(1)命令不区分大小写,而 key 区分大小写。
(2)help @ 可以快速查看命令。
# 1: 命令不区分大小写,而 `key` 区分大小写
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> set k1 v1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> SET K1 v1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> KEYS *
1) "k1"
2) "K1"
# 2: help @string 快速查看命令
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> help @string
APPEND key value
summary: Append a value to a key
since: 2.0.0
BITCOUNT key [start end]
summary: Count set bits in a string
since: 2.6.0
BITFIELD key [GET type offset] [SET type offset value] [INCRBY type offset increment] [OVERFLOW WRAP|SAT|FAIL]
summary: Perform arbitrary bitfield integer operations on strings
since: 3.2.0
BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
summary: Perform bitwise operations between strings
since: 2.6.0
BITPOS key bit [start] [end]
summary: Find first bit set or clear in a string
since: 2.8.7
DECR key
summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by one
since: 1.0.0
DECRBY key decrement
summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by the given number
since: 1.0.0
GET key
summary: Get the value of a key
since: 1.0.0# 1: 最常用
# SET key value
# GET key
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> SET k1 v1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> get k1
"v1"
# 2: 同时设置/获取多个键值
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> MSET k1 v1 k2 v2 k3 v3
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> MGET k1 k2 k3
1) "v1"
2) "v2"
3) "v3"
# 3: 数值增减
# 3.1: 递增数字
INCR key
# 3.2: 增加指定的整数
INCRBY key increment
# 3.3: 递减数值
DECR key
# 3.4: 递减指定的整数
DECRBY key decrement
# 4. 获取字符串长度
STRLEN key# 1: SETNX key value
# 2: SET key value [EX seconds|PX milliseconds] [NX|XX]
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> SET k1 v1 EX 10 NX
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> TTL k1
(integer) 6
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> TTL k1
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> TTL k1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> TTL k1
(integer) -2
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> KEYS *
(empty array)
EX:key在多少秒后过期。PX:key在多少毫秒后过期。NX:当 key 不存在时,才创建key,效果等同于 SETNX。XX:当 key 存在的时候,覆盖 key。
(1)商品编号、订单号采用 INCR 命令生成。
(2)喜欢/踩的人数统计。
// Redis的Hash对应的就是 Java 中的Map
Redis Hash ---> Map<String, Map<Object, Object>># 1:HSET key field value [field value ...]
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> HSET person name zs age 18 score 98
(integer) 3
# 2:HGETALL key
# 获得 key 中所有的属性和值
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> HGETALL person
1) "name"
2) "zs"
3) "age"
4) "18"
5) "score"
6) "98"
# 3: HINCRBY key field increment
# Increment the integer value of a hash field by the given number(1)购物车、点餐、送快递 数量统计。
# 1: LINDEX key index
summary: Get an element from a list by its index
since: 1.0.0
# 2: LINSERT key BEFORE|AFTER pivot element
summary: Insert an element before or after another element in a list
since: 2.2.0
# 3: LLEN key
summary: Get the length of a list
since: 1.0.0
# 4: LPOP key
summary: Remove and get the first element in a list
since: 1.0.0
# 5:LPUSH key element [element ...]
summary: Prepend one or multiple elements to a list
since: 1.0.0
# 6: LRANGE key start stop
# LRANGE key start stop 表示遍历
summary: Get a range of elements from a list
since: 1.0.0(1)微信订阅文章推送。
# 用户 1024 订阅的公众号, 推送了 35 66 77 号三篇文章
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> LPUSH like_article:uid:1024 35 66 77
(integer) 3
# 将文章全部遍历出去。
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> LRANGE like_article:uid:1024 0 -1
1) "77"
2) "66"
3) "35"# Set中的值是无序的并且不能重复的!
# 1: 在Set集合中添加元素
SADD key member [member ...]
# 2: 删除Set集合中一个或多个元素
SREM key member [member ...]
# 3: 获取集合中的元素数
SCARD key
# 4: 获得集合中所有元素
SMEMBERS key
# 5: 集合运算
# 5.1: 多个集合的差集
SDIFF key [key ...]
# 5.2: 多个集合的交集
SINTER key [key ...]
# 5.3: 多个集合的并集
SUNION key [key ...]
# 6: 随机移除并返回 1 个或多个
SPOP key [count]
# 7: 随机返回一个或多个(不会删除)
SRANDMEMBER key [count](1)微信抽奖小程序。
# 1: 创建抽奖名字 chouj:10.1
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD chouj:10.1 uid:1 uid:2 uid:3 uid:4
(integer) 4
# 2: 展示参加抽奖的人
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS chouj:10.1
1) "uid:2"
2) "uid:4"
3) "uid:3"
4) "uid:1"
# 3: 查询参加抽奖的总人数
127.0.0.1:6379> SCARD chouj:10.1
(integer) 4
# 4: 随机抽取两个人(会删除)
127.0.0.1:6379> SPOP chouj:10.1 2
1) "uid:3"
2) "uid:1"
# 5: 随机抽取两个人(不会删除)
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER chouj:10.1 1
1) "uid:2"(2)微信朋友圈点赞。
# 1: 发布文章 id1 id2 id3 id4 id5 五个人点赞
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD pub:msgId:39 id1 id2 id3 id4 id5
(integer) 5
# 2: 5号用户取消了赞
127.0.0.1:6379> SREM pub:msgId:39 id5
(integer) 1
# 3: 查看谁点赞了
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS pub:msgId:39
1) "id4"
2) "id3"
3) "id1"
4) "id2"
# 4: 点赞人数
127.0.0.1:6379> SCARD pub:msgId:39
(integer) 4(3)微博好友共同关注。
# 1: person1 关注了 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD person1:focus p2 p3 p4 p5 p6
(integer) 5
# 2: person2 关注了 p5 p6 p7 p8
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD person2:focus p5 p6 p7 p8
(integer) 4
# 3: person1 和 person2 共同关注?
127.0.0.1:6379> SINTER person1:focus person2:focus
1) "p6"
2) "p5"(4)QQ内推可能认识的人。
# 1: s1 认识 1 2 3 4 5
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD s1 1 2 3 4 5
(integer) 5
# 2: s2 认识 3 4 5 6 7 8
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD s2 3 4 5 6 7 8
(integer) 6
# 3: s1 - s2 获得 s1 可能认识的人
127.0.0.1:6379> SDIFF s1 s2
1) "1"
2) "2"
# 4: s2 - s1 获得 s2 可能认识的人
127.0.0.1:6379> SDIFF s2 s1
1) "6"
2) "7"
3) "8"# 1: Add one or more members to a sorted set, or update its score if it already exists
ZADD key [NX|XX] [CH] [INCR] score member [score member ...]
# 2: 返回指定下标的 member
# ZRANGE key 0 -1 返回所有的 member
# Return a range of members in a sorted set, by index
ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
# 3: Get the number of members in a sorted set
ZCARD key
# 4: Count the members in a sorted set with scores within the given values
ZCOUNT key min max
# 5: Increment the score of a member in a sorted set
ZINCRBY key increment member
# 6: 求多个集合的交集并输出到 destination
# WEIGHTS 每个集合的权重 要 × 这个权重
# AGGREGATE 默认是 SUM 求和
ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]- XX: 仅仅更新存在的成员,不添加新成员。
- NX: 不存在就添加新成员。
- CH: 返回多少个值被修改了。注:
ZADD默认返回新添加元素的数量。 - INCR: 当
ZADD指定这个选项时,成员的操作就等同ZINCRBY命令,对成员的分数进行递增操作。
(1)抖音、微博热搜。
# 1: 两条热搜
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD hot 3000 aaaa 4000 bbb
(integer) 2
# 2: 从高到低排列
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREVRANGEBYSCORE hot +inf -inf WITHSCORES
1) "bbb"
2) "4000"
3) "aaaa"
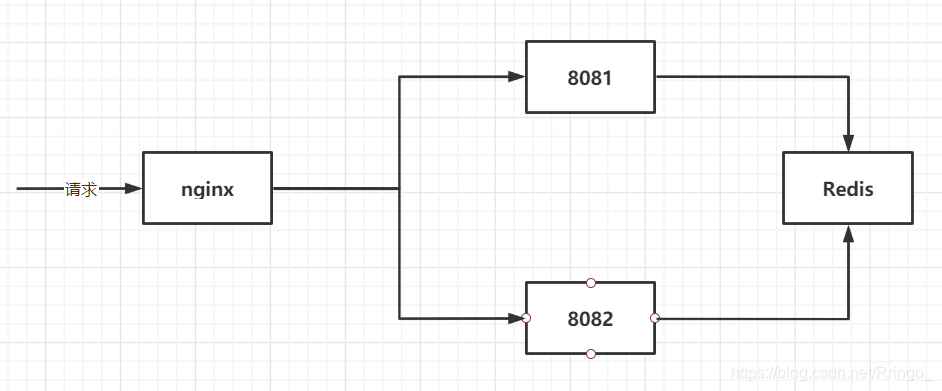
4) "3000"为了方便测试,该案例使用的是 nginx/windows。下载地址
注意:
windows/nginx下载之后是压缩包,无需安装,解压即可使用。- 使用
windows/nginx需要到安装目录下,打开 cmd 窗口。- 配置文件位置
conf/nginx.conf。
# nginx/window 命令
# 1: 启动 nginx
# 建议使用第一种,第二种会使你的cmd窗口一直处于执行中,不能进行其他命令操作。
start nginx
nginx.exe
# 2: 停止 nginx
# stop是快速停止nginx,可能并不保存相关信息;quit是完整有序的停止nginx,并保存相关信息。
nginx -s stop
nginx -s quit
# 3: 重新载入 nginx
nginx -s reload
# 4: 查看 nginx 版本
nginx -v# nginx.conf 配置文件
http {
# 负载均衡
# 权重是 1, 轮询机制
# 8081 和 8082 业务代码相同(使用 nginx 进行转发)
upstream myserver {
server 127.0.0.1:8081 weight=1;
server 127.0.0.1:8082 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 80; # nginx监听 80 端口
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://myserver; # nginx 反向代理
}
}
}<!-- pom.xml -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>service: com.ymy.boot.service.SaleService。controller: com.ymy.boot.controller.SaleController。
注意:
8081 和 8082 代码完全一样,只是端口不一样, 以上路径只写一次代表两个应用!
/**
* @author Ringo
* @date 2021/4/22 11:35
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 1: 字符串序列化
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
// 2: 对象序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
// 解决 Java 8 LocalDateTime 不能反序列化问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
om.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 3: 设置 string key value hashKey hashValue 的序列化器
template.setStringSerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
}// 单机版我们的业务
@GetMapping("/sale")
public String saleShop() {
return saleService.sale(); // 业务代码
}单机版业务出现的问题?
单机版没有加锁。
多个线程并发的访问同一个资源类,没有任何控制手段不能保证数据的一致性。
那么加锁 synchronized 还是 ReentrantLock?????
// java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock 中有 tryLock() 方法
/* 用法
Lock lock = ...;
if (lock.tryLock()) {
try {
// manipulate protected state
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
// perform alternative actions
}
*/
public interface Lock {
boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
}单机版加锁改进代码
// v1.0 单机版没有加锁 synchronized
// 高并发下, synchronized 会发生死等, 线程的阻塞和拥堵
@GetMapping("/sale")
public String saleShop() {
synchronized (this) {
return saleService.sale();
}
}
// v1.1. 单机版没有加锁 ReentrantLock
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@GetMapping("/sale")
public String saleShop() throws Exception {
// 带有超时时间了!
if (lock.tryLock(3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
try {
return saleService.sale();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
String msg = "没有抢到锁, 稍后再试";
System.out.println(msg);
return msg;
}
}public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "REDIS_LOCK";
// v2.0 单机锁不能解决分布式项目数据一致性问题: 分布式锁
@GetMapping("/sale")
public String saleShop() {
String current = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + Thread.currentThread().getName();
// setNX
Boolean flag = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, current);
if (!flag) {
System.out.println("没有抢到锁!");
return "没有抢到锁!";
}
try {
return saleService.sale();
} finally {
redisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
}
}当前问题:
这样设置的 REDIS_LOCK 默认是用不过期的,除非要求 redisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
如果当前服务器挂了,那么永远都无法删除 REDIS_LOCK 。
因此,需要为 REDIS_LOCK 设置过期时间。
// 注意: 加锁 和 设置过期时间必须是原子操作!
Boolean flag =
redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, current, 10L,TimeUnit.SECONDS); // setNXredisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK); 只能释放自己的锁,不能动别人的锁!
