LightBulb is an open source python framework for auditing web application firewalls and filters.
The framework consists of two main algorithms:
-
GOFA: An active learning algorithm that infers symbolic representations of automata in the standard membership/equivalence query model.
Active learning algorithms permits the analysis of filter and sanitizer programs remotely, i.e. given only the ability to query the targeted program and observe the output.
-
SFADiff: A black-box differential testing algorithm based on Symbolic Finite Automata (SFA) learning
Finding differences between programs with similar functionality is an important security problem as such differences can be used for fingerprinting or creating evasion attacks against security software like Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) which are designed to detect malicious inputs to web applications.
LightBulb is available in BApp Store as an extesion for the Burp Suite. You can directly install LightBulb by navigating at the Burp Extender tab. You can also import latest the standalone version of the extension.
Web Applications Firewalls (WAFs) are fundamental building blocks of modern application security. For example, the PCI standard for organizations handling credit card transactions dictates that any application facing the internet should be either protected by a WAF or successfully pass a code review process. Nevertheless, despite their popularity and importance, auditing web application firewalls remains a challenging and complex task. Finding attacks that bypass the firewall usually requires expert domain knowledge for a specific vulnerability class. Thus, penetration testers not armed with this knowledge are left with publicly available lists of attack strings, like the XSS Cheat Sheet, which are usually insufficient for thoroughly evaluating the security of a WAF product.
In this presentation we introduce a novel, efficient, approach for bypassing WAFs using automata learning algorithms. We show that automata learning algorithms can be used to obtain useful models of WAFs. Given such a model, we show how to construct, either manually or automatically, a grammar describing the set of possible attacks which are then tested against the obtained model for the firewall. Moreover, if our system fails to find an attack, a regular expression model of the firewall is generated for further analysis. Using this technique we found over 10 previously unknown vulnerabilities in popular WAFs such as Mod-Security, PHPIDS and Expose allowing us to mount SQL Injection and XSS attacks bypassing the firewalls. Finally, we present LightBulb, an open source python framework for auditing web applications firewalls using the techniques described above. In the release we include the set of grammars used to find the vulnerabilities presented.
Main interface commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| core | Shows available core modules |
| utils | Shows available query handlers |
| info <module> | Prints module information |
| library | Enters library |
| modules | Shows available application modules |
| use <module> | Enters module |
| start <moduleA> <moduleB> | Initiate algorithm |
| help | Prints help |
| status | Checks and installs required packages |
| complete | Prints bash completion command |
Module commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| back | Go back to main menu |
| info | Prints current module information |
| library | Enters library |
| options | Shows available options |
| define <option> <value> | Set an option value |
| start | Initiate algoritm |
| complete | Prints bash completion command |
Library commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| back | Go back to main menu |
| info <folder\module> | Prints requested module information (folder must be located in lightbulb/data/) |
| cat <folder\module> | Prints requested module (folder must be located in lightbulb/data/) |
| modules <folder> | Shows available library modules in the requested folder (folder must be located in lightbulb/data/) |
| search <keywords> | Searches available library modules using comma separated keywords |
| complete | Prints bash completion command |
First you have to verify that your system supports flex, python dev, pip and build utilities:
For apt platforms (ubuntu, debian...):
sudo apt-get install flex
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo apt-get install build-essential(Optional for apt) If you want to add support for MySQL testing:
sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-devFor yum platforms (centos, redhat, fedora...) with already installed the extra packages repo (epel-release):
sudo yum install -y python-pip
sudo yum install -y python-devel
sudo yum install -y wget
sudo yum groupinstall -y 'Development Tools'(Optional for yum) If you want to add support for MySQL testing:
sudo yum install -y mysql-devel
sudo yum install -y MySQL-pythonIn order to use the application without complete package installation:
git clone https://github.com/lightbulb-framework/lightbulb-framework
cd lightbulb-framework
make
lightbulb statusIn order to perform complete package installation. You can also install it from pip repository. This requires first to install the latest setuptools version:
pip install setuptools --upgrade
pip install lightbulb-framework
lightbulb statusIf you want to use virtualenv:
pip install virtualenv
virtualenv env
source env/bin/activate
pip install lightbulb-framework
lightbulb statusThe "lightbulb status" command will guide you to install MySQLdb and OpenFst support. If you use virtualenv in linux, the "sudo" command will be required only for the installation of libmysqlclient-dev package.
