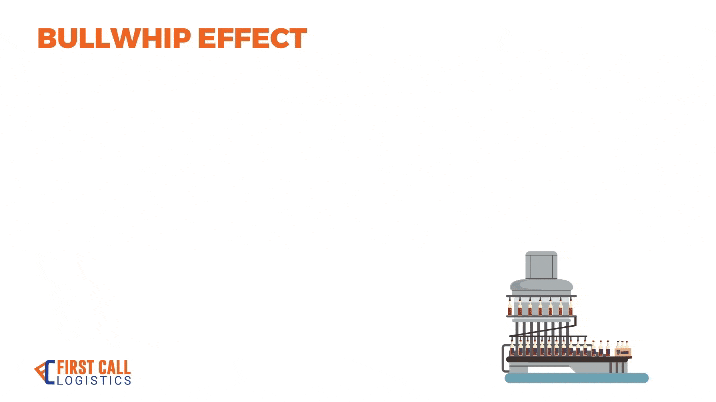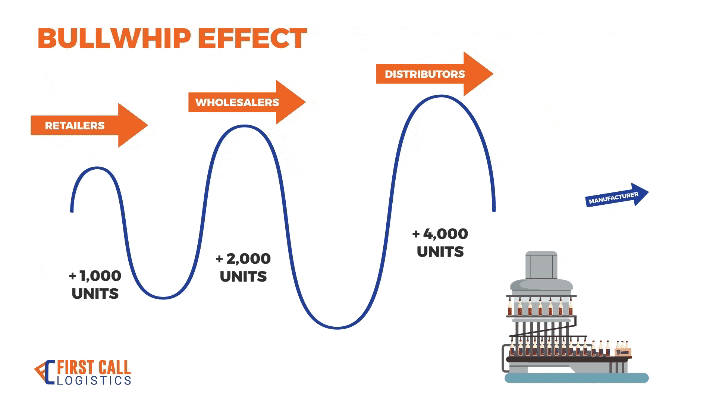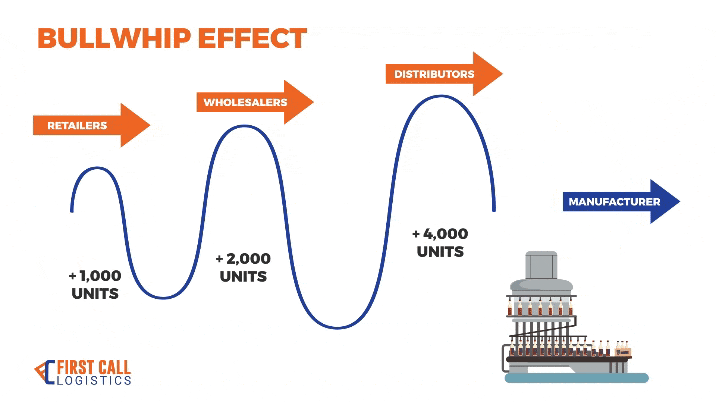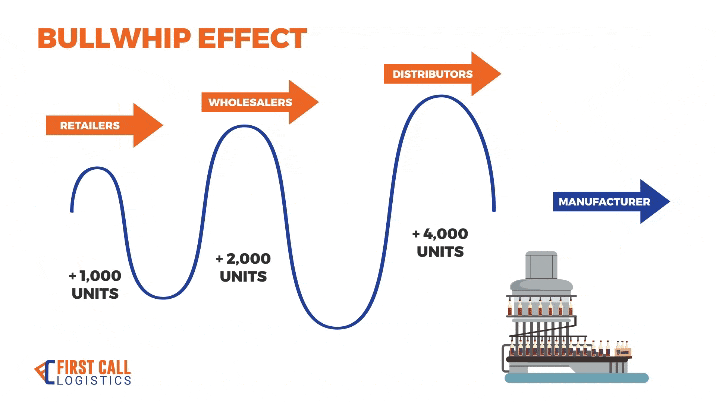
1. Costs Over Time
This plot displays the cumulative costs incurred by each actor (Retailer, Wholesaler, Distributor, and Factory) in the supply chain over time, measured weekly. Each line represents the total costs for a different actor. The costs include inventory holding costs and backorder penalties:
- Retailer (Red Line): Shows a gradual cost increase, indicating relatively stable demand management and inventory control.
- Wholesaler (Yellow Line): Experiences a more pronounced cost increase after around 15 weeks, likely due to demand amplification effects and backorders.
- Distributor (Purple Line): Demonstrates the steepest cost increase, especially after week 20, indicating significant challenges in managing fluctuating demand.
- Factory (Blue Line): Also shows a steep cost increase after week 15, suggesting difficulties in balancing production with the increased order volatility.
This plot highlights the bullwhip effect as costs increase disproportionately for upstream actors (Distributor and Factory) due to amplified demand variability.
2. Effective Inventory Over Time
This plot tracks the effective inventory levels for each actor over time, where effective inventory is the difference between stock and outstanding orders:
- Retailer (Red Line): Maintains a mostly stable inventory level with slight fluctuations, indicating a balance in supply and demand until a drop after week 20.
- Wholesaler (Yellow Line): Experiences a dip around week 15 but stabilizes again, showing some ability to manage inventory despite upstream disruptions.
- Distributor (Purple Line): Shows a sharp inventory decrease followed by a large spike after week 20, reflecting difficulties in balancing supply and demand in response to the bullwhip effect.
- Factory (Blue Line): Also experiences a sharp inventory dip and recovery, aligning with high volatility in demand from downstream actors.
This plot reveals how each actor's inventory stability is impacted by demand variability, with upstream actors facing more pronounced fluctuations due to the bullwhip effect.
3. Orders Over Time
This plot illustrates the number of orders placed by each actor over time, providing insight into how demand is amplified as it moves up the supply chain:
- Retailer (Red Line): Shows a relatively consistent order pattern with minor increases, reflecting direct customer demand.
- Wholesaler (Yellow Line): Experiences a more noticeable increase in orders starting around week 15, amplifying the initial demand.
- Distributor (Purple Line): Shows a significant spike in orders around weeks 20-25, indicating strong demand amplification due to the bullwhip effect.
- Factory (Blue Line): Reaches the highest peak in order volume, showing how demand volatility is most severe for the Factory due to cumulative effects from downstream actors.
This plot illustrates the bullwhip effect in action, where small fluctuations in customer demand lead to large order spikes upstream, especially affecting the Factory.