角灰的文本工具箱
下载并安装依赖:
git clone https://github.com/jiaohuix/nmt_data_tools.git
# 设置环境变量
export TOOLS=$PWD/nmt_data_tools/
pip install -r nmt_data_tools/requirements.txt
cd nmt_data_tools- 1. 多进程分词
- 2. 词表相关
- 3. 文本过滤
- 4. 提取xml
- 5. 写入xml
- 6. 流式处理
- 7. 合并拆分语料(列)
- 8. 数据划分
- 9. 上下采样
- 10. 打乱文本
- 11. 去重
- 12. nmt数据处理
- 13. moses后处理
- 14.fast_align抽取词典
- 15. 随机对齐替换(RAS)
- 16.中文乱码过滤
- 17.ngram纠错
- 18. MUSE多语言词典
- 19.Annoy加速相似向量查找
- 21. bpe dropout
- 22. 可视化:len-bleu
- 23. 相似句子查找(LASER编码)
- 24. TextPruner
支持:
-
中、泰多进程分词
-
中:jieba、thulac、ltp,速度如下(10w句,AMD EPYC 7601cpu10核并行)
注意:ltp使用了torch模型,速度较慢,不建议用来分词;若要用则用cut.py而非cut.sh,因为ltp自带了多核优化。
jieba thulac ltp 4.08s 16.572s 1h+.. -
data/userwords.txt从THUOCL:清华大学开放中文词库提取11类共22w中文词,可以作为用户定义词典提高分词的精度。
# bash my_tools/cut.sh <workers> <infile> <outfile>
# 可选参数:<lang> <backend> <userdict>
# lang=zh/th, backend=jieba/thulac(chinese segment)
# userdict: 用户定义词典,一行一个词
# exp1: “那么我们都可以在这个平台上面可以拿到它所有源代码去加以运用。”
# zh-jieba speed=2.42
bash my_tools/cut.sh 4 data/train.zh data/train.tok.zh
# zh-thulac speed=3.67s
bash my_tools/cut.sh 4 data/train.zh data/train.tok.zh zh thulac
# jieba-res: 那么 我们 都 可以 在 这个 平台 上面 可以 拿到 它 所有 源代码 去 加以 运用 。
# thulac-res: 那 么 我们 都 可以 在 这个 平台 上面 可以 拿 到 它 所有 源 代码 去 加以 运用 。
# exp3: ltp默认带了多核优化,若再用shell开多进程会被kill
python my_tools/cut.py 4 data/train.zh data/train.tok.zh ltp
# exp4: 用户词典
bash my_tools/cut.sh 4 data/train.zh data/train.tok.zh zh thulac data/userwords.txt
# exp5: "ผม/ฉันมาจากสหรัฐอเมริกา"
# th-pythainlp
bash my_tools/cut.sh 4 data/train.zh data/train.tok.zh th
# res: ผม / ฉัน มาจาก สหรัฐอเมริกา# 英文后处理
python my_tools/decaser.py <infile> <outfile> en json->vocab(paddle)->dict(fairseq)
新增2: 多进程获取词典,速度快了2倍多。 22/9/13
# 单进程
python my_tools/build_dictionary.py $infile
# 多进程
bash my_tools/build_dictionary_paral.sh $workers $infile
# 输出:infile.json
#eg: wiki.train.tokens, 1801350 lines
time python my_tools/build_dictionary.py wiki.train.tokens
# real 0m40.372s
time bash my_tools/build_dictionary_paral.sh 4 wiki.train.tokens
#real 0m18.201s
新增:1. json2dict,不再需要从vocab中转,且能保留词频信息。 2.json2vocab和json2dict加入min_freq,参数,支持按照频率过滤词表 22/8/12
# 1.json 转 paddle vocab
#python my_tools/json2vocab.py $infile $outfile $min_freq(optional)
python my_tools/json2vocab.py data/train.bpe.zh.json data/vocab.zh
# 2.json 转 fairseq dict
#python my_tools/json2dict.py $infile $outfile $min_freq(optional)
# 3.paddle vocab 转 fairseq dict
# python my_tools/vocab2dict.py $infile $outfile $min_freq(optional)
python my_tools/vocab2dict.py data/vocab.zh data/dict.zh.txt
# 4.fairseq dict 转 paddle vocab
# python my_tools/dict2vocab.py $infile $outfile
python my_tools/dict2vocab.py data/dict.zh.txt data/vocab.zh1.⭐语言标识过滤
使用fasttext
# 1.下载权重(放nmt_data_tools目录下)
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/fasttext/supervised-models/lid.176.bin
# 2.过滤平行语料
python ./my_tools/data_filter.py --src-lang $SRC --tgt-lang $TRG --in-prefix data/train --out-prefix data/trainlang --threshold 0.5
# 3.example
python ./my_tools/data_filter.py --src-lang zh --tgt-lang en --in-prefix data/train --out-prefix data/trainlang --threshold 0.1
# result: lang id filter| [967/1000] samples retained, [33/1000] were deleted.
2.长度过滤
替代moses的clean-corpus,打印统计信息。
# 长度检测 (用于tokenize后,bpe前)
# python my_tools/check_pair.py <in_prefix> <SRC> <TRG> <upper> <ratio> <write_trash>(0/1)
python my_tools/check_pair.py data/train.tok zh th 175 1.5 0
# 默认write_trash=0,只打印,不写trash;0时会把范围外的异常数据写入 <inprefix.trash.lang>
# 长度过滤 (替代moses的clean-corpus;可以使用在bpe之后,先获得词表,再按不同的参数过滤数据)
python my_tools/length_filter.py --src-lang zh --tgt-lang th --in-prefix data/train.bpe --out-prefix data/train.clean --low 1 --up 200 --ratio 1.5 --remove-bpe --wt
# --remove-bpe可选,开启后判断长度时删掉@@ ,不影响写入; --wt可选,效果同check_pair的write_trashcheck 结果:
ratio src_len tgt_len
count 1.503344e+06 1.503344e+06 1.503344e+06
mean 1.613559e+00 7.379560e+00 8.033880e+00
std 9.832292e-01 5.450975e+00 5.950167e+00
min 1.000000e+00 1.000000e+00 1.000000e+00
25% 1.142857e+00 4.000000e+00 5.000000e+00
50% 1.333333e+00 6.000000e+00 7.000000e+00
75% 1.714286e+00 9.000000e+00 1.000000e+01
max 8.500000e+01 5.100000e+02 5.010000e+02
84 lines len > 175, 65409 lines ratio > 3.0.
step info: {'1.5': 494654, '2': 194131, '2.5': 118475, '3': 65409}# 1.command:
python my_tools/process_xml.py $infile $outfolder
# 2.example:
python my_tools/process_xml.py data/xml/bgzh/val.bg-zh.bg.xml data/
# result:
#total 1000 lines.
#write to data/val.bg-zh.bg.txt success.############### input ############### :
data/xml
├── bgzh
│ ├── val.bg-zh.bg.xml
│ └── val.bg-zh.zh.xml
└── ruzh
├── val.ru-zh.ru.xml
└── val.ru-zh.zh.xm
############### output ############### :
xml_out/
├── bgzh
│ ├── val.bg-zh.bg.txt
│ └── val.bg-zh.zh.txt
└── ruzh
├── val.ru-zh.ru.txt
└── val.ru-zh.zh.txt
# 1.command:
bash my_tools/process_xml_folder.sh <infolder> <outfolder>
# 2.example:
bash my_tools/process_xml_folder.sh data/xml/ xml_out# 1.生成xml
python my_tools/write_xml.py data/train.en data/result.xml
# 2.再在xml开头添加
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
# input: So this is our last stop, and we came back to our headquarter in Beijing.
# output:
<tstset setid="nestest2019" srclang="zh" trglang="en">
<DOC docid="news" sysid="1">
<p>
<seg id="1">So this is our last stop, and we came back to our headquarter in Beijing.</seg>如:
大
大家
大家晚 <=========> 大家晚上好
大家晚上
大家晚上好
# 1.command:
python my_tools/stream_preprocess.py <infile> <outfile> <1(towhole)|2(tostream)> <lang>
# 2.example:
# 流式->整句(data/whole.zh)
python my_tools/stream_preprocess.py data/stream.zh data/whole.zh 1 zh
# 整句->流式(data/stream2.zh)
python my_tools/stream_preprocess.py data/whole.zh data/stream2.zh 2 zh# 1.python
# python {sys.argv[0]} <infile1> <infile2> <outfile> <sep> (space/tab)
# 空格分隔
python my_tools/merge.py data/train.zh data/train.en data/outfile.txt space
# 制表符分割
python my_tools/merge.py data/train.zh data/train.en data/outfile.txt tab
# 2.shell
paste data/train.zh data/train.en > data/outfile.txt
# paste -d ' ' 空格分割不好用,默认\t# src
cut -f 1 data/outfile.txt > data/cut.zh
# tgt
cut -f 2 data/outfile.txt > data/cut.en划分训练和验证集
# 1.command:
python my_tools/train_dev_split.py <src-lang> <tgt-lang> <inprefix> <outfolder> <dev len>
# 2.example:
python my_tools/train_dev_split.py zh en data/train data 500
# 从train中随机取500条到data/dev.zh/en,其余的data/train.zh/en,result:
write to data\train.zh success.
write to data\train.en success.
write to data\dev.zh success.
write to data\dev.en success.# 1.command:
python my_tools/upsample.py <src-lang> <tgt-lang> <inprefix> <outfolder> <upsample len>
# 2.example:
python my_tools/upsample.py zh en data/train data 10000
# result:
write to data\upsample.zh success.
write to data\upsample.en success.直接使用第8节数据划分,取dev.lang作为下采样结果
新增:可以直接使用shell命令shuf进行打乱,对大文件非常友好。
seed=1
shuf --random-source=<(yes $seed) train.src > train.shuf.src
shuf --random-source=<(yes $seed) train.src > train.shuf.tgt或者合并文件后shuf,再拆分: 注:paste的分隔符d只能用一个字符,多个字符拼接使用该命令:paste -d '@@@' file1 /dev/null /dev/null file2
paste -d '@@@' train.src /dev/null /dev/null train.tgt | shuf > train.all
# 取第1列
cat train.all | awk -F'@@@' '{print $1}' > train.src
cat train.all | awk -F'@@@' '{print $2}' > train.tgt # 1.command:
python my_tools/shuffle_pair.py <src_lang> <tgt_lang> <data_prefix> <out_folder>
# 2.example:
python my_tools/shuffle_pair.py zh en data/train data/
# result:
write to data/shuffle.zh success.
write to data/shuffle.en success.新增2:从语料1中,删除语料2中的数据:
# python my_tools/drop_specific_pairs.py <src_lang> <tgt_lang> <main_prefix> <drop_prefix> <workers>
# 从main_prefix.lang中删除drop_prefix.lang中的数据,写入到main_prefix.drop.lang
# eg:
python my_tools/drop_specific_pairs.py zh en data/train data/dev 4
#Corpus pair to be deleted: [493] pairs.
#500it [00:00, 4761.99it/s]
#Delete the specified language is complete! Total [0/500] paris.
# 其中train和dev数据相同,所以train全被删了,结果train.drop.lang为空新增1: 双语去重。(无序,比有序快25%)
# python my_tools/deduplicate_pairs.py <in_prefix> <src_lang> <tgt_lang> <workers>
# 会默认写到in_prefix.dedup.lang里,example:
python my_tools/deduplicate_pairs.py data/train zh en 4old:单语多文件去重 。(无序)
# 1.command:
python my_tools/deduplicate_lines.py --workers $workers files > $outfile
# 2.example:
python my_tools/deduplicate_lines.py --workers 4 data/upsample.zh > data/dedup.zh
wc data/dedup.zh
# 493 499 48302 data/dedup.zh以zh en为例进行数据处理:
bash preprocess.sh对英文detokenize+detruecase
# bash postprocess.sh <prefix>
bash postprocess.sh data/zhen_bpe/train.bpe可以直接或间接从MUSE获取词典,见18。
注:linux环境,可在aistudio运行。
# 1.分词
bash my_tools/cut.sh 4 data/train.zh data/train.tok.zh
bash my_tools/cut.sh 4 data/dev.zh data/dev.tok.zh
mv data/train.tok.zh data/train.zh
mv data/dev.tok.zh data/valid.zh
# 2.fast align 对齐 (data/fast_align/dict.zh-en)
# bash my_tools/fast_align_dict.sh <src> <tgt> <infolder> <outfolder> <topk>
bash my_tools/fast_align_dict.sh zh en data/ align_output/ 1000
# result
head align_output//dict.zh-en
我们 we 74
的 of 50
一个 a 48
是 is 44
# 3.抽取词典(可使用停用词过滤、语言标识过滤)
# python my_tools/dict_filter.py <src_lang> <tgt_lang> <in_file> <out_file> <src_stop_file>(optional) <tgt_stop_file>(optional) <model_path>(optional)
# src_stop_file和tgt_stop_file是停用词文件,model_path是fasttext的模型权重路径,两个都是可选参数
# 3.1简易抽取(去除1:m,m:1,m:n的对应)
python my_tools/dict_filter.py zh en align_output/dict.zh-en align_output/dict.zh-en.txt
# result
head -n 10 align_output/dict.zh-en.txt
我们 we 74
的 of 50
是 is 44
可以 can 41
# 3.2去除停用词、语言标识过滤(中英为例子)
git clone https://github.com/goto456/stopwords.git
git clone https://github.com/stopwords-iso/stopwords-en.git
# fast-text weight
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/fasttext/supervised-models/lid.176.bin
python my_tools/dict_filter.py zh en align_output/dict.zh-en align_output/dict.zh-en.txt stopwords/cn_stopwords.txt stopwords-en/stopwords-en.txt lid.176.bin
# result
机器人 robot 17
语音 voice 15
开发者 developers 12
用户 user 12
# 4.其他停用词
stop words:
zh: https://github.com/goto456/stopwords.git stopwords/cn_stopwords.txt
en: https://github.com/stopwords-iso/stopwords-en.git stopwords-en/stopwords-en.txt
de: https://github.com/stopwords-iso/stopwords-de.git
fr: https://github.com/stopwords-iso/stopwords-fr
es: https://github.com/stopwords-iso/stopwords-es.git
vi: https://github.com/stopwords/vietnamese-stopwords.git
ru: https://github.com/stopwords-iso/stopwords-ru
目前已经可以抽取词典,后续准备添加停用词过滤,然后清洗词典,或者检测并保留些实体词,就不放在抽取词典上了。
随机对齐替换, mRASP翻译模型使用该方法进行预训练,用词典将source的词典词按一定几率替换为其他语言的同义词。
python my_tools/replace_word_bilingual.py --langs de;en --dict-path dic --data-path data --prefix train --num-repeat 1 --moses-detok --replace-prob 0.3 --vocab-size 1000
tree:
/dic
de-en.txt # de_word en_word \n (空格分隔)
/data
train.src # <lang_id> src_text
train.tgt # <lang_id> tgt_text
python nmt_data_tools/my_tools/replace_word_bilingual.py --langs de;en --dict-path dic --data-path data --num-repeat 1 --moses-detok --replace-prob 0.3 --vocab-size 1000
完整文档和demo参考ras_sample
1.对于部分乱码,编码成gbk后会报错,如此可以剔除一部分:
def check_is_encode_error(string):
try:
string.encode('gbk')
except UnicodeEncodeError:
return True
return False
# eg:s="硂或ㄓ и籔羆琌畉˙ぇ换"
# print(check_is_encode_error(s)) # True2.对于不会报错的罕见词,可以在文本进行分词后用unicode编码区分中文和其他字符,大多数情况是符号或者日语,所以用日语的unicode来区分是不是正常的词。
def is_all_japanese(strs):
for _char in strs:
if not '\u0800' <= _char <= '\u4e00':
return False
return True
# 如得到下面奇怪的词表:
'''
['ㄛ', '①', '⼈', '┅', '◎', '●', 'ㄧ', '〈', '〖', '≥', '②', '\u200b', '•', '⼀', 'ㄓ', '〇', 'ㄚ', '③', '⻔', '⼝', 'Ⅲ', '④', '⑤', '│', '∩', 'ぃ', '⼦', 'ส', '์', 'ร', 'ぎ', '㖊', 'ㄩ', '≤', '⾕', 'ぐ', '⊿', 'Ⅳ', 'ย', '⾯', 'ヶ', '∣', 'ㄤ', '⊙', '▲', 'ㄍ', 'ㄞ', '⾃', '⾮', '※', 'จ', 'す', 'れ', '✘', 'レ', '⼩', 'ㄈ', 'ิ', '⽤', '⑦', '⑥', '❤', 'ㄇ', 'ㄐ', '⽽', 'ㄘ', 'ㄗ', '⼴', '⼊', '‰', '⼼', '⼯', '▓', '┕', '⾛', '〜', '䴕', 'Ⅵ', '⽣', 'い', 'น', 'ゅ', 'え', 'ㄅ', 'ㄎ', '∕', '㎡', 'ㄥ', 'わ', 'Ⅴ', '✔', 'ไ', 'พ', 'ค', 'ต', 'ม', 'า', 'อ', 'ซ', 'เ', '㖞', '⽿', '⽶', '⻄', '⽬', '⽂', 'ฮ', 'ว', 'ง', 'ุ', '้', 'が', 'ば', 'ヴ', 'か', '╩', '㓥', '㎝', '═', 'オ', '㈱', '┣', '⑩', 'ㄖ', 'ㄌ', 'ㄆ', 'ボ', 'ヘ', 'も', 'デ', 'ㄨ', 'ㄉ', 'ㄠ', 'ァ', 'む', 'ェ', 'ゴ', '√', '⽞', '⼜', '⾜', 'Ⅷ', 'Ⅶ', '∨', '≠', '⻅', '⾄', '∪', 'Ⅸ', 'ะ', 'ื', 'ั', 'ท', 'ี', '่', '⑧', 'ㄙ', '⼤', 'ト', 'ッ', 'プ', 'グ', 'イ', 'ン', 'を', '⾸', '⺟', '⾏', '・', '⽉', '⽴', 'ㄒ', 'ㄢ', 'の', 'ど', 'こ', 'ん', 'に', 'ち', '╰', '╭', '″', 'せ']
''' 找出含这些词的句子,这部分句子有很大概率是无意义的句子(全是乱码),也有可能只是包含些特殊符号,我们对这些嫌疑句进行打分,规则如下:
$$ Score(i)=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{k=0}^{k=n}I(freq_{k}<100)* \frac{(100-freq_{k})}{100} $$ 对于第i个句子si,有n个word。句子分数Score(i)为,n个word的分数求平均。指示函数I当词频小于100时为1, 对于词频freq>100的词,分数为0;对于freq<100的词,分数为归一化的100-freq,这样词频低就分数高;若乱码多,基本上分数很容易超过0.5,俺把超过0.45的都当初乱码丢掉了。对于score<0.45的嫌疑句,俺按规则删掉些乱码词后放回原语料。
# python my_tools/zh_abnormal_filter.py --zh-lang zh --other-lang th --in-prefix data_zhth/train.tok --out-prefix data_zhth/train.clean --threshold 0.45 --min-freq 20 --wt
# 用在tokenize之后,bpe前
# --wt可选,加了后会把嫌疑句存到out_prefix.update.zh 和out_prefix.trash.zh
'''
update: (score<0.45)
Score: [0.140], Sentence: [◎ 我 都 会 等 你
]Score: [0.213], Sentence: [◎ 在 那些 我 无法 忘怀 的
]Score: [0.210], Sentence: [◎ 所有 熟悉 的
]Score: [0.280], Sentence: [◎ 老 地方
]Score: [0.210], Sentence: [◎ 等 着 你
trash: (score>0.45)
Score: [0.829], Sentence: [※ 涴 汊 唒 # § 庈 部 塑 毽 斯 剟 覂 ※ 扥 酗 盛 赽 わ 晒 赵塑 §
]Score: [0.475], Sentence: [395 ) 若 吾 起舞 吾 が 舞 え ば
]Score: [0.790], Sentence: [惕 К - 凌 岆 勤祥 れ
]Score: [0.784], Sentence: [膻寿 炵 ㄛ 梗 温 婓 陑 奻
]Score: [0.741], Sentence: [辣 茩 蝠 霜 ﹛ QQ ㄩ 31946467
]Score: [0.823], Sentence: [祥 岆 珨 跺 艘 善 か 谣艺 羹 憩霜谙 厄腔 伎 寤 橾 啄
'''22/9/13
-
最近有遇到需要处理几句相似但存在错误的句子(ocr输出),使用深度学习模型的纠正方法似乎不是很work, 如pycorrector
# eg1: 昨天早上扔垃圾的时候\t昨天早上扔圾的时候\t咋天早上扔垃圾的时候 -
我尝试使用以word为单位的ngram模型为句子打分,效果较差,原因是词粒度太大, 打分时容易出现OOV的词,如词表有"雨伞",而要为"我 去 拿 伞" 和 "我 去 拿 平" 两句句子打分时, 因为"伞" 不单独出现在词表, 所以分数一样
-
最后我用以char为单位的ngram模型对句子进行打分, 缓解了OOV的问题, 并且句子得分很合理,见以下demo:
-
TODO: 1.添加用新语料更新模型的功能, 将从新的领域语料得到的ngram的count提高, 从而让得分对领域词更敏感. 2. 以候选句中得分最高的为模板, 找到错误后替换为别的句子中对应词, 取得分高的从而达到纠错的效果.
# eg1: 昨天早上扔垃圾的时候\t昨天早上扔圾的时候\t咋天早上扔垃圾的时候
'''
Sentence: 昨天早上扔垃圾的时候, Score: -12.5425 √
Sentence: 昨天早上扔圾的时候, Score: -13.5297
Sentence: 咋天早上扔垃圾的时候, Score: -14.132
'''
# eg2:
'''
Sentence: 他似乎总是缺乏一位掌门人应有的清晰思路和价值判断, Score: -4.171 √
Sentence: 他似夫总似缺乏一位掌门人应有的清晰思路和价紫判断, Score: -10.397
'''
# eg3:
'''
Sentence: 被送到医院后确认死亡, Score: -10.2888 √
Sentence: 破送到医院后确认死亡, Score: -12.5591
'''使用如下:
from my_tools.ngram_char import nGramChar
# build model
model = nGramChar(n_gram=3)
# train model
model.train_ngram(text_file="cnews/cnews.test.txt")
# save model
model.save_model(path="./")
# load model
model.load_model(path="./")
# score
s1 = '他似乎总是缺乏一位掌门人应有的清晰思路和价值判断'
s2 = '他似夫总似缺乏一位掌门人应有的清晰思路和价紫判断'
prob1 = model.sentence_logprob(sentence=s1)
prob2 = model.sentence_logprob(sentence=s2)
print(f"Sentence: {s1}, Score: {prob1}")
print(f"Sentence: {s2}, Score: {prob2}")
'''
Sentence: 他似乎总是缺乏一位掌门人应有的清晰思路和价值判断, Score: -4.171
Sentence: 他似夫总似缺乏一位掌门人应有的清晰思路和价紫判断, Score: -10.397
'''22/9/26
说明: muse的词典是x-en.txt的,以英文为中心,本节利用lang1-en.txt和lang2-en.txt 两个到英文的词典,获取lang1-lang2.txt的词典。
# eg:获取俄中词典
## 1. 下载俄英,中英词典
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/arrival/dictionaries/ru-en.txt
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/arrival/dictionaries/zh-en.txt
## 2.转俄中
python my_tools/get_pivot_dict.py ru-en.txt zh-en.txt
# write to ./ru-zh.txt success, total 13852 lines.22/9/27
对于635965x300的词表,构建索引需要26秒,而查找只需1毫秒左右。
参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/clqJhvk-HJnYsTh9tg2VAw
from my_tools.annoy_indexer import AnnoyIndexer
# 1.get weight
from paddlenlp.embeddings import TokenEmbedding
token_embedding = TokenEmbedding(embedding_name="w2v.baidu_encyclopedia.target.word-word.dim300")
weight = token_embedding.weight.numpy()
# 2.build ann tree
vocab_size = len(token_embedding.vocab)
indices = list(range(vocab_size))
tokens= token_embedding.vocab.to_tokens(indices)
print(tokens[:10])
print("build annoy indexer...")
indexer = AnnoyIndexer(tokens,weight,num_trees=10)
indexer.build_indexer()
# 3. save params
print("save annoy indexer...")
indexer.save(path="save")
# 4.load indexer
print("load annoy indexer...")
indexer_new = AnnoyIndexer()
indexer_new.load(path="save")
print(indexer_new)
print(len(indexer_new))
# 5.search sim word
print("search sim words ...")
word = "电影"
# word = "国王"
# idx = indexer_new.token2idx(word)
vec = indexer_new.search_vector(word)
topk=5
ids, distances = indexer_new.most_similar(vec,topk)
nearest_tokens = [indexer_new.idx2token(idx) for idx in ids]
print(f"{word}'s {topk} nearest_tokens",nearest_tokens)
# 电影's 5 nearest_tokens ['电影', '影片', '电视剧', '影视作品', '导演']
# 国王's 5 nearest_tokens ['国王', '雅赫摩斯', '雨果·卡佩', '塞利姆', '法王路易']# eg: zh-ar
# 1.code
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/MUSE.git
cd MUSE/data
# 2.download embed
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/arrival/vectors/wiki.multi.ar.vec
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/fasttext/vectors-wiki/wiki.zh.vec
# 2.download dictionary (ar/zh train/test)
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/arrival/dictionaries/ar-en.txt
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/arrival/dictionaries/zh-en.txt
cd ..
# 3.make zh-ar dictionary by zh-en ar-en
python ../my_tools/get_pivot_dict.py data/zh-en.txt data/ar-en.txt
head -n 8000 data/zh-ar.txt > data/zh-ar.train.txt
tail -n +8001 data/zh-ar.txt > data/zh-ar.eval.txt
# align zh-ar in a common space
python supervised.py --src_lang zh --tgt_lang ar --src_emb data/wiki.zh.vec --tgt_emb data/wiki.multi.ar.vec --n_refinement 5 --dico_train data/zh-ar.train.txt --dico_eval data/zh-ar.eval.txtBPE-Dropout是一种简单的子词正则化方法,它随机破坏 BPE 的分割过程,导致在同一个固定 BPE 框架内产生多个分割。与 BPE 相比,在训练期间使用 BPE-dropout 和在推理期间使用标准 BPE 可将翻译质量提高高达 2.3 BLEU
# 单核
python my_tools/bpe_dropout.py <infile> <outfile> <bpecode> <num_iter=5>(opt) <drop_rate=0.1>(opt)
# 多核
bash my_tools/apply_bpedrop_paral.sh <infile> <outfile> <bpe_code> <workers=4>(opt) <num_iter=5>(opt) <drop_rate=0.1>(opt)
# example
bash my_tools/apply_bpedrop_paral.sh data/train.en data/train.bpe.en data/codes.bep.en 4 5 0.1使用bpe dropout会有分词失败的情况,会返回文本“ErrorTokenize”,需要用grep -v "ErrorTokenize" 过滤,以data/train为例:
# 使用各自的bpe code(这里都用en的),num_iter=3 drop_rate=0.1
cp -r nmt_data_tools/data .
python nmt_data_tools/my_tools/bpe_dropout.py data/train.zh data/tmp.zh data/codes.bpe.en 3 0.1
python nmt_data_tools/my_tools/bpe_dropout.py data/train.en data/tmp.en data/codes.bpe.en 3 0.1
# 去除空行
paste data/tmp.zh data/tmp.en > data/tmp
grep -v "ErrorTokenize" data/tmp > data/tmp.ok
cut -f 1 data/tmp.ok > data/train.drop.zh
cut -f 2 data/tmp.ok > data/train.drop.en
rm data/tmp*
# 数据会翻num_iter倍,这里是500*3=1500
head data/train.drop.en
#We chan@@ g@@ ed the mode@@ l@@ ing un@@ it f@@ r@@ o@@ m pre@@ vi@@ ous Chinese charac@@ ter u@@ n@@ it to the cu@@ r@@ ren@@ t high@@ -@@ f@@ re@@ qu@@ enc@@ y ph@@ o@@ ne@@ me un@@ it.
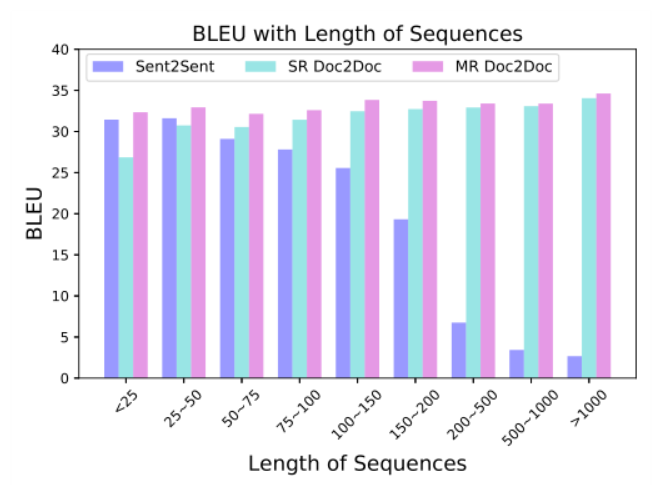
#W@@ e chan@@ g@@ ed t@@ he model@@ ing un@@ it f@@ r@@ o@@ m pre@@ vi@@ ous Chinese charac@@ ter un@@ it to th@@ e curren@@ t high@@ -@@ f@@ re@@ qu@@ enc@@ y ph@@ o@@ ne@@ me un@@ it@@ . 在字节关于篇章机器翻译的工作Rethinking Document-level Neural Machine Translation中提出在不修改网络结构,改变训练方法就能达到很好效果。具体的,把长的篇章按不同分解度等分为若干份,如篇章有16句,则分别分为{1,2,4,8}组,每组分别有16、8、4、2句,将这些不同粒度的语料对混合训练。实验结果显示该方法能显著提升长句的分数,并且在短句上的分数也比句子级翻译模型更好:
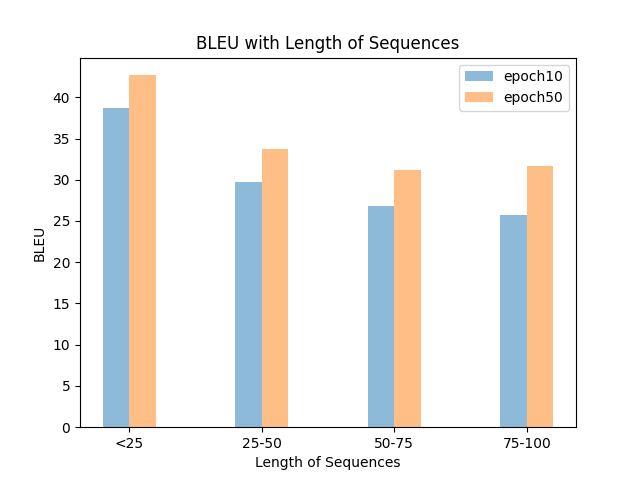
为了方便画图,于是有:
# --tags --ref --out hypos*
python visual/len_bleu4.py -t "epoch10,epoch50" -r data/ref.txt -o bleu_len.png data/hypo10.txt data/hypo50.txtPS: 颜色就懒得换了。此外,发现一个超好用的画图包:compare-mt,可以全面分析不同系统的翻译效果差异。
23/2/28
23/2/28
**TextPruner**是由HFL开发的用于预训练语言模型的模型裁剪的工具包,可以通过词表裁剪、结构裁剪来减少冗余神经元,加快模型训练推理速度。(用于裁剪transformers的模型)
本节记录下用TextPruner对mbert进行词表裁剪,保留2种语言以适应双向翻译任务。
23/4/19