It should be noted that the "lightbulb status" command is not necessary if you are going to use the Burp Extension. The reason is that this command installs the "openfst" and "mysql" bindings and the extension by default is using Jython, which does not support C bindings. It is recommended to use the command only if you want to change the Burp extension configuration from the settings and enable the native support.
It is also possible to use a docker instance:
docker pull lightbulb/lightbulb-frameworkIf you wish to use the new GUI, you can use the extension for the Burp Suite.
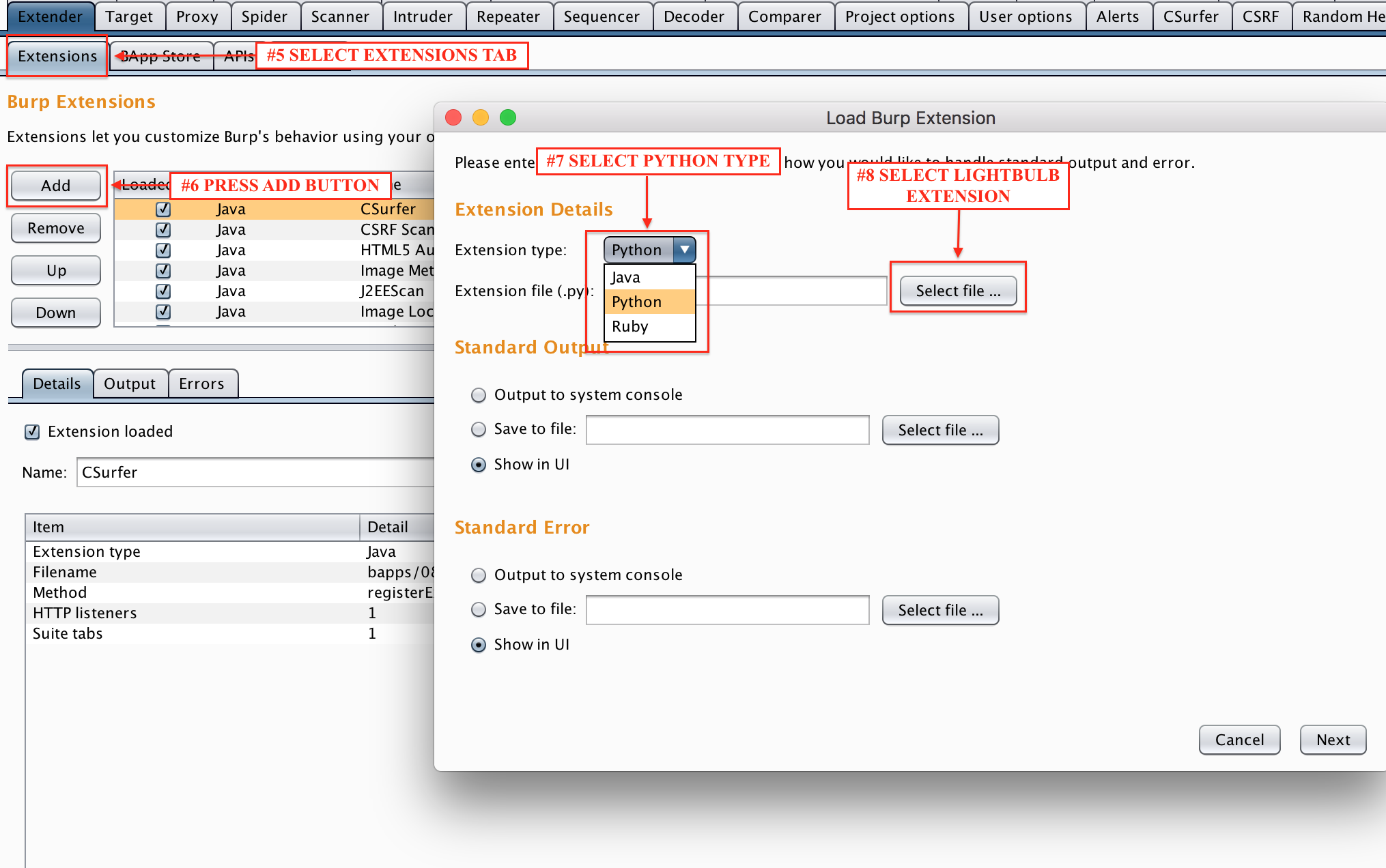
The extension is already available in the BApp Store. You can directly install LightBulb by navigating at the Burp Extender tab.
