.txt")); while((thisLine = buf.readLine()) != null) { cnt++; System.out.println(thisLine); } System.out.println("一共读取了" + cnt + "行"); buf.close(); } catch(IOException e) { System.out.println("读写异常"); } } } -
BufferedWriter
10.4 文件的处理与随机访问
11.1 线程的概念
11.2 Java的Thread线程类与Runnable接口
Java实现多线程的方法有两种:一种是继承Java.lang包中的Thread类,另一种是用户在定义自己的类中实现Runnable接口。
// 利用Thread的类的子类来创建线程
class Thread1 extends Thread {
private String who;
public Thread1(String str) {
who = str;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println(who + " is running");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Thread1 a = new Thread1("A");
Thread1 b = new Thread1("B");
a.start();
b.start();
System.out.println("main() is ended!") ;
}
}
// 利用Runnable接口来创建线程
import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
class MyThread implements Runnable {
private String who;
public MyThread(String str) {
who = str;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println(who + " is running");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
MyThread a = new MyThread("A");
MyThread b = new MyThread("B");
Thread aa = new Thread(a);
Thread bb = new Thread(b);
aa.start();
bb.start();
}
}
join:当某一线程调用join方法时,其他线程会等到该线程结束后才开始执行
class MyThread extends Thread {
private String who;
public MyThread(String s) {
who = s;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println(who + " is running");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
MyThread you = new MyThread("you");
MyThread she = new MyThread("she");
you.start();
try {
you.join();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
she.start();
try {
she.join();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println("main is ended");
}
}
比较两种创建线程的方式:
直接继承Thread:编写简单,可以直接操控线程,但若继承Thread类就不能再继承其他类
使用Runnable接口:可以将Thread类与要处理的任务的类分开,多重继承,且可以实现数据的共享
Thread类中this指的是当前线程,Runnable要在此类中获得当前线程,必须使用Thread.currentThread()
线程间的数据共享
多个线程的执行代码来自同一个类的run方法时,称他们共享相同的代码。
class MyThread implements Runnable {
private int tickets = 10;
public void run() {
while(true) {
if(tickets > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售机票第" + tickets-- + "号");
}
else {
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
MyThread t = new MyThread();
Thread a = new Thread(t);
Thread b = new Thread(t);
Thread c = new Thread(t);
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
}
}
11.3 多线程的同步控制
class MBank {
private static int sum = 2000;
public synchronized static void take(int k) {
int temp = sum;
temp -= k;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
sum = temp;
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
class Customer extends Thread {
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) {
MBank.take(100);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Customer a = new Customer();
Customer b = new Customer();
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
11.4 线程之间的通信
// 用两个线程模拟存票,售票过程。但要求每存入一张票,就售出一张票,售出后,再存入,直至售完为止。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Tickets t = new Tickets(10);
new Producer(t).start();
new Consumer(t).start();
}
}
class Tickets {
protected int size;
int number = 0;
boolean available = false;
public Tickets(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public synchronized void put() {//存入
if(available) {
try {
wait();
} catch(Exception e) {}
}
System.out.println("存入第" + (++number) + "号票");
available = true;
notify();
}
public synchronized void sell() {
if(!available) {
try {
wait();
} catch(Exception e) {}
}
System.out.println("售出第" + number + "号票");
available = false;
notify();
if(number == size) {
number = size + 1;
}
}
}
class Producer extends Thread {
Tickets t = null;
public Producer(Tickets t) {
this.t = t;
}
public void run() {
while(t.number < t.size) {
t.put();
}
}
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
Tickets t = null;
public Consumer(Tickets t) {
this.t = t;
}
public void run() {
while(t.number < t.size) {
t.sell();
}
}
}
12.1 泛型
12.1.1 泛型的概念
12.1.2 泛型类及应用
public class Main<T> {
private T obj;
public T getObj() {
return obj;
}
public void setObj(T obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Main<String> name = new Main<String>();
Main<Integer> age = new Main<Integer>();
name.setObj("xiao ming");
System.out.println("name: " + name.getObj());
age.setObj(25);
System.out.println("age: " + age.getObj());
}
}
12.1.3 泛型方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Integer[] num = {1,2,3,4,5};
String[] str = {"12","13","14","15","16"};
Main.display(num);
Main.display(str);
}
public static<E> void display(E[] list) {
for(int i=0;i<list.length;i++) {
System.out.println(list[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
12.1.4 限制泛型的可用类型
class App12_1_4 {...}
12.1.5 泛型的类型通配符和泛型数组的应用
12.1.6 继承泛型类与实现泛型接口
12.2 容器类
12.2.1 Java容器框架
12.2.2 Collection接口(均是抽象方法)
12.2.3 列表List
实现List接口的类主要有LinkedList和ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
List<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
al.add(new Integer(i));
}
System.out.print("列表初始数据: " + al);
ListIterator<Integer> it = al.listIterator();
it.add(new Integer(0));
System.out.print("列表数据: " + al);
if(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.nextIndex());
System.out.println(it.next());
it.set(new Integer(9));
System.out.print("列表数据: " + al);
}
it = al.listIterator(al.size());
System.out.println("reverse:");
while(it.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(it.previous() + " ");
}
}
}
12.2.4 集合接口Set
HashSet
TreeSet
12.2.5 映射接口Map
HashMap
TreeMap
13.1 图形用户界面概述
13.2 图形用户界面工具包 —— Swing
13.3 创建组件
13.4 布局管理器
// 基本框架演示
// MyFrame.java
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
JLabel timeLabel = new JLabel("00:00:00");
JButton button = new JButton("显示时间");
public MyFrame(String s) {
super(s);
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
contentPane.add(button);
showTime();
contentPane.add(timeLabel);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
showTime();
}
});
}
public void showTime() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
String timestr = sdf.format(new Date());
timeLabel.setText(timestr);
}
}
// Main
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main {
private static void CreateGUI() {
MyFrame frame = new MyFrame("Swing Demo");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateGUI();
}
}
示例
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
JComboBox<String> colorList = new JComboBox<>();
JLabel label = new JLabel(" 文本示例 This is a Sample");
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
Container cta = getContentPane();
cta.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
cta.add(colorList);
cta.add(label);
colorList.addItem("red");
colorList.addItem("blue");
colorList.addItem("green");
update();
colorList.addAct ionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
update();
}
});
}
public void update() {
String color = (String)colorList.getSelectedItem();
Color c = null;
if(color.equals("red")) {
c = Color.RED;
} else if(color.equals("green")) {
c = Color.GREEN;
} else {
c = Color.BLUE;
}
label.setForeground(c);
}
}
示例
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
private JLabel jl1 = new JLabel("hello java!");
private JLabel jl2 = new JLabel("文本示例");
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
Container cta = getContentPane();
cta.setLayout(new SampleLayout());
cta.add(jl1);
cta.add(jl2);
}
private class SampleLayout implements LayoutManager {
@Override
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp) {
}
@Override
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp) {
}
@Override
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void layoutContainer(Container parent) {
int w = parent.getWidth();
int h = parent.getHeight();
System.out.println("father: " + w + "," + h);
if(jl1.isVisible()) {
Dimension size = jl1.getPreferredSize();
int x = (w - size.width) / 2;
int y = (h - size.height) / 2;
jl1.setBounds(x,y,size.width,size.height);
}
if(jl2.isVisible()) {
Dimension size = jl2.getPreferredSize();
int x = (w - size.width);
int y = 0;
jl2.setBounds(x,y,size.width,size.height);
}
}
}
}
示例
import javax.swing.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.applet.AudioClip;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
AudioClip auu ;
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
JPanel root = new JPanel();
setContentPane(root);
root.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JMenuBar menubar = new JMenuBar();
setJMenuBar(menubar);
JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("文件");
menubar.add(fileMenu);
JMenuItem fileOpenCmd = new JMenuItem("打开");
JMenuItem fileSaveCmd = new JMenuItem("保存");
JMenuItem fileSaveAsCmd = new JMenuItem("另存为...");
fileMenu.add(fileOpenCmd);
fileMenu.add(fileSaveCmd);
fileMenu.add(fileSaveAsCmd);
fileMenu.addSeparator();
JMenuItem exit = new JMenuItem("退出");
exit.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
fileMenu.add(exit);
JMenu help = new JMenu("帮助");
JMenuItem about = new JMenuItem("关于");
JMenuItem hhelp = new JMenuItem("打开帮助");
help.add(about);
help.addSeparator();
help.add(hhelp);
menubar.add(help);
}
}
示例
import sun.plugin.javascript.navig.Image;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.applet.AudioClip;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
setContentPane(jp);
jp.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JToolBar jbt = new JToolBar();
jbt.setFloatable(false);
jp.add(jbt,BorderLayout.PAGE_START);
jbt.add(toolButton("打开.png","file_open","open"));
jbt.add(toolButton("保存.png","file_save","save"));
jbt.add(toolButton("另存为.png","file_saveas","save as"));
jbt.addSeparator();
jbt.add(toolButton("帮助.png","file_help","help"));
JLabel jl = new JLabel("123");
jl.setIcon(new ImageIcon(("D:\\IDEA文件\\绩点计算器\\src\\icon\\香港地铁.png")));
jp.add(jl,BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
protected JButton toolButton(String imageName,String action,String prompt) {
URL imageURL = getClass().getResource("/icon/" + imageName);
JButton jb = new JButton();
jb.setActionCommand(action);
jb.setToolTipText(prompt);
jb.setIcon(new ImageIcon(imageURL));
jb.setFocusPainted(false);
jb.addActionListener(actionListener);
return jb;
}
private ActionListener actionListener = new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String action = e.getActionCommand();
System.out.println(action);
if(action.equals("file_open")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(MyFrame.this,action);
}
}
};
}
示例
import sun.plugin.javascript.navig.Image;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.applet.AudioClip;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
setContentPane(jp);
jp.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPopupMenu jpo = new JPopupMenu();
jpo.add(createMenuItem("打开","file_open","打开.png"));
jpo.add(createMenuItem("保存","file_save","保存.png"));
jpo.add(createMenuItem("另存为","file_saveas","另存为.png"));
jp.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
@Override
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
if(e.getButton() == MouseEvent.BUTTON3) {
jpo.show(e.getComponent(),e.getX(),e.getY());
}
}
});
}
protected JMenuItem createMenuItem(String name,String action,String path) {
JMenuItem it = new JMenuItem(name);
it.setActionCommand(action);
it.addActionListener(actionListener);
it.setIcon(new ImageIcon(getClass().getResource("/icon/" + path)));
return it;
}
private ActionListener actionListener = new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String action = e.getActionCommand();
System.out.println(action);
if(action.equals("file_open")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(MyFrame.this,action);
}
}
};
}
示例
import sun.plugin.javascript.navig.Image;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.applet.AudioClip;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
setContentPane(jp);
jp.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton jb = new JButton("test");
jp.add(jb);
jb.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String str = getUserInput();
System.out.println("用户输入了: " + str);
}
});
}
protected String getUserInput() {
JDialog jd = new JDialog(this,"test",true);
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
jp.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jd.setContentPane(jp);
JTextField jl = new JTextField(16);
JButton jb = new JButton("confirm");
jd.add(jl);
jd.add(jb);
jb.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
jd.setVisible(false);
}
});
jd.setSize(300,100);
jd.setVisible(true);
String rec = jl.getText();
return rec;
}
}
示例
import sun.plugin.javascript.navig.Image;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.Border;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.applet.AudioClip;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
public MyFrame(String name) {
super(name);
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
jp.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
setContentPane(jp);
DefaultListModel<String> jl = new DefaultListModel<>();
jl.addElement("123");
// ...
