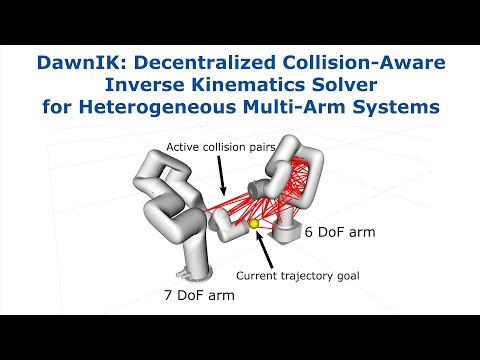
DawnIK [1] is a real-time inverse kinematics solver for robotic arms focusing on observation capabilities with collision avoidance and multiple objectives. This repository contains the accompanying code for the paper "DawnIK: Decentralized Collision-Aware Inverse Kinematics Solver for Heterogeneous Multi-Arm Systems" by Salih Marangoz, Rohit Menon, Nils Dengler, Maren Bennewitz submitted for IEEE-RAS Humanoids 2023. you can find the paper at https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.12750
DawnIK has different goals defined in goals.h which can be combined specifically for a use-case. There are some examples:
- Position Goal: [Video]
- Position Goal + Orientation Goal: [Video]
- Look-at Goal (+ Position Goal with a small weight): [Video]
$ cd catkin_ws/src
# This package
git clone https://github.com/RePAIRProject/repair_dawnik.git
# Fake Joints (optional alternative to Gazebo) (forked and modified)
git clone https://github.com/salihmarangoz/fake_joint
# repair packages
git clone --recurse-submodules -j8 https://github.com/RePAIRProject/repair_ros_robot.git
# Others
$ cd catkin_ws
$ rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r
$ sudo apt install python3-yaml python-is-python3
$ pip install pyyaml pyquaternion
################## EXTERNAL DEPENDENCIES ############################
# Ceres Solver 2.x.x (http://ceres-solver.org/installation.html)
cd $HOME
#git clone git@github.com:salihmarangoz/ceres-solver.git
git clone git@github.com:ceres-solver/ceres-solver.git -b 2.2.0rc1
sudo apt-get install cmake libgoogle-glog-dev libgflags-dev libatlas-base-dev libeigen3-dev libsuitesparse-dev
cd ceres-solver
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DUSE_CUDA=OFF ..
make -j8
sudo make install
# Update dynamic linker run-time bindings
sudo ldconfigInstall XBot2 to use the real robot drivers.
cd catkin_ws
# Build
catkin build
# After successful build, source the workspace in all the terminals
source devel/setup.bash-
Start roscore
roscore
-
Start XBot2
cd catkin_ws source devel/setup.bash # source xbot2 setup echo ". /opt/xbot/setup.sh" >> ~/.bashrc # source repair config for xbot2 set_xbot2_config ~/repair_robot_ws/src/repair_ros_robot/repair_cntrl/config/repair_basic.yaml # start xbot2 core (dummy) xbot2-core --hw dummy
# select one!
# For Fake Joints:
roslaunch dawn_ik repair_fake.launch
# For Gazebo:
roslaunch dawn_ik repair_fake.launch launch_gazebo:=true
# For xbot2 (dummy):
roslaunch dawn_ik repair_xbot_dummy.launch- Make sure that the robot joints don't have further position limits (e.g. for improving MoveIt's planninng behavior where it is limited between [-PI,+PI]).
- If you would like to use collisions objects other than spheres you need to modify the code. Modify
dawn_ik.cpparound line 295 to createCollisionAvoidanceGoalNumericinstead ofCollisionAvoidanceGoal. With this change, dawn_ik will use numerical diff instead of autodiff. Be careful because the convergence performance may be affected. - DawnIK can be used to isolate an arm from the collision computations in an multi-arm system. This is usually done by disabling collisions for the controlled arm. However, for the ACM computations with MoveIt make sure all collisions are enabled.
Make sure the robot description is loaded. (if the fake/sim is running then it is probably loaded). Re-compile the project after this step.
# To skip the code generation step, replace autogen_test.h with pre-generated headers (repair_arm_1.h, repair_arm_2.h.)
roscd dawn_ik/include/dawn_ik/robot_configuration
# select one!
cp repair_arm_1.h autogen_test.h
cp repair_arm_1.h autogen_test.h
############################################
# To do the code generation step:
# select one!
rosrun dawn_ik robot_parser_node _cfg:=repair_arm_1
rosrun dawn_ik robot_parser_node _cfg:=repair_arm_2
# Re-compile the project after this step.
catkin buildStart the solver. This command will also launch RViz for providing input to the controller. There will be two interactive markers, one is for the endpoint pose and the other one is for the look-at goal. Right click one of the markers to set the current mode.
roslaunch dawn_ik repair_solver.launchBefore doing the experiments make sure that:
-
Generated code is for that robot, while using dawn_ik.
-
settings.yamlis set for that robot, while using collision_ik. -
Requires the following to be running
- roscore
- xbot2-core (dummy)
- repair_xbot_dummy.launch
# Fake Joints + Rviz (only run this one command) roslaunch dawn_ik run_experiment_old.launch robot_name:=repair solver:=dawn_ik # Gazebo + Rviz (only run this one command) roslaunch dawn_ik run_experiment_old.launch robot_name:=repair solver:=dawn_ik use_gazebo:=true
Both arms move in XZ plane.
- Arm_1 follows a Circle.
- Arm_2 follows an Eight.
- Waypoints are located in
waypointsfolder.
Waypoints are located in waypoints folder. Results are saved into the results folder. For analyzing and generating figures see results/analyze_results.ipynb notebook.
# in a new terminal
roscore
# in a new terminal
source /opt/xbot/setup.sh
xbot2-core --hw dummy
# in a new terminal (home the robot)
rosservice call /xbotcore/homing/switch 1
# in a new terminal
# Xbot2 dummy (dummy) + Rviz
roslaunch dawn_ik run_experiment_repair_dummy.launch
# in a new terminal
rosrun repair_interface motion_planner_test.py-
Solver crashes:
- Make sure to disable
horti_acm_tricksif it is not Horti.horti_acm_tricksdisabled collision checking between the external arms. So, if you have a multi-arm robotic system with more than 2 arms, you may need to adapt the code inrobot_parser.cppfor your use case.
- Make sure to disable
-
Parser crashes:
- Only single-axis revolute joints and static joints are supported.
- [1] Ceres Solver is heavily used in this project so we named this project similar to how Ceres Solver is named. Dawn is the spacecraft launched in 2007 by NASA, reached to Ceres in 2015 and acquired the dwarf planet's information of global shape, mean density, surface morphology, mineralogy, etc. by the middle of 2016.