You can also use the following steps to install the latest version of the extension from this repository manually in Burp.
First, it is recommended to increase the available memory for Burp using the following command:
java -jar -Xmx2048M /path/to/burpbinary
Also, Lightbulb uses the native binary of flex parser. As a result, it is recommended to install flex before using the tool. In Debian system it can be installed with the following command:
apt install flex
Fir# LightBulb LightBulb is an open source python framework for auditing web application firewalls and filters.
The framework consists of two main algorithms:
-
GOFA: An active learning algorithm that infers symbolic representations of automata in the standard membership/equivalence query model.
Active learning algorithms permits the analysis of filter and sanitizer programs remotely, i.e. given only the ability to query the targeted program and observe the output.
-
SFADiff: A black-box differential testing algorithm based on Symbolic Finite Automata (SFA) learning
Finding differences between programs with similar functionality is an important security problem as such differences can be used for fingerprinting or creating evasion attacks against security software like Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) which are designed to detect malicious inputs to web applications.
LightBulb is available in
Web Applications Firewalls (WAFs) are fundamental building blocks of modern application security. For example, the PCI standard for organizations handling credit card transactions dictates that any application facing the internet should be either protected by a WAF or successfully pass a code review process. Nevertheless, despite their popularity and importance, auditing web application firewalls remains a challenging and complex task. Finding attacks that bypass the firewall usually requires expert domain knowledge for a specific vulnerability class. Thus, penetration testers not armed with this knowledge are left with publicly available lists of attack strings, like the XSS Cheat Sheet, which are usually insufficient for thoroughly evaluating the security of a WAF product.
In this presentation we introduce a novel, efficient, approach for bypassing WAFs using automata learning algorithms. We show that automata learning algorithms can be used to obtain useful models of WAFs. Given such a model, we show how to construct, either manually or automatically, a grammar describing the set of possible attacks which are then tested against the obtained model for the firewall. Moreover, if our system fails to find an attack, a regular expression model of the firewall is generated for further analysis. Using this technique we found over 10 previously unknown vulnerabilities in popular WAFs such as Mod-Security, PHPIDS and Expose allowing us to mount SQL Injection and XSS attacks bypassing the firewalls. Finally, we present LightBulb, an open source python framework for auditing web applications firewalls using the techniques described above. In the release we include the set of grammars used to find the vulnerabilities presented.
Main interface commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| core | Shows available core modules |
| utils | Shows available query handlers |
| info <module> | Prints module information |
| library | Enters library |
| modules | Shows available application modules |
| use <module> | Enters module |
| start <moduleA> <moduleB> | Initiate algorithm |
| help | Prints help |
| status | Checks and installs required packages |
| complete | Prints bash completion command |
Module commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| back | Go back to main menu |
| info | Prints current module information |
| library | Enters library |
| options | Shows available options |
| define <option> <value> | Set an option value |
| start | Initiate algoritm |
| complete | Prints bash completion command |
Library commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| back | Go back to main menu |
| info <folder\module> | Prints requested module information (folder must be located in lightbulb/data/) |
| cat <folder\module> | Prints requested module (folder must be located in lightbulb/data/) |
| modules <folder> | Shows available library modules in the requested folder (folder must be located in lightbulb/data/) |
| search <keywords> | Searches available library modules using comma separated keywords |
| complete | Prints bash completion command |
First you have to verify that your system supports flex, python dev, pip and build utilities:
For apt platforms (ubuntu, debian...):
sudo apt-get install flex
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo apt-get install build-essential(Optional for apt) If you want to add support for MySQL testing:
sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-devFor yum platforms (centos, redhat, fedora...) with already installed the extra packages repo (epel-release):
sudo yum install -y python-pip
sudo yum install -y python-devel
sudo yum install -y wget
sudo yum groupinstall -y 'Development Tools'(Optional for yum) If you want to add support for MySQL testing:
sudo yum install -y mysql-devel
sudo yum install -y MySQL-pythonIn order to use the application without complete package installation:
git clone https://github.com/lightbulb-framework/lightbulb-framework
cd lightbulb-framework
make
lightbulb statusIn order to perform complete package installation. You can also install it from pip repository. This requires first to install the latest setuptools version:
pip install setuptools --upgrade
pip install lightbulb-framework
lightbulb statusIf you want to use virtualenv:
pip install virtualenv
virtualenv env
source env/bin/activate
pip install lightbulb-framework
lightbulb statusThe "lightbulb status" command will guide you to install MySQLdb and OpenFst support. If you use virtualenv in linux, the "sudo" command will be required only for the installation of libmysqlclient-dev package.
It should be noted that the "lightbulb status" command is not necessary if you are going to use the Burp Extension. The reason is that this command installs the "openfst" and "mysql" bindings and the extension by default is using Jython, which does not support C bindings. It is recommended to use the command only if you want to change the Burp extension configuration from the settings and enable the native support.
It is also possible to use a docker instance:
docker pull lightbulb/lightbulb-frameworkIf you wish to use the new GUI, you can use the extension for the Burp Suite.
The extension is already available in the BApp Store. You can directly install LightBulb by navigating at the Burp Extender tab.
You can also use the following steps to install the latest version of the extension from this repository manually in Burp.
First, it is recommended to increase the available memory for Burp using the following command:
java -Xmx2048M -jar /path/to/burpbinary
Also, Lightbulb uses the native binary of flex parser. As a result, it is recommended to install flex before using the tool. In Debian system it can be installed with the following command:
apt install flex
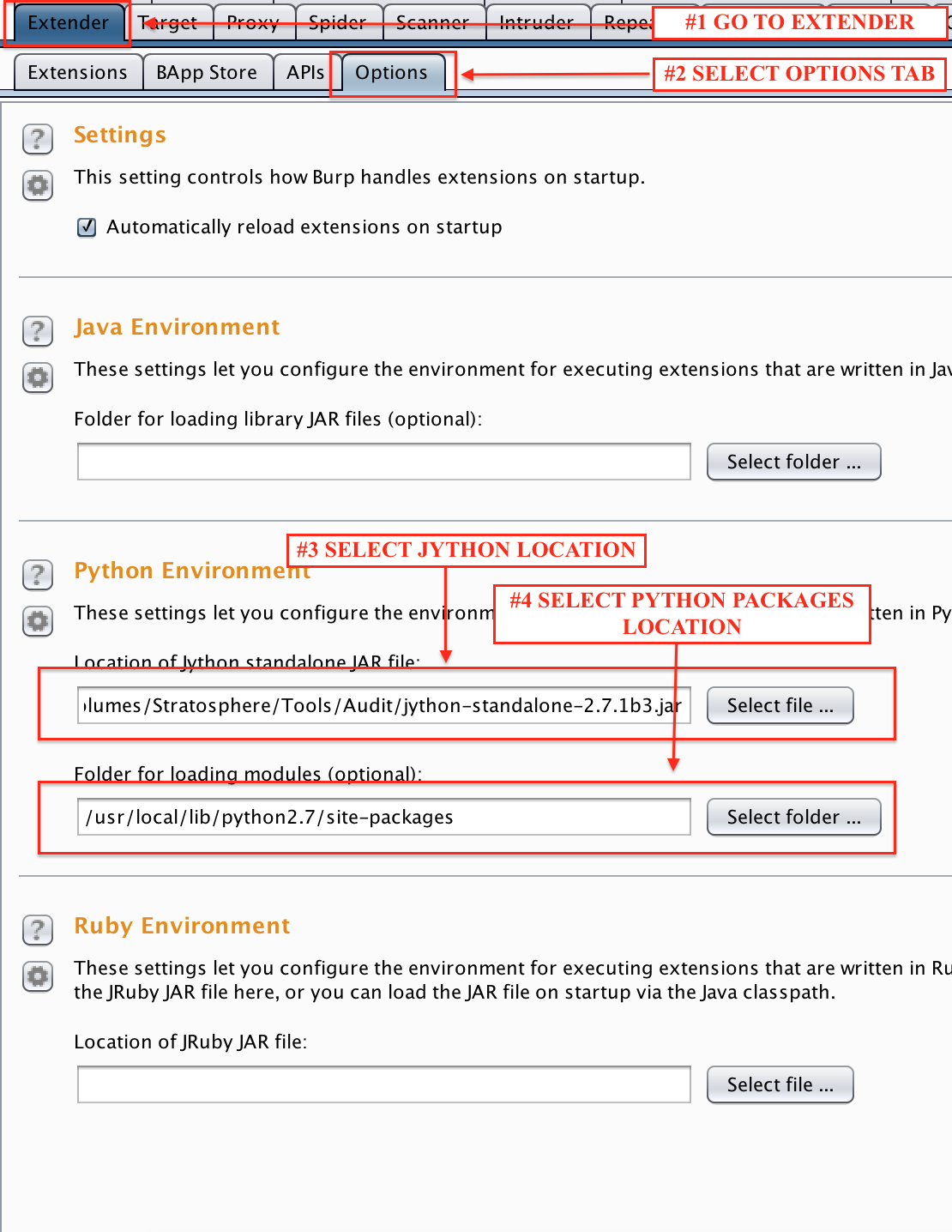
Then, you have to setup a working environment with Burp Proxy and Jython
- Download the latest Jython from here**
- Find your local python packages installation folder*
- Configure Burp Extender to use these values, as shown below*
- Select the new LightBulb module ("BurpExtension.py") and set the extension type to be "Python"
*You can ignore this step, and install the standalone version which contains all the required python packages included. You can download it here
** The latest Jython 2.7.X is supported. However MySQL Differential Learning may still require an older version (eg. Jython 2.5.X) since the MySQL connector jar cannot be dynamically imported in the classpath.
Check out the Wiki page for usage examples.
- George Argyros
- Ioannis Stais
- Suman Jana
- Angelos D. Keromytis
- Aggelos Kiayias
- G. Argyros, I. Stais, S. Jana, A. D. Keromytis, and A. Kiayias. 2016. SFADiff: Automated Evasion Attacks and Fingerprinting Using Black-box Differential Automata Learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS '16). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 1690-1701. doi: 10.1145/2976749.2978383
- G. Argyros, I. Stais, A. Kiayias and A. D. Keromytis, "Back in Black: Towards Formal, Black Box Analysis of Sanitizers and Filters," 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, 2016, pp. 91-109. doi: 10.1109/SP.2016.14
This research was partly supported by ERC project CODAMODA, #259152.
MIT License as described in LICENSE file