JList<String> jll= new JList<>();
jll.setModel(jl);
jll.setSelectionMode(ListSelectionModel.SINGLE_SELECTION);
JScrollPane js = new JScrollPane(jll);
jp.add(js,BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
示例
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.api.streaming.XMLStreamReaderFactory;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.TableModelListener;
import javax.swing.table.DefaultTableCellRenderer;
import javax.swing.table.DefaultTableModel;
import javax.swing.table.TableModel;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Vector;
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
DefaultTableModel tm = new DefaultTableModel();
public MyFrame (String name) {
super(name);
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
jp.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
setContentPane(jp);
Student stu[] = {new Student("19635","JiananYuan","male","大一","中国大陆"),
new Student("10001","Cralim.K","female","研究生","美国加州"),
new Student("15630","Maria Zheng","female","大二","中国香港")};
tm.addColumn("唯一编号");
tm.addColumn("名字");
tm.addColumn("性别");
tm.addColumn("年级");
tm.addColumn("地区");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
Vector<Object> v = new Vector<>();
v.add(stu[i].num);
v.add(stu[i].name);
v.add(stu[i].sex);
v.add(stu[i].grade);
v.add(stu[i].area);
tm.addRow(v);
}
JTable jt = new JTable();
jt.setModel(tm);
jt.setFont(new Font("楷体",Font.BOLD,25));
jt.getTableHeader().setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",0,25));
jt.setFillsViewportHeight(true);
jt.setRowHeight(30);
// jt.setRowSelectionAllowed(true);
JScrollPane js = new JScrollPane(jt);
jp.add(js,BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
class Student {
String num;
String name;
String sex;
String grade;
String area;
Student(String a,String b,String c,String d,String e) {
num = a;
name = b;
sex = c;
grade = d;
area = e;
}
}
创建单选按钮:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("单选按钮");
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
ButtonGroup bt = new ButtonGroup();
JRadioButton[] jb = new JRadioButton[4];
jb[0] = new JRadioButton("A.这是一个P问题");
jb[1] = new JRadioButton("B.这是一个NP问题");
jb[2] = new JRadioButton("C.这是一个NPC问题");
jb[3] = new JRadioButton("D.这是一个NPH问题");
for (int i=0;i<4;i++) {
bt.add(jb[i]);
frame.add(jb[i]);
}
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
创建选项卡窗格:
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main extends JFrame {
JTabbedPane jtab = new JTabbedPane(JTabbedPane.TOP);
public Main(String name) {
super(name);
JLabel[] lab = new JLabel[4];
for (int i=0;i<4;i++) {
lab[i] = new JLabel("This is " + (i+1) + " page");
jtab.add("Page" + i,lab[i]);
}
this.add(jtab);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main frame = new Main("选项卡");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
14.1 Java语言的事件处理机制 —— 委托事件模型
14.2 Java语言的事件类
14.3 适配器类
14.4 命令按钮及相应的事件处理
14.5 复选框、单选按钮相应的事件处理
14.6 文本组件及相应的事件处理
14.7 窗口组件及窗口事件处理
14.8 对话框设计及相应的事件处理
14.9 按键事件类及相应的事件处理
14.10 鼠标事件类及相应的事件处理
14.11 列表框及相应的事件处理
14.12 组合框及相应的事件处理
14.13 菜单设计
14.14 工具栏设计
14.15 滑动条设计及相应的事件处理
14.16 文件选择对话框
14.17 颜色选择对话框
14.18 定时器
示例
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ItemEvent;
import java.awt.event.ItemListener;
public class Main extends JFrame implements ItemListener {
static Main frm = new Main();
static JCheckBox chk1 = new JCheckBox("粗体");
static JCheckBox chk2 = new JCheckBox("斜体");
static JRadioButton rb1 = new JRadioButton("red");
static JRadioButton rb2 = new JRadioButton("blue");
static JTextArea ta = new JTextArea("我们一起学猫叫",8,30);
public static void main(String[] args) {
ButtonGroup grp = new ButtonGroup();
frm.setTitle("选项事件处理");
frm.setLocation(200,150);
frm.setSize(260,220);
frm.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
grp.add(rb1); grp.add(rb2);
chk1.addItemListener(frm);
chk2.addItemListener(frm);
rb1.addItemListener(frm);
rb2.addItemListener(frm);
frm.add(chk1); frm.add(chk2); frm.add(rb1);
frm.add(rb2); frm.add(ta);
frm.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frm.setVisible(true);
}
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e) {
Font f1 = ta.getFont();
int s1 = f1.getStyle();
if(rb1.isSelected()) ta.setForeground(Color.RED);
if(rb2.isSelected()) ta.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
if((e.getSource() == chk1) || (e.getSource() == chk2)) {
if(e.getSource() == chk1) s1 = s1 ^ 1;
if(e.getSource() == chk2) s1 = s1 ^ 2;
ta.setFont(new Font(f1.getName(),s1,f1.getSize()));
ta.append("\n样式style = " + s1 + ";" + "状态 = " + e.getStateChange() + "[1:选中 2:取消]");
}
}
}
数据库基础:
-
启动MySQL服务器:net start mysql80 //停止:net stop mysql80
-
命令行中连接mysql服务器:mysql -u root -p
-
退出命令:exit;
-
创建数据库:create database xxx;
-
删除数据库:drop database xxx;
-
选择数据库:use xxx;
-
创建数据表:
mysql> CREATE TABLE runoob_tbl( -> runoob_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> runoob_title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, -> runoob_author VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, -> submission_date DATE, -> PRIMARY KEY ( runoob_id ) -> )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -
查看数据表内容:select * from xxx;
-
删除数据表:drop table xxx;
-
插入数据:
mysql> INSERT INTO runoob_tbl -> (runoob_title, runoob_author, submission_date) -> VALUES -> ("学习 MySQL", "菜鸟教程", NOW()); Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
插入后效果:
+-----------+--------------+---------------+-----------------+
| runoob_id | runoob_title | runoob_author | submission_date |
+-----------+--------------+---------------+-----------------+
| 1 | 学习 PHP | 菜鸟教程 | 2020-02-06 |
| 2 | 学习 MySQL | 菜鸟教程 | 2020-02-06 |
| 3 | JAVA 教程 | RUNOOB.COM | 2016-05-06 |
+-----------+--------------+---------------+-----------------+
-
筛选查找:select * from xxx(某数据表) WHERE xxx(关键字)='xxx'(指定内容);
-
更新数据:update runoob_tbl SET runoob_title='学习C++' WHERE runoob_id=3;
-
删除数据:delete from runoob_tbl WHERE runoob_id=1;
-
模糊搜索语句:select * from runoob_tbl where runoob_author like "%COM";
+-----------+--------------+---------------+-----------------+ | runoob_id | runoob_title | runoob_author | submission_date | +-----------+--------------+---------------+-----------------+ | 3 | 学习C++ | RUNOOB.COM | 2016-05-06 | | 4 | Java编程思想 | ORACLE.COM | 2020-02-06 | +-----------+--------------+---------------+-----------------+ -
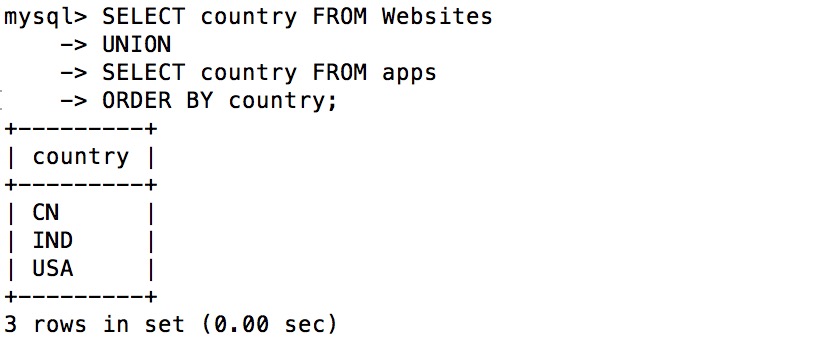
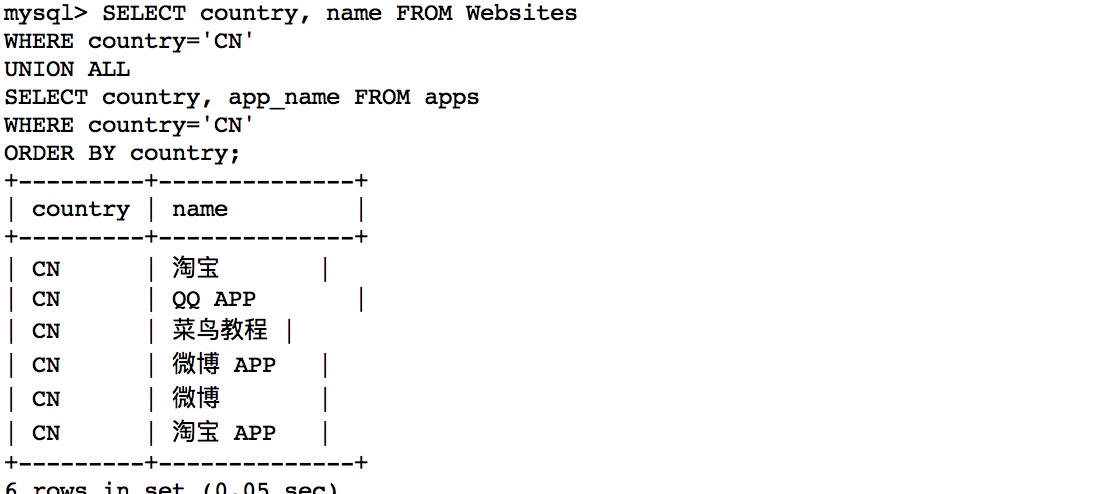
合并查询操作:
另一个例子:
-
排序:select * from runoob_tbl ORDER BY submission_date ASC;
-
GROUP BY语句,连接语句,NULL值处理,正则表达式,
-
MySQL事务:
一个事务(transaction)中的所有操作,要么全部完成,要么全部不完成,不会结束在中间某个环节。事务在执行过程中发生错误,会被回滚(Rollback)到事务开始前的状态,就像这个事务从来没有执行过一样。
