https://github.com/QuoSecGmbH/os_timestamps/
- Profile the Operating System, standard libraries (libc), middleware, applications and commands line utilities
- Test against POSIX compliance
- Tested on Linux (Ubuntu, Arch), OpenBSD, FreeBSD, macOS
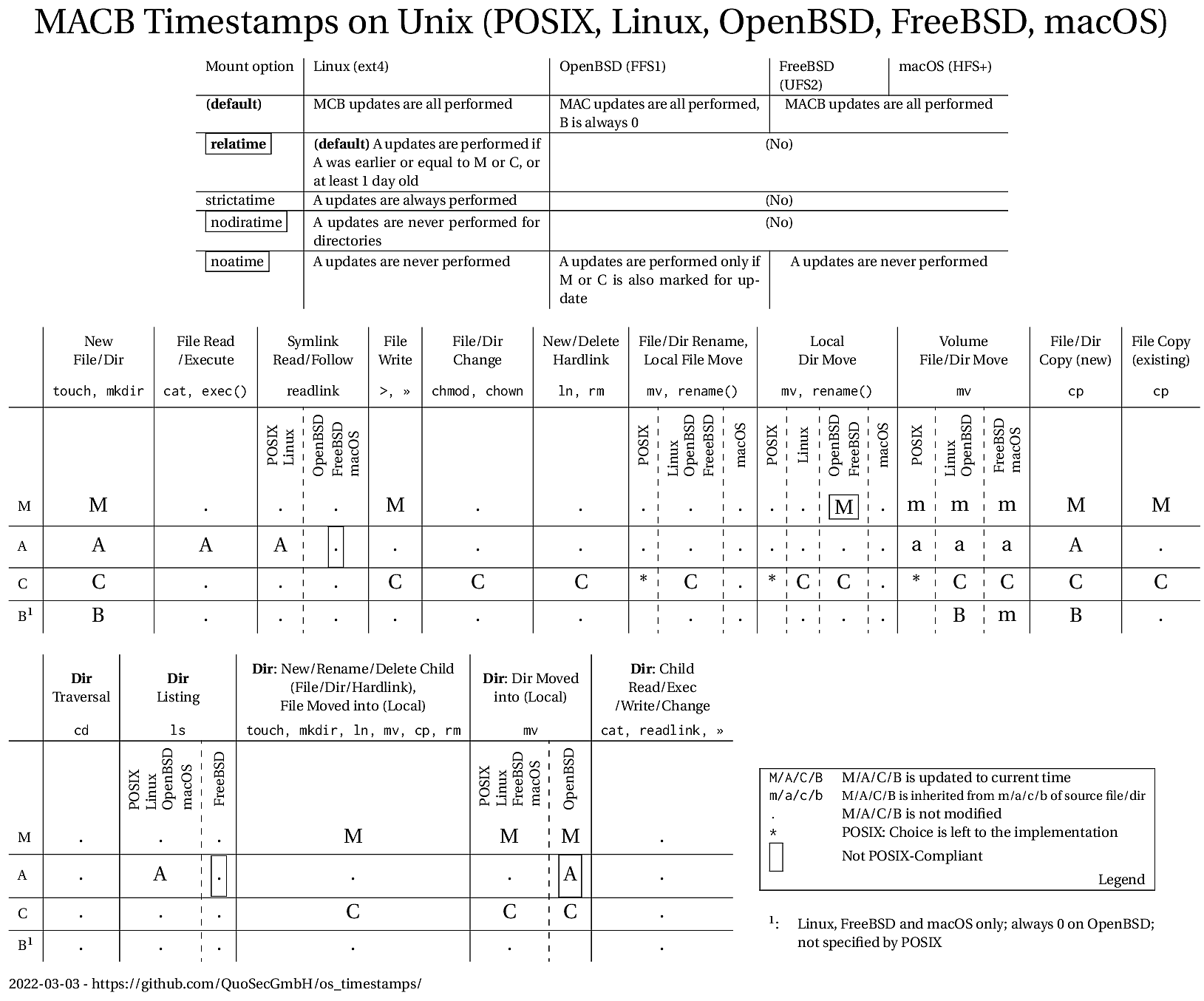
- M: Last data modification timestamp
- A: Last data access timestamp
- C: Last file status change timestamp (typically updated by
chmodorchown) - B: File creation (birth)
- 2022 - A systematic approach to understanding MACB timestamps on Unix-like systems (DFRWS-EU 2022) - [paper] [pdf] [slides] [video] [transcript]
- 2020 - OS Profiling: https://yaps8.github.io/blog/01_macb_timestamps_across_POSIX.html
- 2019 - Tests against POSIX Compliance: https://yaps8.github.io/blog/02_Testing_POSIX.html
The main result is the following comparative table for timestamp updates provoked by POSIX utilities, standard libraries (libc) and kernel system calls.
mkdir build; cd build/cmake ../src/make
You may need to install the following (tested on Ubuntu 22.04):
- pip packages: pyautogui
- Other packages: python3-dev python3-tk qtbase5-dev
profile_os profiles common file operations:
- New file/dir
- File read (cat)
- File write (echo AA > file)
- File change (chown, chmod)
- Local File Copy
- Volume file copy
- ...
To have complete results you will need:
- For "Volume Copy" (copy a file to a different file system): the other file system to test, mounted into mnt/
- On Linux you can create an Ext4 fs with:
dd if=/dev/zero of=profileos.ext4 bs=4M count=10mkfs.ext4 -O extra_isize -I 256 profileos.ext4
- On OpenBSD you may use /tmp/ as it is typically on a separate partition
- On Linux you can create an Ext4 fs with:
- For reliable chown tests ("File Change"...): the GID of a group you can attribute to a file (you shall be able to do
chown :GID file)- On OpenBSD & FreeBSD, GID 0 (wheel) can be used
$ ./profile_os -m mnt/ -G 1000
INFO: Directory for tests is: tmp_os_profile_10/
INFO: Volume path is: mnt/tmp_os_profile_10/
File Creation (PROFILE.OS.FILE.NEW):
dir/
M.C.
newfile
MACB
File Copy (new) (PROFILE.OS.FILE.COPY.NEW):
src
.A..
srcdir/
....
dst
MACB
dstdir/
M.C.
[...]
Symbols you will encounter:
M/A/C/B - M/A/C/B was updated to current time
m/a/c/b - M/A/C/B was set to the same m/a/c/b value as the source file/dir
> - M/A/C/B was set to the same value as the source file/dir (same as m/a/c/b but for the same timestamp)
s - M/A/C/B was set to the same value as multiple m/a/c/b timestamps of the source file/dir
. - M/A/C/B was not modified
d - M/A/C/B seem to have been updated after the command ended (delay - this may hidden with -d option)
0 - M/A/C/B was 0 after command execution
! - Error (mostly: the file did not exist anymore)
Two CSV files are also created:
- os_profile_results.csv - Contains a condensed view of the results, can be used for comparison
- os_profile_flags.csv - Contains a more detailed view of the results, explaining precisely what happens to each timestamp
The provided results will need some interpretation and a bit of context (mount options, OS configuration...) to be fully understood and turned into tables (RESULTS.md).
profile_qt and profile_gio provide similar capabilities to profile functions from Qt and GIO.
They are only compiled (see CMakeLists.txt) and tested on Linux.
The python package pyautogui is needed, it can be installed in a virtual env as follows:
python3 -m venv venv_pyautogui
source venv_pyautogui/bin/activate
pip3 install pyautogui
A number of text editors can be profiled with code based on pyautogui, for instance with:
python3 profile_gui.py: run all testspython3 profile_gui.py -t list: list testspython3 profile_gui.py -t EDITOR.nano: run only tests for nanopython3 profile_gui.py -t EDITOR.nano --sleeptime 0.1 --empty --small: quick test (short sleeptime, test only with empty and small files)
Please do not touch the keyboard or mouse while the tests are running.
Output is given in a file named editors_profile.txt:
Small File Test
Vim Version: 8.1
vim --clean
VIM ACCESS TEST: |A| | |
VIM MODIFY TEST: M|A|C|B|I
VIM SAVE WITHOUT MODIFICATION TEST: M|A|C|B|I
VIM MODIFY BUT DONT SAVE TEST: |A| | |
Additionnally to MACB, I indicates that the inode of the watched file changed.
profile_cmd is an interactive tool to profile shell commands.
You need to manually define which files/dirs you want to watch for change.
The first watched path is considered as the source file/dir (for > and m/a/c/b), so be careful to define it correctly.
New File (Linux):
$ ./profile_cmd -w file 'touch file'
file
MACB
Dir Move (Linux):
$ ./profile_cmd -w dir/ -w dst/ -w dst/dir/ 'mv dir/ dst/'
dir/
!!!!
dst/
M.C.
dst/dir/
>>C>
run_tests will test OS behavior against POSIX tests. The file results.csv will be created with parsable information on tests that were run and the results.
./run_testsby default will run all non-interactive tests./run_tests --dry-runwill not perform tests but can be used to enumerate them./run_tests -t GENERAL.NEW_FILE_REALTIMEwill run specific test only (can be used multiple times)
By default details are only shown when a test fails but it can be forced in verbose mode (-v). Output when something fails look like the following.
./run_tests -t GENERAL.NEW_FILE_REALTIME
INFO: Directory for tests is: tmp_tests_19/
WARNING: check_general_new_file_realtime - M not updated
WARNING: check_general_new_file_realtime - A not updated
WARNING: check_general_new_file_realtime - C not updated
INFO: check_general_new_file_realtime:
INFO: Before: 1590125151s 5644975ns ; After: 1590125151s 5684126ns
INFO: M: 1590125151s 4162603ns
INFO: A: 1590125151s 4162603ns
INFO: C: 1590125151s 4162603ns
INFO: B: 1590125151s 4162603ns
RESULT: No - No(.UNKNOWN) - New file shall have MAC updated (CLOCK_REALTIME) - GENERAL.NEW_FILE_REALTIME - check_general_new_file_realtime
It means that:
- Folders and files for this test are in folder with relative path
tmp_tests_19/ - Test determined that MAC were not updated when it was expected
- Test occurs in function called
check_general_new_file_realtime - Timestamp before the action were: 1590125151.5644975s
- Timestamp after the action were: 1590125151.5684126s
- Relevant MAC for comparison are all equal to: 1590125151.4162603s
prototype_file_ts TARGET [MODE] [-i/--print-inode] will output the target's MACB timestamps.
As it uses the stat() (and statx() on Linux) system calls, it shall not update any timestamp of the target.
Mode can be:
- 0 (default): uses stat to get MAC and gets B by OS-specific method that follows symlinks
- 1: Same as 0 but outputs as csv
- 11: Same as 1 but omits the file name (prints only timestamps and, when requested, inode number)
- 2: same as 0 but with lstat and OS-specific method that does not follow symlinks
- 3: Linux only: gets MACB with statx, with the AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW flag (do not follow symlinks)
- 4: Linux only: same as 3 but outputs with the format second.nanosecond for easier parsing
Implemented OS-specific methods to read B:
- Linux: use the statx system call
- OpenBSD: struct stat has a field called __st_birthtim
- FreeBSD: struct stat has a field called st_birthtim
$ ./prototype_file_ts file
file: (stat + B)
M: Mon Dec 2 13:59:38 2019 - ns: 766478455
A: Mon Dec 2 13:59:36 2019 - ns: 870434493
C: Mon Dec 2 13:59:42 2019 - ns: 554566399
B: Mon Dec 2 13:42:32 2019 - ns: 126956318