This repository containc Python files that will implement and test our computer vision algorithms that we intend to use on our vehicle for Mission 9 of IARC.
While our code base is written in C++ primarily, we are composing our algorithms in Python because the OpenCV library is available for both languages, and Python allows an easy way to test code and import the OpenCV library while avoiding the hassles that come with including OpenCV using CMake, ROS with catkin_ws, etc.
Additionally, this gives members of our team experience working with Python.
By the end of this README, you should be able to run the sample code without difficulties:
python3 hello.pyDepending on some other factors involving pyrealsense2, you might also
be able to run the Depth Camera sample code if you have an Intel D4XX camera:
python3 hello-rs.pyI encourage you to look at the code and modify it. For example, change the image used, modify the image using OpenCV functions, or do anything else creative you can think of!
This tutorial was intended for Ubuntu / Linux, and modified for support in Mac and Windows WSL environments. While most issues have been worked out, you may have some difficulties still - reach out if you have trouble.
First, clone this repository. You can either use HTTPS or SSH with a key setup through your account.
git clone <link>
cd maav-cvNext, install required software to create a Python virtual environment for installing dependencies and working on CV projects.
# WSL / Linux:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install virtualenv
# Mac with Homebrew:
brew install python@3.8
pip install virtualenvSetup your virtual environment using Python 3.8.x.
# WSL / Linux:
virtualenv env
source env/bin/activate
# Mac:
virtualenv --python=/usr/local/Cellar/python@3.7/3.7.9/bin/python3.7
source env/bin/activateNOTE: You MUST source the activate file everytime you begin any testing or development!! That lets your terminal know what package install directory to use for the code.
We have included requirements.txt to install OpenCV and any other required
Python libraries. To install these requirements,
run the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtNormally OpenCV GUI code can run just fine in this environment. However, if you attempt to run this code in Windows with WSL, you will encounter an error similar to one of these:
python3 hello.py
...
qt.qpa.xcb: could not connect to display
...
# OR
...
: cannot connect to X serverThis is because Windows and WSL do not natively support Linux GUI applications. We will install an external program to host an X-Server, which will process data and display a GUI that interacts with your program.
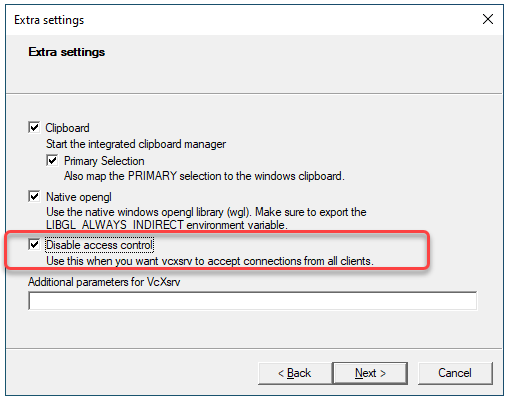
The X-Server application we will use is vcXsrv, which you can download here. After installing, start the application, and start it with default settings EXCEPT FOR ONE: Disable Access Control
Then, you need to set an environment variable in your WSL terminal so that the X-Server will be used for displaying GUI apps.
First, see what version of WSL you are using. Open Windows Powershell, and run the following command:
wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Ubuntu-18.04 Running 2
...
In this example, I am running WSL2. So, once you know which version you are
running, use the appropriate DISPLAY environment variable below:
# WSL1:
export DISPLAY="localhost:0"
# WSL2:
export DISPLAY="`grep nameserver /etc/resolv.conf | sed 's/nameserver //'`:0"Tip: Add this line to the end of your ~/.bashrc so that it will run
everytime you start a new bash terminal. It's an extra step you won't have
to remember.
If you are still having trouble connecting to the X-Server for image display, you may have vcXsrv blocked in your Windows firewall. Make sure that you allows vcXsrv through your firewall to display results.
This section is subject to change throughout the course of development. At times, Google can be your friend with Git, but reach out to us with any help you may need!
When in doubt, check out "Oh Shit! Git!"
Make sure your identity through Git is setup well.
# List current global config, which may contain identity info
git config --global -l
user.name=Jacob Minock
user.email=jaminock@umich.edu
core.editor=vim
...
# Set or Change some things (for any repository you use)
# Omit --global to just make it for THIS repository
git config --global user.name "Jacob Minock"
git config --global user.email "jaminock@umich.edu"When developing a specific, new feature or set of changes, we suggest making
a branch for new files or the modifications of existing files. This will
allow your master branch to stay clean and organized in terms of commit
history and other qualities. Generally changes to the master branch only
happen with very small fixes - like updating a README.md or one doc.
# List branches
git branch
# Create a new branch
git checkout -b <branch>
# Switch to a branch
git checkout <branch>Simple GitHub Forking Tutorial:
https://guides.github.com/activities/forking/
Cloning repositories is a straightforward approach to making changes to shared repositories. 'Forked' repositories are personal copies of a shared project, in which you can make changes, and then offer those changes up to the original project.
OpenCV in Python Tutorials Page:
https://docs.opencv.org/master/dc/d4d/tutorial_py_table_of_contents_gui.html
Intel RealSense Python Wrapper Docs:
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/master/wrappers/python
You might run into the following, especially on a Mac, when running
pip install -r requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
...
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement pyrealsense2>=2.2This is because Intel has not written pyrealsense packages for Python that will run on the hardware architecture commonly found in Macs. This is very annoying, and really sucks for making the environment install process a smooth one. (╯°□°)╯︵ ┻━┻
However, building the RealSense library from source and placing the .so files
into the env/ folder manually will work for running programs that need the
RealSense library. This section will detail the process for this manual
work-around.
TODO Make cleaner.
Follow GitHub issue below, but need to use
cmake .. -DBUILD_EXAMPLES=false -DBUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS=trueor else compile errors will ensue. Connor needed to comment out sections in
CMakeLists.txt file because the -DBUILD_EXAMPLES=false wasn't working...?
Once compile is successful and complete, DO NOT DO sudo make install.
The .so files will be in the librealsense/build/ folder, and these need to
be moved to env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ in the maav-cv repo folder.
Github Issue with details on how to fix this by compiling from source: