 |
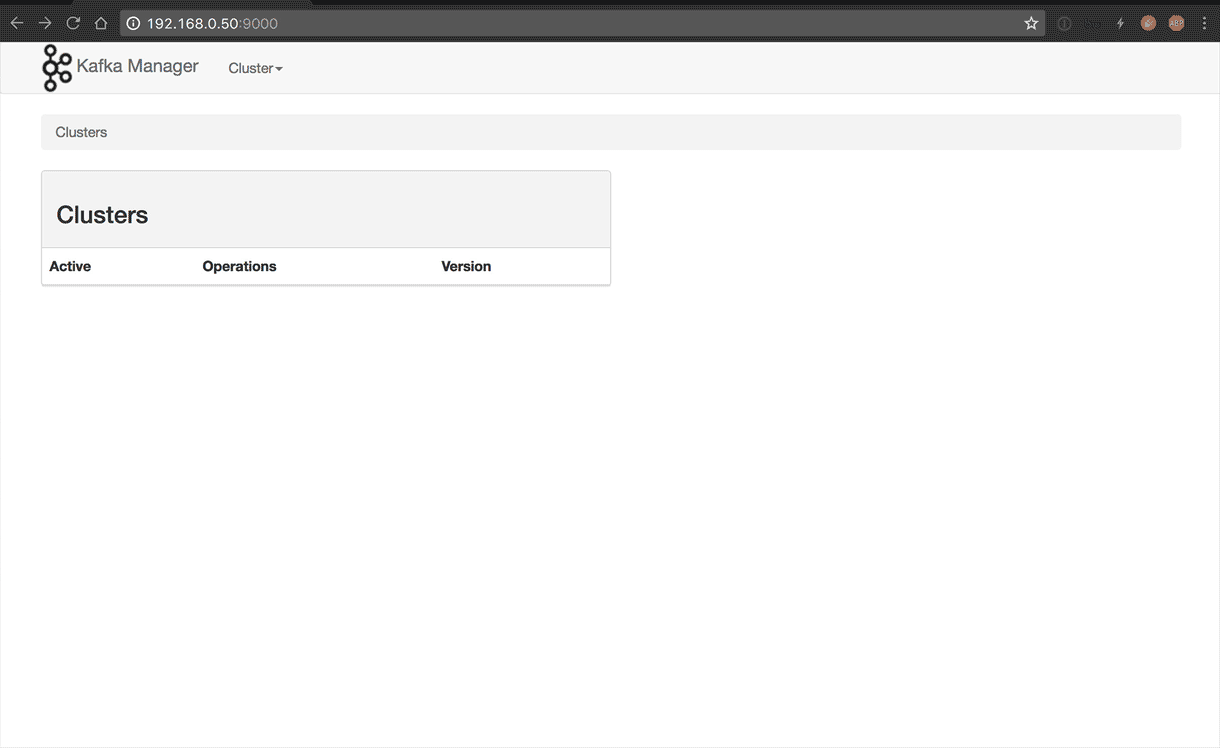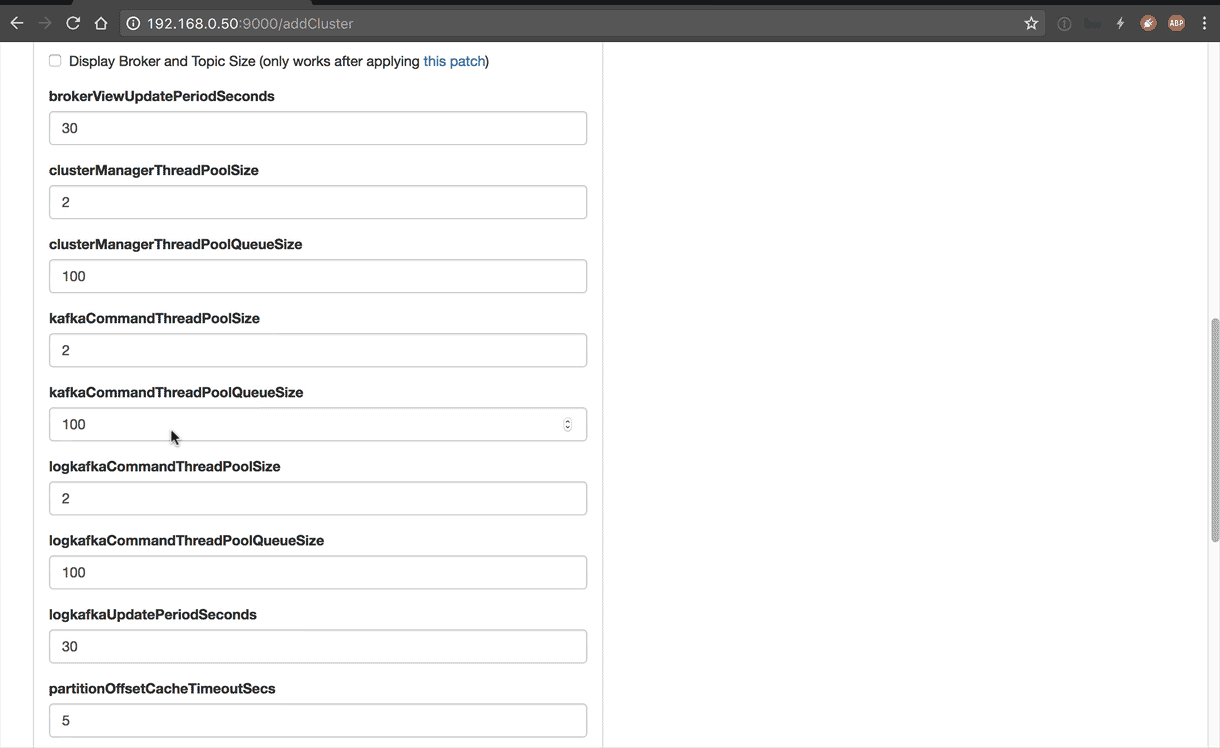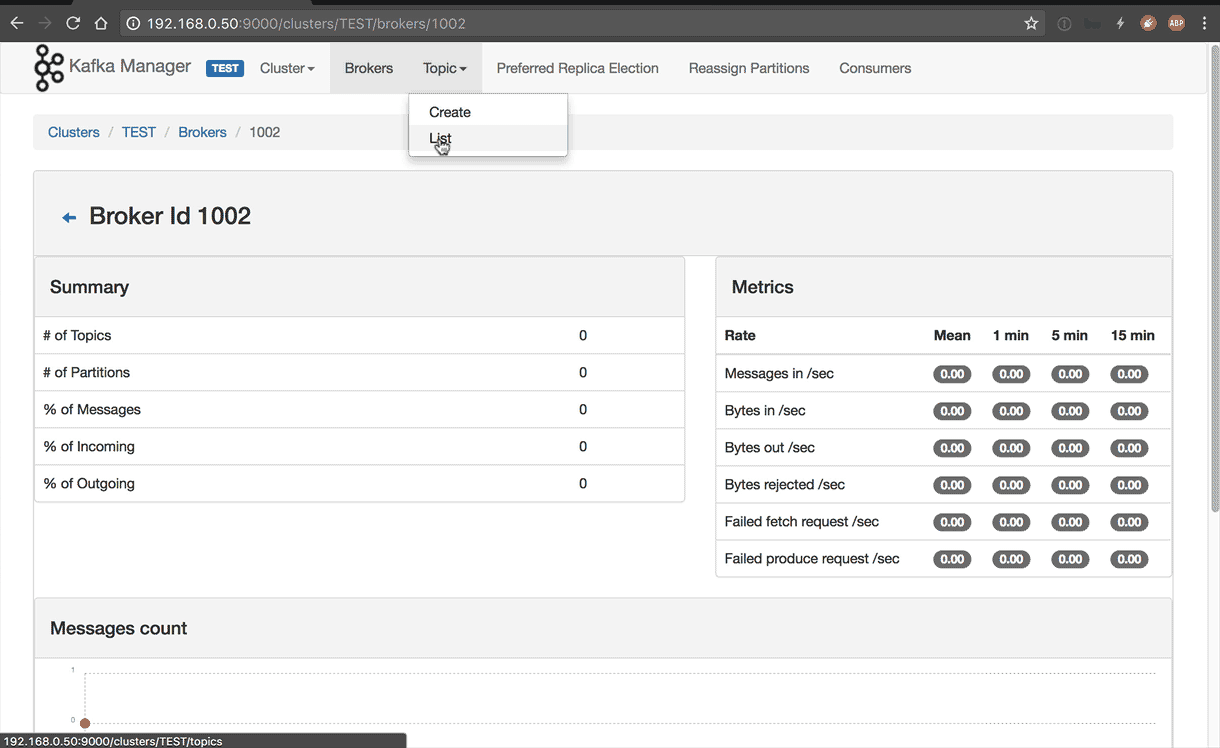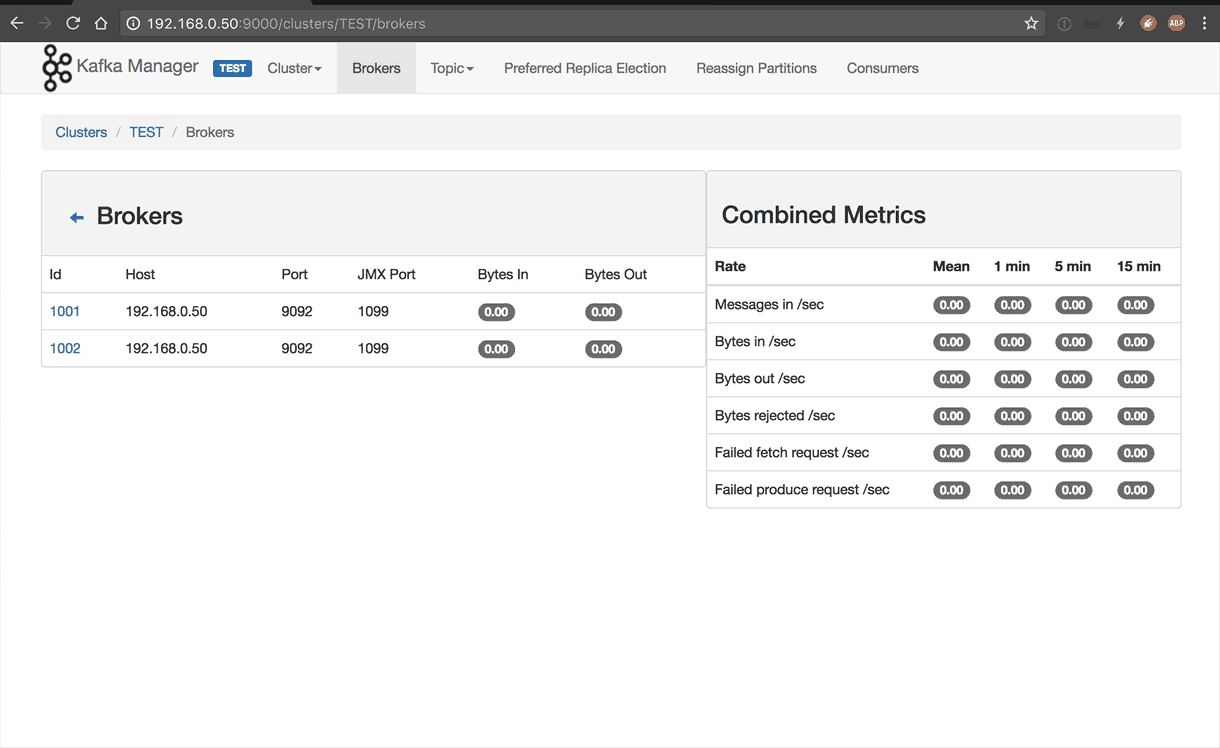
Kafka in a docker. This image is on steroids version of wurstmeister/kafka. In this image we have added scaling. All images are behing HAproxy load balancer which allows for spinning multiple replicas of kafka. On top of that there is Kafka Manager which can be access under [host IP]:9000 (see screenshots) |
|---|---|
| The image is available directly from Docker Hub |
- installed docker-compose https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
- set default address to match your docker host IP. Use script called
set-address with a paramater -a or --address
Examle:./set-address --address 192.168.1.200this scrip will edit all required files.
Note: Do not use localhost or 127.0.0.1 as the host ip if you want to run multiple brokers. - if you want to customise any Kafka parameters, simply add them as environment variables in
docker-compose.yml, e.g. in order to increase themessage.max.bytesparameter set the environment toKAFKA_MESSAGE_MAX_BYTES: 2000000. To turn off automatic topic creation setKAFKA_AUTO_REATE_TOPICS_ENABLE: 'false'
./set-address --address 192.168.200.100
start-kafka-cluster - can deploy everything for you. It has all delays set to make sure all services are run in correct order and wait until they are availeble to the cluster.
There are few versions of how to use this image. For easy deployment I have added docker-compose.yml file which have all needed parameters specified. Another addition are bash scripts that you can use.
start-kafka-cluster have few option that can be specified on run
--replicas (-r) - sets the amount of replicas that should be spin up on cluster creation
--test (-t) - Runs tests to make sure that producer and consumer can work with the cluster. It downloads polinux/php:7.1 image and builds missing package inside of that image and runs the tests against new kafka cluster. Bare in mind that this can take a while to finish
Example 1 simple start:
./start-kafka-cluster
It will start single instance of kafka and ask if user is ok with default depoyment.
Example 2 specify 4 replicas and run tests agains new cluster
./start-kafka-cluster --replicas 4
Example 3 add more replicas
docker-compose scale kafka=5
Start with simple:
docker-compose up -d
Script based:
./destroy-kafka-cluster
docker-compose:
docker-composer stop
docker-compose rm -f
| Start Cluster | Kafka Manager |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Scale | Destroy Cluster |
|---|---|
 |
 |
If you don't specify a broker id in your docker-compose file, it will automatically be generated (see https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/KAFKA-1070. This allows scaling up and down. In this case it is recommended to use the --no-recreate option of docker-compose to ensure that containers are not re-created and thus keep their names and ids.
If you want to have kafka-docker automatically create topics in Kafka during
creation, a KAFKA_CREATE_TOPICS environment variable is
added in docker-compose.yml.
Here is an example snippet from docker-compose.yml:
environment:
KAFKA_CREATE_TOPICS: "Topic1:1:3,Topic2:1:1:compact"
Topic 1 will have 1 partition and 3 replicas, Topic 2 will have 1 partition, 1 replica and a cleanup.policy set to compact.
You can configure the advertised hostname in different ways
- explicitly, using
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME - via a command, using
HOSTNAME_COMMAND, e.g.HOSTNAME_COMMAND: "route -n | awk '/UG[ \t]/{print $$2}'"
When using commands, make sure you review the "Variable Substitution" section in https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/
If KAFKA_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME is specified, it takes presendence over HOSTNAME_COMMAND
For AWS deployment, you can use the Metadata service to get the container host's IP:
HOSTNAME_COMMAND=wget -t3 -T2 -qO- http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4
Reference: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-instance-metadata.html
For monitoring purposes you may wish to configure JMX. Additional to the standard JMX parameters, problems could arise from the underlying RMI protocol used to connect
- java.rmi.server.hostname - interface to bind listening port
- com.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port - The port to service RMI requests
For example, to connect to a kafka running locally (assumes exposing port 1099)
KAFKA_JMX_OPTS: "-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote=true -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=192.168.0.50 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port=1099 -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true"
JMX_PORT: 1099
Jconsole can now connect at jconsole 192.168.0.50:1099
Przemyslaw Ozgo (linux@ozgo.info)
Inspired by [wurstmeister]https://hub.docker.com/r/wurstmeister/)'s wurstmeister/kafka image. Thanks!!!







