Zezhou Wang1, Ziyun Zhang2, Xiaoyi Zhang3, Zhuzhong Qian1, Yan Lu3
1Nanjing University, 2Peking University, 3Microsoft Research Asia
🌐 Website | 📑 arXiv (coming soon) | 🤖 Model | 🤗 Dataset (coming soon)
🏆 #1 Open-Source End-to-End Model on OSWorld (15 steps): Achieves 32.13% success rate, surpassing all open-source end-to-end models.
📊 Extreme Data Efficiency: Matches GUI-OWL-7B performance using only 128 training tasks.
- 2026-01: We release the webpage and model BEPA-7B-S2. Check it out!
We propose BEPA (Bi-Level Expert-to-Policy Assimilation), a framework that turns static expert traces into dynamic, policy-aligned guidance for GUI agents. BEPA improves UITARS1.5-7B from 22.87% to 32.13% on OSWorld-Verified (+9.26 points).
Vision-language models are increasingly deployed as computer-use agents (CUAs) that operate desktops and browsers. Top-performing CUAs are framework-based systems that decompose planning and execution, while end-to-end screenshot-to-action policies are easier to deploy but lag behind on benchmarks such as OSWorld-Verified.
We ask: How can reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) best exploit a small pool of expert trajectories to train end-to-end policies?
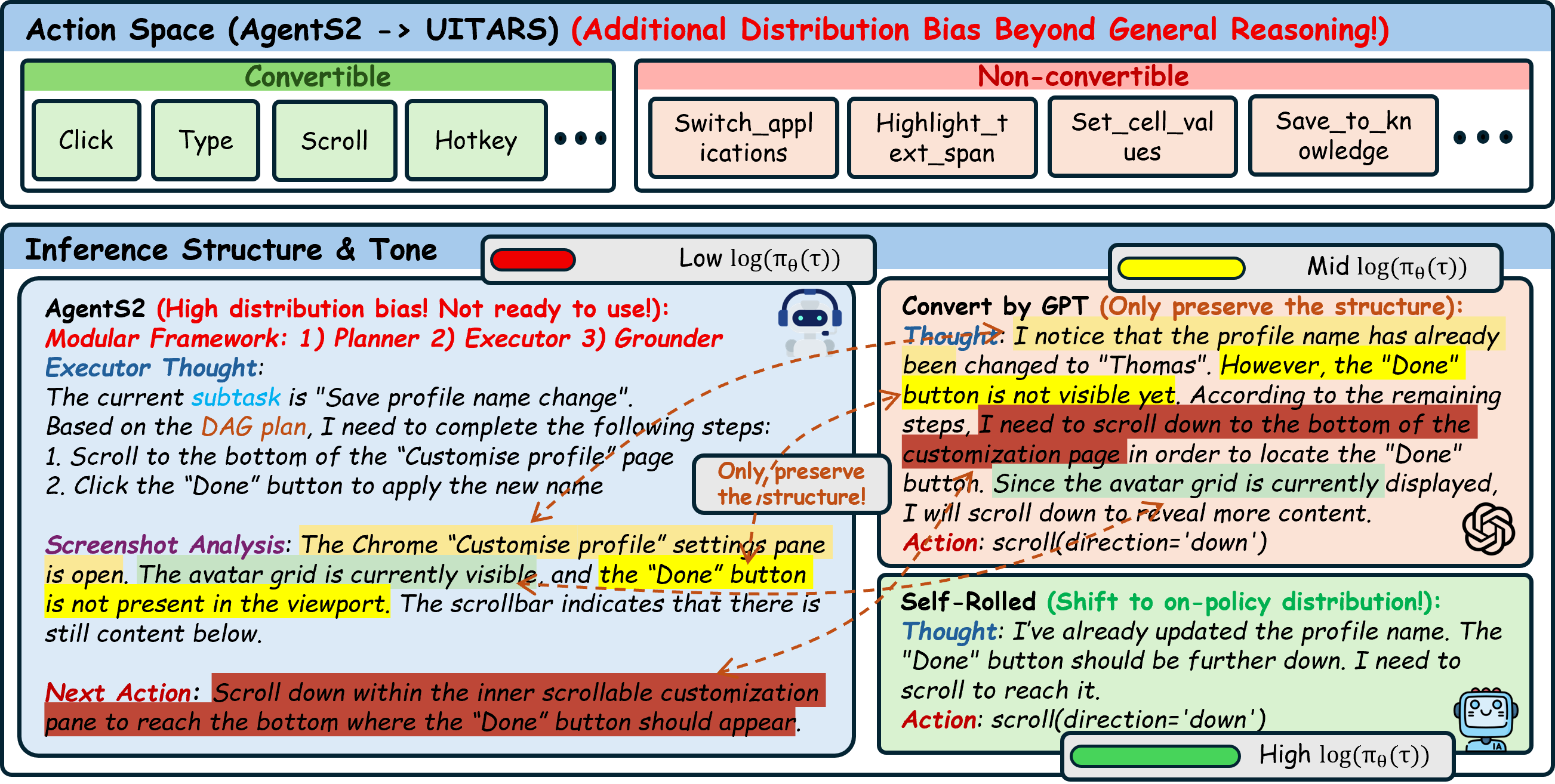
Naively mixing these off-policy traces into on-policy RLVR is brittle due to:
- Structural Mismatch: Framework traces interleave multiple roles (planning, execution, grounding) that end-to-end policies cannot directly imitate.
- Distribution Gap: Even after format conversion, trajectories remain far from the base-policy manifold.
BEPA operates in two complementary stages:
Transforms alien expert traces into policy-compatible trajectories. We abstract the expert trajectory into a compact natural-language plan, then let the base policy act in the environment with plan conditioning. This produces trajectories that lie much closer to the policy's manifold.
Dynamically maintains a per-task cache, injecting guided trajectories into GRPO updates only upon total on-policy failure. The cache is continuously refreshed with the policy's own successful executions, ensuring the off-policy signal evolves alongside the agent.
BEPA achieves 32.13% success on OSWorld-Verified, improving over UITARS1.5-7B (22.87%) by +9.26 points (+40.5% relative) and over GRPO (23.60%) by +8.53 points (+36.1% relative).
| Method | Dexpert_only | Dtrain | Dheld_out | Overall (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UITARS1.5-7B | 18.52 | 55.12 | 5.74 | 22.87 |
| GRPO | 11.11 | 58.02 | 5.32 | 23.60 |
| Trace Replacement | 18.52 | 66.50 | 1.29 | 23.91 |
| LUFFY | 19.01 | 65.44 | 2.16 | 24.11 |
| LEVEL-1 | 25.93 | 69.20 | 5.05 | 27.30 |
| LEVEL-2 | 29.18 | 71.65 | 7.48 | 29.74 |
| BEPA (ours) | 35.19 | 73.23 | 10.30 | 32.13 |
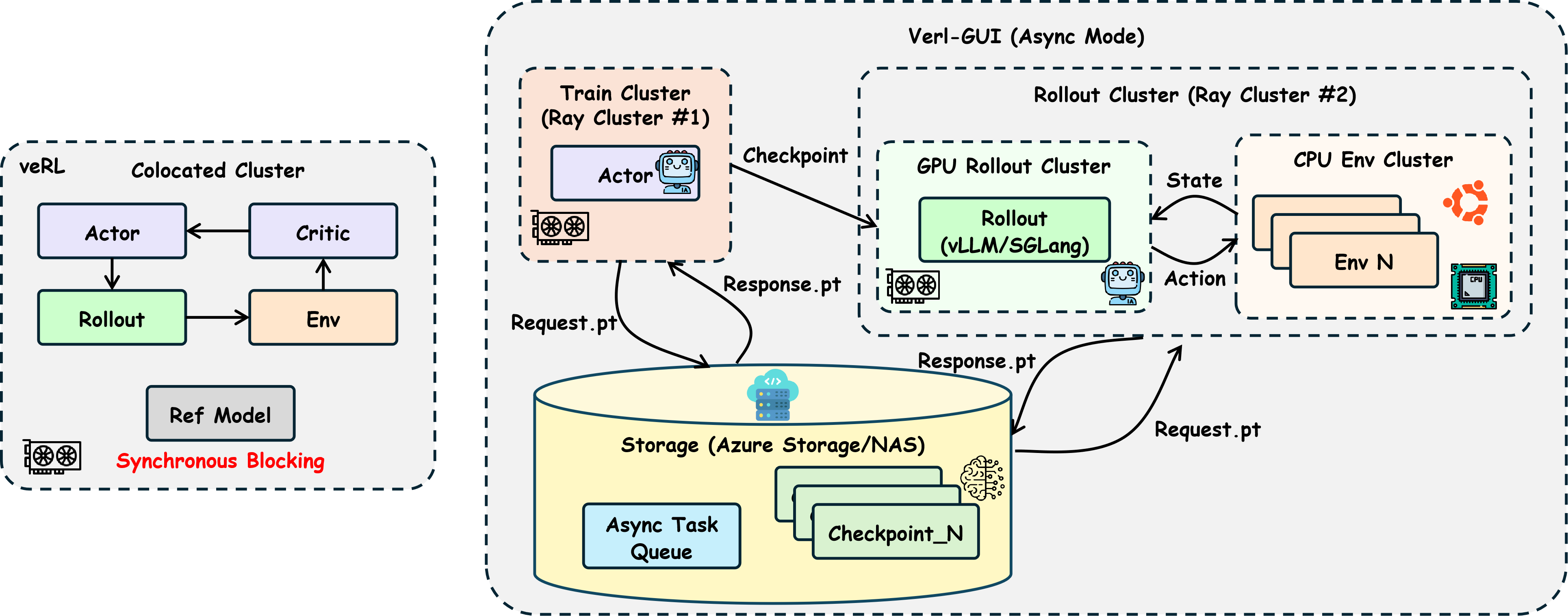
As part of this work, we release Verl-GUI, a highly scalable distributed training framework for long-horizon, multi-turn vision-language GUI agent training built upon veRL.
-
Heterogeneous Cluster Architecture: Completely separates trainer and rollout into independent Ray clusters, enabling deployment across heterogeneous compute resources (IB/NVLink nodes for training, PCIe nodes for rollout).
-
Multiple Storage Backends: Supports Azure Blob Storage, NAS, and local filesystems through a unified abstraction layer.
-
Async Task Queue: Dynamically maintains a task queue for the rollout cluster to consume, enabling decoupled and non-blocking task processing.
-
K-round Rollout Processing: Intelligently splits batches across multiple rounds when trainer's global batch size exceeds rollout cluster capacity.
-
Scalable Parallel Environments: Number of concurrent environments scales with rollout cluster compute capacity, with Ray-based orchestration and automatic Docker cleanup.
-
Service-oriented Orchestration: Modular components including CheckpointManager, EnvWorkerPool, RolloutService, and ValidationAdapter.
@misc{wang2026offpolicyonpolicyenhancinggui,
title={From Off-Policy to On-Policy: Enhancing GUI Agents via Bi-level Expert-to-Policy Assimilation},
author={Zezhou Wang and Ziyun Zhang and Xiaoyi Zhang and Zhuzhong Qian and Yan Lu},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.05787},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.05787},
}This project is released under the MIT License.
We thank the following open-source projects for making this work possible: