Set up environment
- Setup up virtual environment with Anaconda, or VENV
$ conda create --name env_name
$ conda activate env_name
-
Install Python 3.7.6
-
Install dependencies with pip:
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
- TO use the App: navigate to root folder, run/test on local computer:
$ python Flask_webapp/app.py
├── .flake8
├── .gitignore
├── Flask_webapp
│ ├── app.py
│ ├── data_preparation_objects
│ │ └── scaler.pkl
│ ├── models
│ │ ├── model_IBM_2_epochs.h5
│ │ └── model_IBM_60_epochs.h5
│ ├── static
│ │ └── js
│ │ ├── stock_info.js
│ │ └── stock_predict.js
│ └── templates
│ ├── index.html
│ ├── price_predict.html
│ └── show_prediction.html
├── LSTM_predictor
│ ├── setup.py
│ └── stockPredictor
│ ├── dataGenerator.py
│ ├── predict.py
│ ├── preload.py
│ └── train.py
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
└── runtime.txt
- We now allow users to provide a simple stock ticker. The price data will be fetched from Yahoo finance.
Long short-term memory (LSTM) unit is a building unit for layers of a recurrent neural network (RNN). A RNN composed of LSTM units is often called an LSTM network. A common LSTM unit is composed of a cell, an input gate, an output gate and a forget gate. The cell is responsible for "remembering" values over arbitrary time intervals; hence the word "memory" in LSTM. Each of the three gates can be thought of as a "conventional" artificial neuron, as in a multi-layer (or feedforward) neural network.
An LSTM is well-suited to classify, process and predict time series given time lags of unknown size and duration between important events. LSTMs were developed to deal with the exploding and vanishing gradient problem when training traditional RNNs.
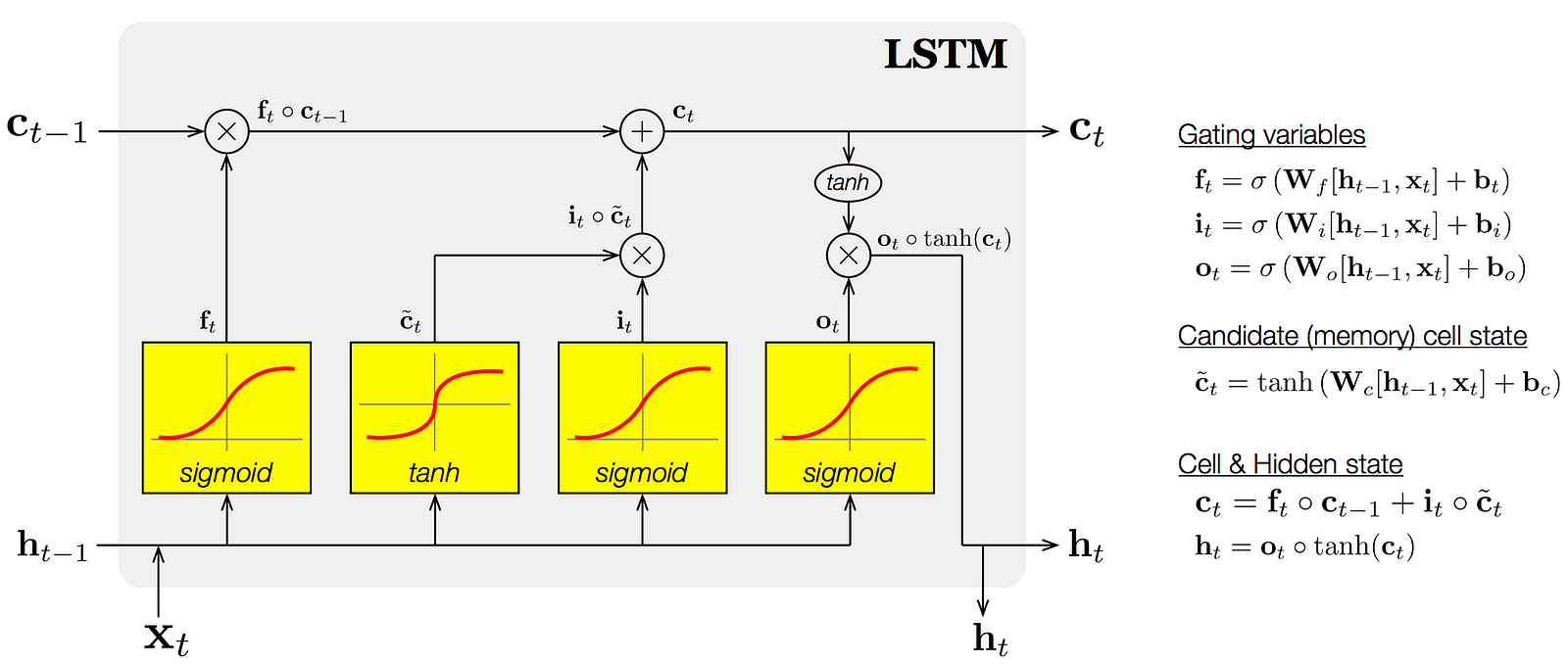
-
Forget Gate “f” ( a neural network with sigmoid)
-
Candidate layer “C"(a NN with Tanh)
-
Input Gate “I” ( a NN with sigmoid )
-
Output Gate “O”( a NN with sigmoid)
-
Hidden state “H” ( a vector )
-
Memory state “C” ( a vector)
-
Inputs to the LSTM cell at any step are Xt (current input) , Ht-1 (previous hidden state ) and Ct-1 (previous memory state).
-
Outputs from the LSTM cell are Ht (current hidden state ) and Ct (current memory state)
requirements.txtspecifies the dependencies of this webapp, it is generated with pipreqs package..gitignorespecifies which files and folders to ignore when pushing to Git remote, i.e. Github..flake8specifies which linting errors to ignore when using flake8 package. Linting errors are the conventions and practice of best formatting the source code, i.e. two empty lines are recommended from the last line of code to the definition of a new function.runtime.txt: by default, new Python applications on Heroku use the Python runtime indicated in Specifying a Python version.Procfilespecifes how to deploy the webapp on HerokuLSTM_predictoris a custom package written by the author to realize customized functions for the webapp. It is installed locally by adding the line-e ./LSTM_predictorin requirements.txt file.
-
Must have gunicorn package specified in requirements.txt file, otherwise the app won't run on Heroku. gunicorn will split the server into "workers" to process requests in parallel. But that means duplicating the code for each "worker". Heroku might default it to 2, we can try to save on memory by scaling back to 1. We can try setting an env variable
WEB_CONCURRENCYto 1, from Heroku dashboard => settings, config vars.The request to our webapp now have to processed serially instead of parralel. This is specified in the Heroku docs as config vars -
Must have Procfile Specifying how to run this app
-
Must have runtime.txt to specify the language of this app
-
Must ensure that you are pushing the branch with your code to heroku master. So instead of:
$ git push heroku master
You would do something like:
$git push heroku (current-branch):master$
The app is available here