This command-line interface (CLI) enables data visualization and communication with embedded platforms.
- Fast prototyping and debugging. Set everything up in a few minutes and start debugging any embedded device efficiently. Forget about
printf. Forever. - Communication-based applications. Stop re-writing custom protocols for each new project.
- Real-time update of embedded application parameters. Tune your application without loosing time compiling & flashing.
- Data-plotting. Plot data from the device in no time, with a single command. Time-varying values, arrays and sparse arrays.
- Reusability. Highly flexible protocol, loosely coupled to your application. Suited for a wide number of application scenarios.
Arduino and ARM mbed are currently officially supported.
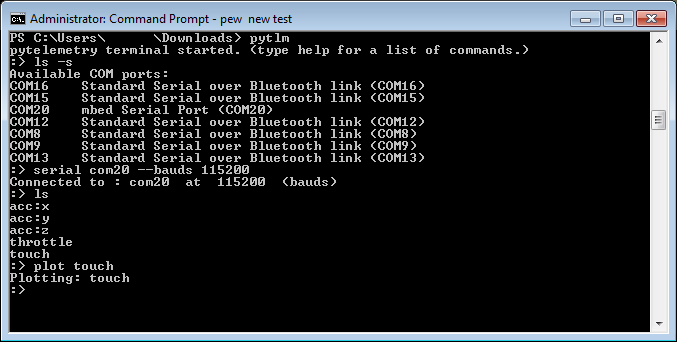
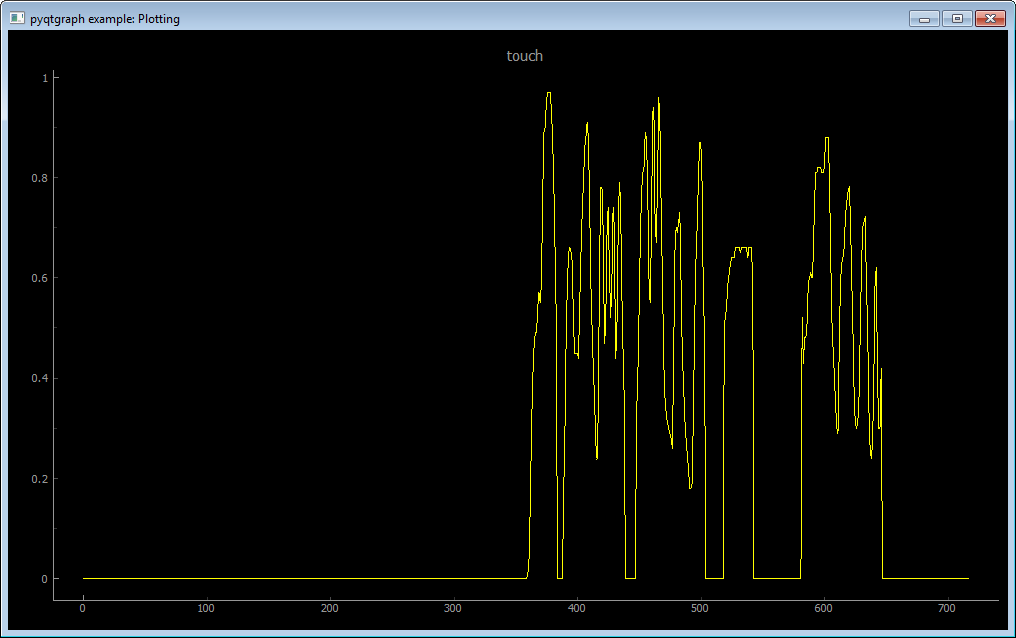
Aan example of listing serial ports ls -s, connecting to a device through COM20 serial com20 --bauds 115200, listing all received topics ls and opening a plot on topic touch plot touch
The CLI provides a set of commands to connect to a device, read, plot, write data on it, log any received and sent data.
The communication protocol that carry all exchanged information is implemented in Python and C:
pytelemetryfor scripting the communication from your PC
telemetry: for enabling communication in the embedded device.
Officially supported embedded platforms are for now Arduino and Mbed.
This CLI runs on Windows, Mac OS and Linux.
See the central documentation for installation tutorials and description of the protocol.
pytelemetrycli requires python 3.3+, PyQt4 and numpy.
It is recommended to download numpy and PyQt4 wheels python packages (courtesy of Christoph Gohlke).
In case you were wondering, no you don't have to install Qt. The binary wheel is enough.
Install with pip the downloaded files
pip install numpy-x.xx.x+vanilla-cp3x-none-winxxx.whl
pip install PyQt4-x.xx.x-cp3x-none-winxxx.whlThen, simply install pytelemetrycli with pip as usual
pip install pytelemetrycliThe easiest way to install numpy and PyQt4 seem to be using homebrew.
lease note that you should also have installed python 3.5 with homebrew for this to work correctly.
Also, avoid to have another python 3.5 distribution on your system otherwise you will face import issues as well.
brew install python3
brew install pyqt --with-python3
pip3 install pytelemetrycliThe setup used for testing relies on miniconda.
conda install numpy
conda install pyqt
conda install pip
pip install pytelemetrycli
However, if you have PyQt4 and numpy already installed in your directory, simply run
pip install pytelemetrycli
The command line interface can be started like this
python3 -m pytelemetrycli.cli
If everything is installed properly, :> should welcome you.
pytelemetry terminal started. (type help for a list of commands.)
:> _
Without arguments, you get a list of all available commands. Otherwise the full command documentation.
Without options, prints a list of all received topics.
With the --serial flag, prints a list of all available COM ports
Usage: ls [options]
Options:
-s, --serial Use this flag to print a list of all available serial portsConnects pytelemetry to the serial port.
Usage: serial <port> [options]
Options:
-b X, --bauds X Connection speed in bauds [default: 9600]Prints X last received samples from <topic>.
Usage: print <topic> [options]
Options:
-a X, --amount X Amount of samples to display [default: 1]Publishes a (value | string) on <topic>.
Usage: pub (--u8 | --u16 | --u32 | --i8 | --i16 | --i32 | --f32 | --s) <topic> <value>Plots <topic> in a graph window.
Usage: plot <topic>Displays different metrics about the active transport (ex : serial port).
This allows you to know if for instance corrupted frames are received, what fraction
of the maximum baudrate is being used, etc.
Usage: statsDisconnects from any open connection.
Usage: disconnectExits the terminal application.
Usage: quit- improve and truly centralize documentation
- export to Excel and CSV and replay command in the CLI for offline inspection.
- support of Matrices, XYZ, and RGB-type codes.