在事务开始之前和事务结束以后,数据库的完整性没有被破坏。这表示写入的资料必须完全符合所有的预设规则,这包含资料的精确度、串联性以及后续数据库可以自发性地完成预定的工作。
数据库允许多个并发事务同时对其数据进行读写和修改的能力,隔离性可以防止多个事务并发执行时由于交叉执行而导致数据的不一致。事务隔离分为不同级别,包括读未提交(Read uncommitted)、读提交(read committed)、可重复读(repeatable read)和串行化(Serializable)。
事务处理结束后,对数据的修改就是永久的,即便系统故障也不会丢失。
JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)是java访问数据库的标准API
18.1 网络基础
针对不同层次的网络通信,Java语言提供的网络功能有四大类:URL(面向应用层),InetAddress(面向IP层),Socket,Datagram(面向传输层)
18.2 URL编程
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL("http://www.edu.cn/index.html");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream()));
String s;
while((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch(MalformedURLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
读取网络上的文件内容一般分3个步骤:
创建URL对象,利用URL对象的openstream方法获得对应的InputStream对象,通过InputStream对象来读取文件内容
18.3 用Java语言实现底层网络通信
18.3.1 InetAddress程序设计
public static InetAddress getByName(String name) // name --> InetAddress
public static InetAddress getByAddress(String name) // ip --> InetAddress
public static InetAddress getLocalHost()
public byte[] getAddress()
public String getHostAddress()
public String getHostName()
public String toString()
18.3.2 基于连接的Socket通信程序设计
Socket类的构造方法:
public Socket(String host,int port)
public Socket(InetAddress address,int port)
public Socket(String host,int port,boolean stream)
public Socket(InetAddress host,int port,boolean stream)
常用方法:
public InetAddress getInetAddress()
public InetAddress getLocalAddress()
public InputStream getInputStream()
public OutputStream getOutputStream()
public int getPort()
public void setRecieveBufferSize()
public int getRecieveBufferSize()
SeverSocket类的构造方法:
public SeverSocket(int port)
public SeverSocket(int port,int backlog)
Socket通信模式:
- 客户建立到服务器的套接字对象
用getinputstream可以获得服务器向客户端的发送流
getoutputstream可以获得客户端向服务器的输出流
连接到数据流datainputstream和dataoutputstream上是为了更好的从流中获取信息
- 建立接受客户套接字的服务器套接字
Socket通信步骤如下:
1)在服务器端创建一个ServerSocket对象,并指定端口号
2)运行ServerSocket的accept方法,等候客户端请求
3)客户端创建一个Socket对象,指定计算机地址和端口号,向服务器端发出连接请求
4)服务器端接受到客户端请求后,创建Socket对象与客户端建立连接
5)服务器端和客户端分别建立输入输出数据流,进行数据传输
6)通信结束后,服务器端和客户端分别关闭相应的Socket链接
7)服务器端程序运行结束后,调用ServerSocket对象close方法停止等候客户端请求
//服务器
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.Buffer;
public class MyServer implements Runnable {
ServerSocket server = null;
Socket clientSocket;
boolean flag = true;
Thread connenThread;
BufferedReader sin;
DataOutputStream sout;
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
MyServer MS = new MyServer();
MS.serverStart();
}
public void serverStart() {
try {
server = new ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("端口号:" + server.getLocalPort());
while(flag) {
clientSocket = server.accept();
System.out.println("连接已经建立完毕!");
sin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
sout = new DataOutputStream(clientSocket.getOutputStream());
connenThread = new Thread(this);
connenThread.start();
String aLine;
while((aLine = sin.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(aLine);
if(aLine.equals("bye")) {
flag = false;
connenThread.interrupt();
break;
}
}
sout.close(); sin.close(); clientSocket.close(); System.exit(0);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public void run() {
while(true) {
try {
int ch;
while((ch = System.in.read()) != -1) {
sout.write((byte)ch);