这里不能直接释放锁。
注意:判断和释放锁也必须是原子操作,不能被打断!
# 解决办法: Redis 事务、Watch乐观锁机制。
# Redis 单个命令都是原子性的。
# Redis事务是 命令集合连续且不被打断。
# Redis 不支持回滚的操作。
# 1、Redis事务特性
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> MULTI # 开启事务
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> SET k1 v111
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> SET k2 v222
# 在执行 EXEC之前, 如果 k1 k2被其他线程修改了
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> EXEC # 执行事务
# EXEC 执行完之后,可以覆盖其他线程的修改!
# 2、watch 乐观锁机制
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> WATCH k1 k2 # watch 监控
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> MULTI
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> SET k1 v111
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> SET k2 v222
QUEUED
# 在执行 EXEC之前, 如果 k1 k2被其他线程修改了
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> EXEC
(nil)
# EXEC 执行返回 (nil) 没有成功!不会去覆盖其他线程的操作使用 lua 脚本删除Key, 释放锁。
https://redis.io/commands/set。
如何保证锁的过期时间大于业务的执行时间?
这个过期时间不能写死,需要动态变化的!
Redis 有集群模式,分布式锁加在 Redis master,如果 master 没有同步到 slaver 但是 master挂了?那怎么办?锁就会丢失了!
解决方案:Redisson
<!-- pom 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.15.4</version>
</dependency> // Redisson 配置
@Bean
public Redisson redisson() {
Config config = new Config();
// 集群: config.useClusterServers().addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7181");
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://39.97.3.60:6379");
return (Redisson) Redisson.create(config);
}// Redis 锁
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "REDIS_LOCK";
// 最终解决方案 分布式锁 Redisson
@Resource
private Redisson redisson;
@Resource
private Redisson redisson;
@GetMapping("/sale")
public String saleShop() {
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(REDIS_LOCK);
lock.lock();
try {
return saleService.sale();
} finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) // 注意细节
lock.unlock();
}
}# redis.conf
# 这个就是 Redis 占用最大内存的配置
# 设置 maxmemory 单位是字节,需要注意单位的转换
# maxmemory <bytes>如果不设置最大内存大小或者设置最大内存为0, 在64位操作系统下不限制内存大小,在32位操作系统下最多使用3GB内存。
一般生产上如何配置最大内存?
一般推荐Redis设置内存为最大物理内存的四分之三。
# 查看 redis 最大内存
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET maxmemory
1) "maxmemory"
2) "0"
# 通过命令: 设置 redis 最大内存
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG SET maxmemory 10
# 查看 redis 使用的内存
127.0.0.1:6379> info memory
# Memory
used_memory:951600
used_memory_human:929.30K
used_memory_rss:10690560
used_memory_rss_human:10.20M
used_memory_peak:403604704
used_memory_peak_human:384.91M
used_memory_peak_perc:0.24%
used_memory_overhead:888762
used_memory_startup:802952
used_memory_dataset:62838
used_memory_dataset_perc:42.27%
allocator_allocated:1017656
allocator_active:1310720
allocator_resident:3584000
total_system_memory:1928933376
total_system_memory_human:1.80G
used_memory_lua:38912
used_memory_lua_human:38.00K
used_memory_scripts:880
used_memory_scripts_human:880B
number_of_cached_scripts:2
maxmemory:0
maxmemory_human:0B
maxmemory_policy:noeviction
allocator_frag_ratio:1.29
allocator_frag_bytes:293064
allocator_rss_ratio:2.73
allocator_rss_bytes:2273280
rss_overhead_ratio:2.98
rss_overhead_bytes:7106560
mem_fragmentation_ratio:11.74
mem_fragmentation_bytes:9779968
mem_not_counted_for_evict:0
mem_replication_backlog:0
mem_clients_slaves:0
mem_clients_normal:84930
mem_aof_buffer:0
mem_allocator:jemalloc-5.1.0
active_defrag_running:0
lazyfree_pending_objects:0如果一个 key 是过期的,那它到了过期时间之后是不是马上就从内存中删除?
