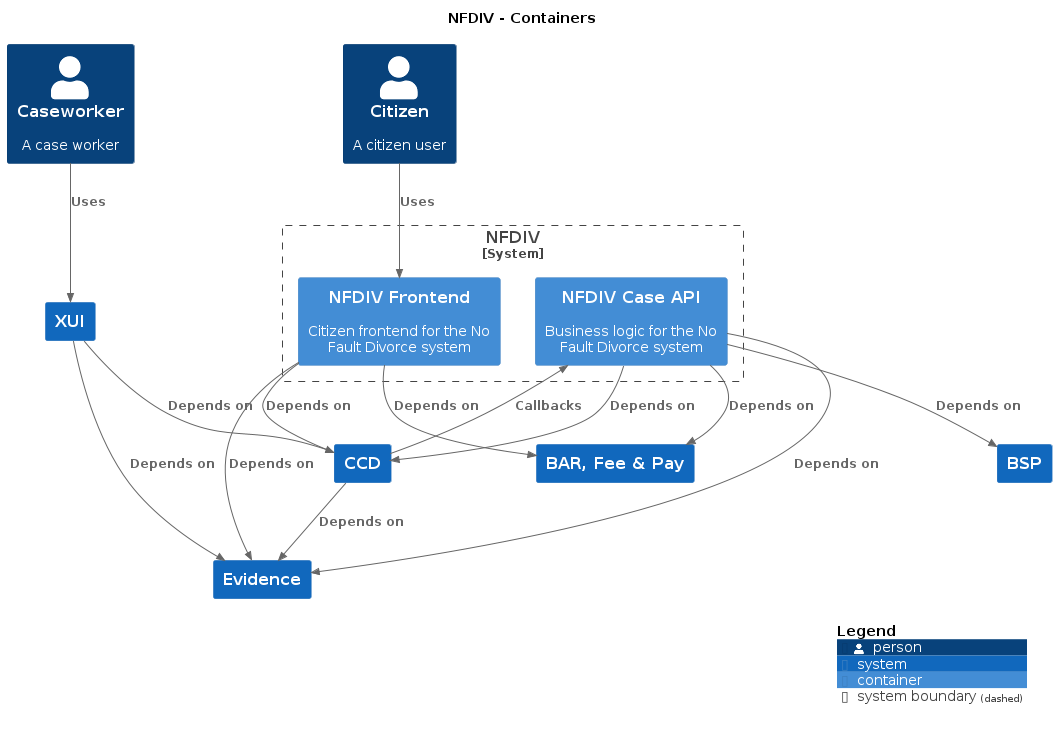
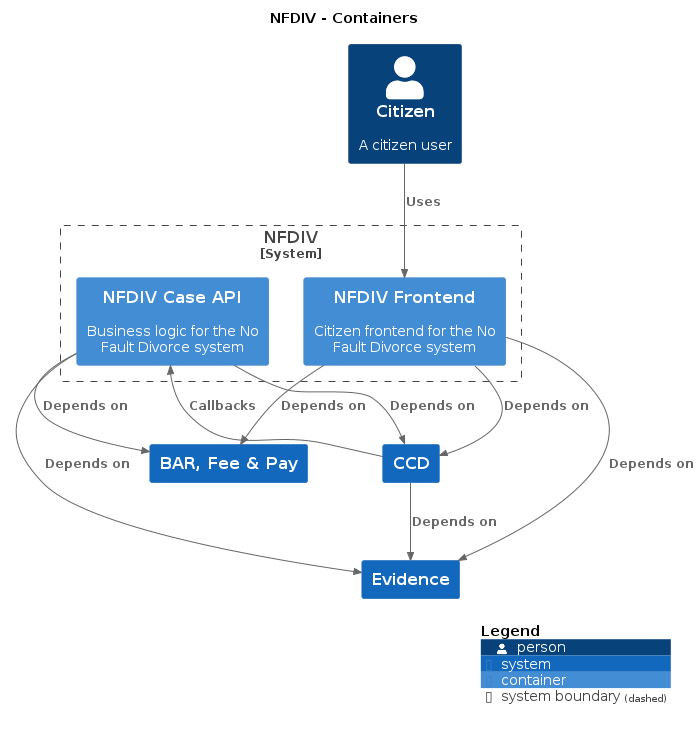
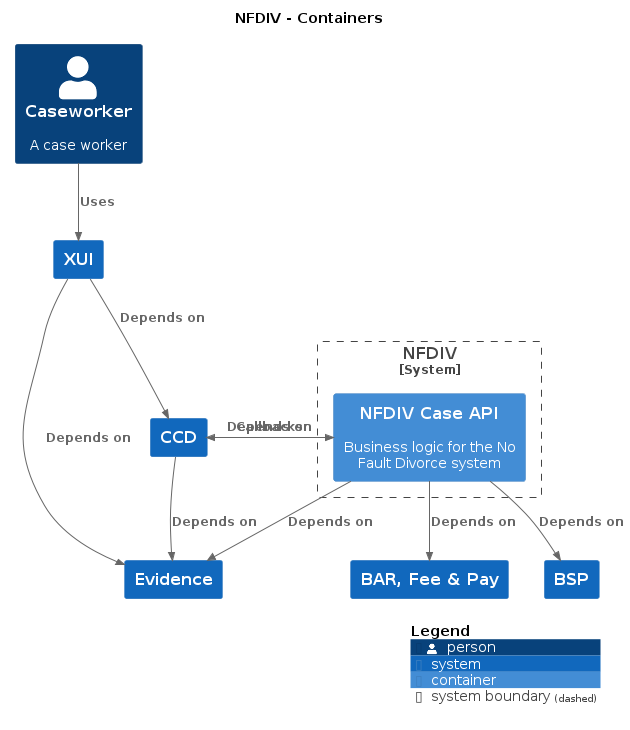
nfdiv-frontend • nfdiv-case-api • nfdiv-shared-infrastructure • nfdiv-performance • nfdiv-solicitor-e2e-tests
Running the application requires the following tools to be installed in your environment:
Install dependencies by executing the following command:
yarn installBundle:
yarn webpackStart server:
yarn startThe application's home page will be available at https://localhost:3001
The application makes calls to case orchestration service. Make sure you have this running to run the frontend e2e.
Running the scripts present would require zsh to be installed.
Please see https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-configure-your-macos-terminal-with-zsh-like-a-pro-c0ab3f3c1156/ if zsh is not installed on your machine. Steps 1 to 3 of the above link should suffice.
Create docker image:
docker-compose buildRun the application by executing the following command:
docker-compose upThis will start the frontend container exposing the application's port 3001.
In order to test if the application is up, you can visit https://localhost:3001 in your browser.
Starting the server in development mode:
yarn build
DEBUG=axios yarn start:devWe use Prettier alongside ESLint and sass-lint
Running the linting with auto fix:
yarn lint --fixWe uses Jest as the test engine. You can run unit tests by executing the following command:
yarn testRunning the functional tests:
TEST_HEADLESS=false yarn test:cucumberNote: By default tests are run heedlessly (i.e. without displaying the browser) setting the TEST_HEADLESS flag to false will open the test browser window allowing you to see whats happening in realtime.
Running the functional tests against local Docker:
NODE_ENV=docker yarn test:cucumberNote: Other options can still be used with the above command
Running a single test:
yarn test:cucumber:grep 'Name of Feature, Scenario, or @tag'Viewing functional test reports locally:
yarn test:cucumber:reportsTo view the report from Jenkins, navigate to the build artefacts page scroll to the bottom and click “Download All”.
Then extract it and run:
npx allure-commandline serve ~/Downloads/archive/functional-output/functional/reportsRunning accessibility tests:
yarn test:a11yBy default all of the pages in listed urls.ts will be tested.
Cross browser tests are run via CodeceptJS using the Playwright plugin which tests Chrome/Edge, Safari and Firefox. The WebDriver plugin is used to test Edge on Windows via Sauce Labs.
Cross browser tests are automatically run via the nightly Jenkins pipeline.
Running cross browser tests locally, start the server then run:
# Playwright - Chrome/Edge, Safari and Firefox
TEST_HEADLESS=false yarn test:crossbrowser:playwrightTo run the cross browser tests using Sauce Labs, install the Sauce Labs connect proxy tunnel and set the following environment variables with your own Sauce Labs account details: SAUCE_USERNAME, SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY, and SAUCE_TUNNEL_IDENTIFIER.
# WebDriver (via Sauce Labs)
sc -u $SAUCE_USERNAME -k $SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY -x https://eu-central-1.saucelabs.com/rest/v1 -i $SAUCE_TUNNEL_IDENTIFIER -B all
yarn test:crossbrowser:sauceSee TESTING.md for more information on testing processes.
Cross-Site Request Forgery prevention has already been set up, at the application level. However, you need to make sure that CSRF token is present in every HTML form that requires it. For that purpose you can use the csrfProtection macro. Your njk file would include it like this:
{% from "macros/csrf.njk" import csrfProtection %}
<form>{{ csrfProtection(csrfToken) }}</form>This application uses Helmet, which adds various security-related HTTP headers to the responses. Apart from default Helmet functions, following headers are set:
There is a configuration section related with those headers, where you can specify:
referrerPolicy- value of theReferrer-Policyheader
Here's an example setup:
"security": {
"referrerPolicy": "origin",
}Make sure you have those values set correctly for your application.
The application exposes a health endpoint https://localhost:3001/health, created with the use of Nodejs Healthcheck library. This endpoint is defined in health.ts file. Make sure you adjust it correctly in your application. In particular, remember to replace the sample check with checks specific to your frontend app, e.g. the ones verifying the state of each service it depends on.
Once you have created a NFDIV-Case-API Pull Request with the case definition changes, update CCD_URL in values.yaml and services.case.url in default.yaml so that the CCD Data Store is pointing at the Preview version deployed as part of your No Fault Divorce Case API pull request.
For example: CCD_URL: 'https://ccd-data-store-api-nfdiv-case-api-pr-232.preview.platform.hmcts.net'
Next, run the generateTypescript Gradle task in the Case API. Once this has completed, navigate to build/ts/index.ts in the Case API and copy the contents of the file. Navigate back to the frontend repository and paste the contents of the file into definition.ts. Depending on how your IDE is configured, the formatting of strings from double to single quotes should be carried out automatically.
Once you have pasted the code into definition.ts you may notice some compilation errors in case.ts, from-api-format.ts and to-api-format.ts. This is typically caused by either changes to the field name or to the field type. You will need to resolve these compilation errors manually.
You will now be in a position to test your changes either in isolation (yarn start:dev) or with Docker (yarn start:docker).
One final important point to remember is that the CCD_URL in values.yaml and services.case.url in default.yaml will need to be reverted to their original values once migration is complete and before any Pull Requests into master are merged.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.