if(ch == '\n') sout.flush();
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
public void finalize() {
try {
server.close();
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
//客户端
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MyClient implements Runnable {
Socket clientSocket;
boolean flag = true;
Thread connenThread;
BufferedReader cin ;
DataOutputStream cout;
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
new MyClient().clientStart();
}
public void clientStart() {
try {
clientSocket = new Socket("localhost",8080);
System.out.println("已经建立连接");
while(flag) {
cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
cout = new DataOutputStream(clientSocket.getOutputStream());
connenThread = new Thread(this);
connenThread.start();
String aLine;
while((aLine = cin.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(aLine);
if(aLine.equals("bye")) {
flag = false;
connenThread.interrupt();
break;
}
}
cout.close(); cin.close(); clientSocket.close(); System.exit(0);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public void run() {
while(true) {
try {
int ch;
while((ch = System.in.read()) != -1) {
cout.write((byte)ch);
if(ch == '\n') cout.flush();
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
18.3.3 无连接的数据报通信程序设计
数据报发送过程:
1)创建一个发送数据的DatagramPacket对象,包含下列信息:
·要发送的数据长度
·数据报分组的长度
·发送目的地主机IP地址和目的端口号
2)在指定的或可用的本机端口创建DatagramSocket对象
3)调用DatagramSocket对象的Send方法,以Datagrampacket对象为参数发送数据报
数据报接收过程:
1)创建一个用于接收数据报的datagrampacket对象,其中包含空白数据缓冲区和指定数据报分组的长度
2)在指定的或可用的本机端口创建datagramsocket对象
3)调用datagramsocket对象的receive方法,以datagrampacket对象为参数接收数据报
// UDPServer
import javax.xml.crypto.Data;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.nio.Buffer;
public class UDPServer {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
UDPServer frm = new UDPServer();
}
String strbuf = "";
SerThread st;
public UDPServer() {
st = new SerThread();
st.start();
}
}
class SerThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
String str1;
try {
DatagramSocket skt = new DatagramSocket(8000);
System.out.println("计算机名:" + InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostName());
while(true) {
byte[] inBuf = new byte[256];
DatagramPacket pkt = new DatagramPacket(inBuf,inBuf.length);
skt.receive(pkt);
str1 = new String(pkt.getData());
str1 = str1.trim();
if(str1.length() > 0) {
int pot = pkt.getPort();
System.out.println("远程端口:" + pot);
System.out.println("服务器已接收到信息: " + str1);
}
}
} catch(IOException e){}
}
}
// Client
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.nio.Buffer;
public class UDPClient {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
UDPClient frm = new UDPClient();
}
CliThread ct;
public UDPClient() {
ct = new CliThread();
ct.start();
}
}
class CliThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
String str1;
String serverName = "LAPTOP-961IKQ0F";
System.out.println("请发送消息给服务器 << " + serverName + " >> ");
try {
DatagramSocket skt = new DatagramSocket();
DatagramPacket pkt;
while(true) {
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入消息: ");
str1 = buf.readLine();
byte[] outBuf = new byte[str1.length()];
outBuf = str1.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName(serverName);
pkt = new DatagramPacket(outBuf,outBuf.length,address,8000);
skt.send(pkt);
}
} catch(IOException e){}
}
}