答案是否定的,Redis有三种不同的过期 key 删除策略。
删除策略:
- 立即删除:立即删除能保证内存中数据的最大新鲜度,key 过期后立马会被删除,其所占的内存就会被释放。但是,当CPU忙的时候,就会给CPU造成额外的压力(对CPU不友好,拿时间换空间)。
- 惰性删除:数据到达过期时间,不做处理,等下次访问该数据时,如果未过期,返回数据,发现已经过期,删除,返回不存在(对内存不友好,用空间换时间)。
- 定期删除:定期删除是对以上两种删除策略的折中。定期删除策略每隔一段时间执行一次删除过期 key 操作,并通过限制删除操作执行的时常和频率来减少删除操作对CPU时间的影响(定期抽样key,判断是否过期,但是抽查还是有落网之鱼)!
# redis.conf
# redis 的内存淘汰策略, 以下 8 选 1
# MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory
# is reached. You can select one from the following behaviors:
#
# 1: 对所有设置了过期时间的 key 使用 LRU 算法进行删除
# volatile-lru -> Evict using approximated LRU, only keys with an expire set.
# 2: 对所有的 key 使用 LRU 算法进行删除
# allkeys-lru -> Evict any key using approximated LRU.
#
# 3: 对所有设置了过期时间的 key 使用 LFU 算法进行删除
# volatile-lfu -> Evict using approximated LFU, only keys with an expire set.
#
# 4: 对所有的 key 使用 LUF 算法进行删除
# allkeys-lfu -> Evict any key using approximated LFU.
#
# 5: 对所有设置了过期时间的 key 随机删除
# volatile-random -> Remove a random key having an expire set.
#
# 6: 对所有的 key 随机删除
# allkeys-random -> Remove a random key, any key.
#
# 7: 删除马上要过期的 key
# volatile-ttl -> Remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL)
# 8: 默认、不会删除任何 key
# noeviction -> Don't evict anything, just return an error on write operations.
#
# LRU means Least Recently Used
# LFU means Least Frequently Used
#
# Both LRU, LFU and volatile-ttl are implemented using approximated
# randomized algorithms.
# The default is:
#
# maxmemory-policy noeviction# 命令查看 Redis 内存淘汰策略
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET maxmemory-policy
1) "maxmemory-policy"
2) "noeviction"
# 命令设置 Redis 内存淘汰策略
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG SET maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET maxmemory-policy
1) "maxmemory-policy"
2) "allkeys-lru"LinkedHashMap复用了HashMap的put()为什么插入后还能保证有序?
// 测试代码:
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> linkedHashMap =
new LinkedHashMap<>(10, 0.75f, true);
linkedHashMap.put("a", 1);
linkedHashMap.put("b", 2);
linkedHashMap.put("c", 3);
linkedHashMap.get("b");
linkedHashMap.get("a");
linkedHashMap.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + " " + v));// 输出结果:
c 3
b 2
a 1// LinkedHashMap 构造方法
// accessOrder = true 的作用是调用get()方法是会将查找到的节点放入尾部!
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}以下是使用 LinkedHashMap 实现的一个 LRU 缓存:
- 设定最大缓存空间 maxEntries;
- 使用 LinkedHashMap 的构造函数将 accessOrder 设置为 true,开启 LRU 顺序;
- 覆盖 removeEldestEntry() 方法实现,在节点多于 MAX_ENTRIES 就会将最近最久未使用的数据移除。
public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
// 最大 k-v 键值对的数量(最大缓存数)
private int maxEntries;
public LRUCache(int maxEntries) {
super(maxEntries, 0.75f, true);
this.maxEntries = maxEntries;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
// size(): 返回 k-v 键值对的数量
return size() > maxEntries;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache<String, Object> lruCache = new LRUCache<>(3);
lruCache.put("a", 1);
lruCache.put("b", 2);
lruCache.put("c", 3);
System.out.println(" -- 初始化 -- ");
lruCache.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + " " + v));
System.out.println(" -- get(a) -- ");
lruCache.get("a");
lruCache.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + " " + v));
System.out.println(" -- put(d, 4) -- ");
lruCache.put("d", 4);
lruCache.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + " " + v));
}
}// 输出结果
-- 初始化 --
a 1
b 2
c 3
-- get(a) --
b 2
c 3
a 1
-- put(d, 4) --
c 3
a 1
d 4